Embed presentation
Download to read offline






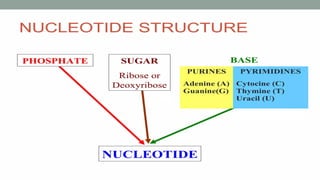



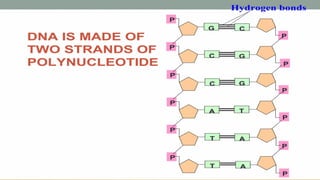


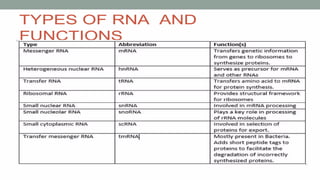

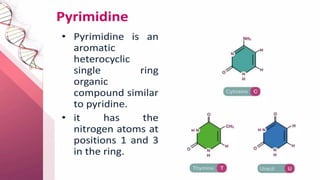

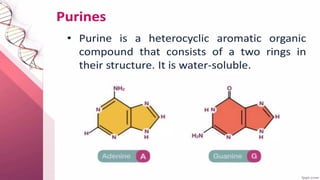



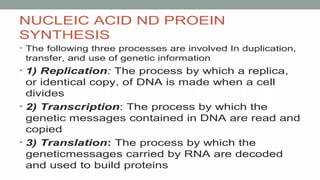
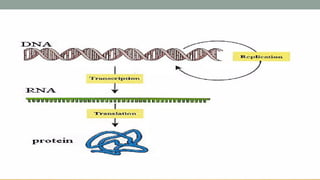
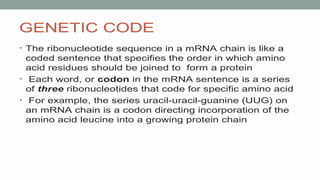
Nucleic acids are large polymers made of nucleotides, which serve as their building blocks. There are two main types: DNA, which carries genetic information and is found in chromosomes, and RNA, which is involved in protein synthesis and located in the nucleus and cytoplasm. The document also details the base pairing rules for both DNA and RNA, highlighting the differences in their nucleotide compositions.

























