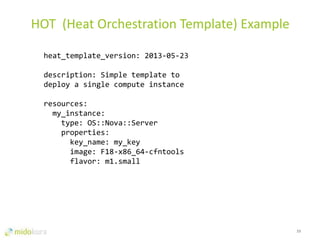
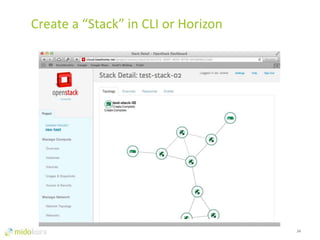
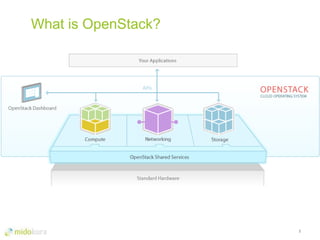
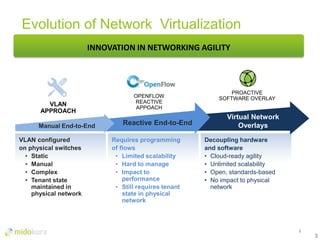
- OpenStack provides network virtualization and automation capabilities through projects like Neutron, Heat, and plugins like Midonet.
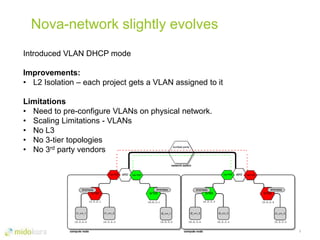
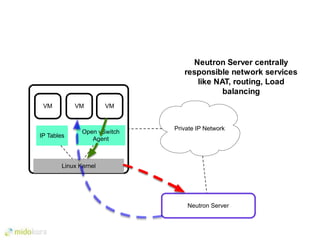
- Neutron evolved networking in OpenStack to allow pluggable networking models beyond the initial Nova networking. It supports overlay technologies and network automation.
- Heat allows you to define infrastructure like servers, networks, and their relationships in templates that can be deployed through the OpenStack API. This provides automation of virtual network deployment.
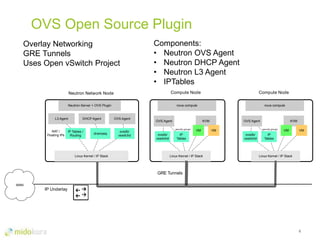
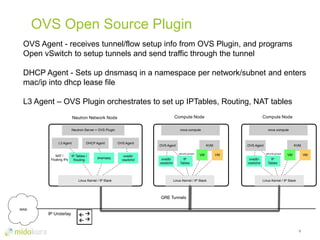
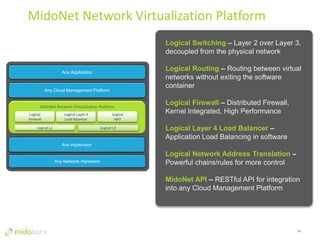
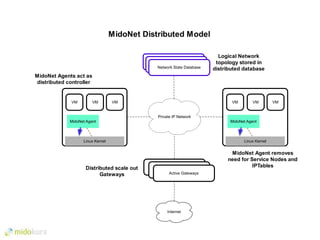
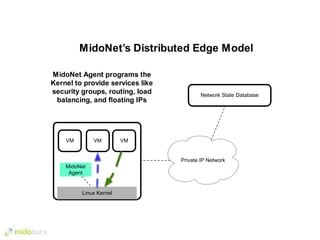
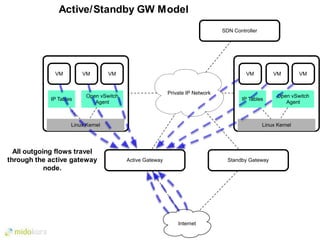
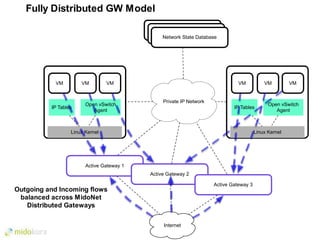
- Plugins like Midonet provide distributed virtual networking models to improve scalability and performance over overlay approaches like OVS. They also allow automation of physical network configuration.









![22
{
"AWSTemplateFormatVersion" : "2010-09-09",
"Description" : "Sample Heat template that
spins up multiple instances and a private
network (JSON)",
"Resources" : {
"heat_network_01" : {
"Type" : "OS::Neutron::Net",
"Properties" : {
"name" : "heat-network-01"
}
},
"heat_subnet_01" : {
"Type" : "OS::Neutron::Subnet",
"Properties" : {
"name" : "heat-subnet-01",
"cidr" : "10.10.10.0/24",
"dns_nameservers" : ["172.16.1.11",
"172.16.1.6"],
"enable_dhcp" : "True",
"gateway_ip" : "10.10.10.254",
"network_id" : { "Ref" :
"heat_network_01" }
}
},
Example Snippet (Cloud Formation Template)
"heat_router_01" : {
"Type" : "OS::Neutron::Router",
"Properties" : {
"admin_state_up" : "True",
"name" : "heat-router-01"
}
},](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openstacknetworking-140611185655-phpapp01/85/OpenStack-Networking-and-Automation-23-320.jpg)