The document discusses the integration of Windows as a guest operating system in OpenStack using Hyper-V, including setup instructions, automation tools like Cloudbase-Init, and image preparation via sysprep. It covers plugins for user creation, password management, and metadata handling, along with various deployment scenarios and environment setups with DevStack and RDO. Additionally, it outlines the use of Open vSwitch with Hyper-V for enhanced networking capabilities and details the installation and configuration processes for OpenStack components on Hyper-V nodes.






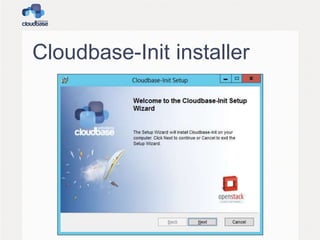
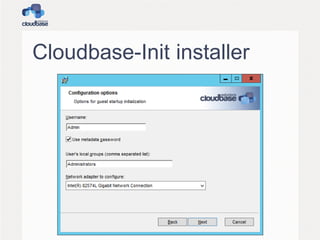





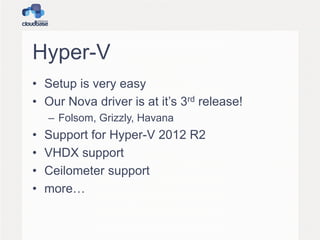
![User creation
• The CreateUser plugin creates a user and
adds it to the local administrators group
– A random password is used at this stage as it’s
needed to create the user profile
• Options:
– username (default “Admin”)
– groups (default “[Administrators]”)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openstacksummit2013hk-openstackandwindows-140310141444-phpapp01/85/OpenStack-Summit-2013-Hong-Kong-OpenStack-and-Windows-16-320.jpg)














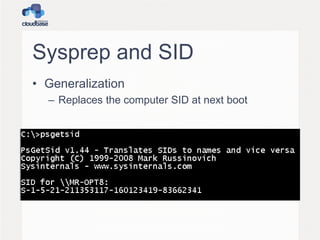
![Simple Heat template 1
"KeyName" : {
"Description" : "Name of an existing EC2 KeyPair to encrypt the Admin password",
"Type" : "String"
},
"InstanceType" : {
"Description" : "EC2 instance type",
"Type" : "String",
"Default" : "m1.small",
"AllowedValues" : [ "m1.sminy", "m1.small", "m1.medium", "m1.large", "m1.xlarge"
],
"ConstraintDescription" : "must be a valid EC2 instance type."
},
"OSImage": {
"Default": "Windows Server 2012 R2 Std Eval",
"Description" : "Windows image of choice",
"Type": "String",
"AllowedValues" : [ "Windows Server 2012 R2 Std Eval" ]
},](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openstacksummit2013hk-openstackandwindows-140310141444-phpapp01/85/OpenStack-Summit-2013-Hong-Kong-OpenStack-and-Windows-34-320.jpg)

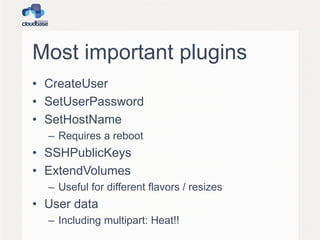
![Simple Heat template 3
"Resources" : {
"SampleServer": {
"Type": "AWS::EC2::Instance",
"Properties": {
"ImageId" : { "Ref" : "OSImage" },
"InstanceType" : { "Ref" : "InstanceType" },
"SubnetId" : { "Ref" : "SubnetId" },
"KeyName" : { "Ref" : "KeyName" },
"UserData" : { "Fn::Base64" : { "Fn::Join" : ["", [
"#ps1_sysnativen",
"$ErrorActionPreference = 'Stop'n",
"Set-Content -path C:message.txt -value", { "Ref" : "Message" }, "')n"
]]}}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openstacksummit2013hk-openstackandwindows-140310141444-phpapp01/85/OpenStack-Summit-2013-Hong-Kong-OpenStack-and-Windows-36-320.jpg)