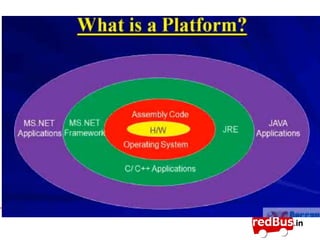
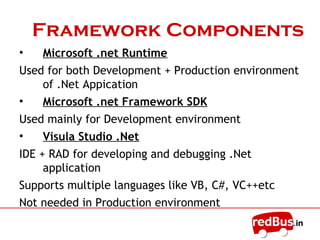
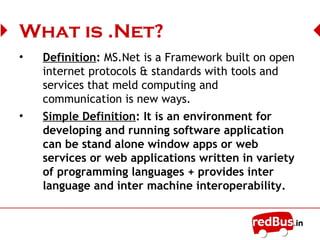
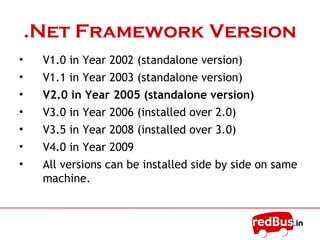
The document discusses the .NET framework, including:
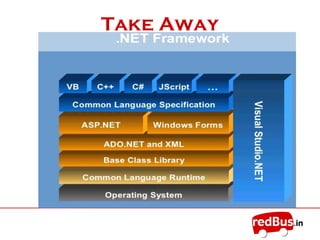
- It defines .NET as a framework built on open standards for developing and running software applications across platforms.
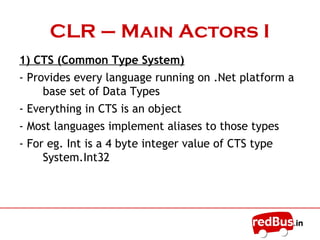
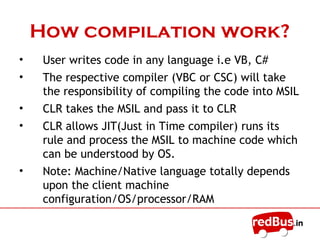
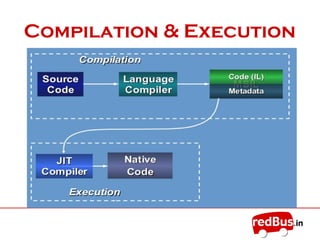
- The core of the .NET framework is the Common Language Runtime (CLR) which manages code compiled for the .NET platform similarly to a Java Virtual Machine.
- Applications are compiled into Microsoft Intermediate Language (MSIL) code then the CLR handles just-in-time compilation to native machine code for execution.