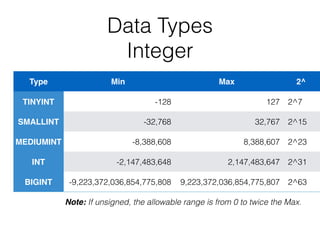
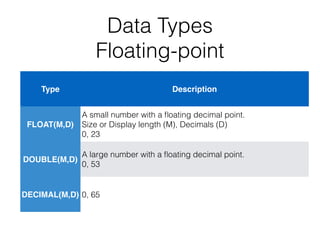
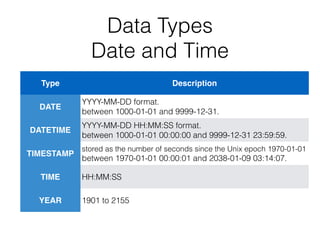
The document serves as an introductory guide to MySQL, covering its installation, SQL commands, syntax, and data types. It provides practical examples for database creation, manipulation, and operation, including SQL commands for data definition, data manipulation, and controls. The document also emphasizes the importance of learning from each other and includes links to further resources.




![Execute SQL Statements
• Interactively
- $ mysql [database]
‣ mysql> stmt;
• Command Line
- $ mysql [database] -e ‘stmt’
• A file or a pipe
- $ mysql [database] < stmt_file
- $ cat stmt_file | mysql [database]
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/j9g9d58gs6waczhk4wsa-signature-7c520f06aeaa4862a1a3eb818b8e577e529f3df3400199ad7109bbdf85563b2d-poli-141211130040-conversion-gate01/85/MySQL-for-beginners-5-320.jpg)





![Basic Syntax
• Create Database
- CREATE DATABASE db_name
• Create Table
- CREATE TABLE table_name (column_name column_type, …);
• Insert Data
- INSERT INTO table_name (field1, field2,...fieldN) VALUES (value1, value2, …valueN);
• Select Data
- SELECT field1, field2,...fieldN table_name1, table_name2... [WHERE condition1 [AND -OR condition2]….]
• Update Data
- UPDATE table_name SET field1=new-value1, field2=new-value2 [WHERE Clause]
• Delete Data
- DELETE FROM table_name [WHERE Clause]
• Sorting Result
- SELECT field1, field2,...fieldN table_name1, table_name2… ORDER BY field1, [field2...] [ASC [DESC]]
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/j9g9d58gs6waczhk4wsa-signature-7c520f06aeaa4862a1a3eb818b8e577e529f3df3400199ad7109bbdf85563b2d-poli-141211130040-conversion-gate01/85/MySQL-for-beginners-14-320.jpg)





