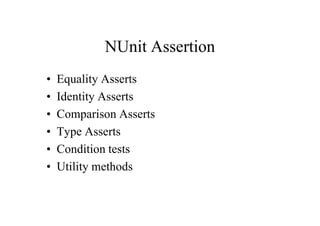
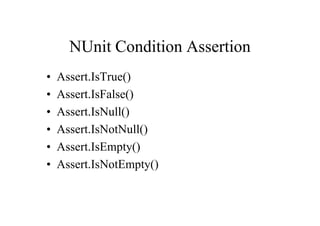
This document provides an introduction to unit testing using the NUnit framework. It defines unit testing as developer tests that validate code works as expected. Unit tests are part of the construction cycle and sit between technical design and QA testing in the software development lifecycle. Benefits of unit testing include early defect detection, better code design, regression protection, and learning new APIs. The document then describes NUnit attributes that mark test fixtures and methods. It also covers NUnit assertions for verification. Examples are provided of test-driven development and using NUnit for continuous integration.



















![NUnit Required Attributes
– [TestFixture]
• Used to indicate that a class contains test methods
– [Test]
• Used to indicate that a method within a test fixture
should be run by the Test Runner application
Example: Test1.cs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nunitintroduction20110503-110504055026-phpapp01/85/An-Introduction-to-Unit-Test-Using-NUnit-20-320.jpg)
![NUnit Optional Attributes
– [SetUp]
• Used to indicate a setup method should be ran before each of
the tests
– [TearDown]
• Used to indicate a tear down method should be ran after each
of the tests are ran
Example: Test2.cs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nunitintroduction20110503-110504055026-phpapp01/85/An-Introduction-to-Unit-Test-Using-NUnit-21-320.jpg)
![NUnit Optional Attributes
– [TestFixtureSetUp]
• Used to indicate a setup method that will be ran once; before
all other tests. This is the first method that is called before the
tests are started.
– [TestFixtureTearDown]
• Used to indicate a tear down method that will be ran once;
after all other tests have run. This is the last method that is
called after all the tests have finished.
Example: Test3.cs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nunitintroduction20110503-110504055026-phpapp01/85/An-Introduction-to-Unit-Test-Using-NUnit-22-320.jpg)
![NUnit Optional Attributes
– [ExpectedException(typeof(Exception))]
• When you want an exception to be thrown
• Will only pass if exception type was thrown
– [Ignore(“Not ready yet")]
Example: Test4.cs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nunitintroduction20110503-110504055026-phpapp01/85/An-Introduction-to-Unit-Test-Using-NUnit-23-320.jpg)