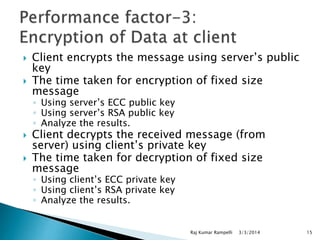
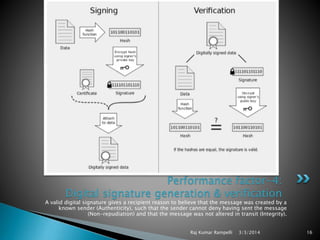
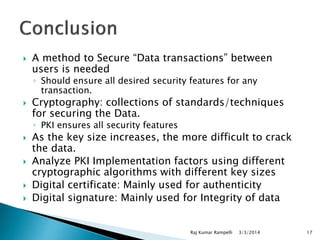
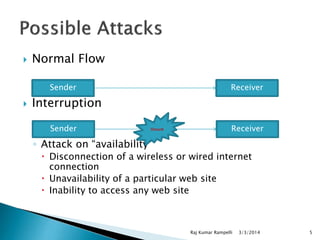
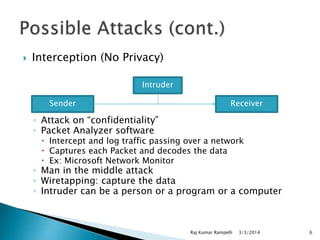
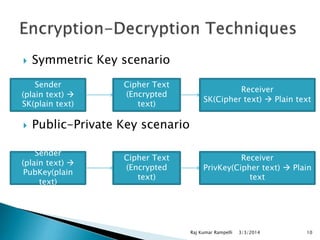
The document discusses the need for network security and the classification of network attacks, emphasizing the importance of protecting data from unauthorized access. It outlines various types of attacks, such as passive and active attacks, along with security mechanisms like cryptography, symmetric and asymmetric encryption techniques, and digital certificates. The conclusion stresses the importance of cryptographic methods in ensuring data integrity, authenticity, and confidentiality in transactions.








![
String of information that binds the unique identifier of each client
to his/her corresponding public key.
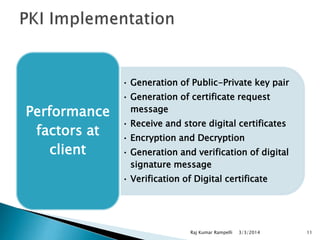
Pre-requite for obtaining Digital certificate
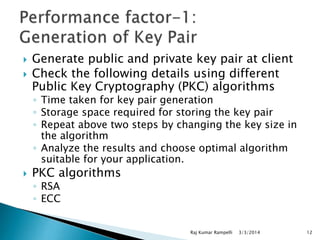
◦ Generate public-private key pair locally
◦ Generate certificate request message
Digital certificate used to authenticate server credentials during
mutual authentication process
Mutual authentication process:
◦ a client authenticating themselves to a server and that server
authenticating itself to the user in such a way that both parties are
assured of the others' identity [wiki]
Authenticating an entity using its Digital certificate:
◦ Check the validity period of certificate
◦ Verify the digital signature of CA on the certificate using CA’s
public key
Raj Kumar Rampelli
3/3/2014
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networksecurityandcryptography-140303114745-phpapp02/85/Network-security-and-cryptography-14-320.jpg)