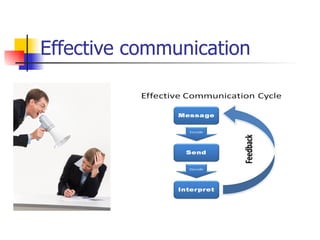
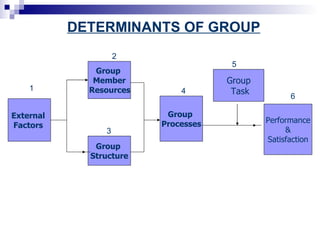
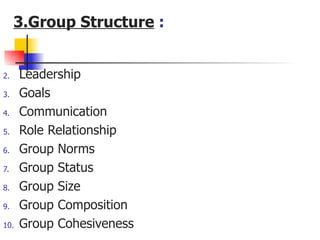
Group is defined as two or more people who interact and influence each other to achieve common objectives. Key aspects of a group include having common goals, interdependence among members, and a sense of group identity. People join groups for reasons such as status, affiliation, security, and goal accomplishment. Group dynamics and processes, including norms, communication patterns, leadership, and tasks, determine group performance and member satisfaction.