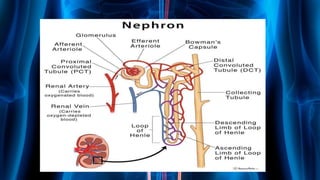
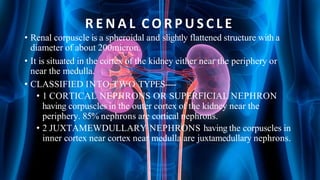
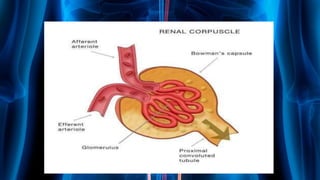
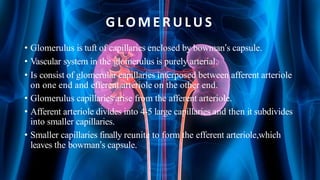
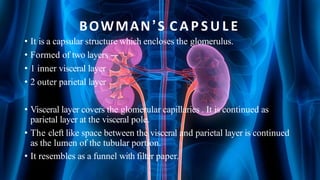
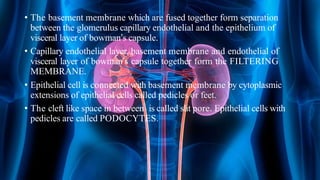
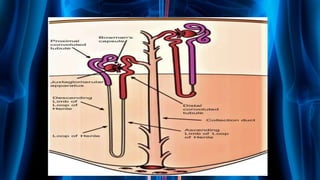
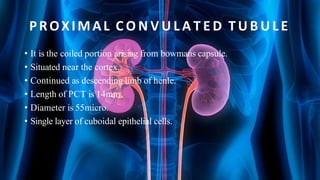
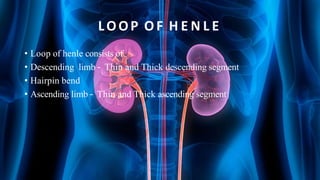
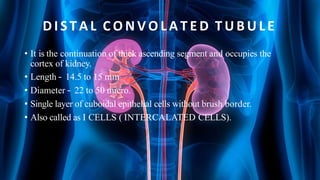
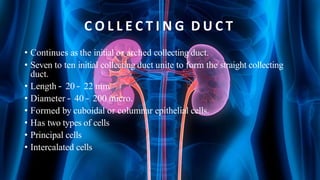
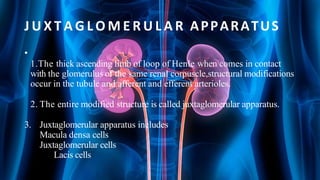
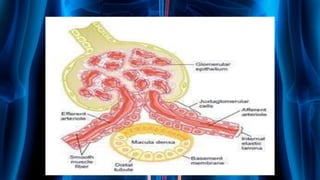
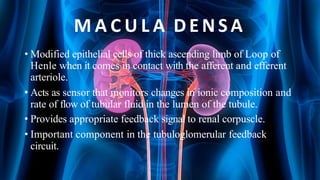
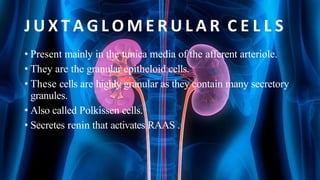
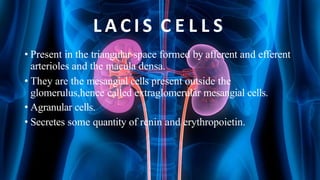
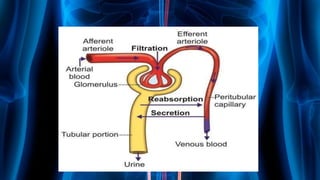
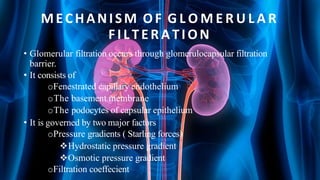
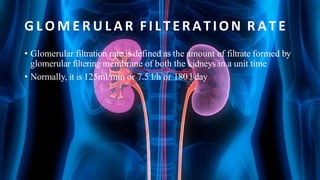
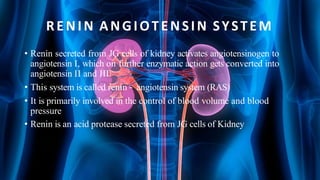
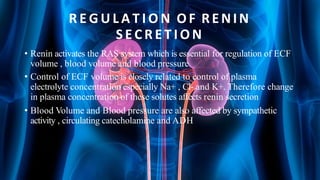
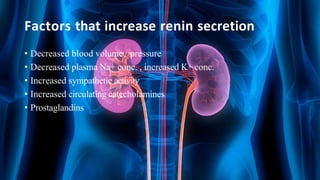
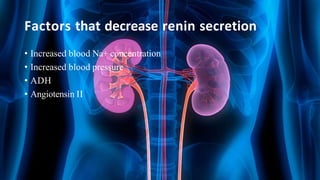
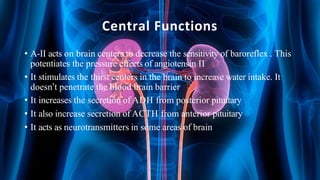
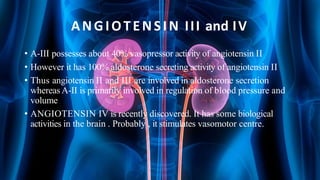
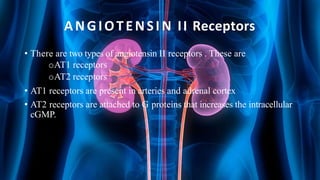
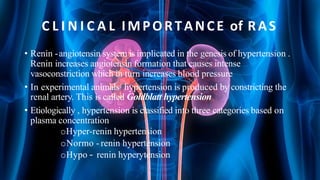
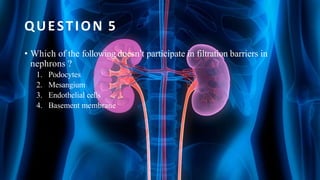
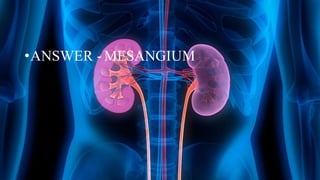
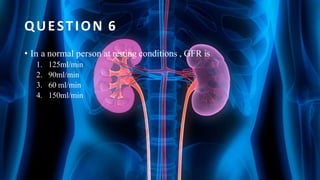
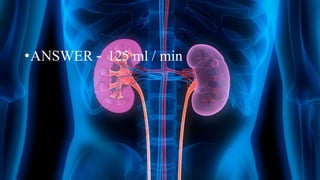
The document summarizes key aspects of nephron structure and function, including glomerular filtration, the juxtaglomerular apparatus, and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. It describes the basic units of nephrons, the structures of the renal corpuscle and tubular portions. It discusses glomerular filtration mechanisms and factors regulating glomerular filtration rate. It also outlines the roles and regulation of renin secretion by the juxtaglomerular apparatus and the actions of angiotensins in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.