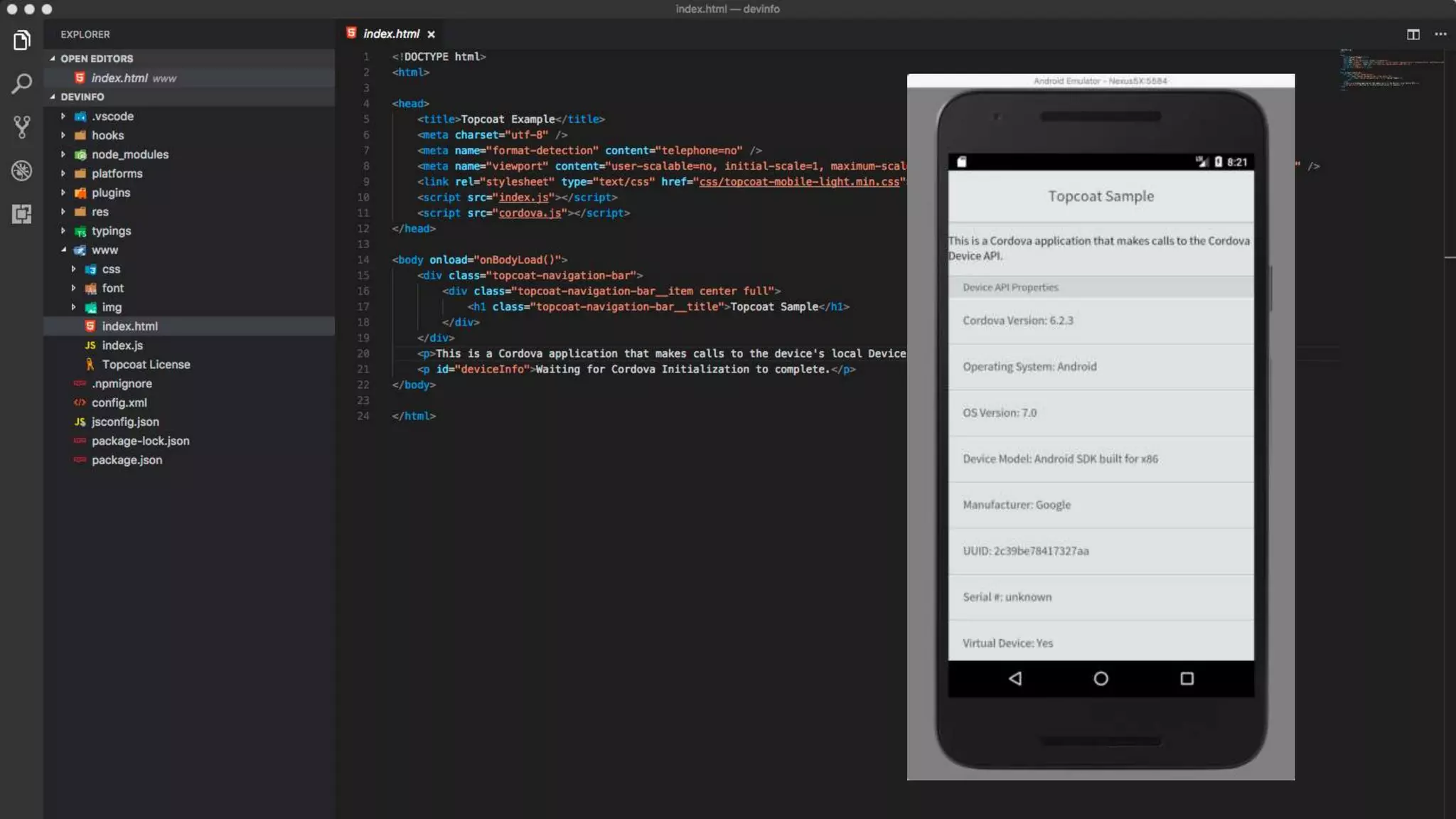
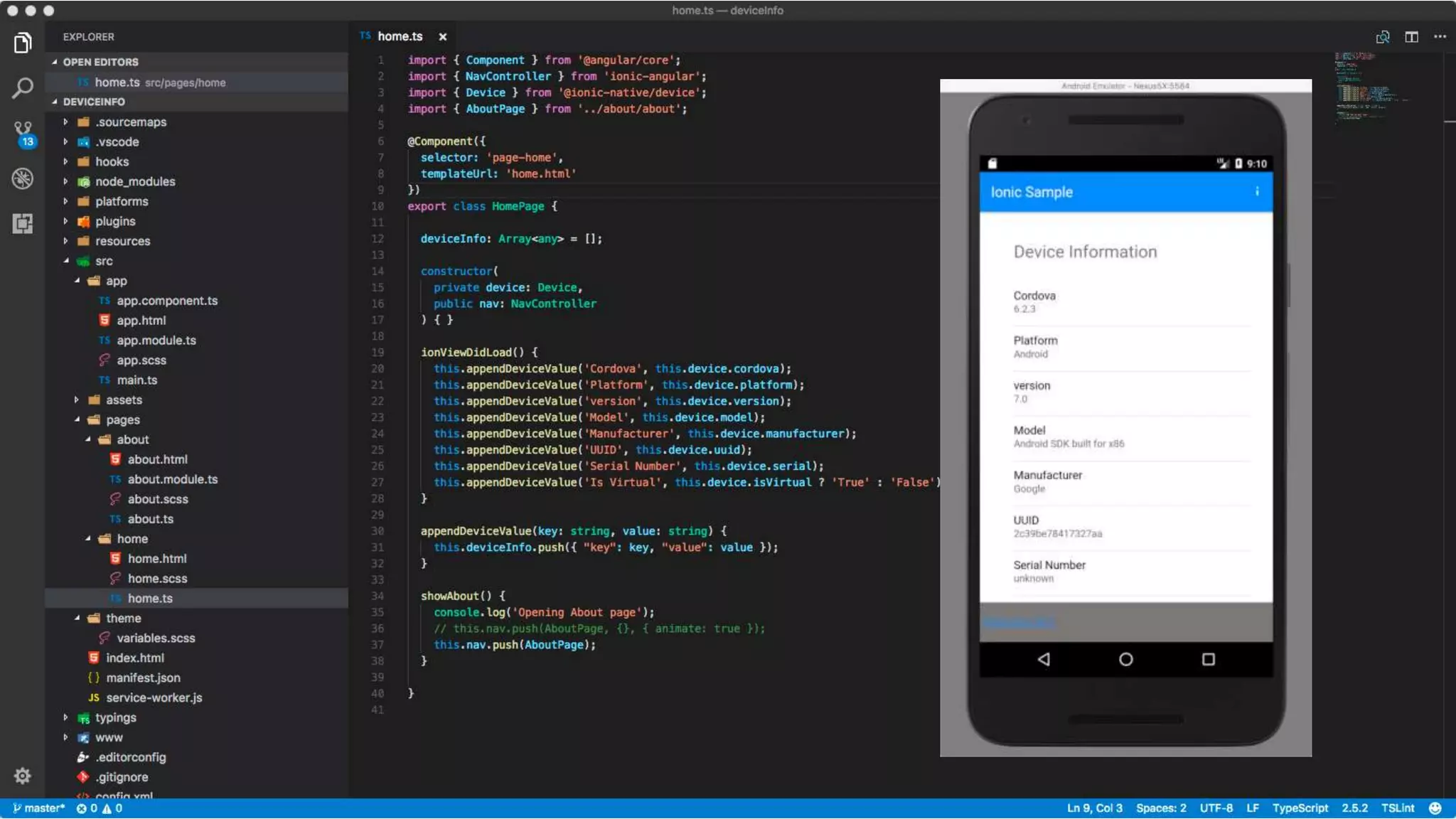
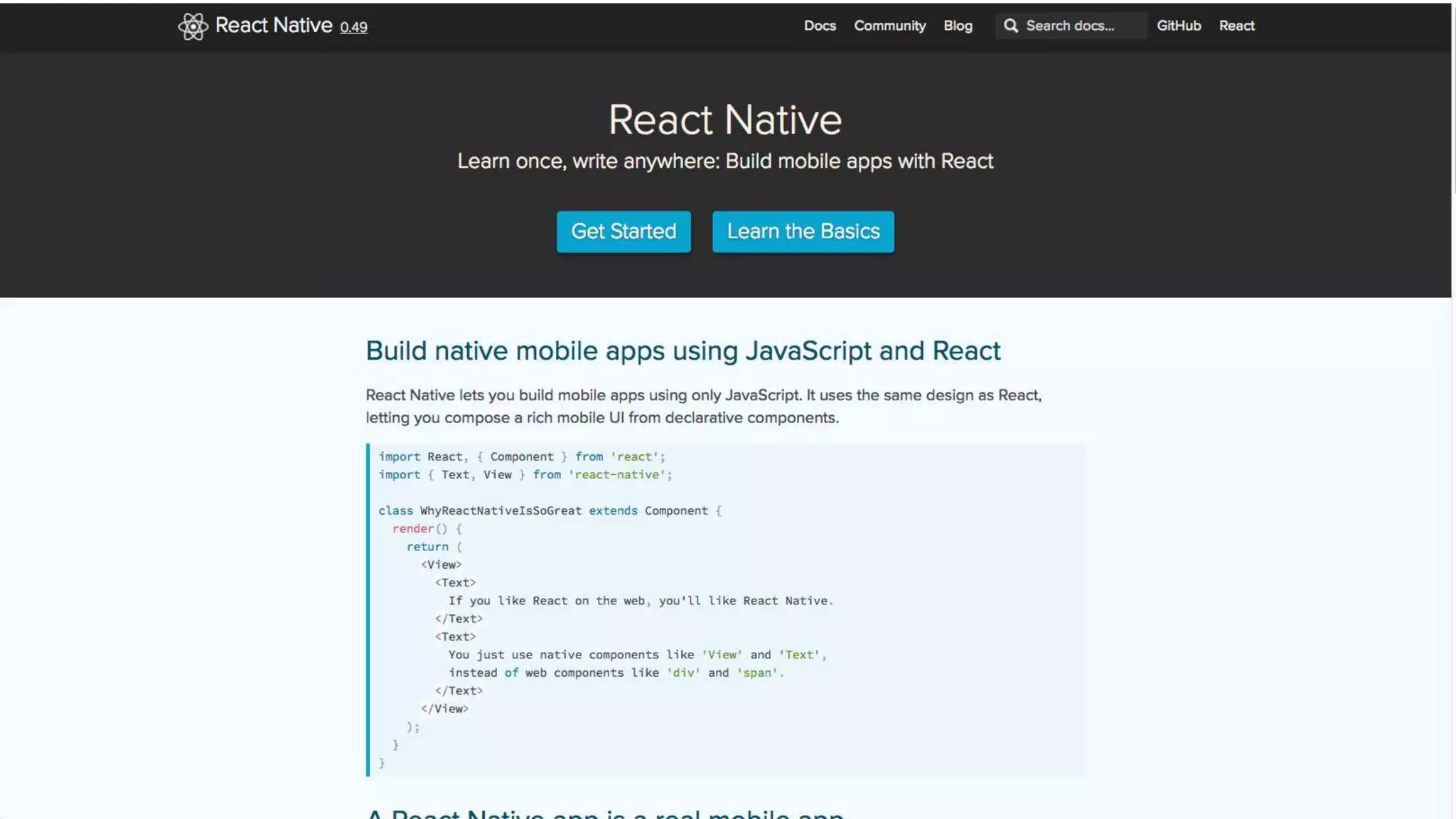
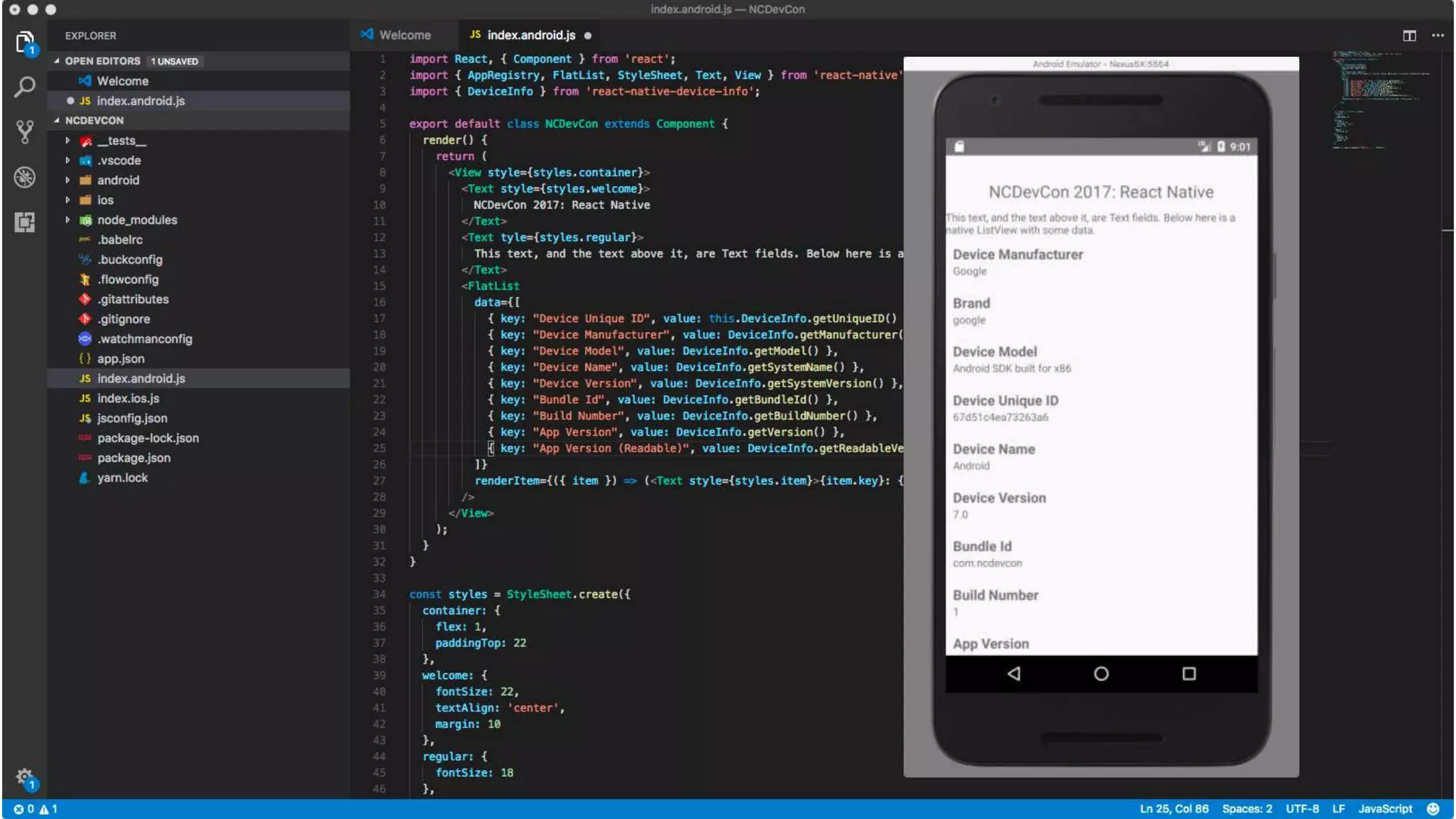
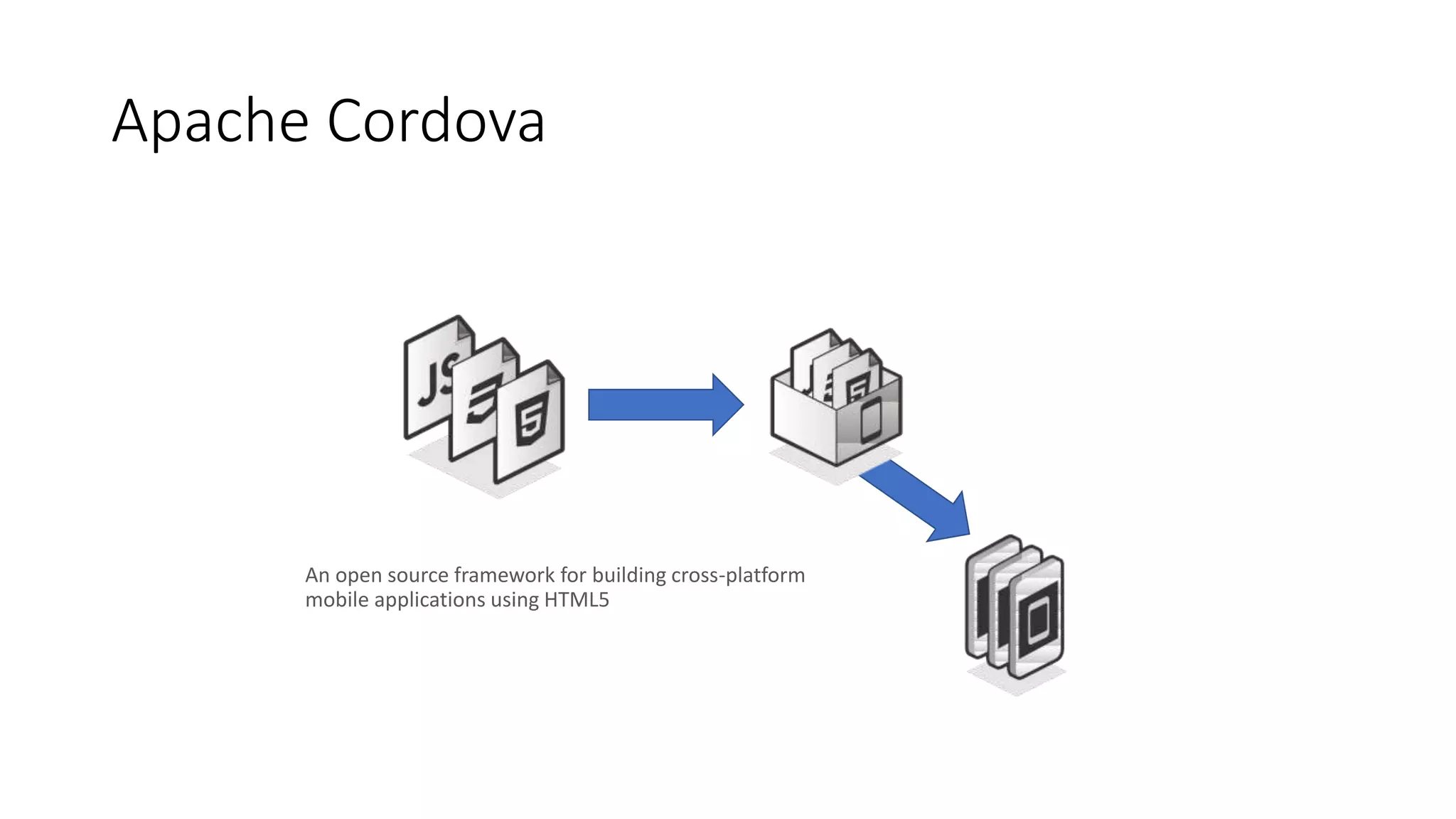
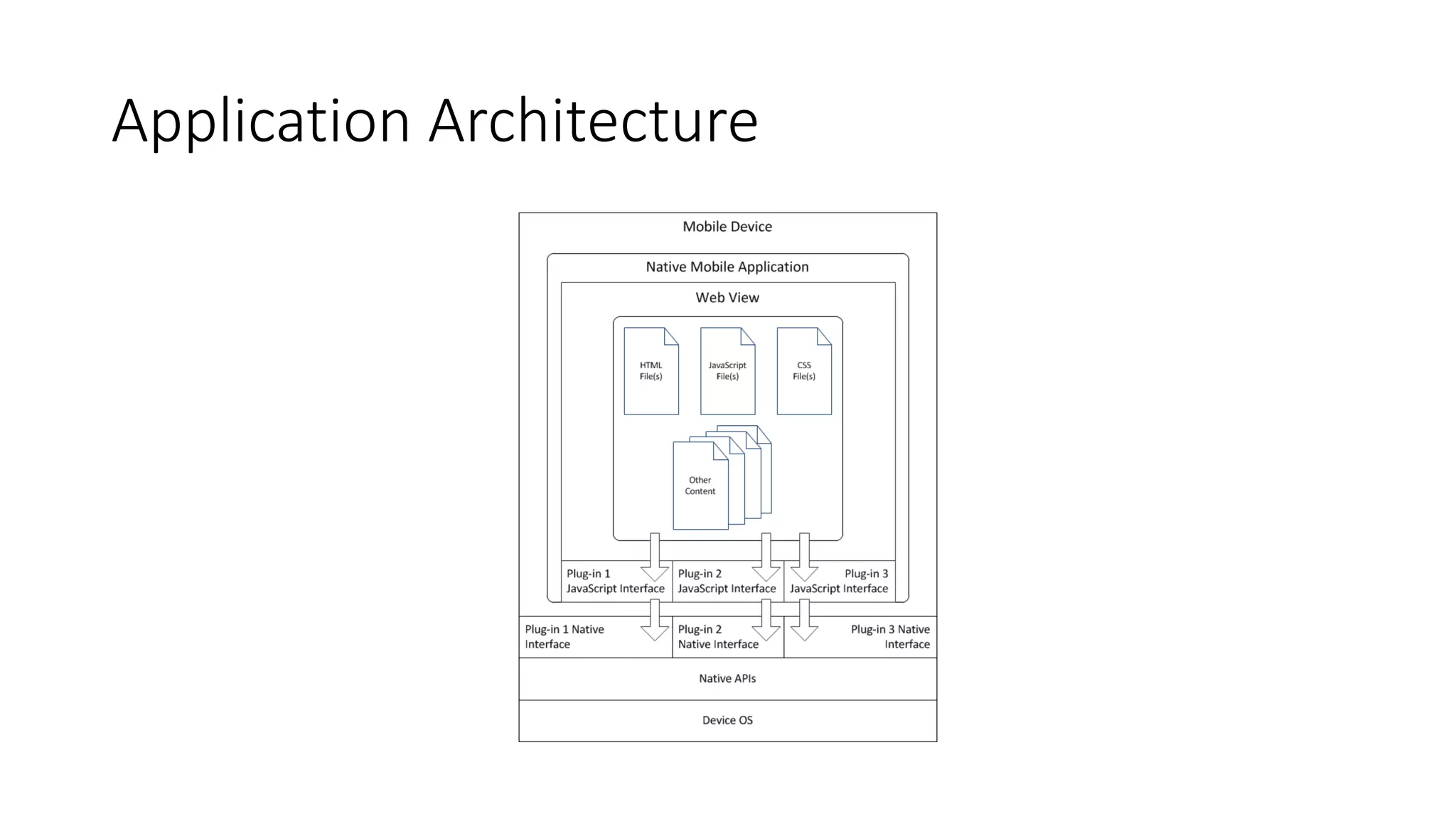
The document discusses the challenges of native mobile development and introduces various open-source cross-platform frameworks like Apache Cordova, Ionic, NativeScript, and React Native. It outlines the features, installation processes, and project creation methods for each framework, emphasizing the benefits of JavaScript-driven native applications for enterprise use. The text concludes with a perspective on the future of hybrid apps and the increasing popularity of these frameworks in mobile development.



















![Configuring cdva-create
{
"platformList":[
"android",
"ios"
],
"pluginList":[
"cordova-plugin-console",
"cordova-plugin-dialogs",
"cordova-plugin-device"
],
"enableDebug":false,
"copyFrom":"",
"linkTo":"",
"createParms":""
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cross-platformmobileopensourcejmw2017-171006141153/75/NCDevCon-2017-Cross-Platform-Mobile-Apps-23-2048.jpg)