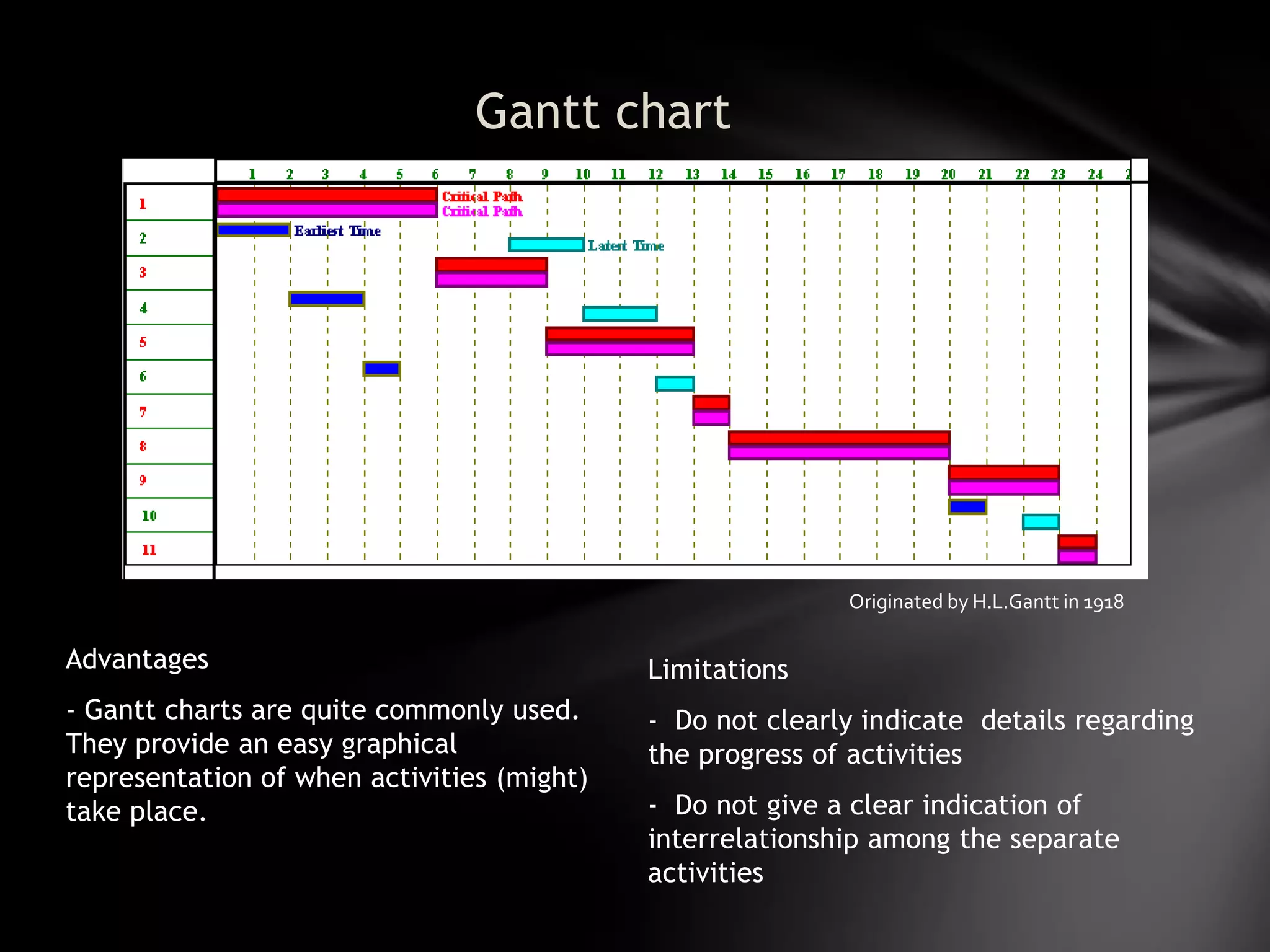
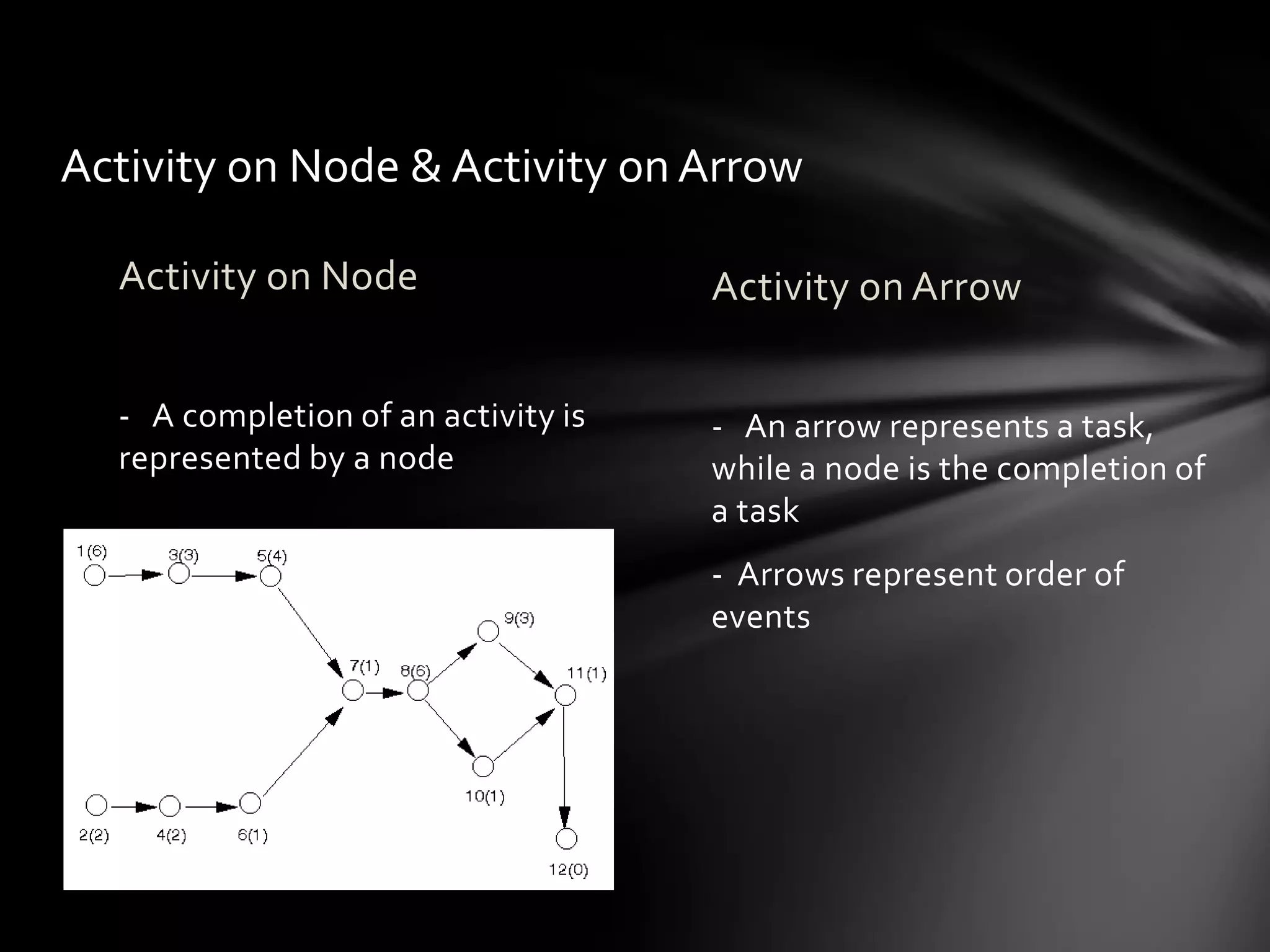
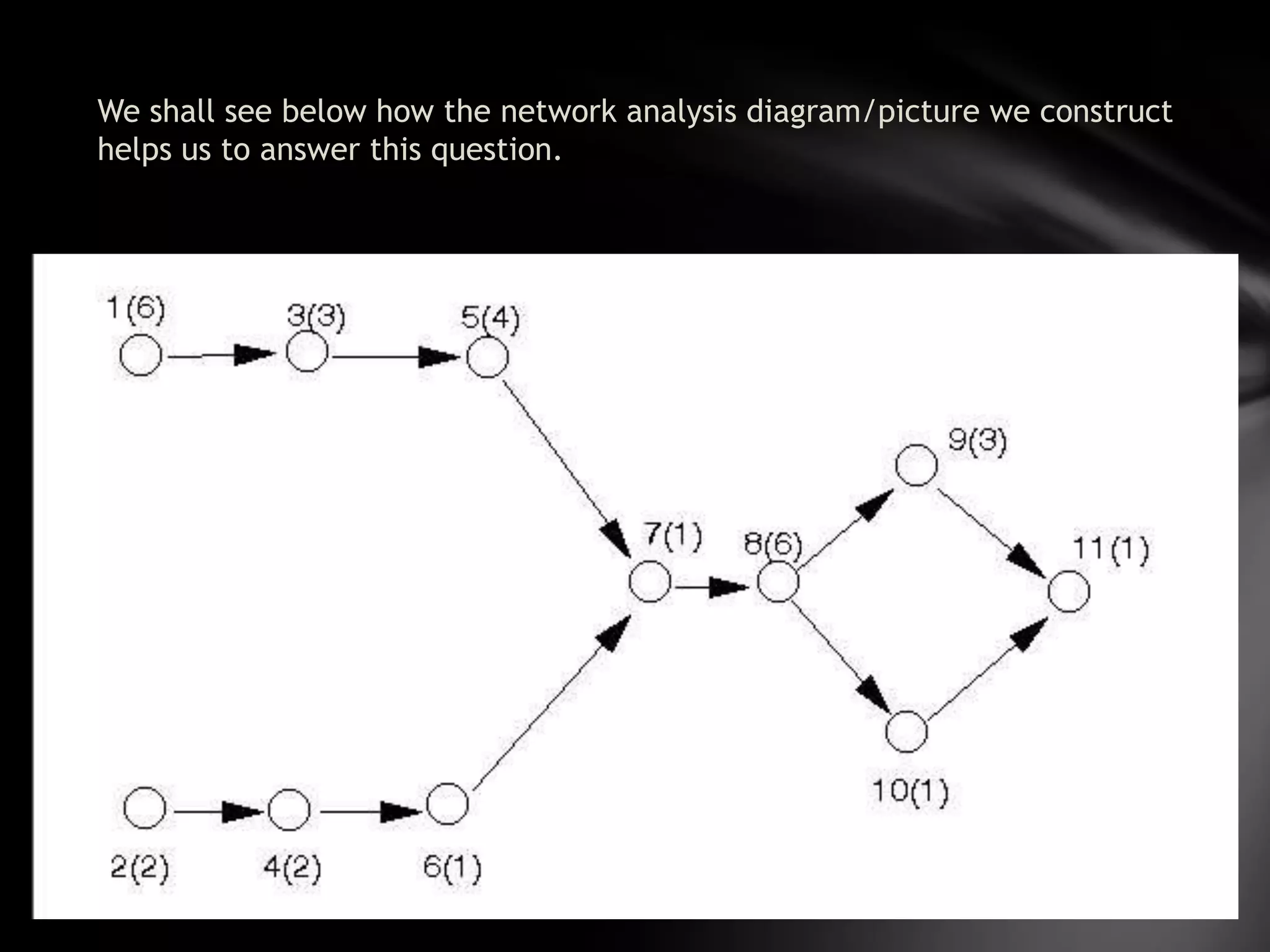
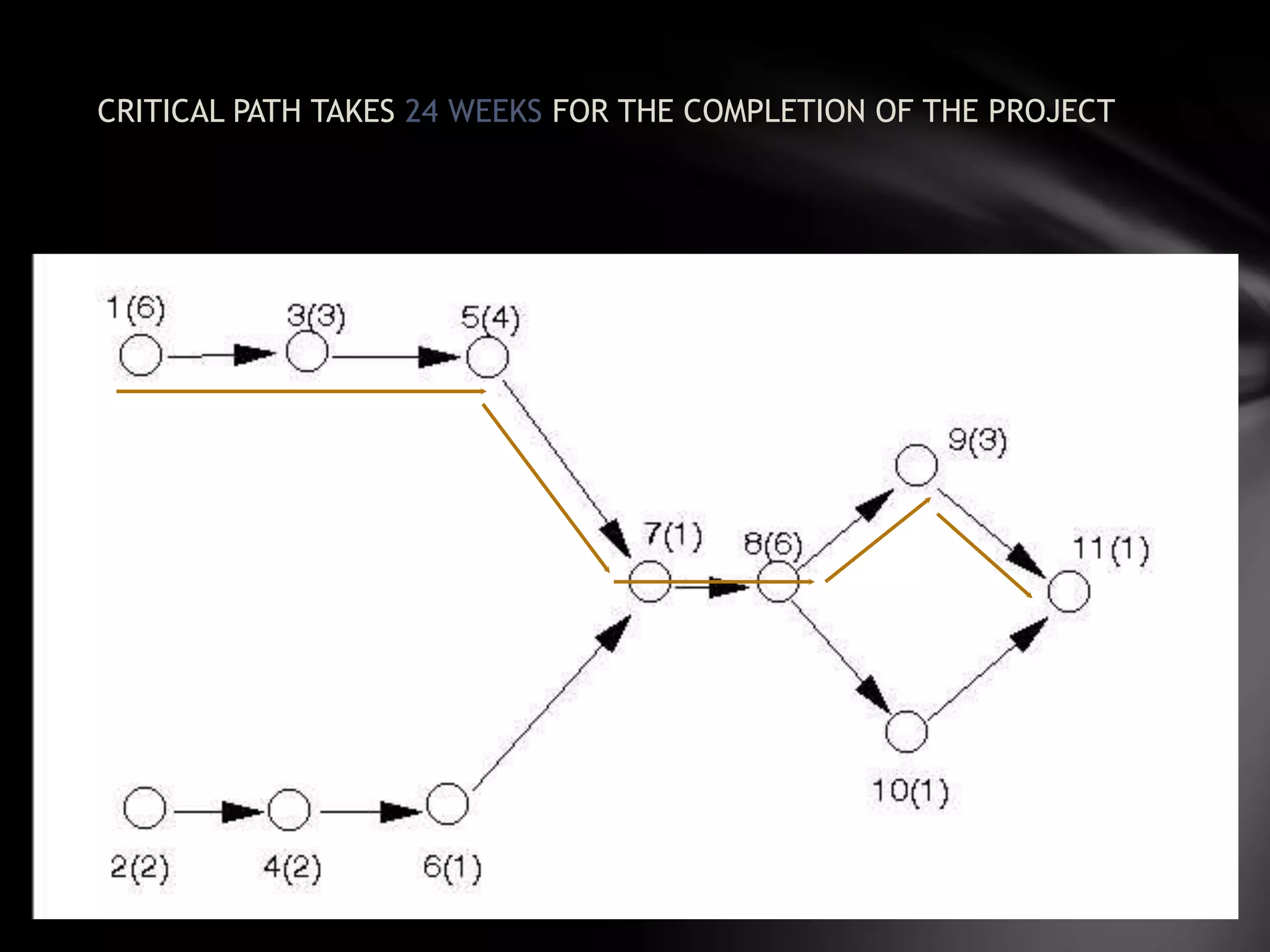
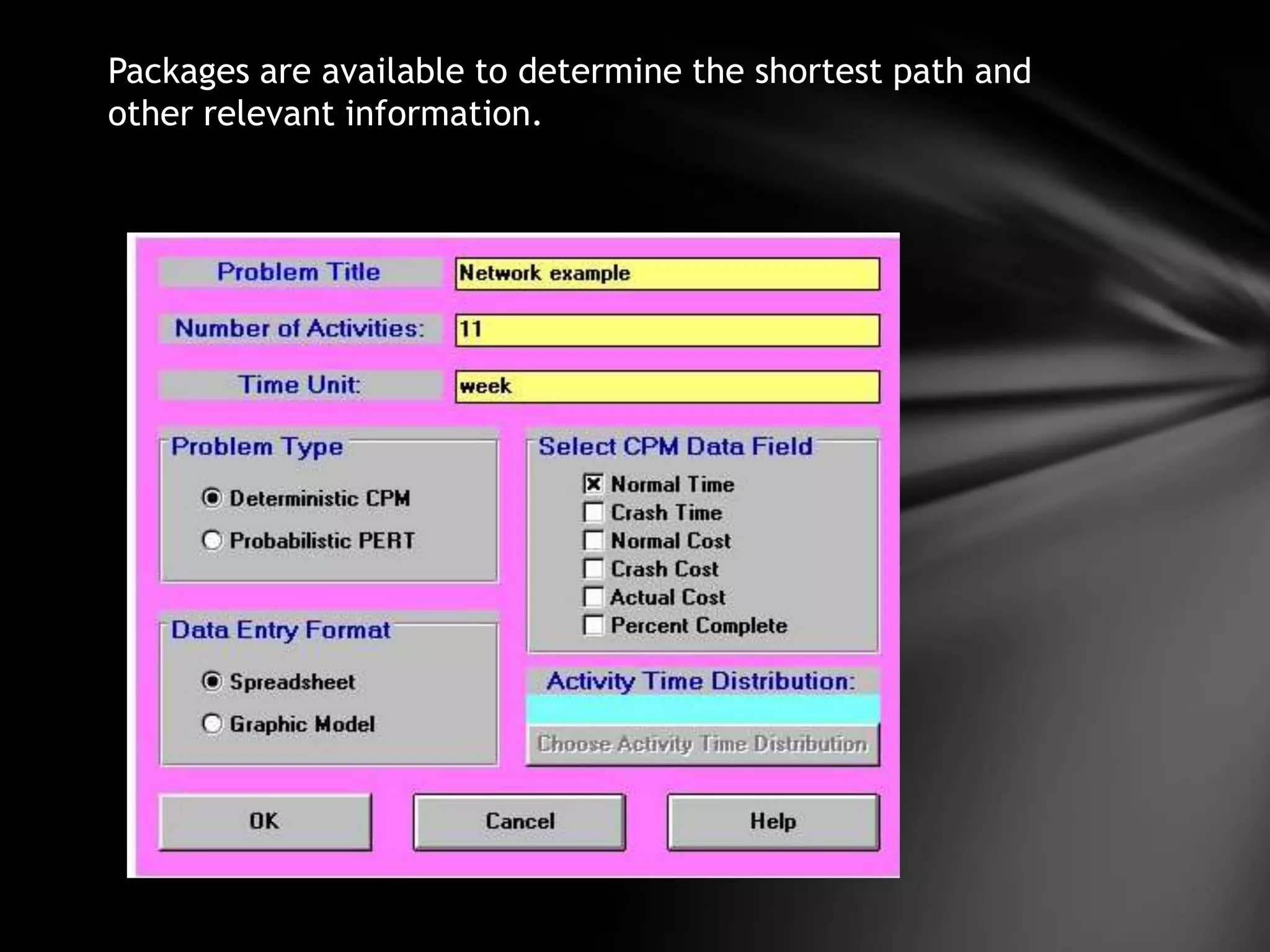
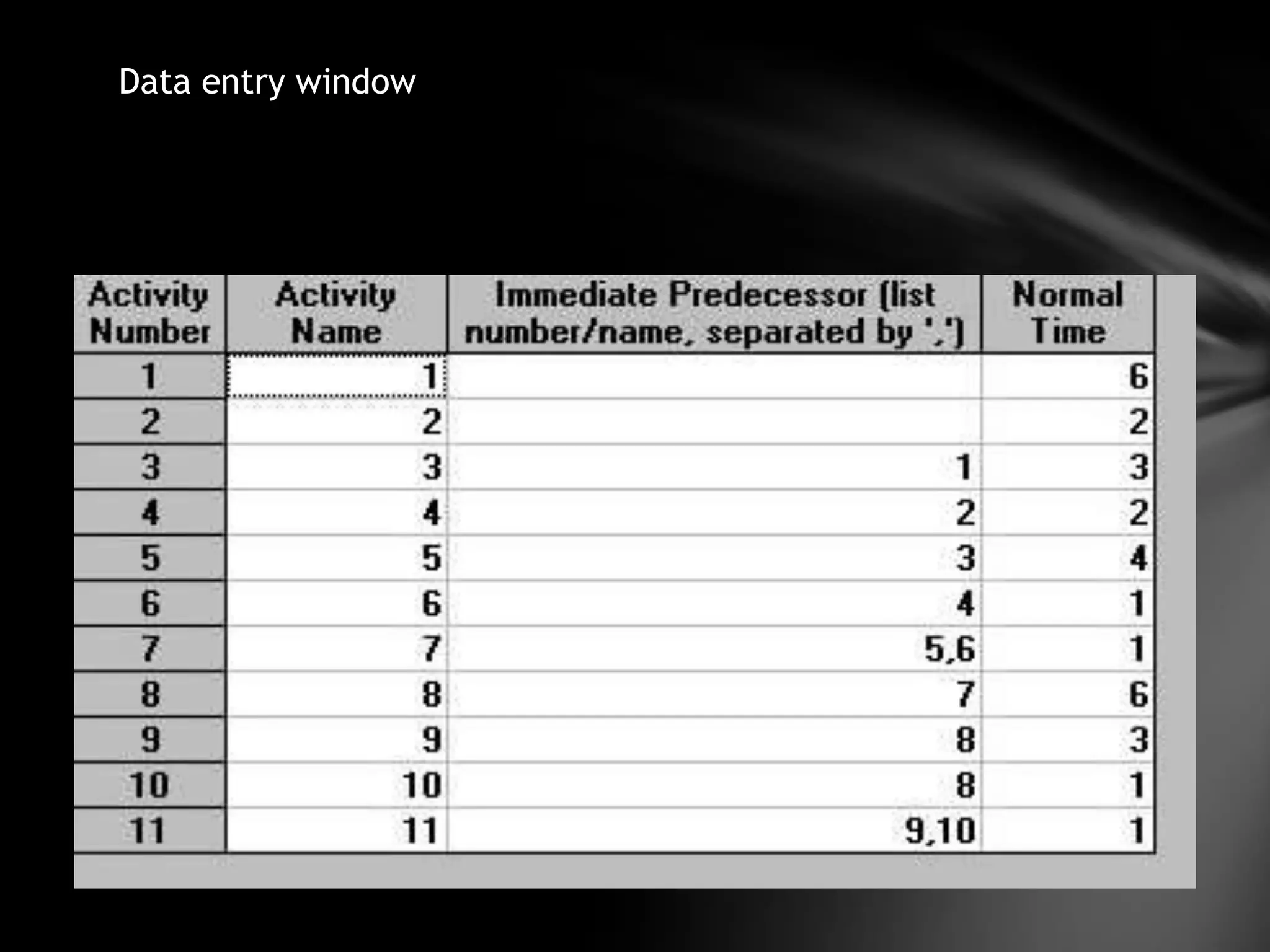
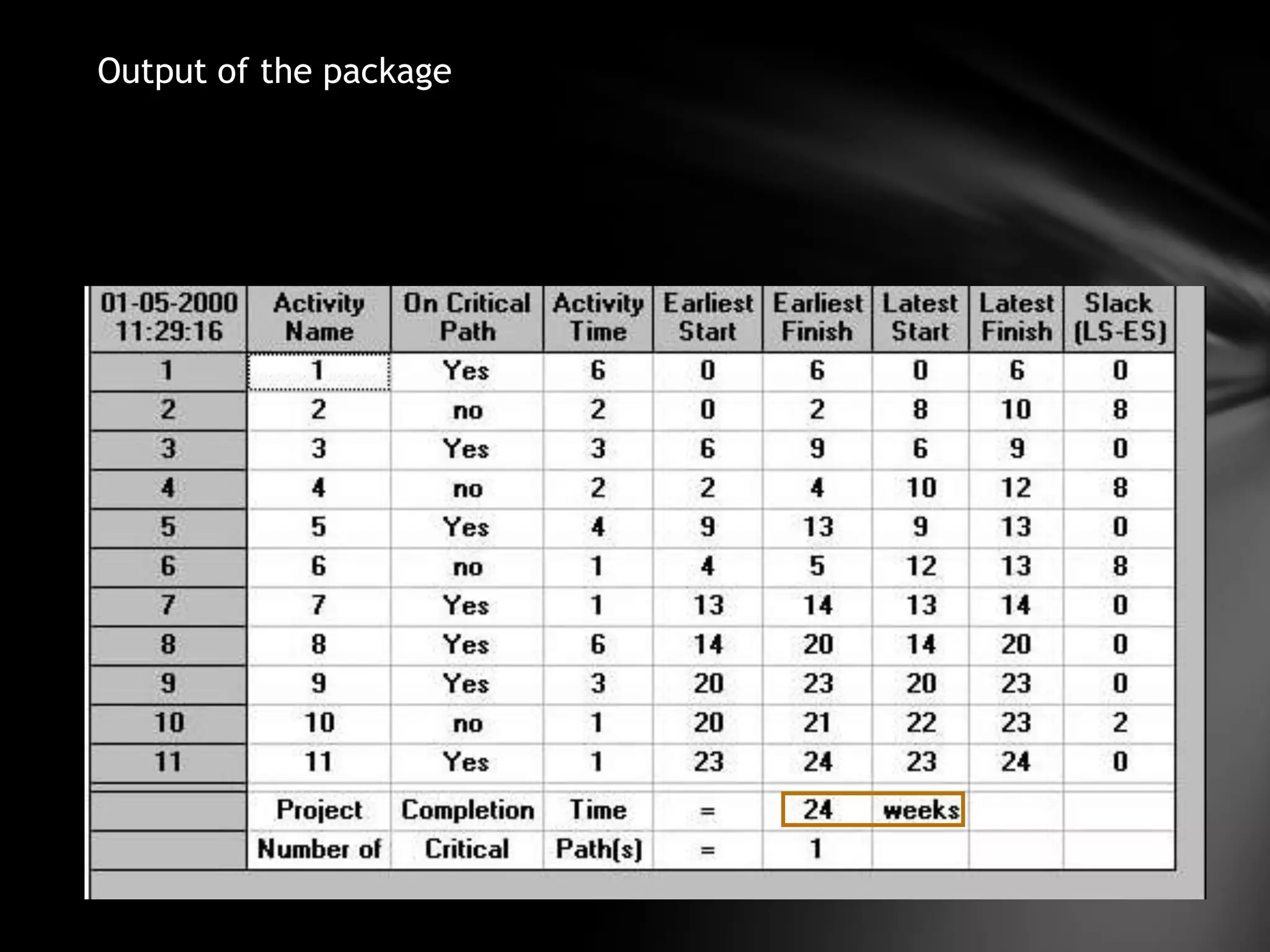
The document discusses project management techniques CPM and PERT. It provides:
1) A brief history of CPM and PERT, including that CPM was developed by DuPont for chemical plants, while PERT was developed by the US Navy for planning the Polaris missile program.
2) An overview of the key differences between CPM and PERT, such as CPM using deterministic activity times while PERT uses probabilistic times to account for uncertainty.
3) An example application of network analysis to determine the minimum time needed to complete a product redesign and packaging project. The analysis identifies a critical path of 24 weeks.