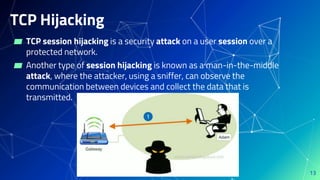
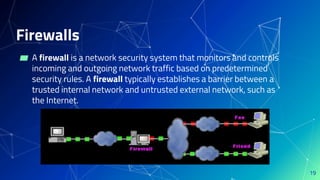
This document discusses network security and outlines common threats and countermeasures. It begins by defining security as freedom from harm caused by others. It then outlines organizations that are vulnerable to network attacks, such as financial institutions, governments, and corporations. Common attacks are discussed like denial of service attacks, software exploits, packet sniffing, and social engineering. Countermeasures recommended include antivirus software, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, virtual private networks, and network access control to monitor devices and users on the network. The document emphasizes the importance of staying aware of security updates to patch vulnerabilities.