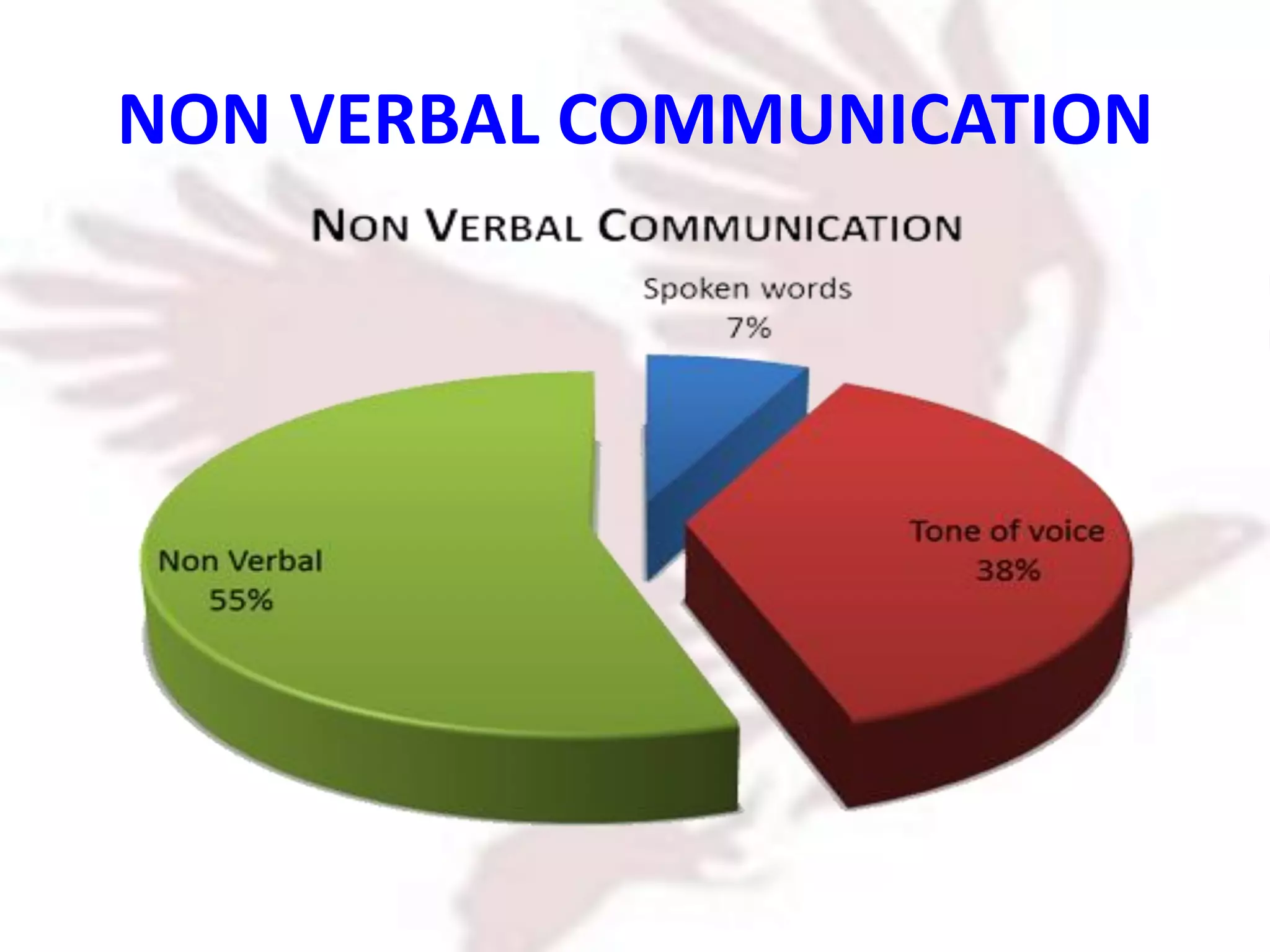
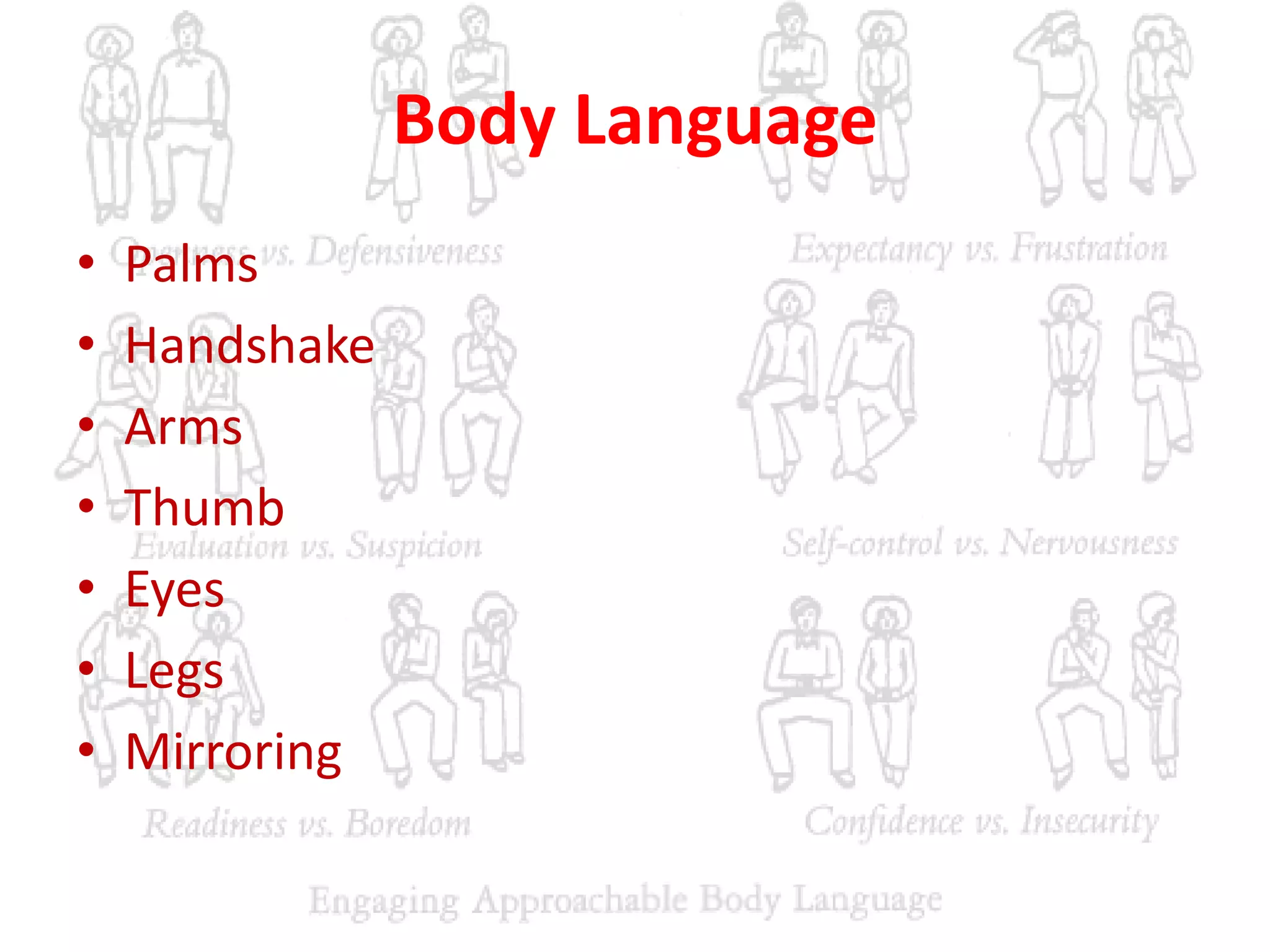
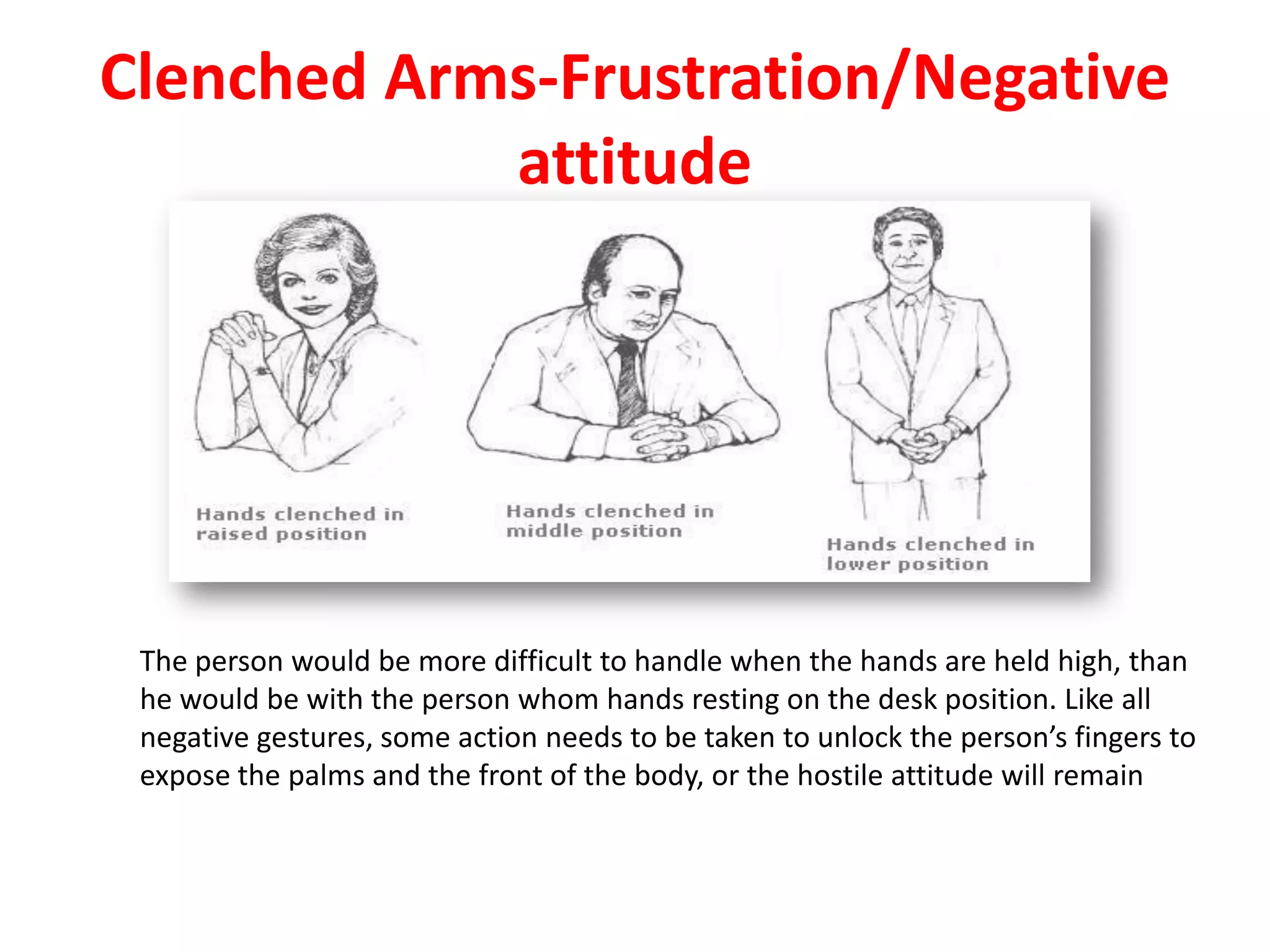
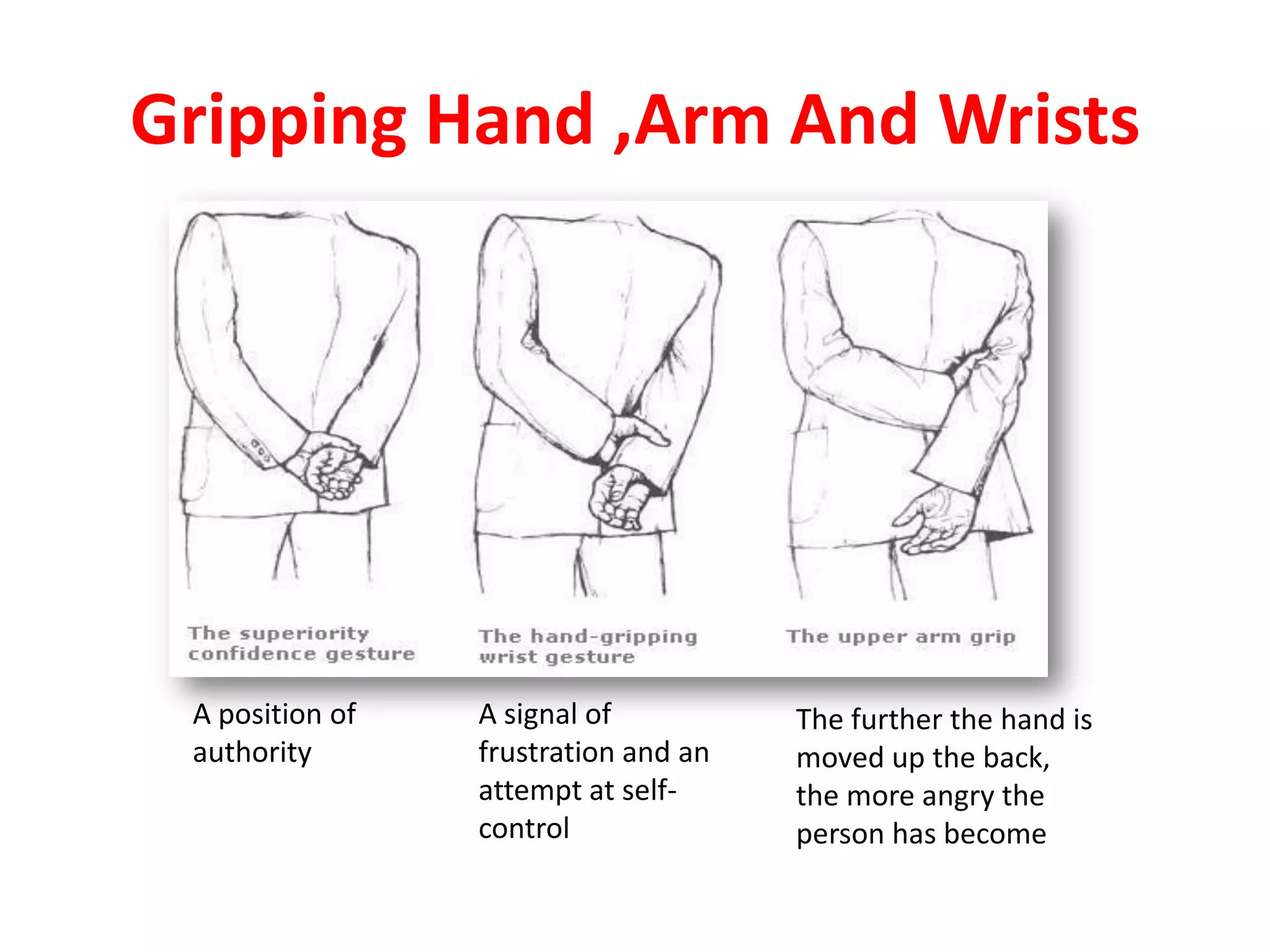
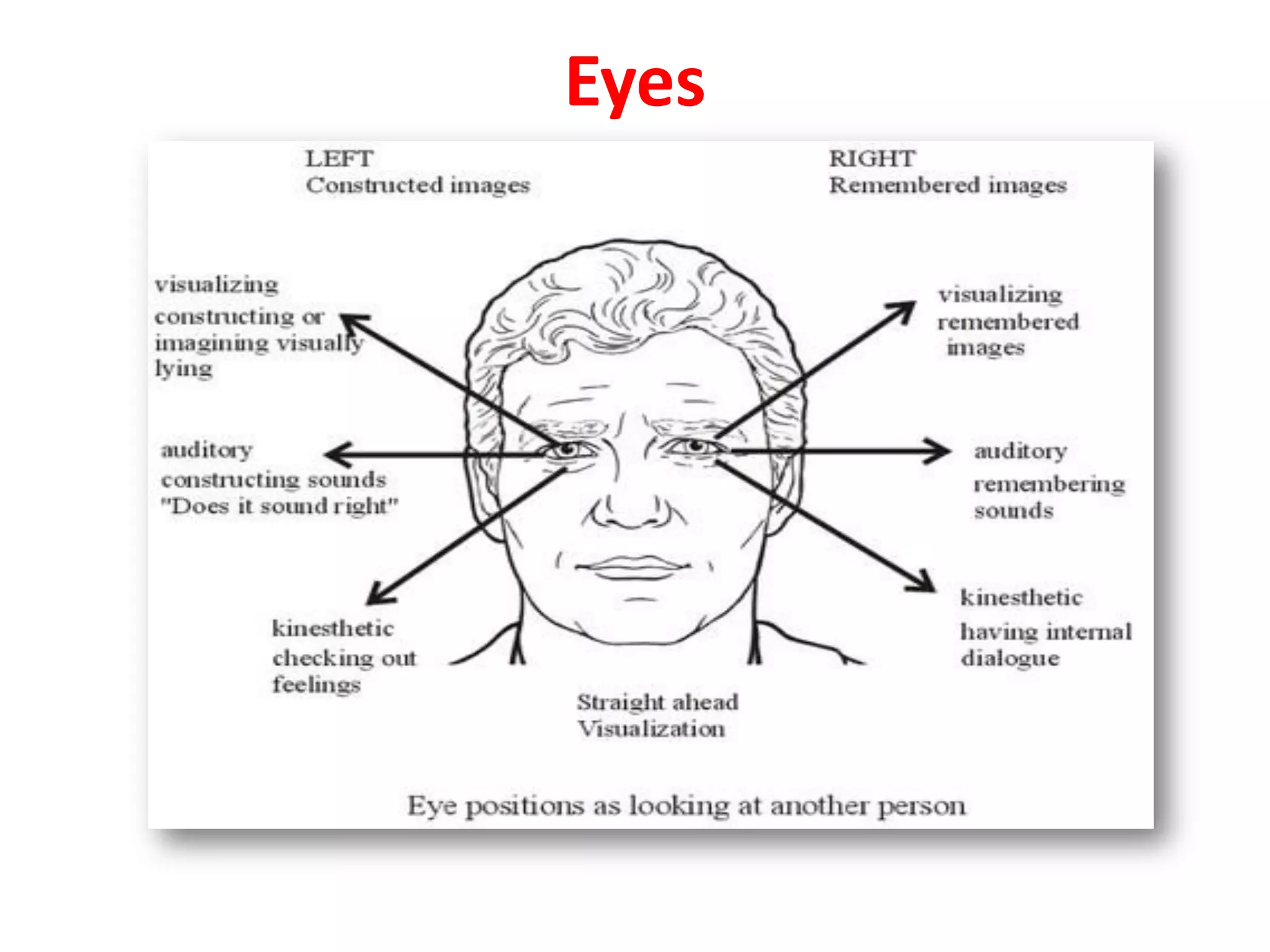
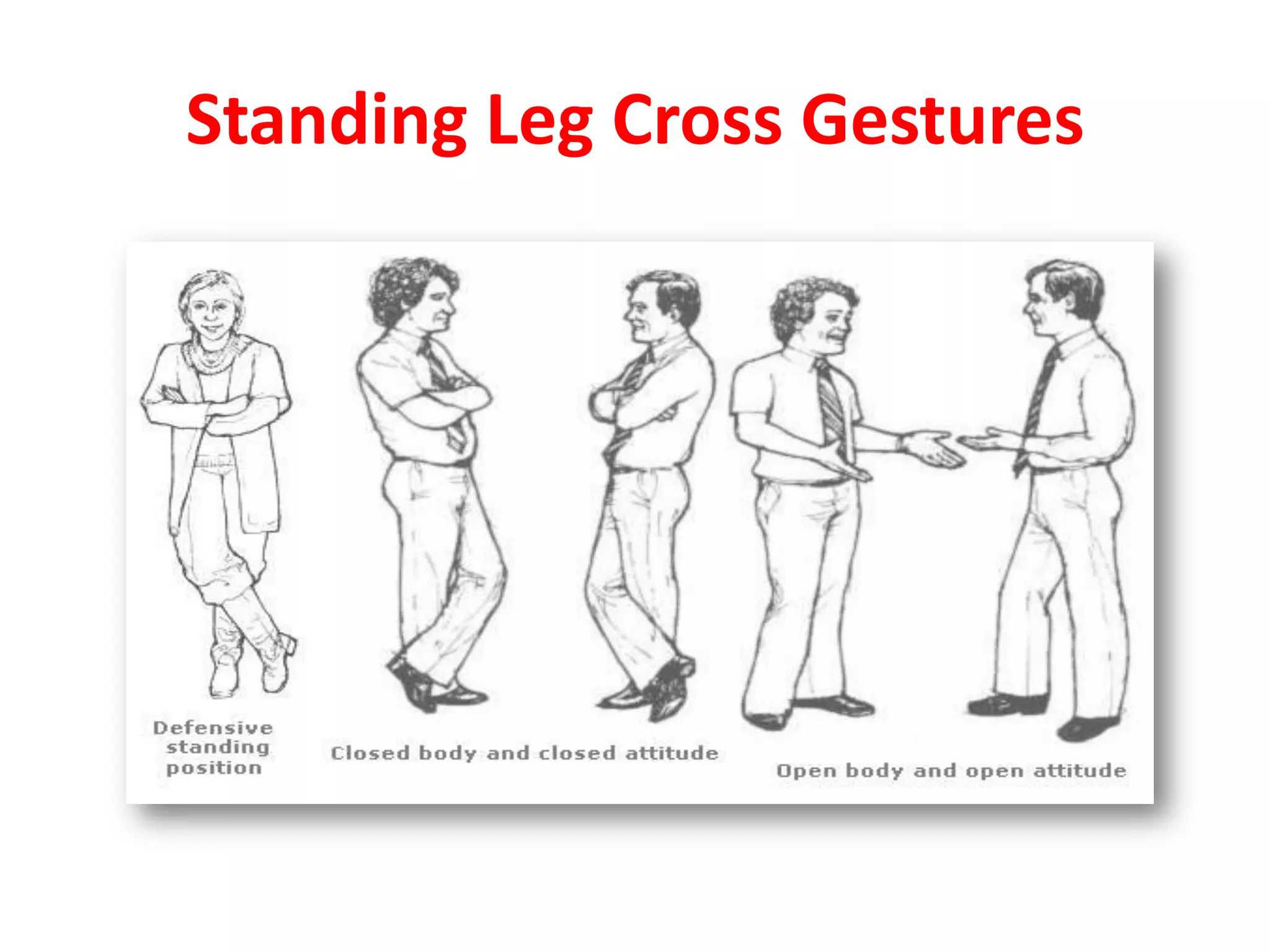
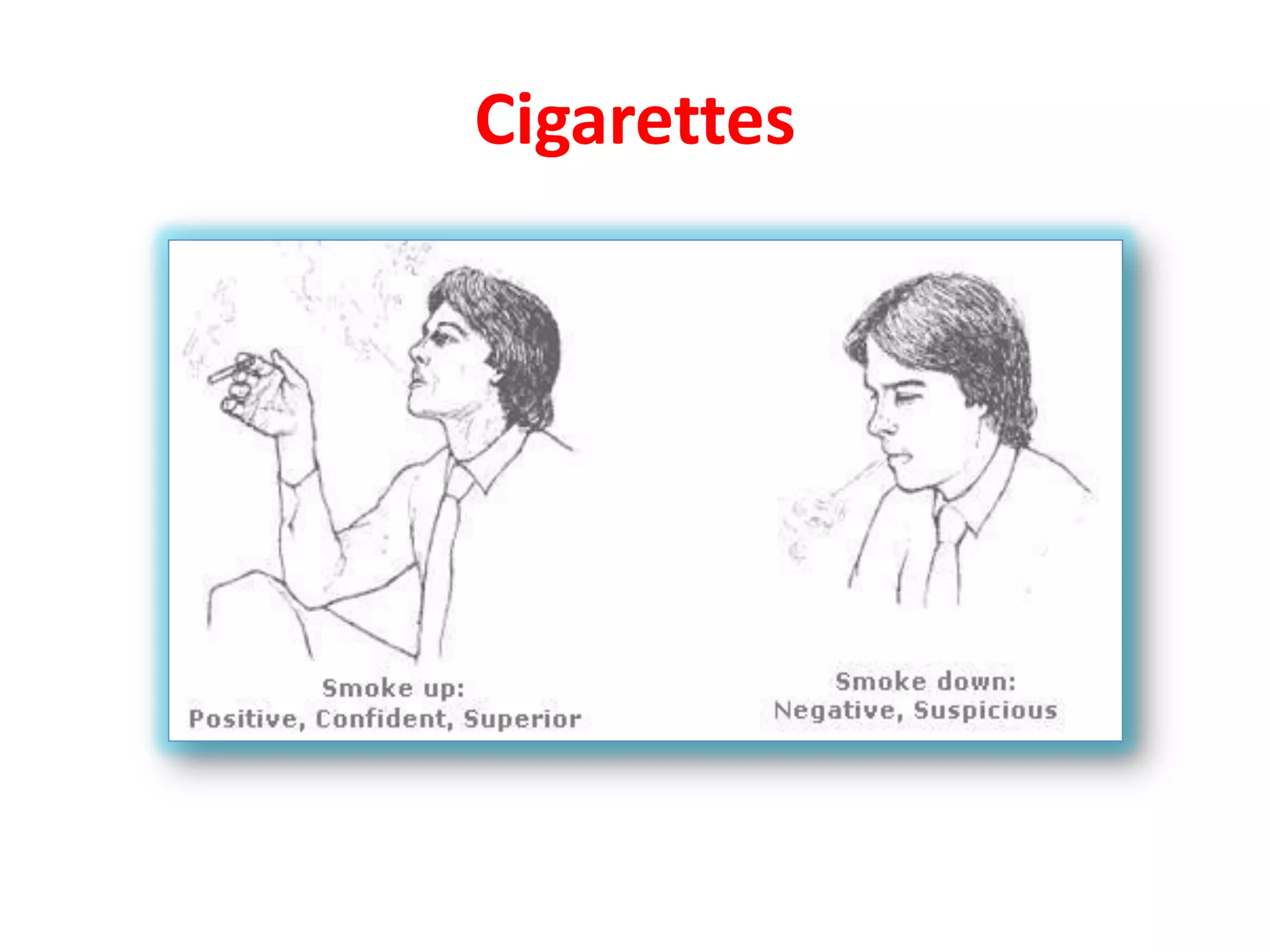
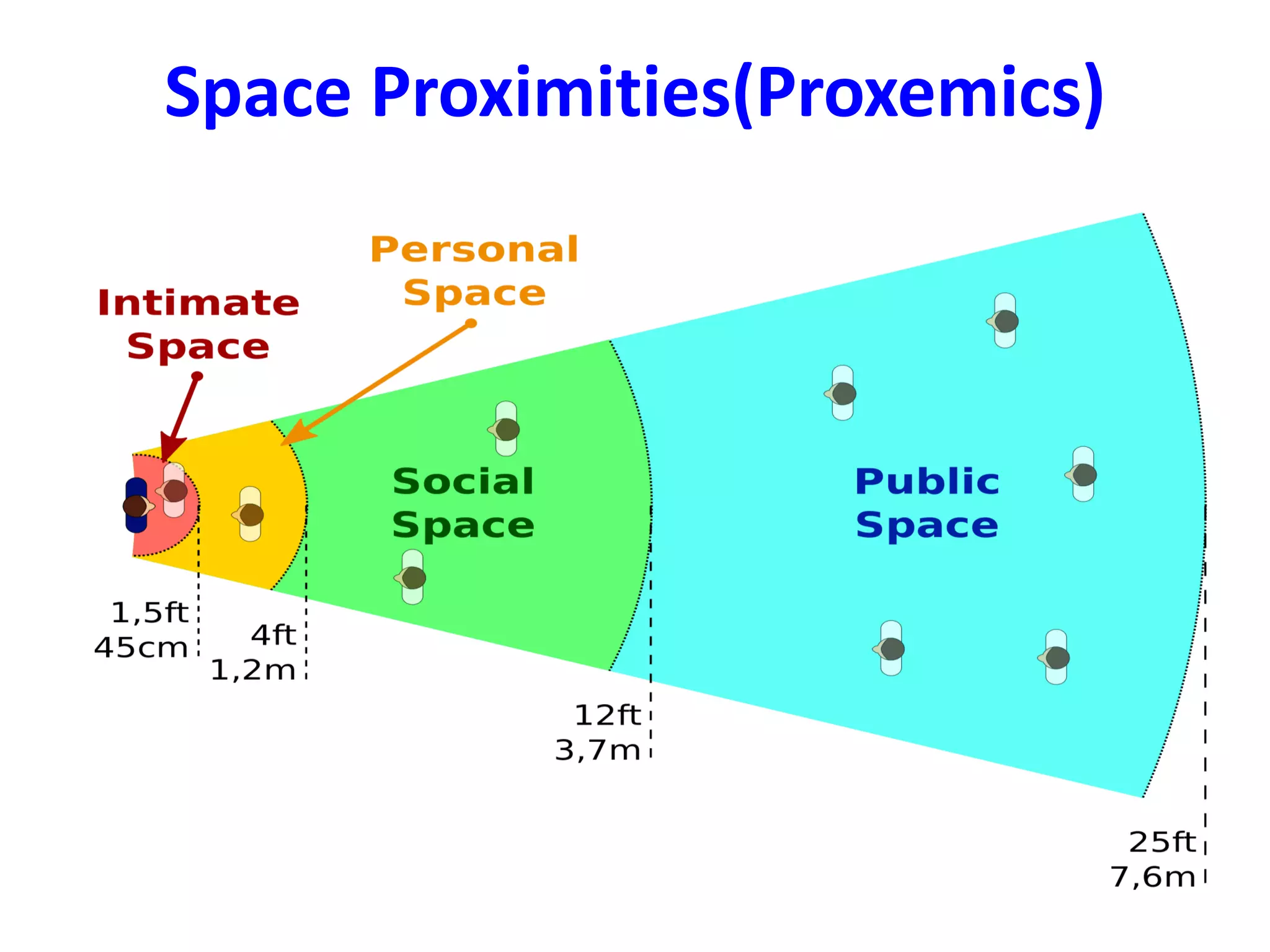
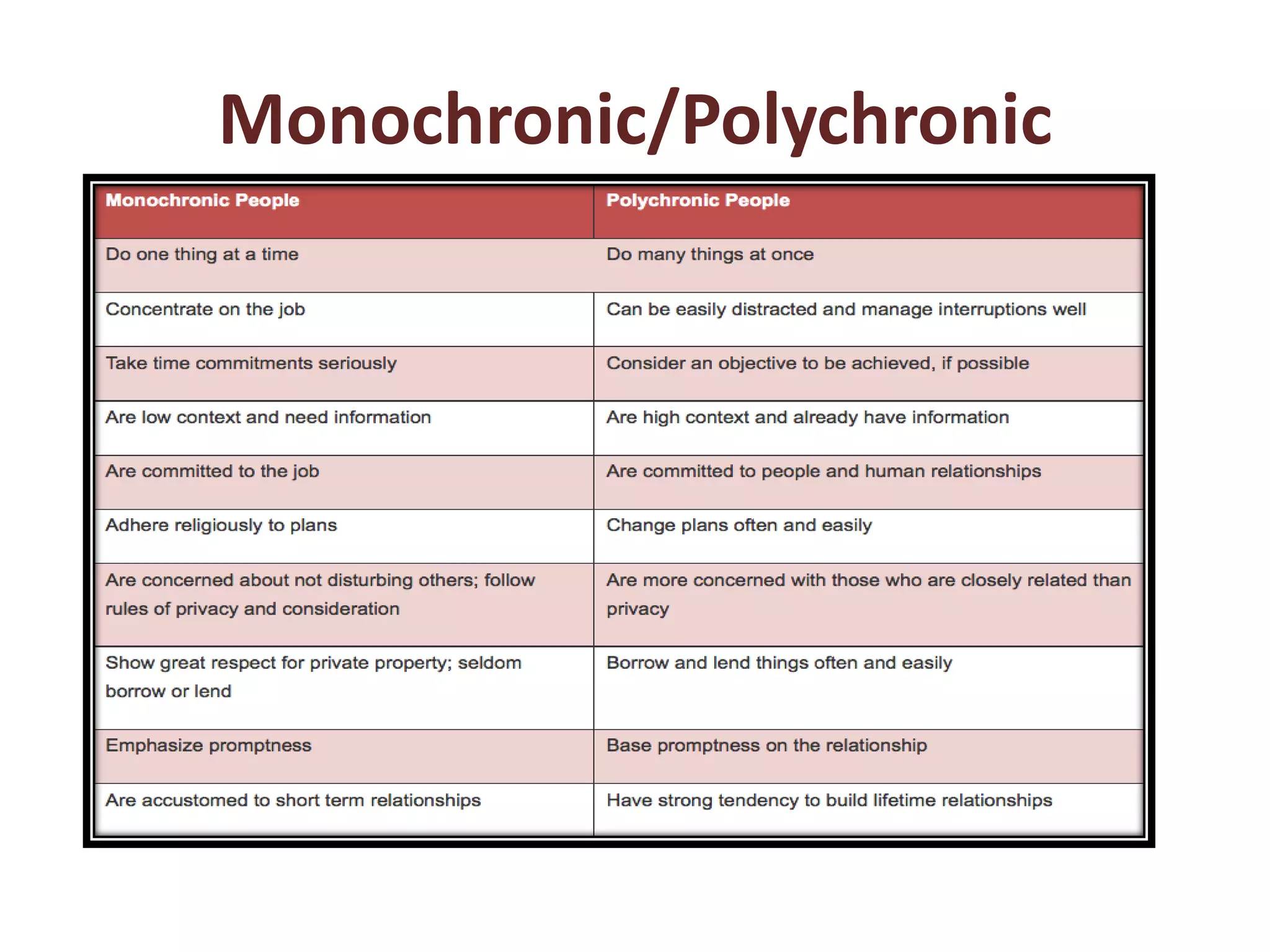
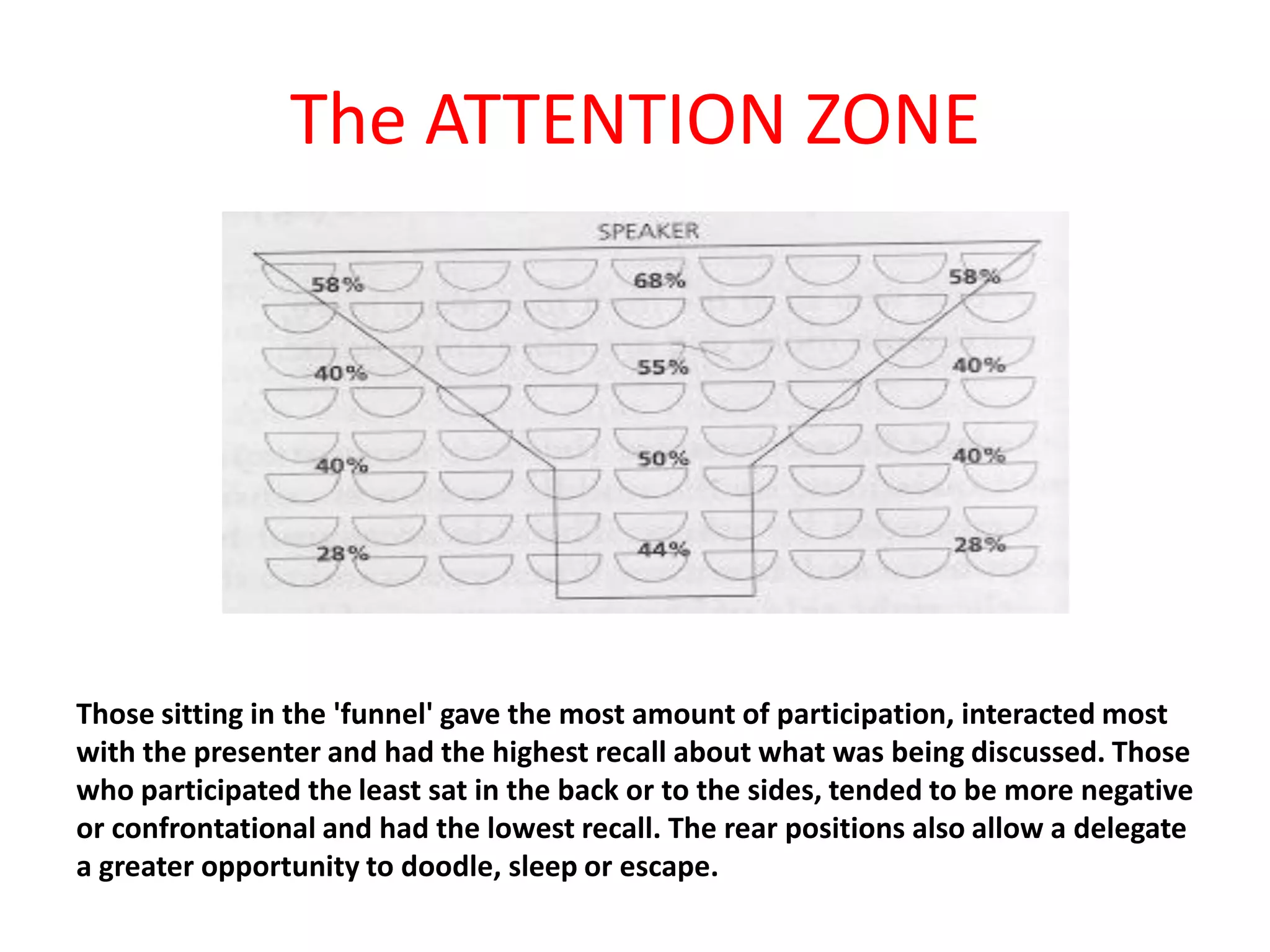
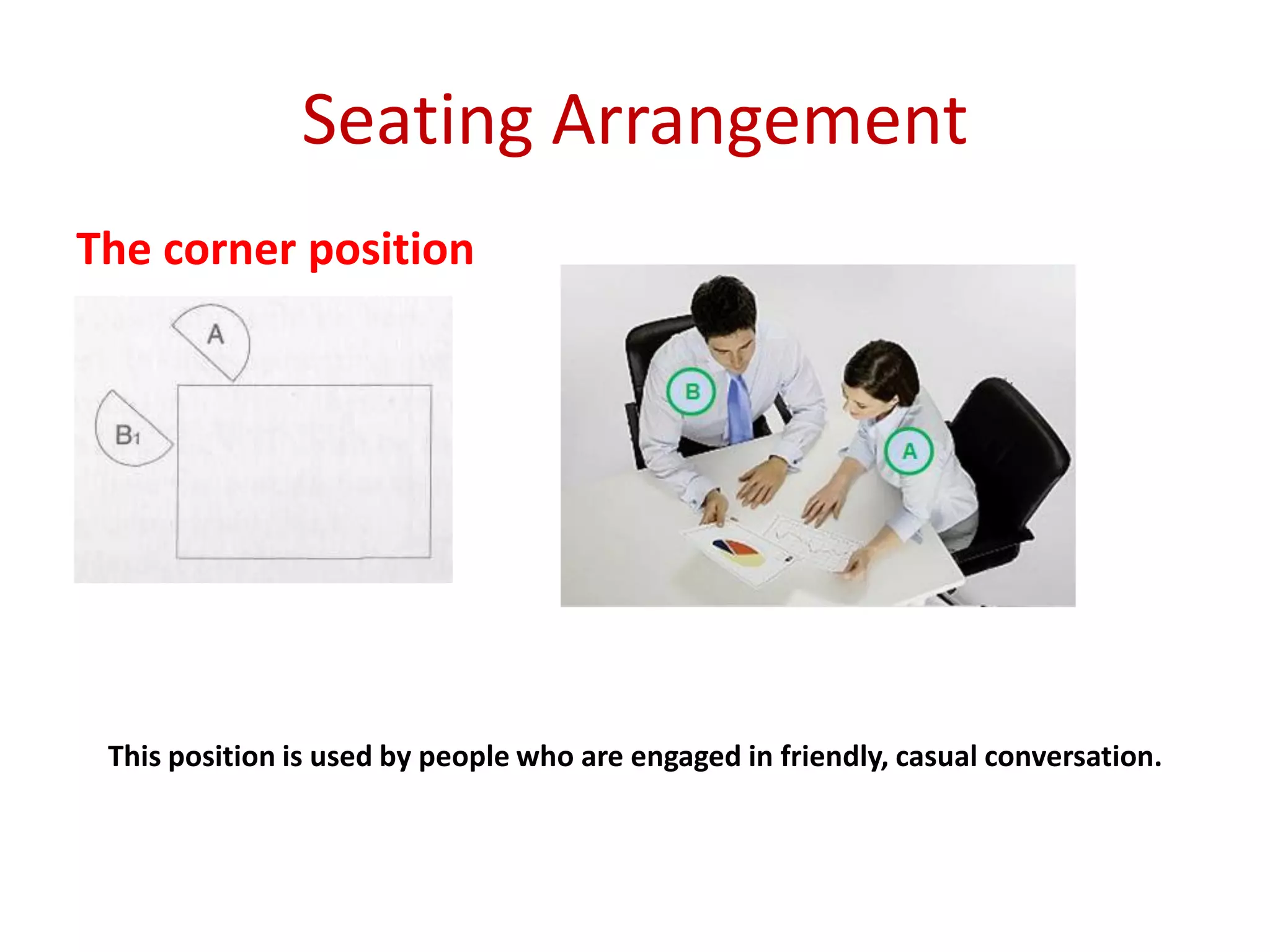
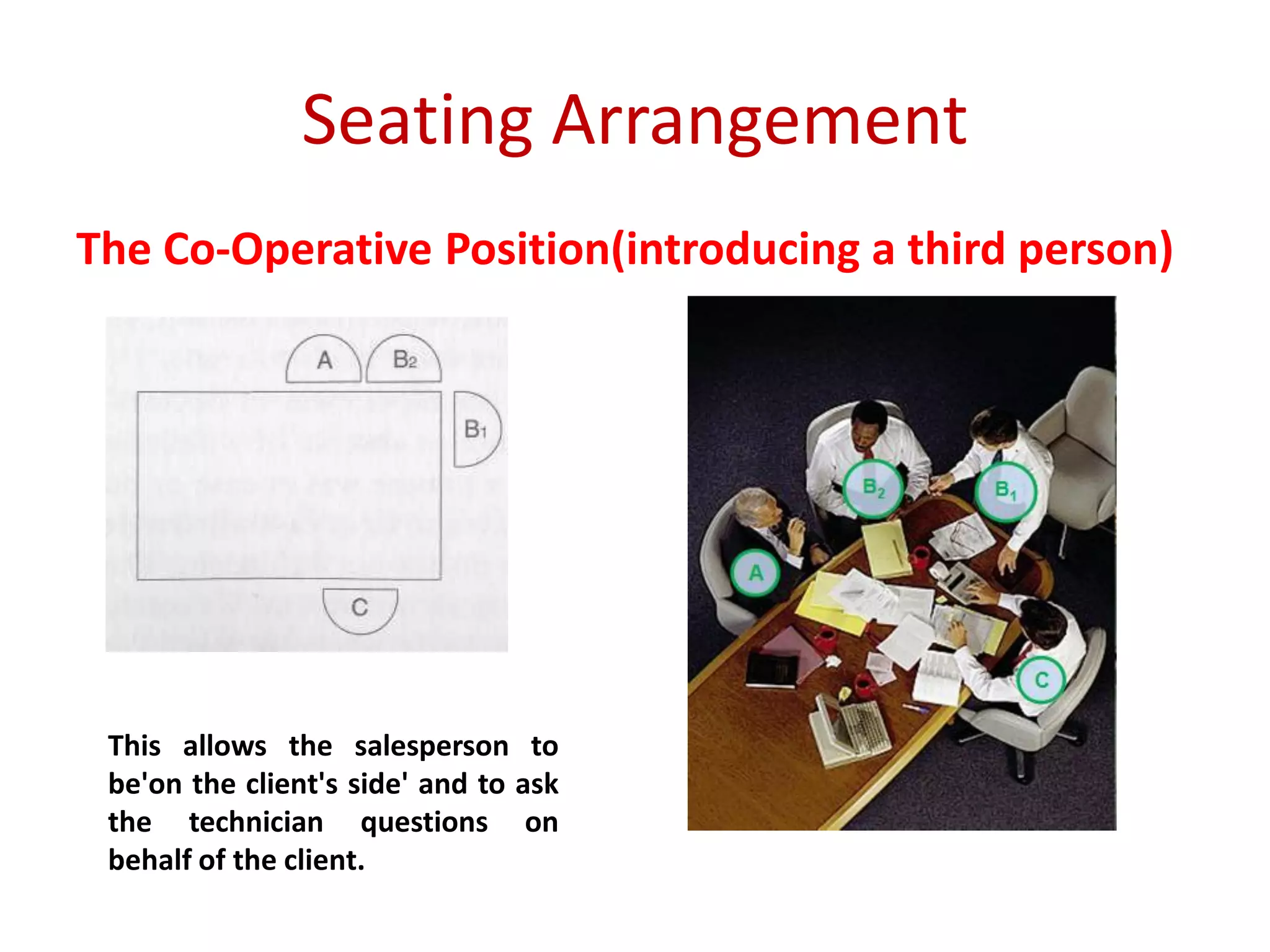
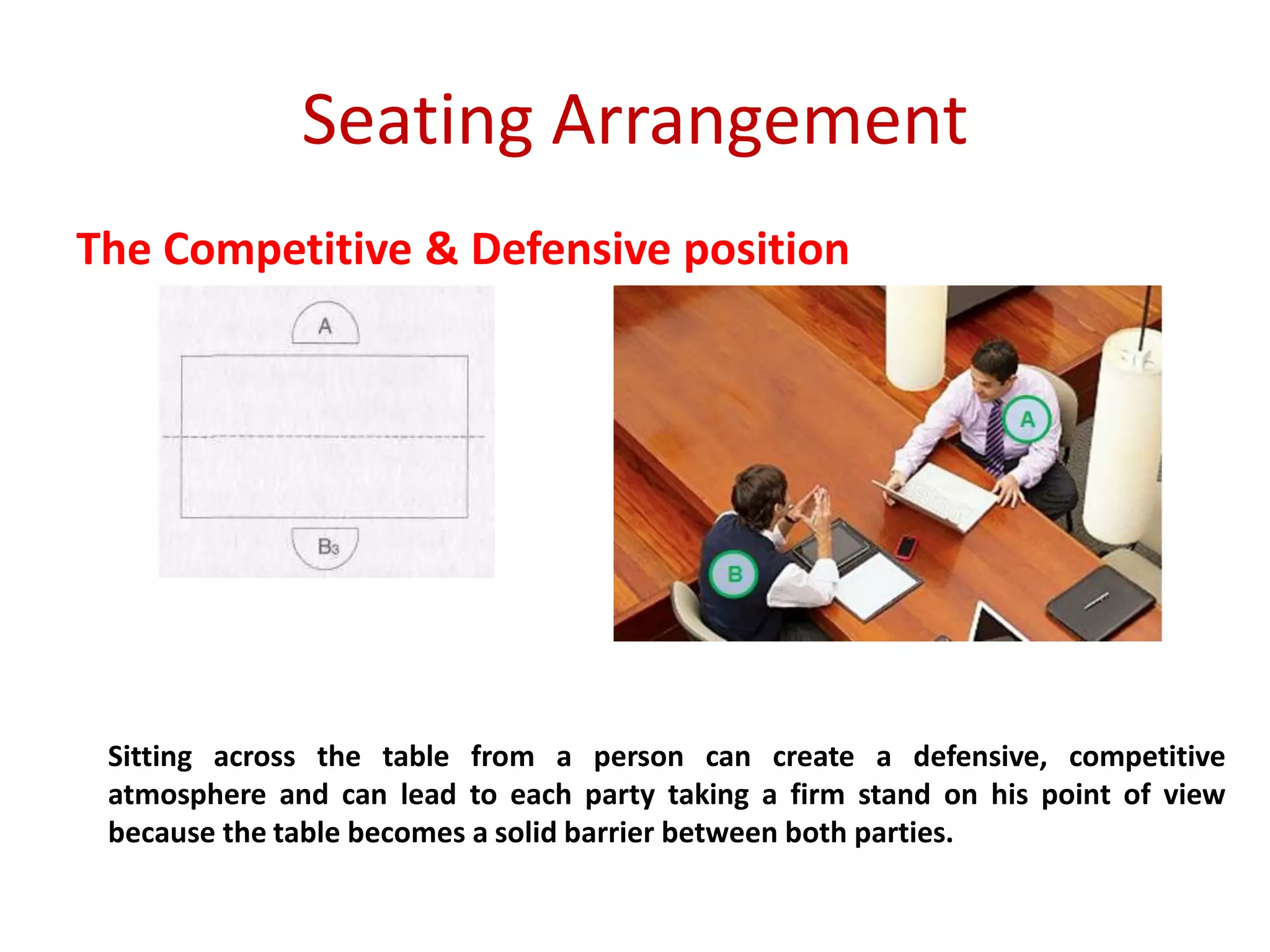
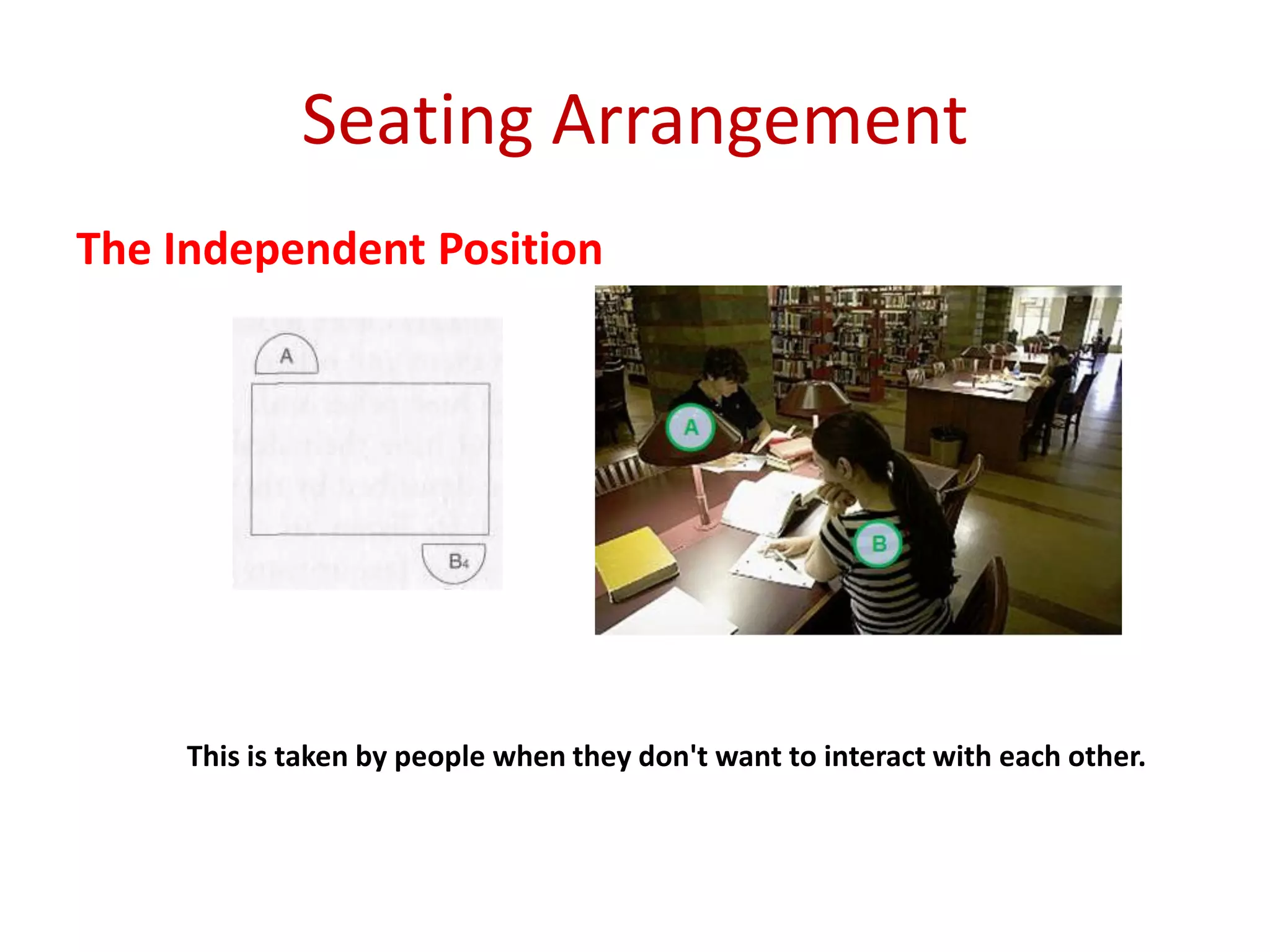
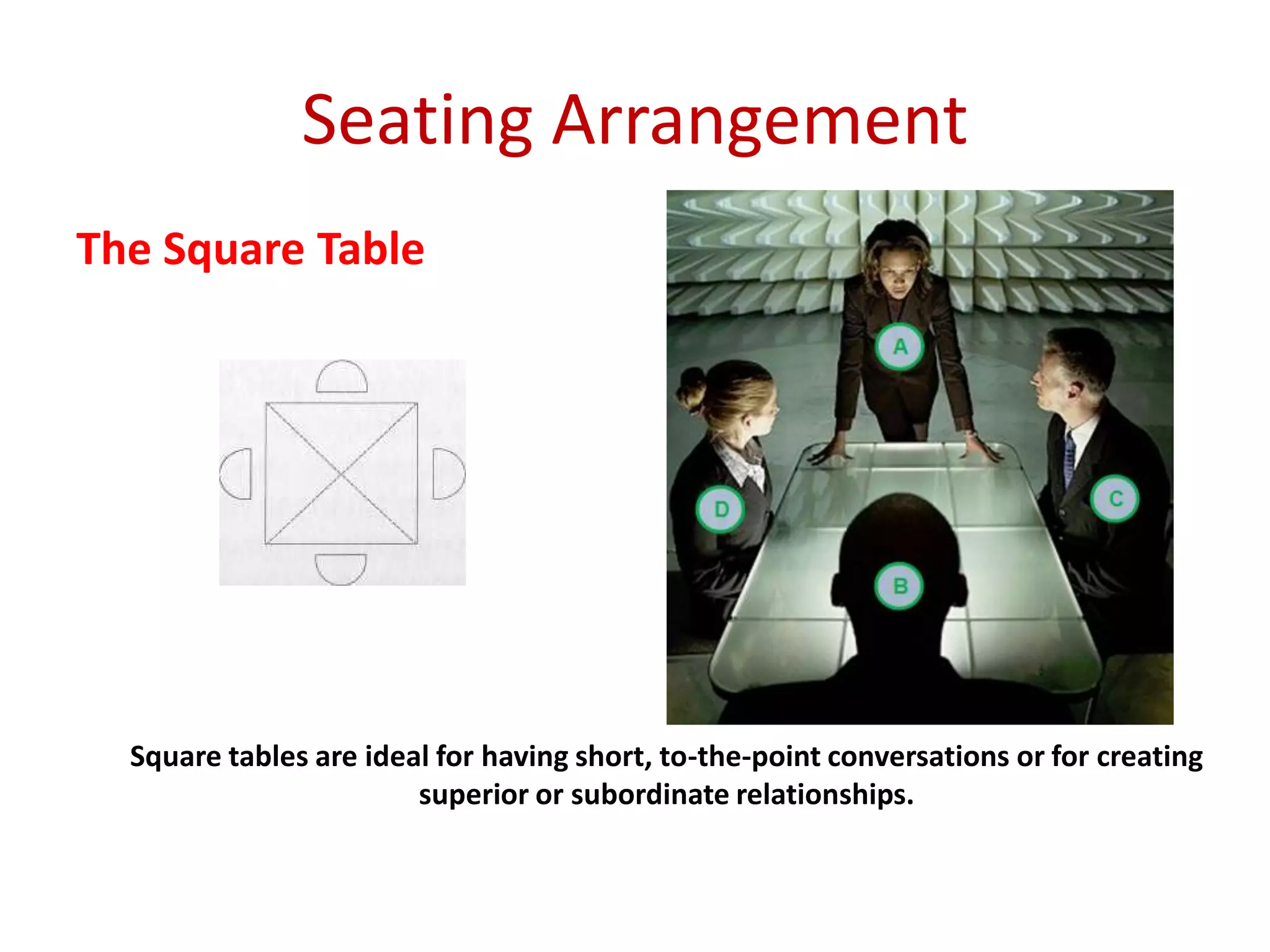
The document provides an extensive overview of non-verbal communication, highlighting its various forms such as body language, proxemics, touch, time, and paralanguage. It discusses how these elements affect communication dynamics and cultural interpretations, including significance in different environments and specific cultural practices related to gift-giving. Key insights include the impact of spatial proximity on interactions and the importance of vocal characteristics in conveying meaning beyond words.