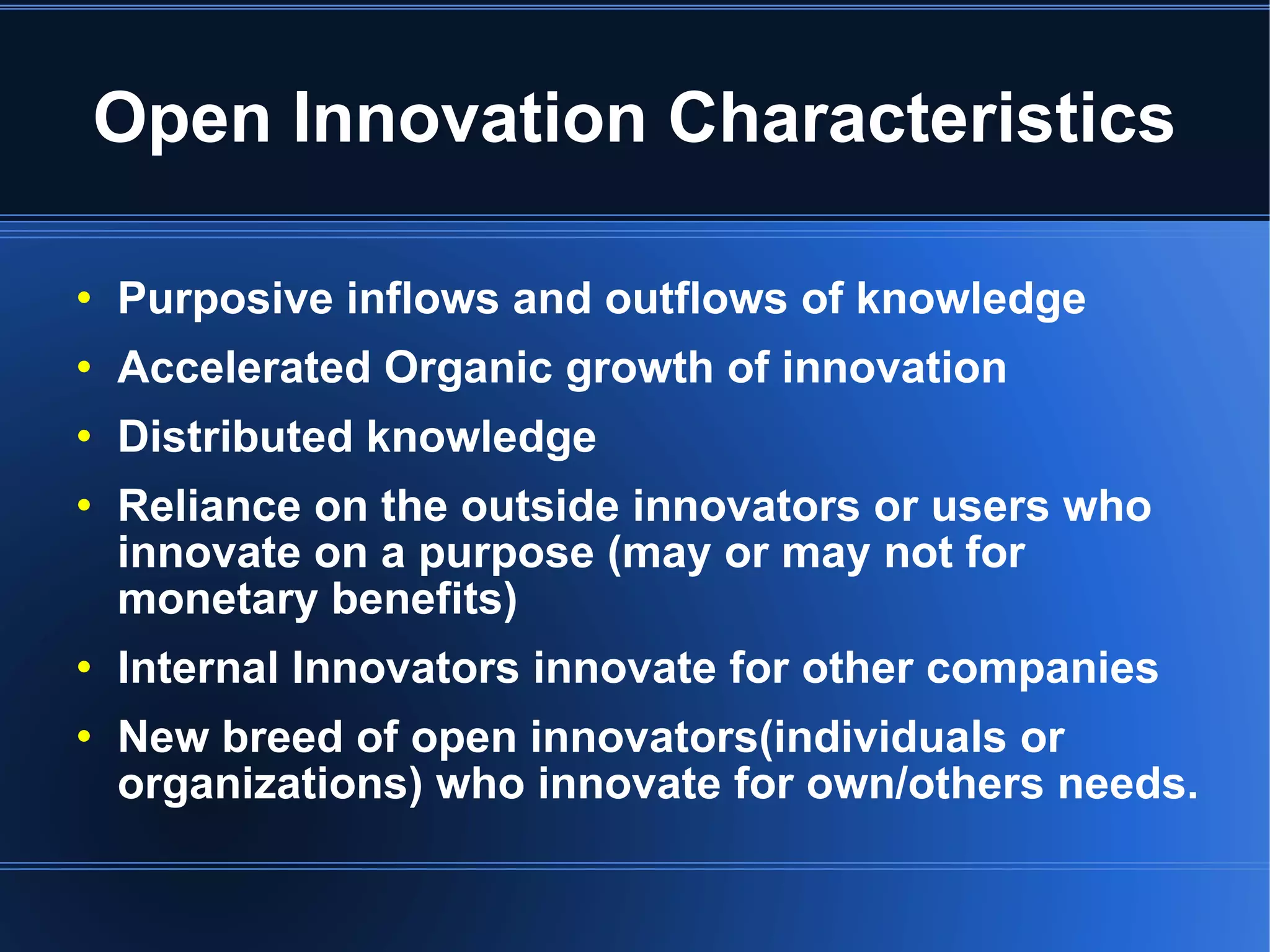
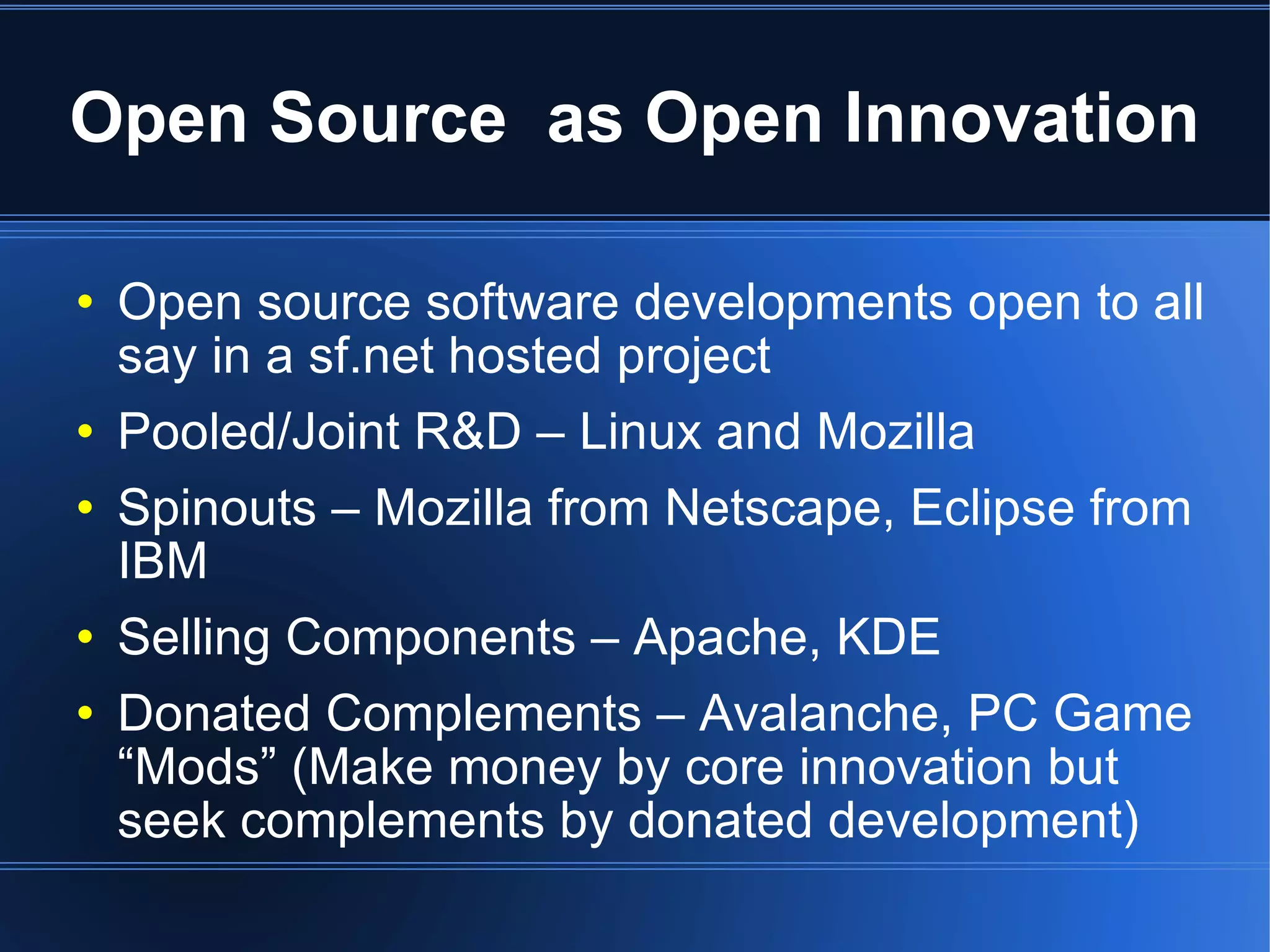
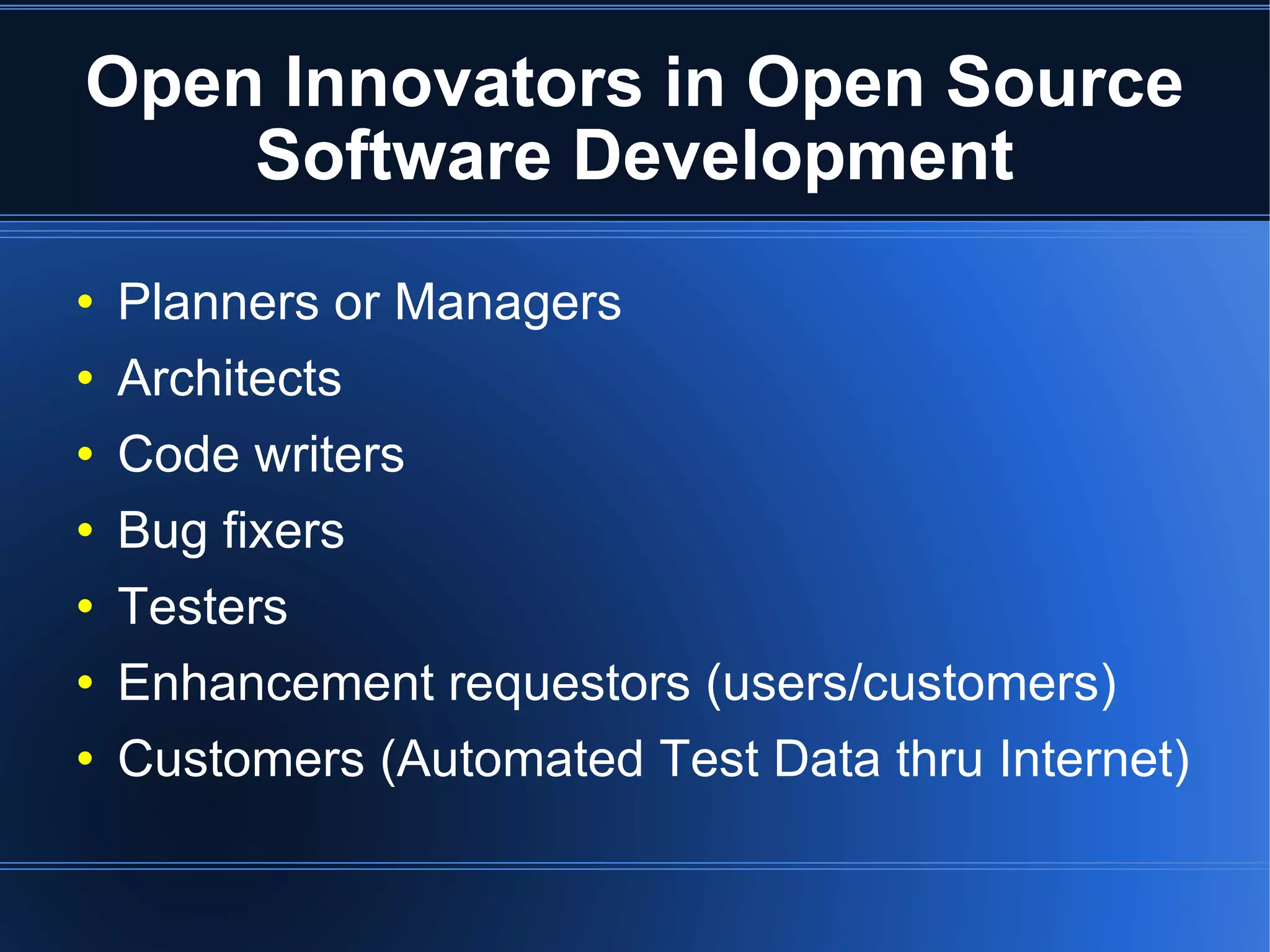
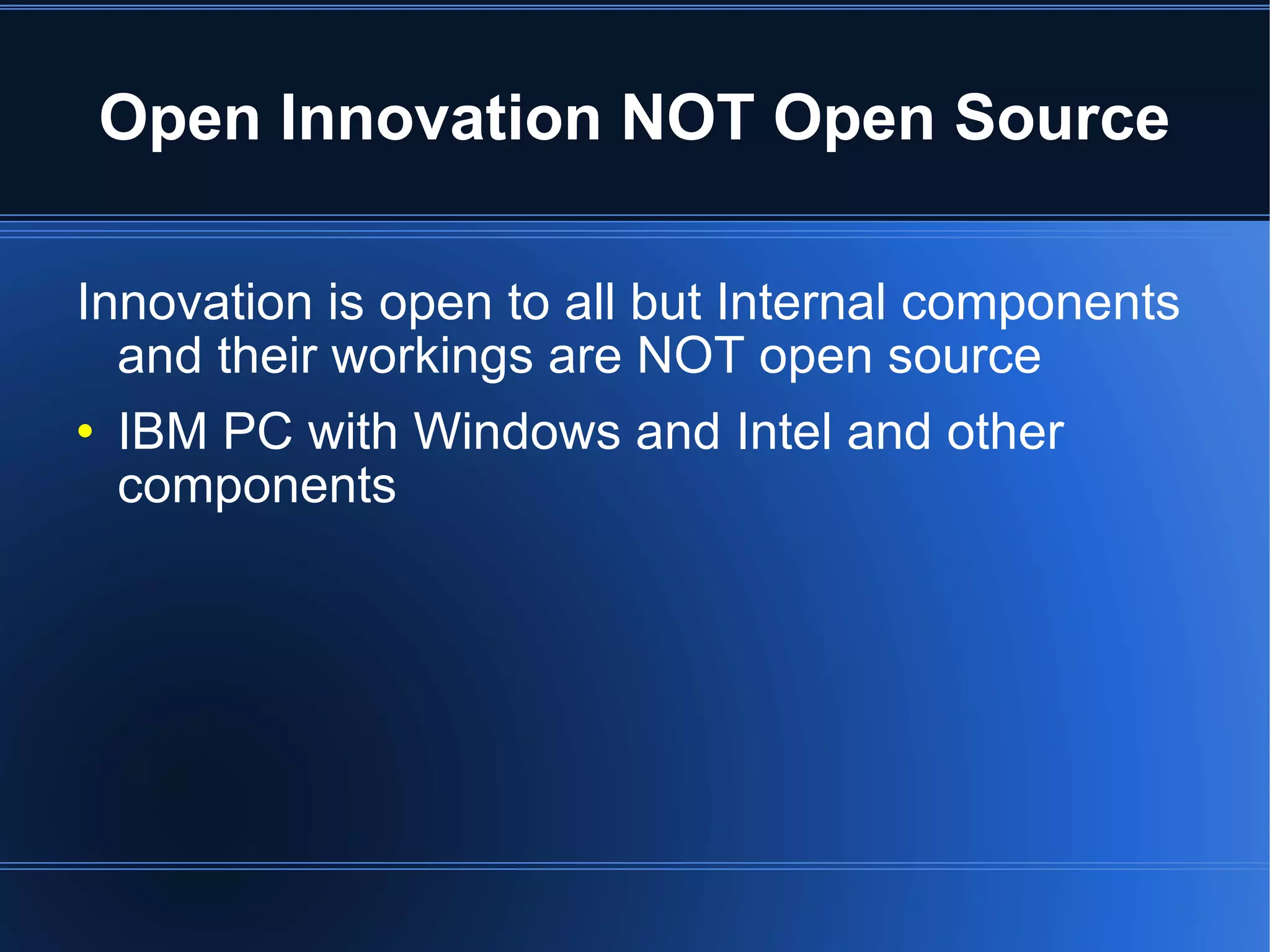
The document discusses open innovation and open source software. Open innovation involves using innovations created by others through processes, products, or knowledge. It is characterized by purposeful knowledge inflows and outflows, organic growth of innovation, and reliance on outside innovators. Open source software development is a form of open innovation where the intellectual property is openly available and projects involve collaboration. However, open innovation does not always involve making internal components openly available as with systems like IBM PCs.