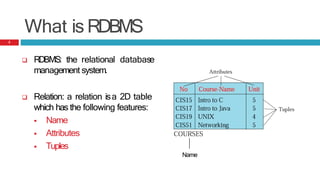
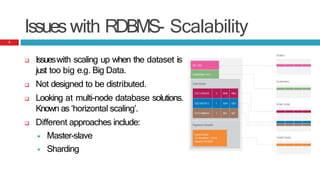
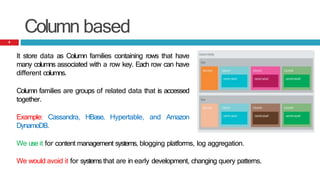
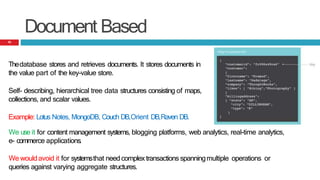
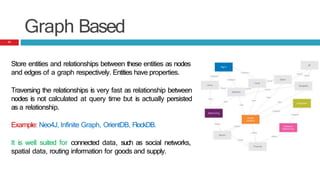
This presentation discusses the differences between Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) and NoSQL databases, highlighting the limitations of RDBMS in scalability and distribution. It outlines the need for NoSQL due to the rise of large data applications and describes four types of NoSQL databases: key-value, column-based, document-based, and graph-based, along with their use cases. The conclusion emphasizes that while NoSQL offers diverse options, RDBMS remains valuable in a landscape featuring multiple data storage technologies.