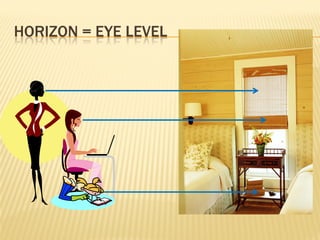
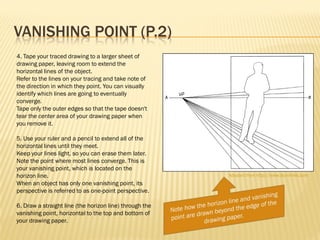
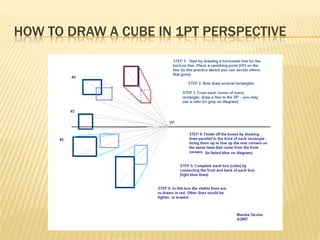
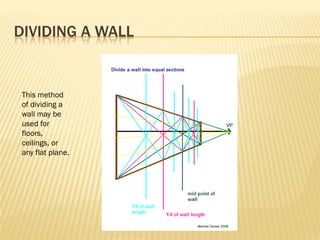
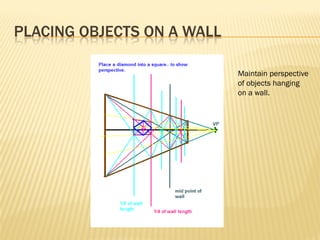
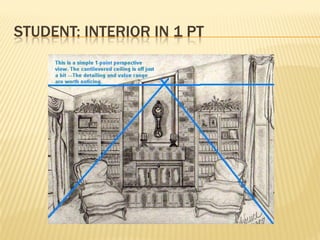
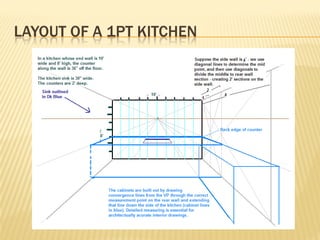
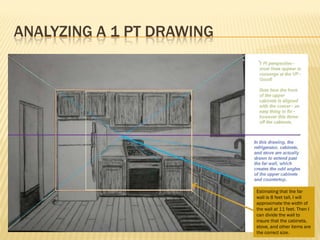
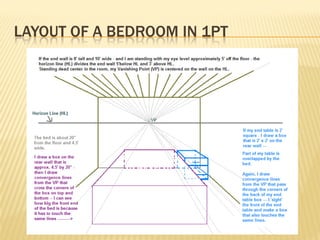
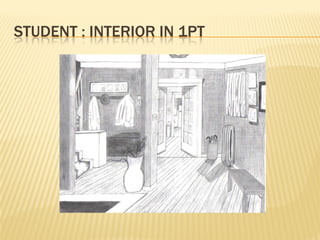
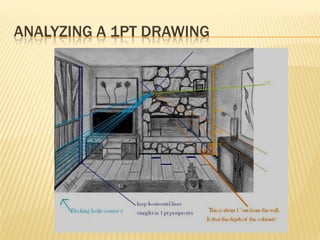
Linear perspective involves using techniques like converging parallel lines and vanishing points to create the illusion of depth and three-dimensionality on a two-dimensional surface. One point perspective uses a single vanishing point that all parallel lines recede towards on the horizon line. This technique was pioneered during the Renaissance by artists like Brunelleschi who studied optics and the visual perception of depth and distance. Key terms in linear perspective include the horizon line, orthogonal lines, and vanishing point, which are used to accurately depict the relative sizes of objects based on their distance from the viewer.