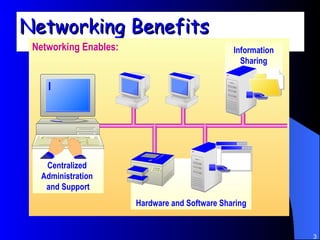
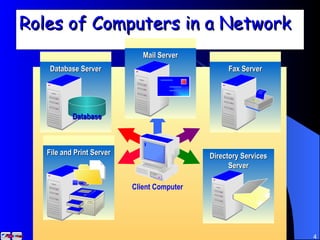
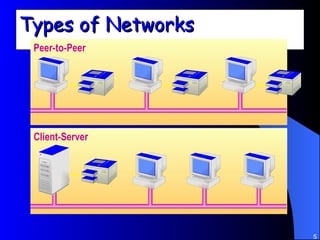
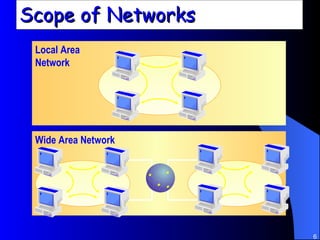
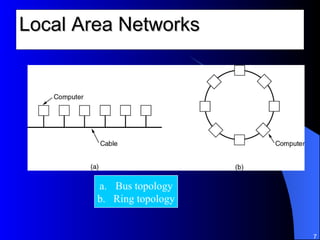
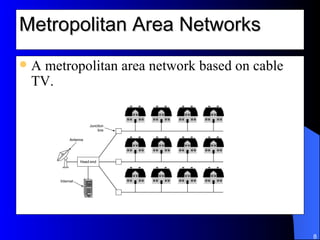
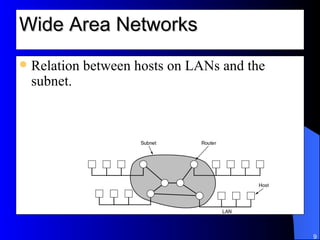
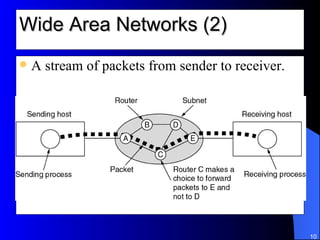
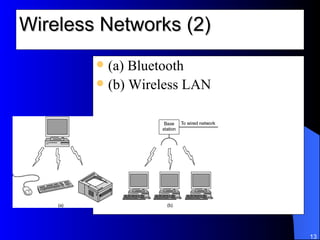
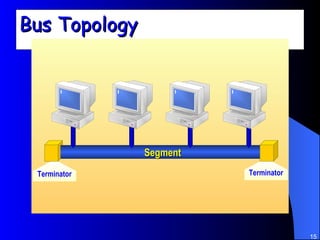
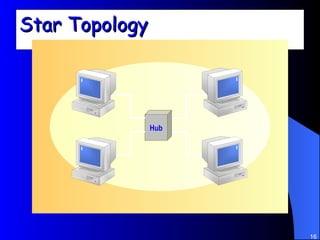
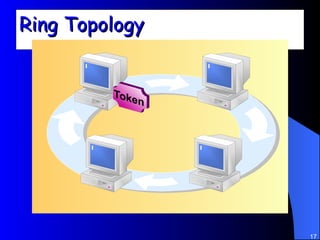
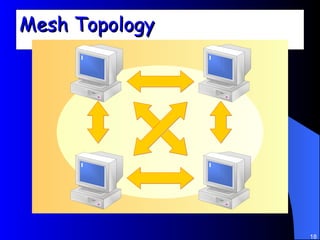
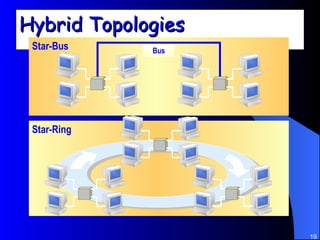
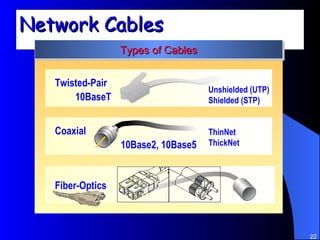
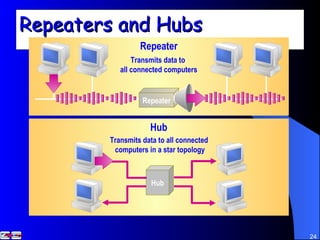
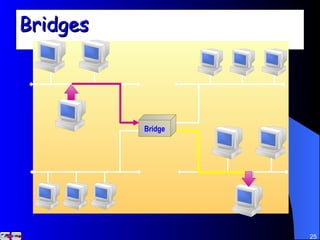
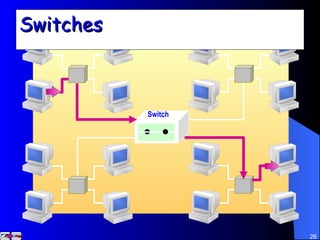
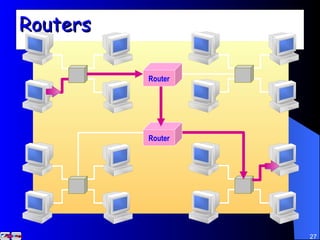
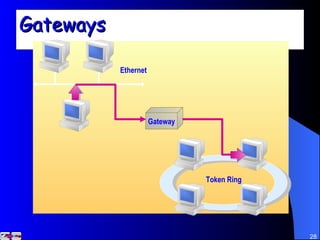
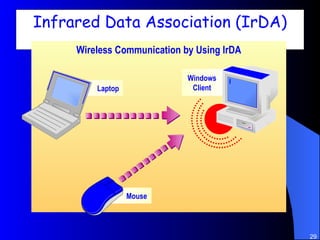
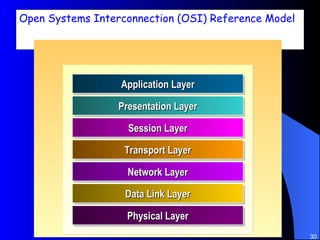
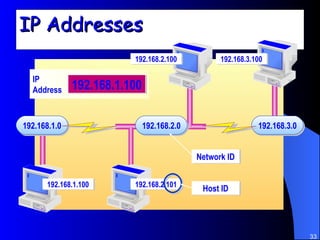
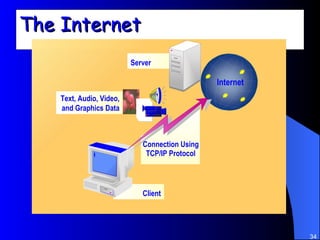
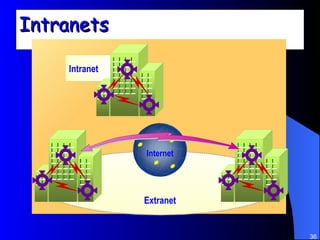
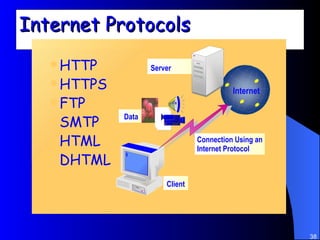
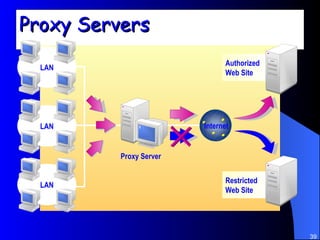
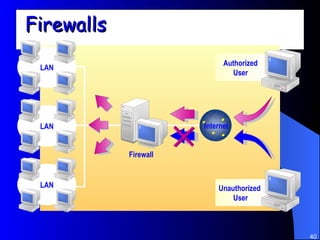
The document discusses various networking concepts including computer networking, networking benefits, network topologies, network devices, protocols, and security measures. It defines computer networking as the connection between two or more computers and discusses how networking enables information sharing, hardware and software sharing, and centralized administration. It also outlines different network topologies like peer-to-peer, client-server, local area networks, and wide area networks. Finally, it discusses network devices, cables, protocols, and security measures like firewalls and proxy servers.