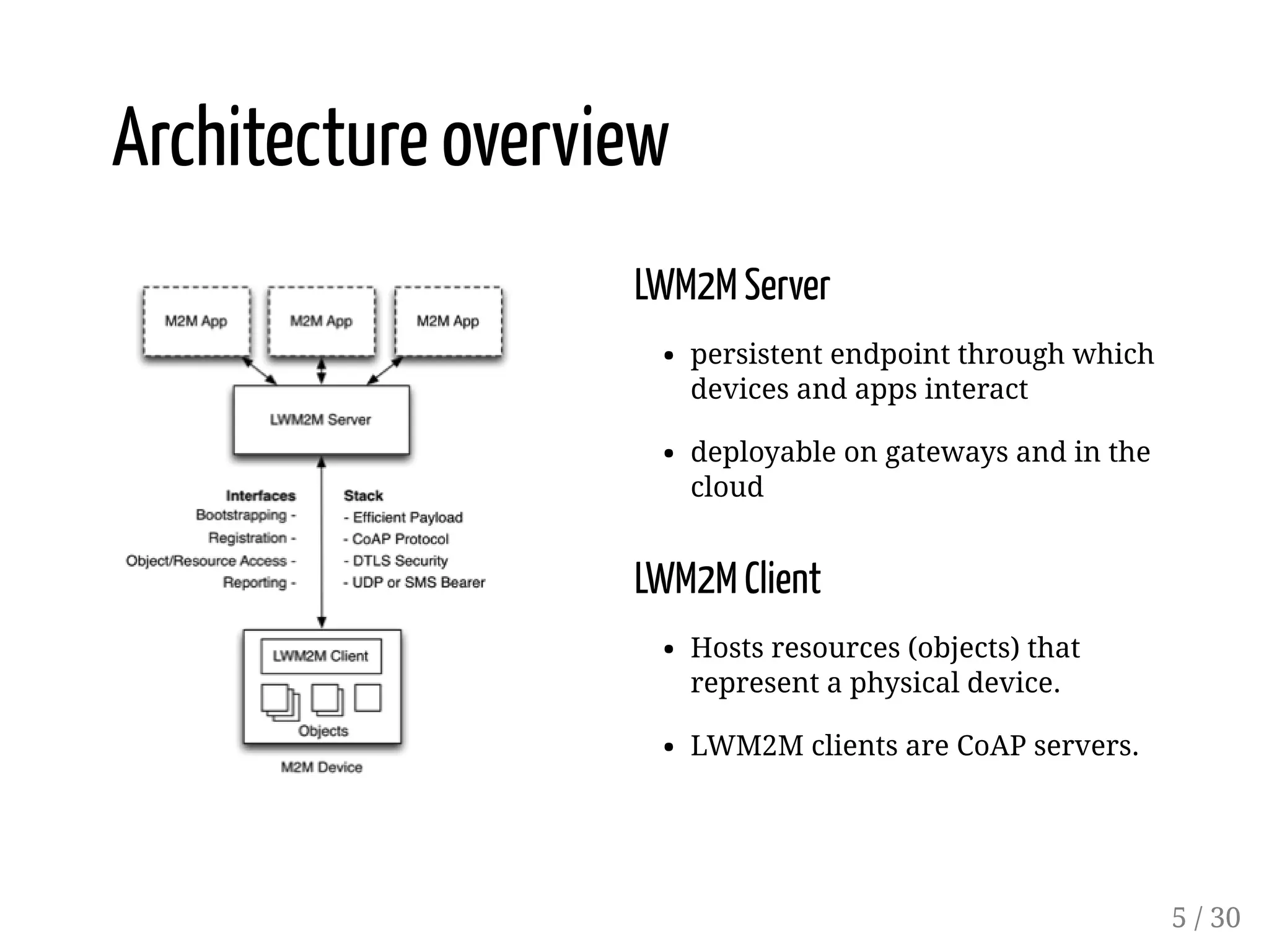
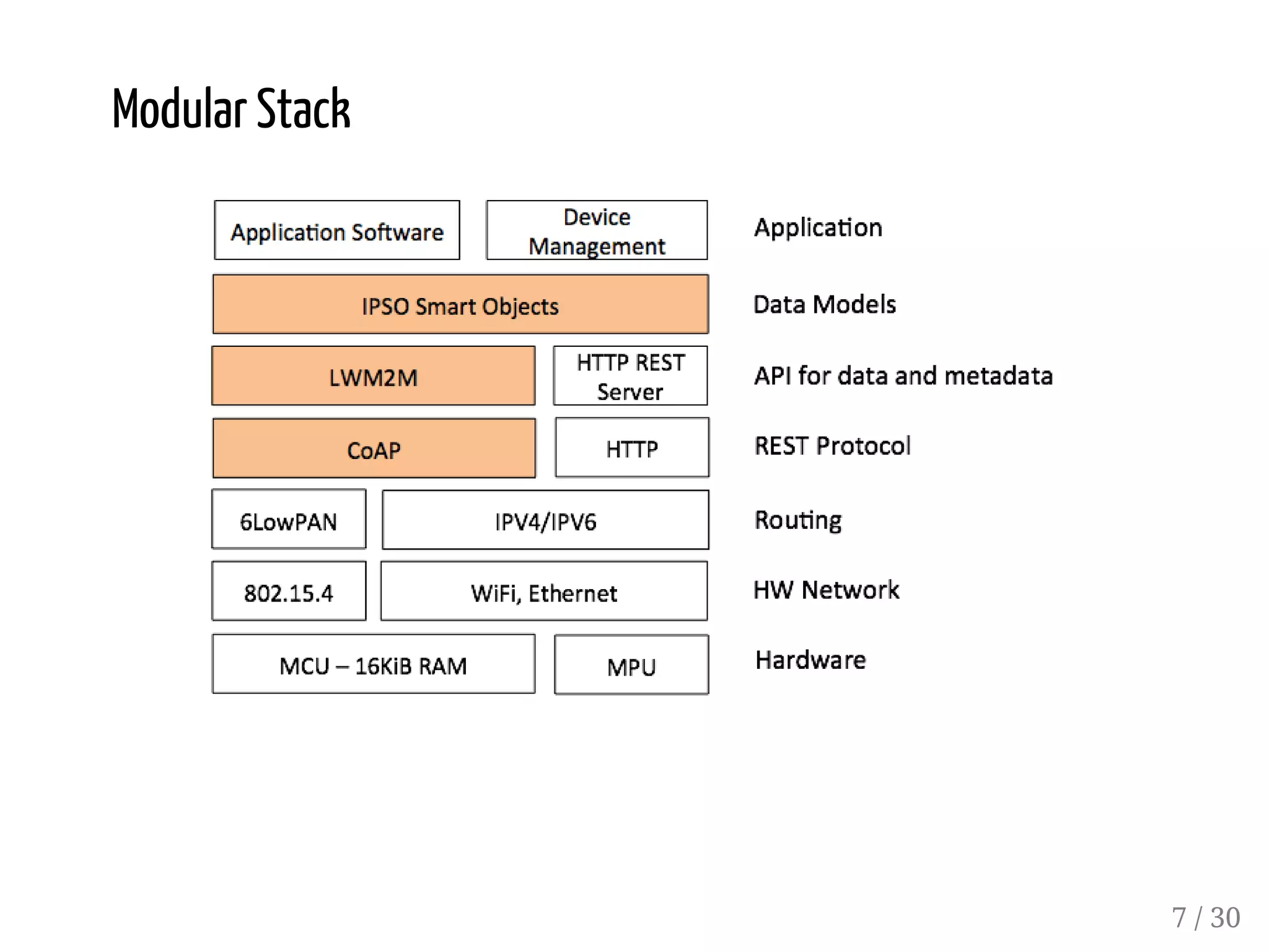
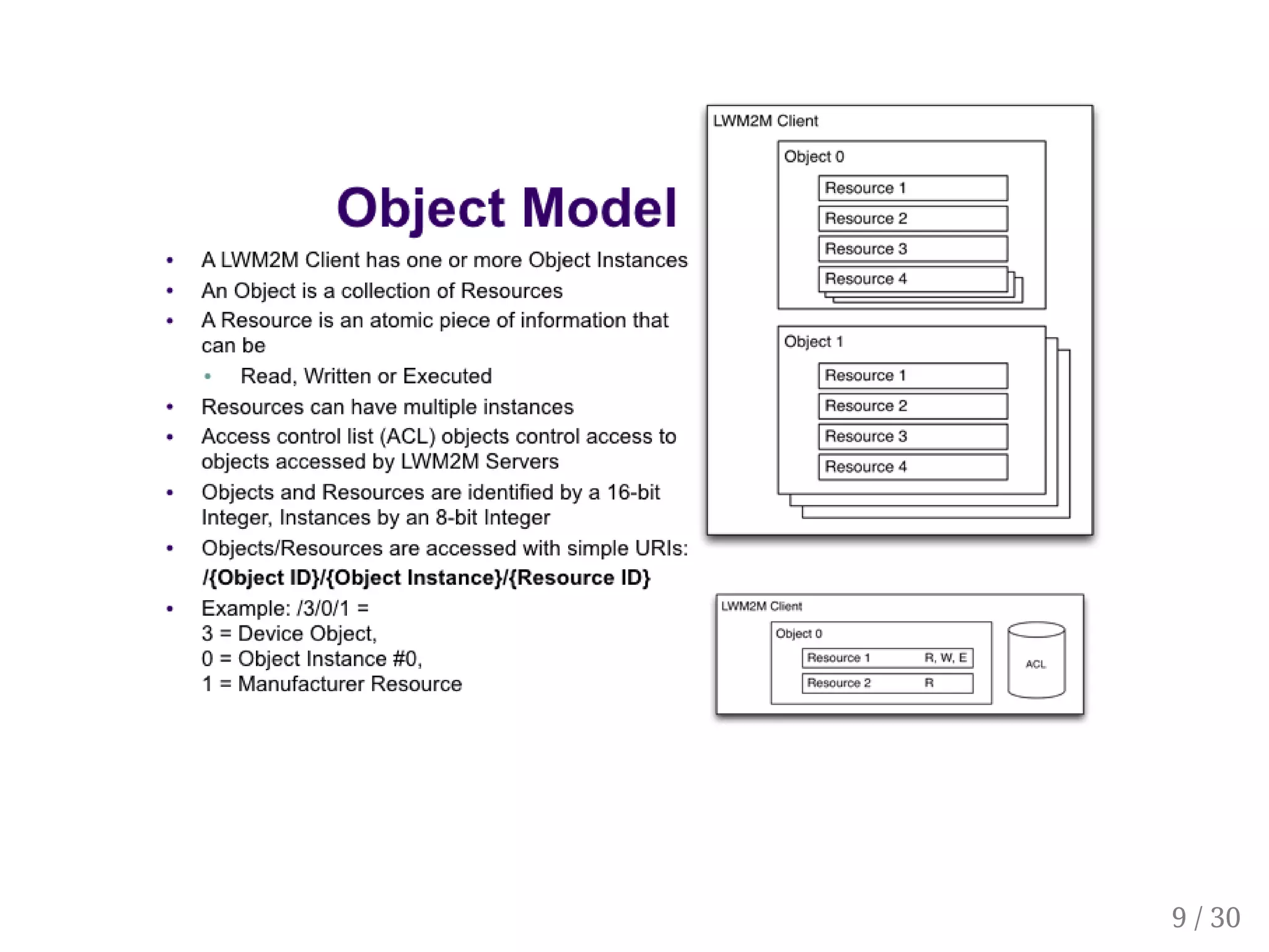
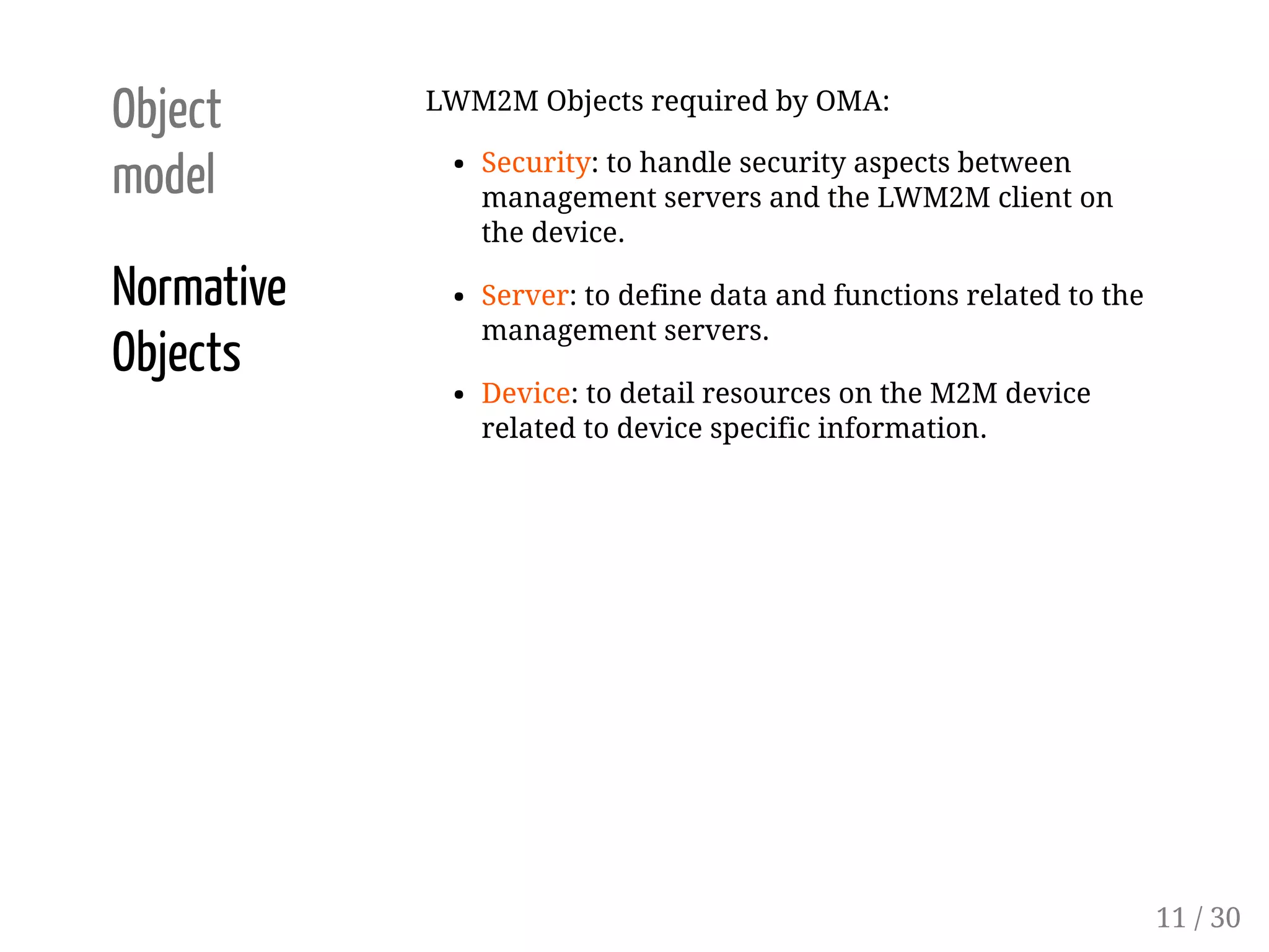
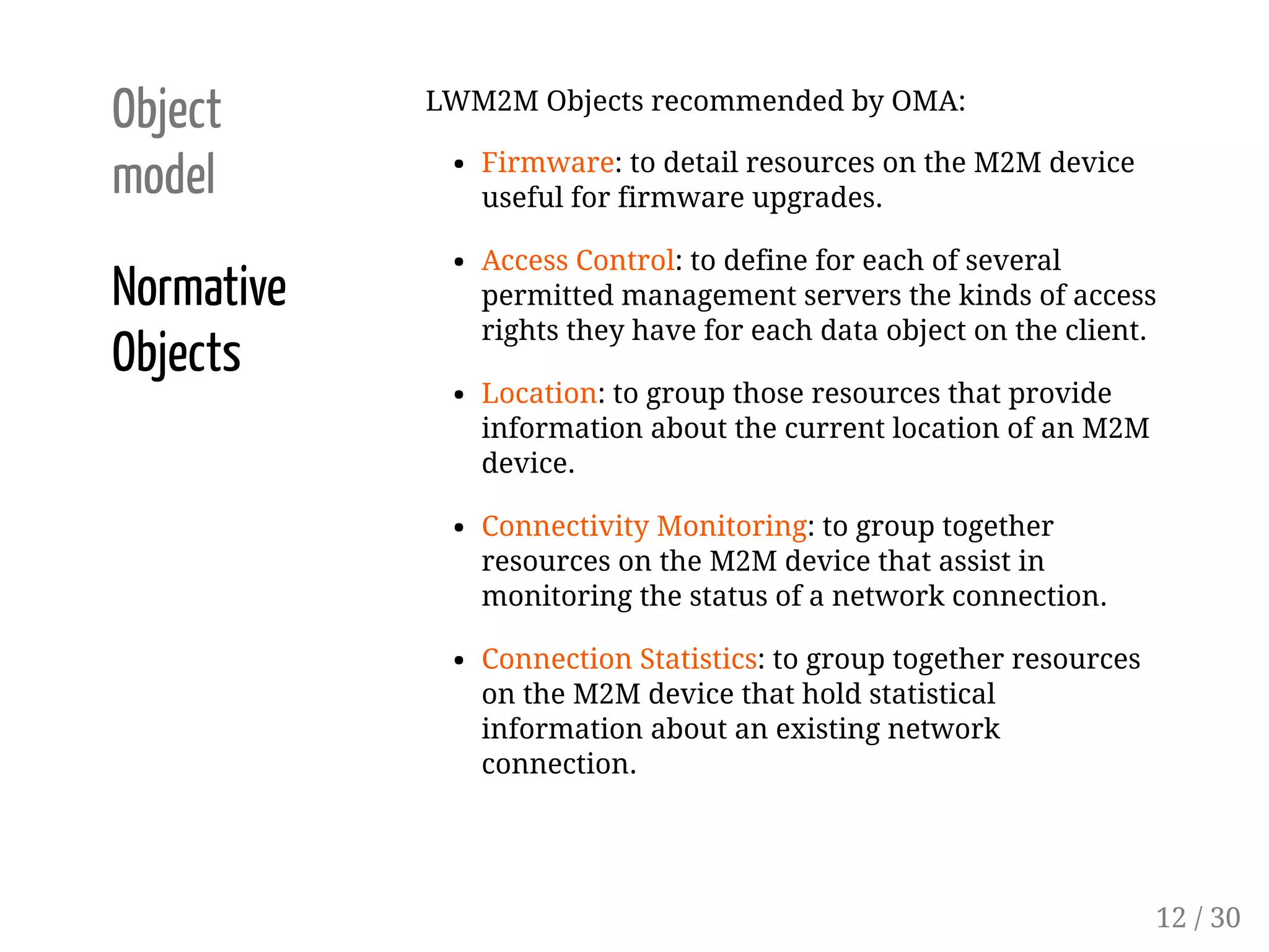
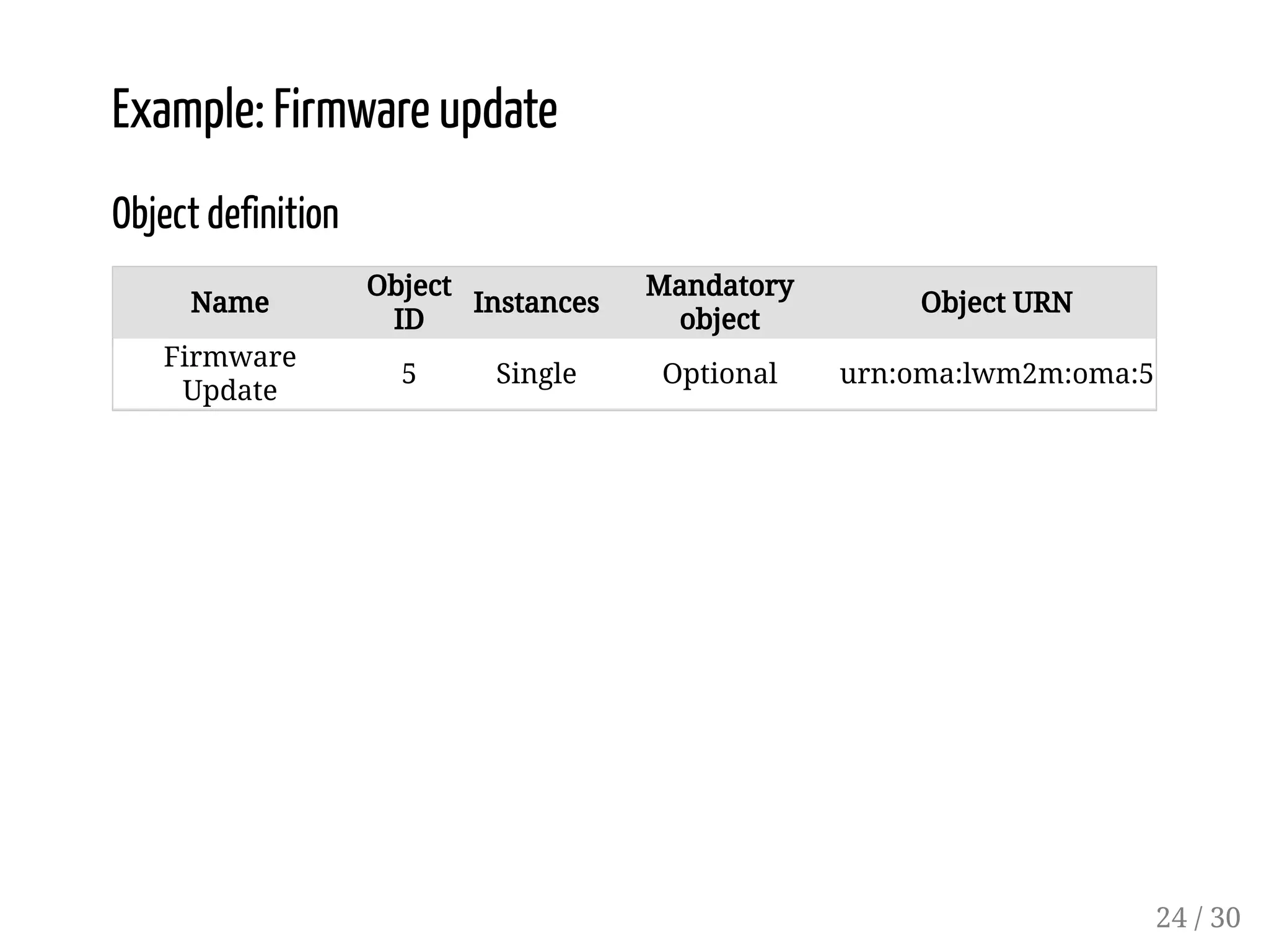
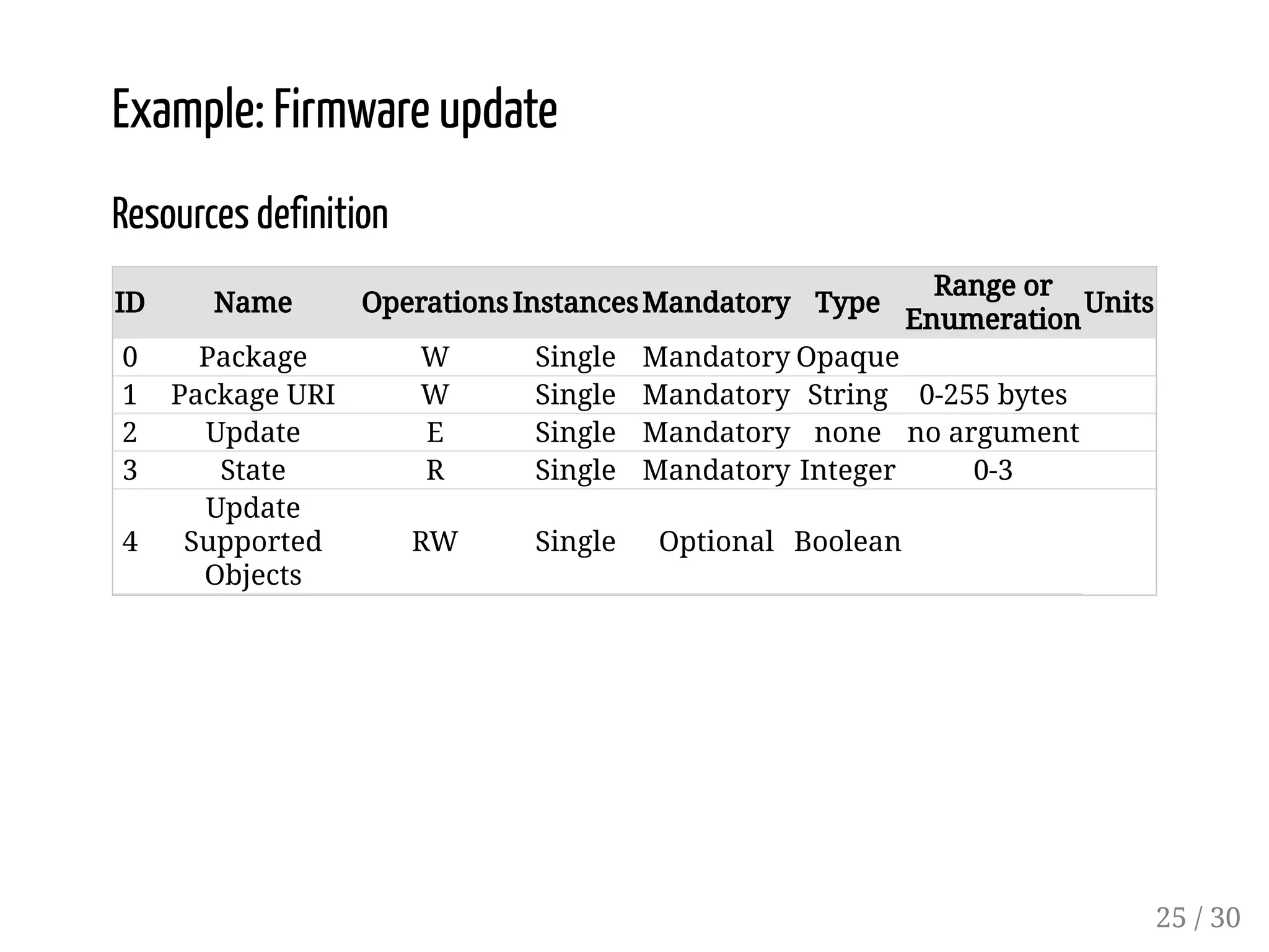
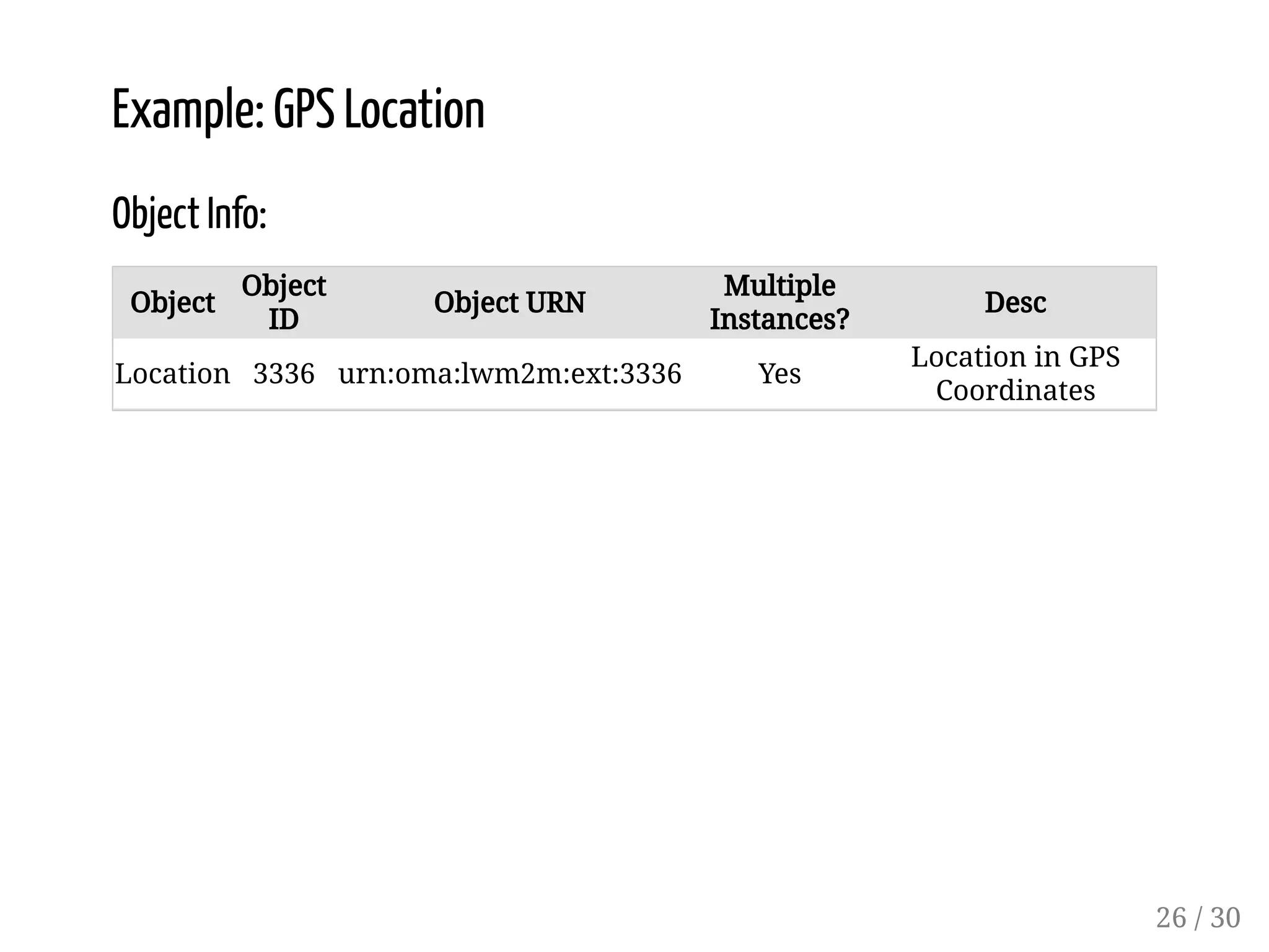
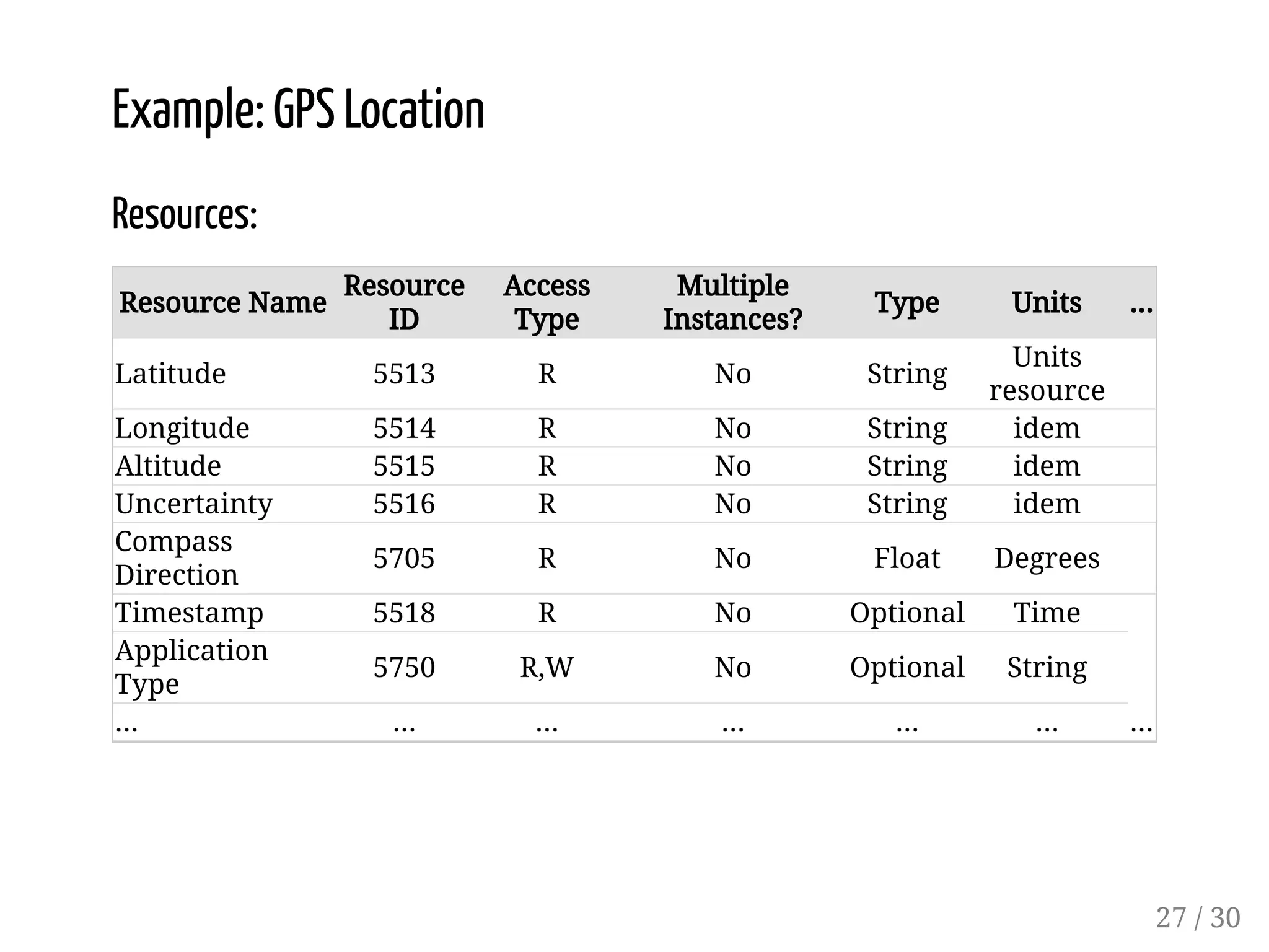
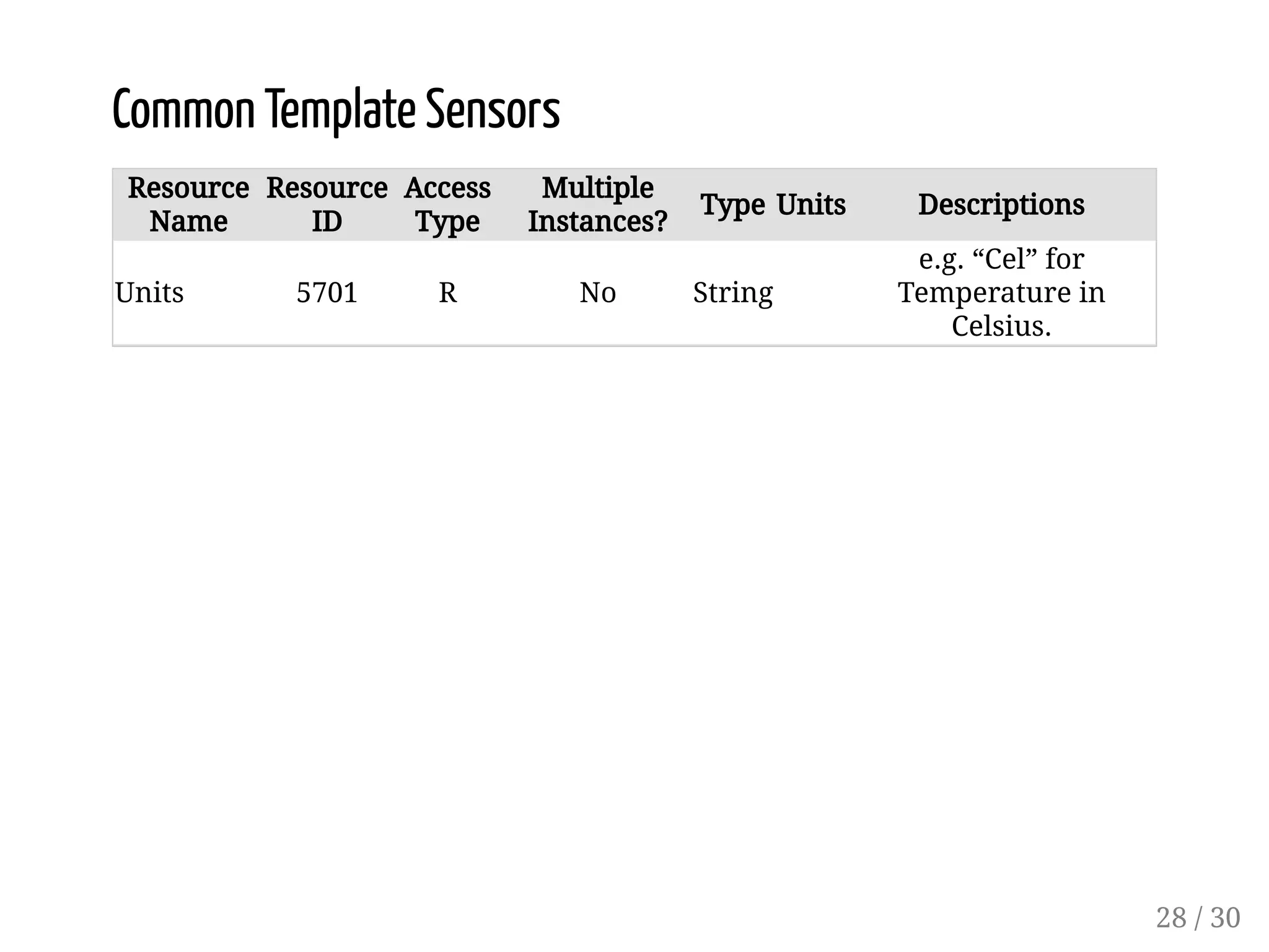
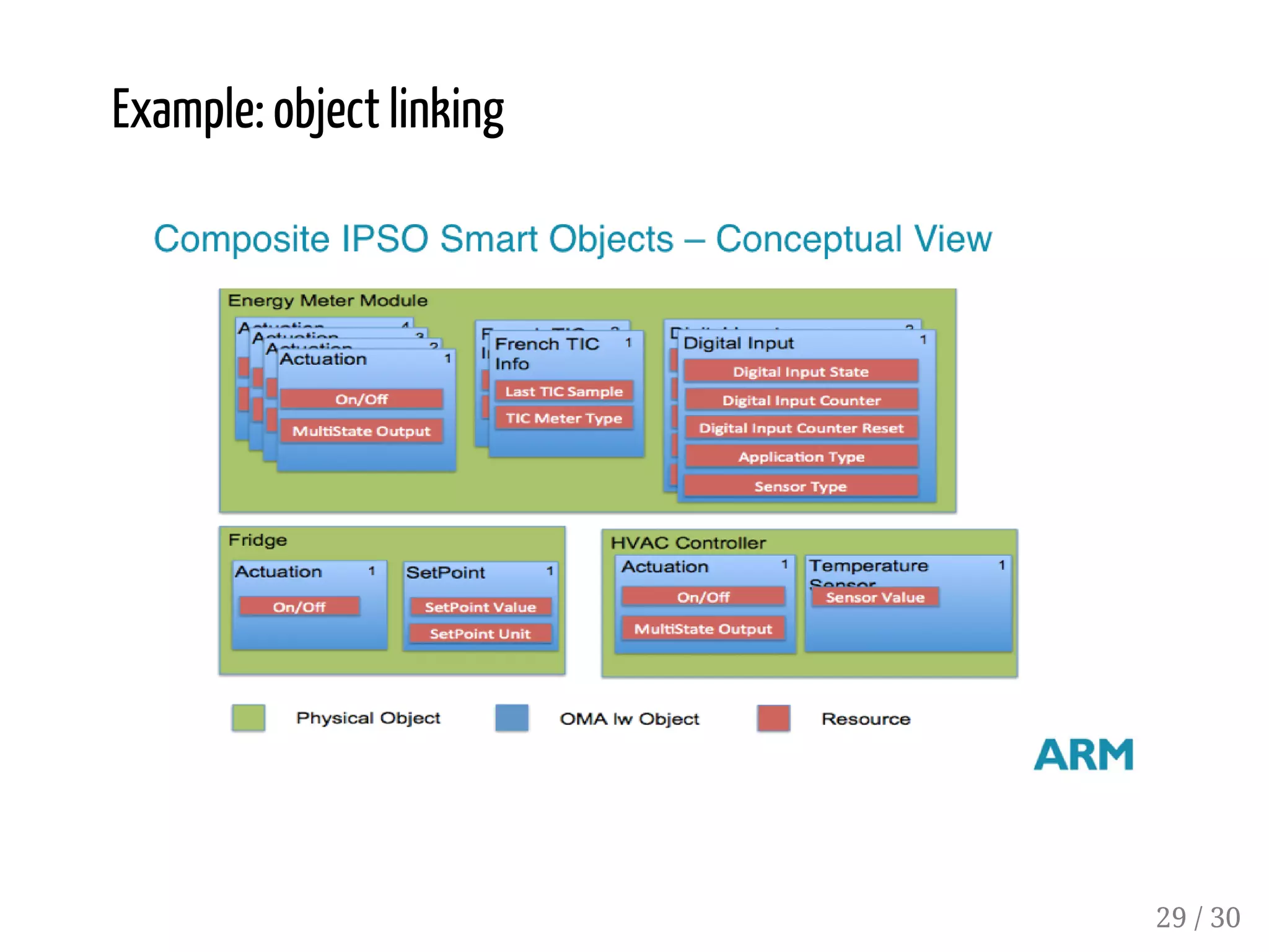
This document provides an overview of device management using OMA Lightweight M2M (LWM2M). It describes the LWM2M architecture, including servers, clients, and interfaces. Key features of LWM2M version 1.0 are presented, such as object-based resources, CRUD operations, and security. Normative and recommended LWM2M objects are outlined, including those for security, firmware updates, and location. IPSO smart objects are also summarized as a way to promote reusable application standards in IoT. Examples of firmware update and GPS location objects are given to illustrate the object model.