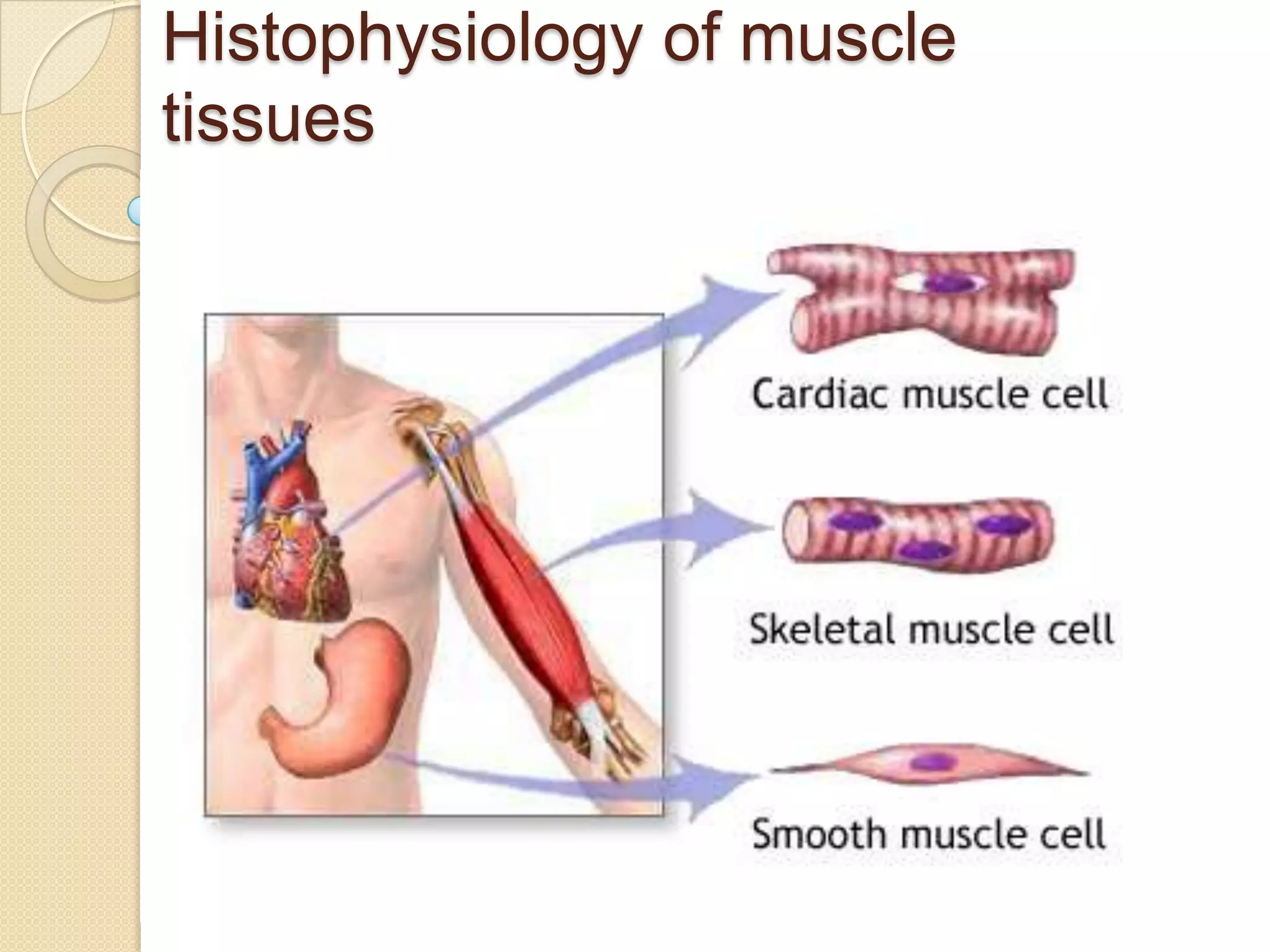
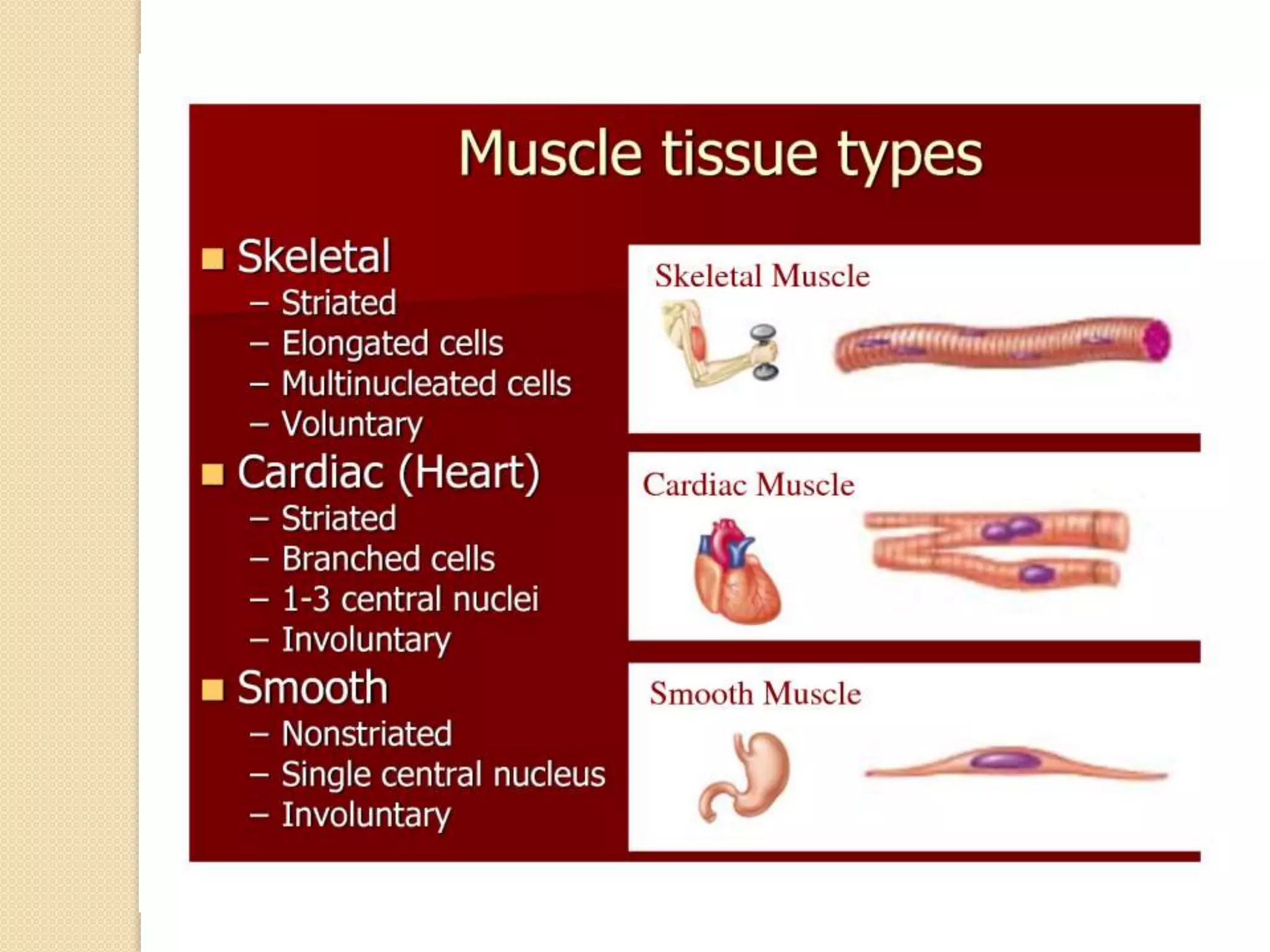
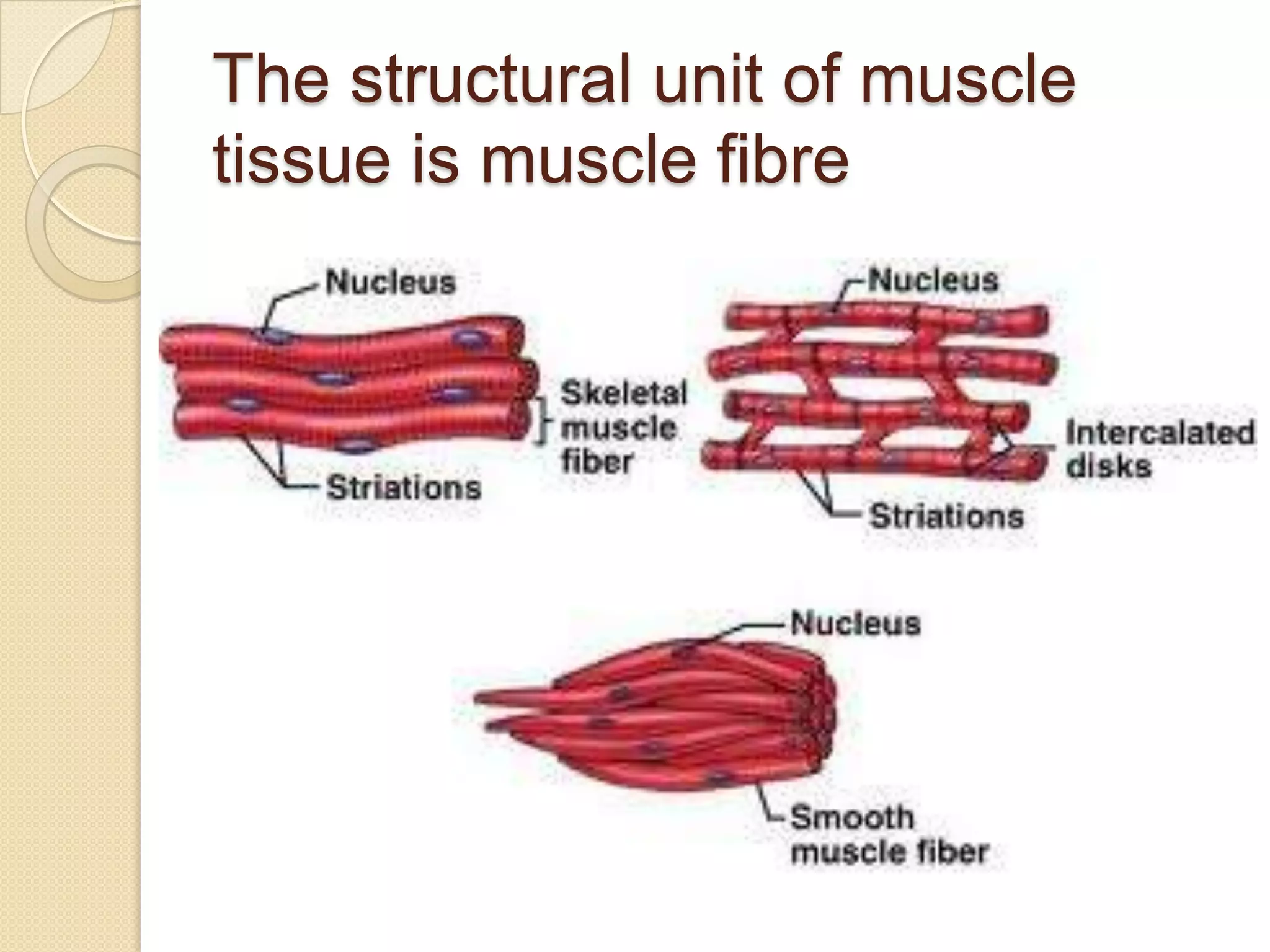
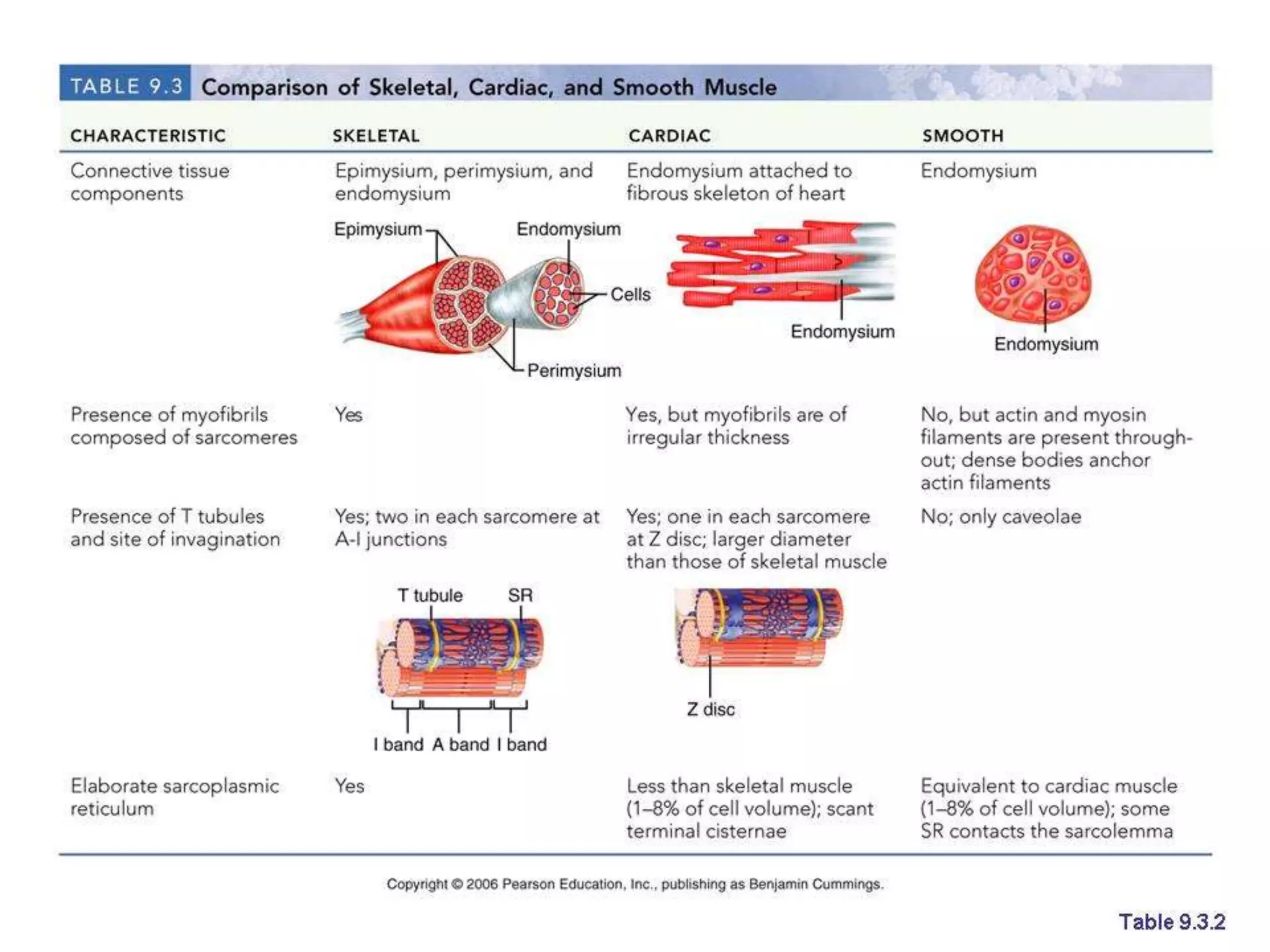
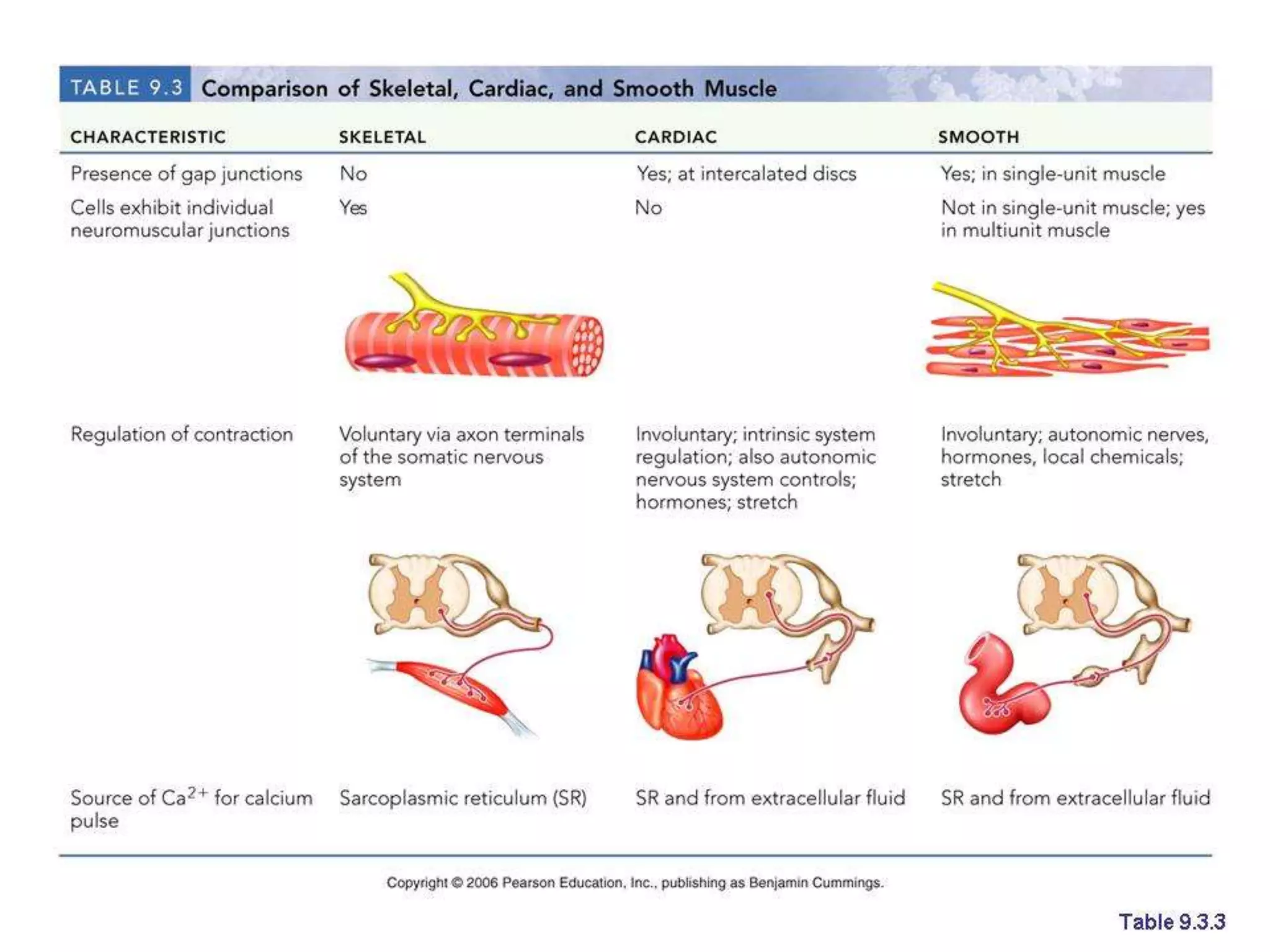
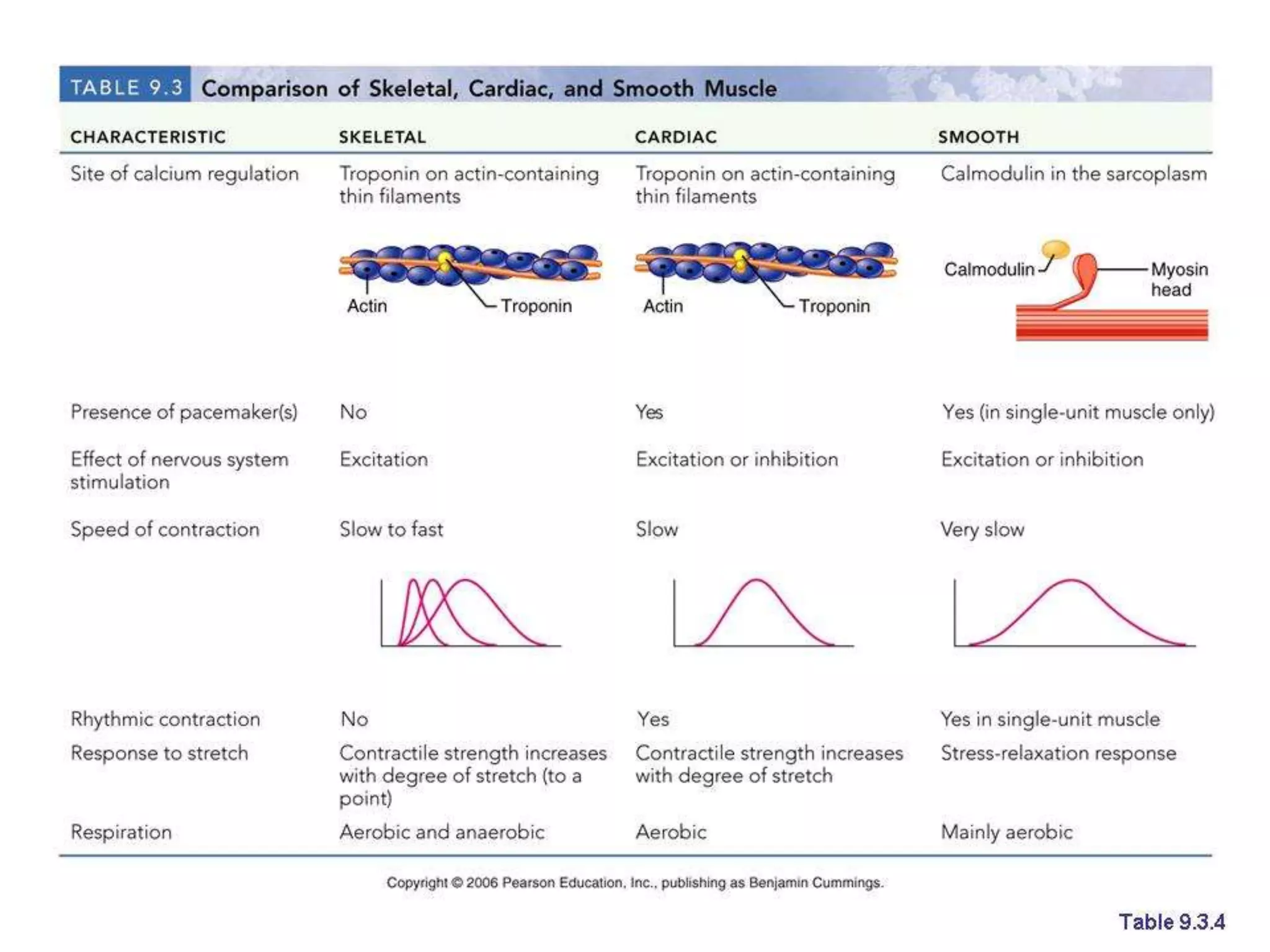
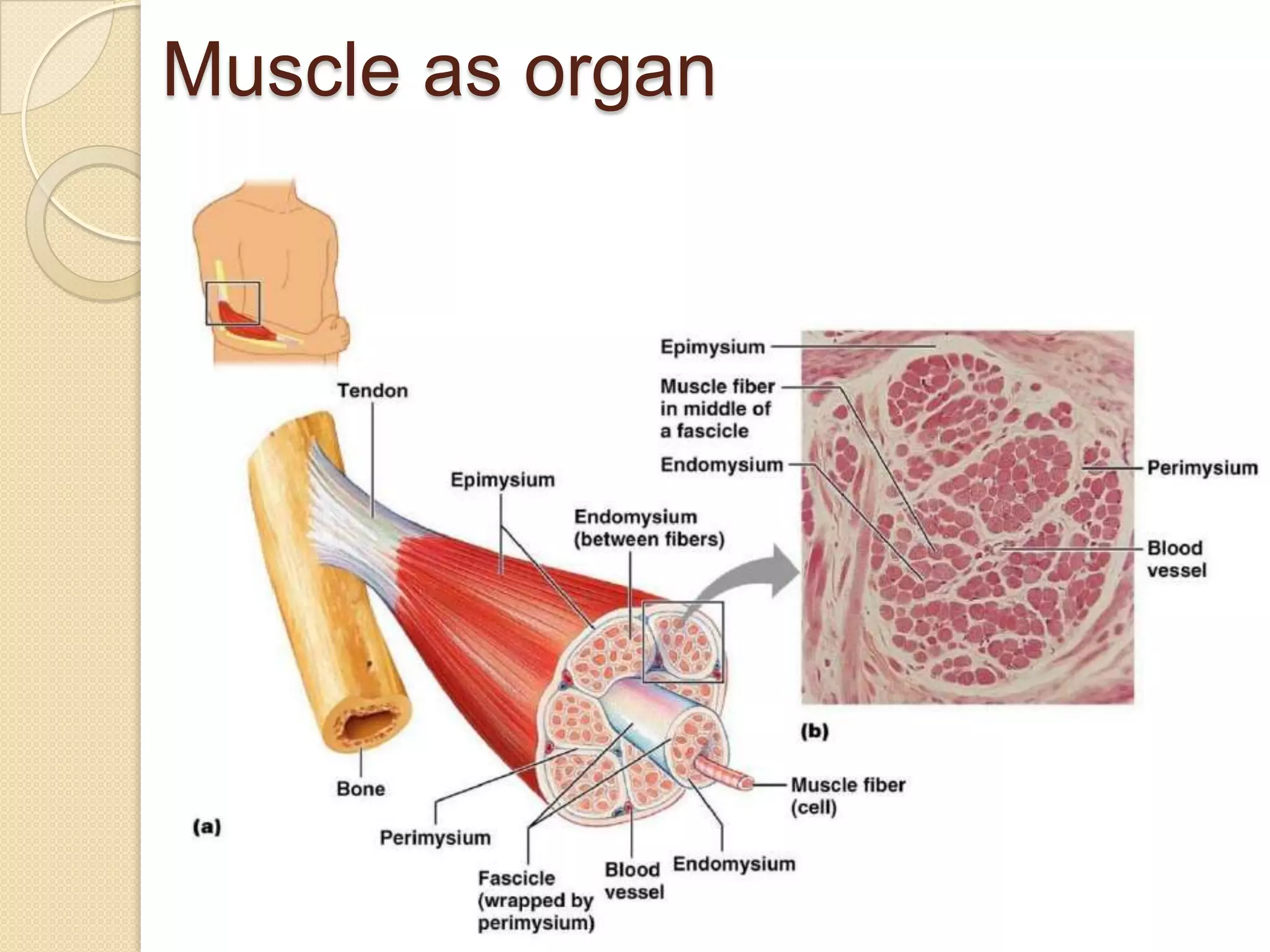
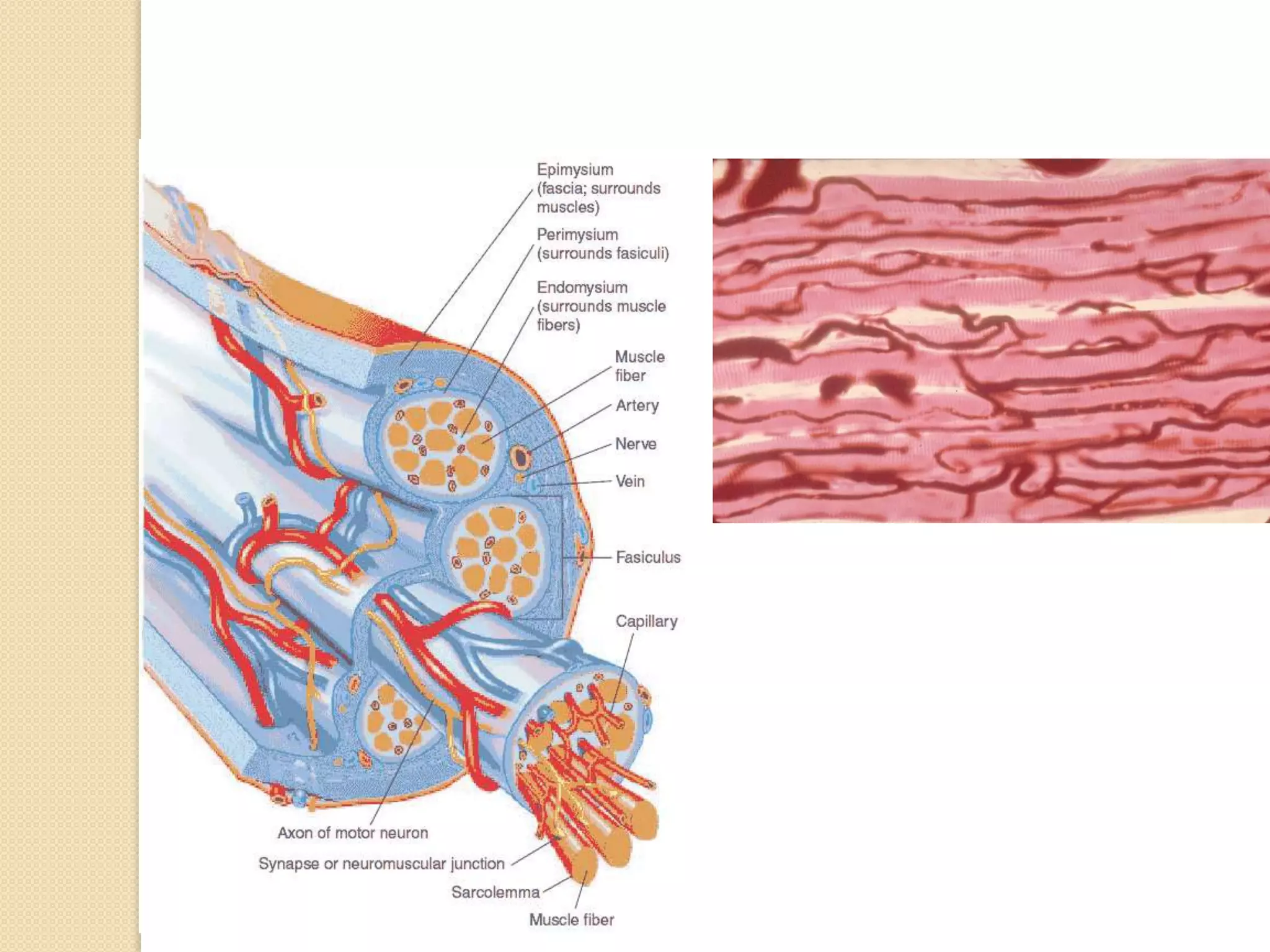
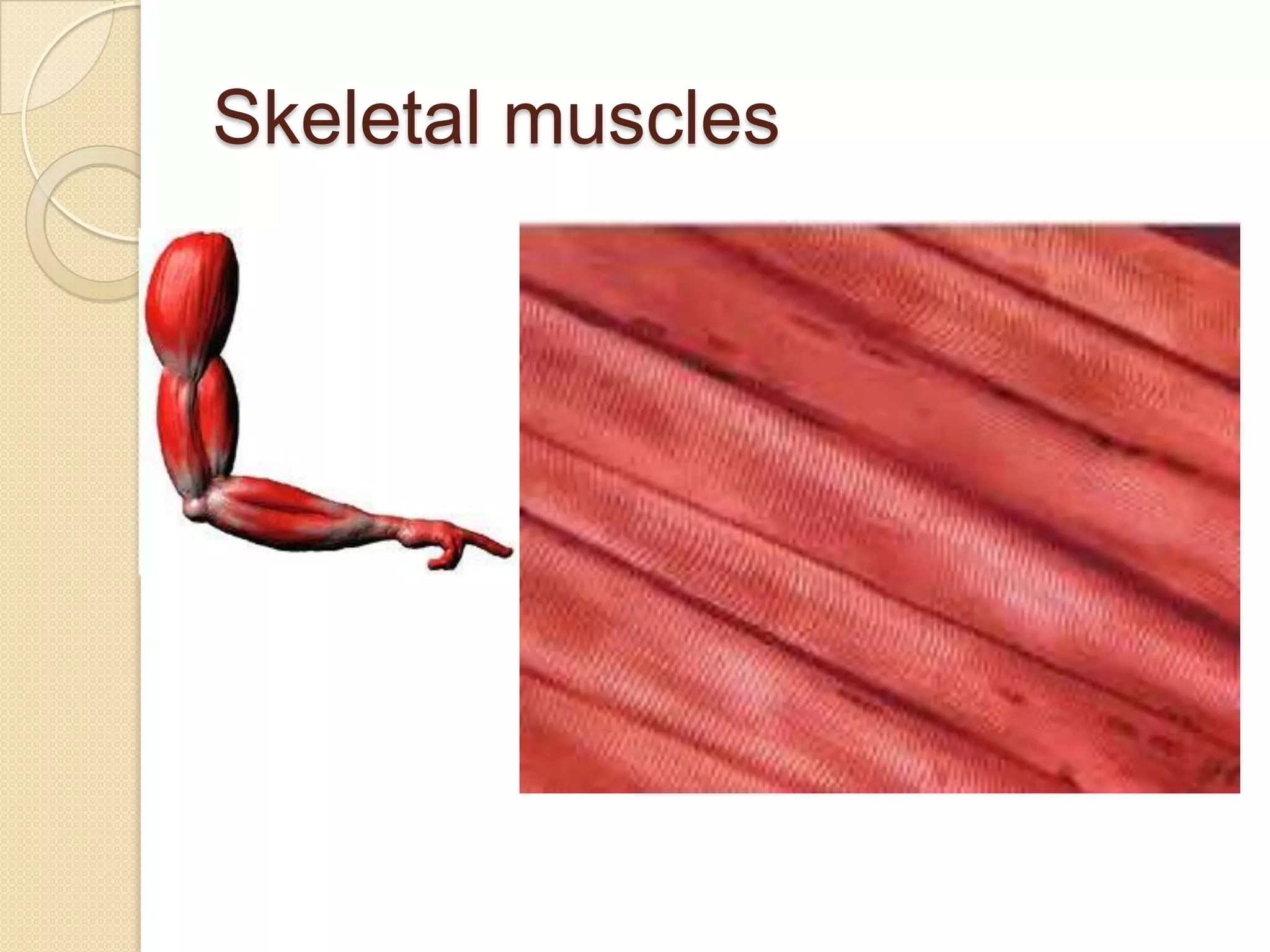
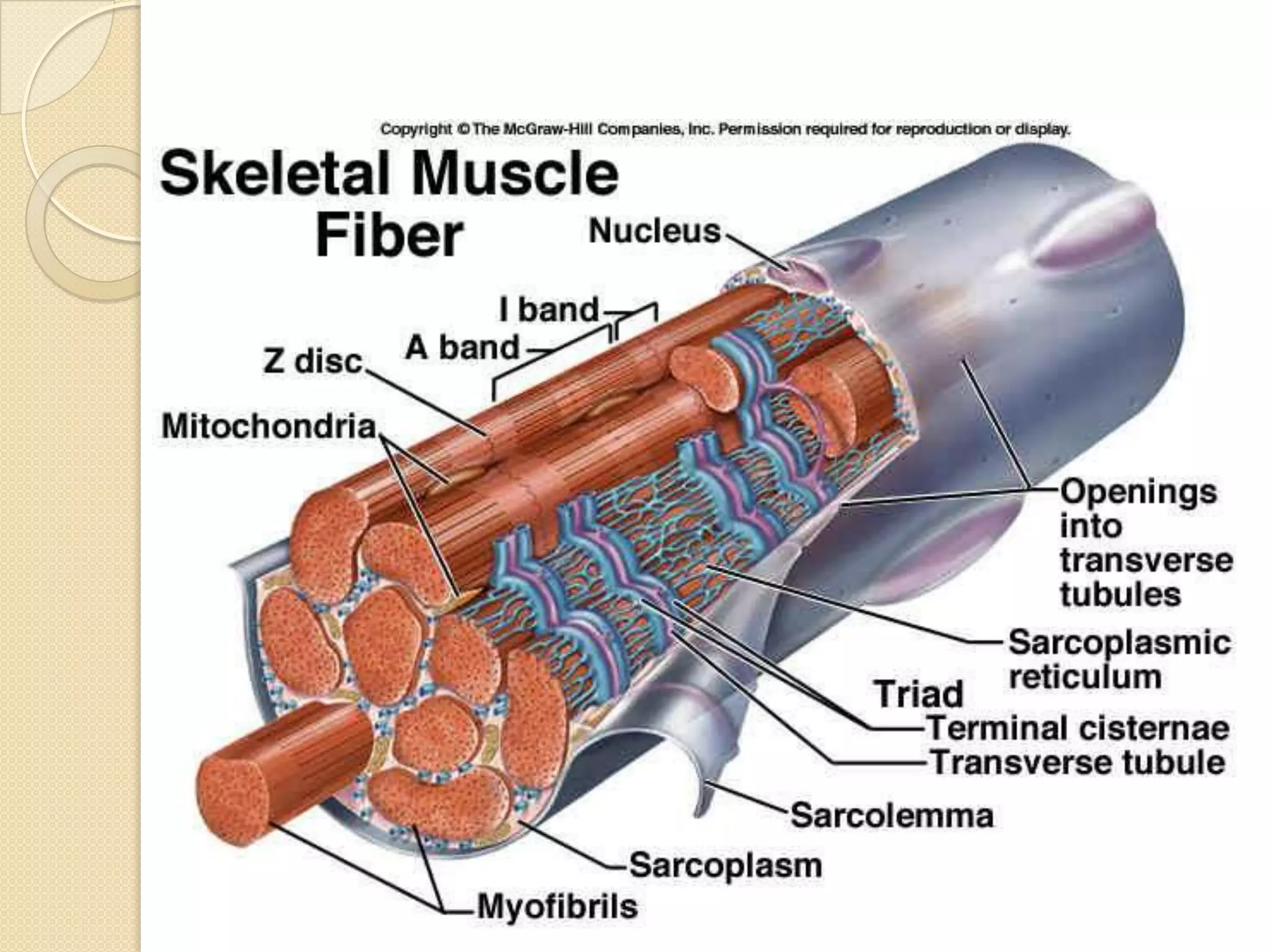
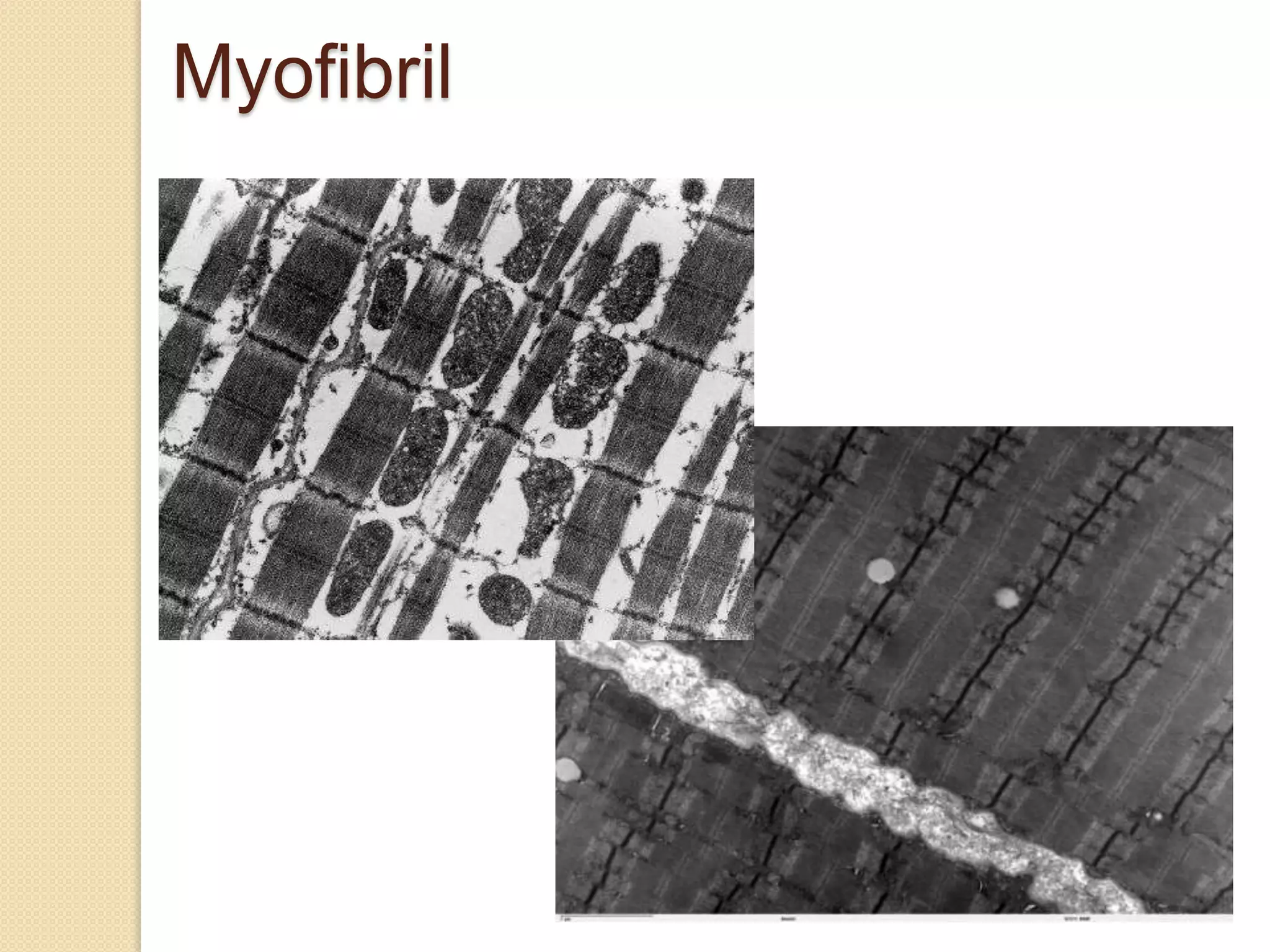
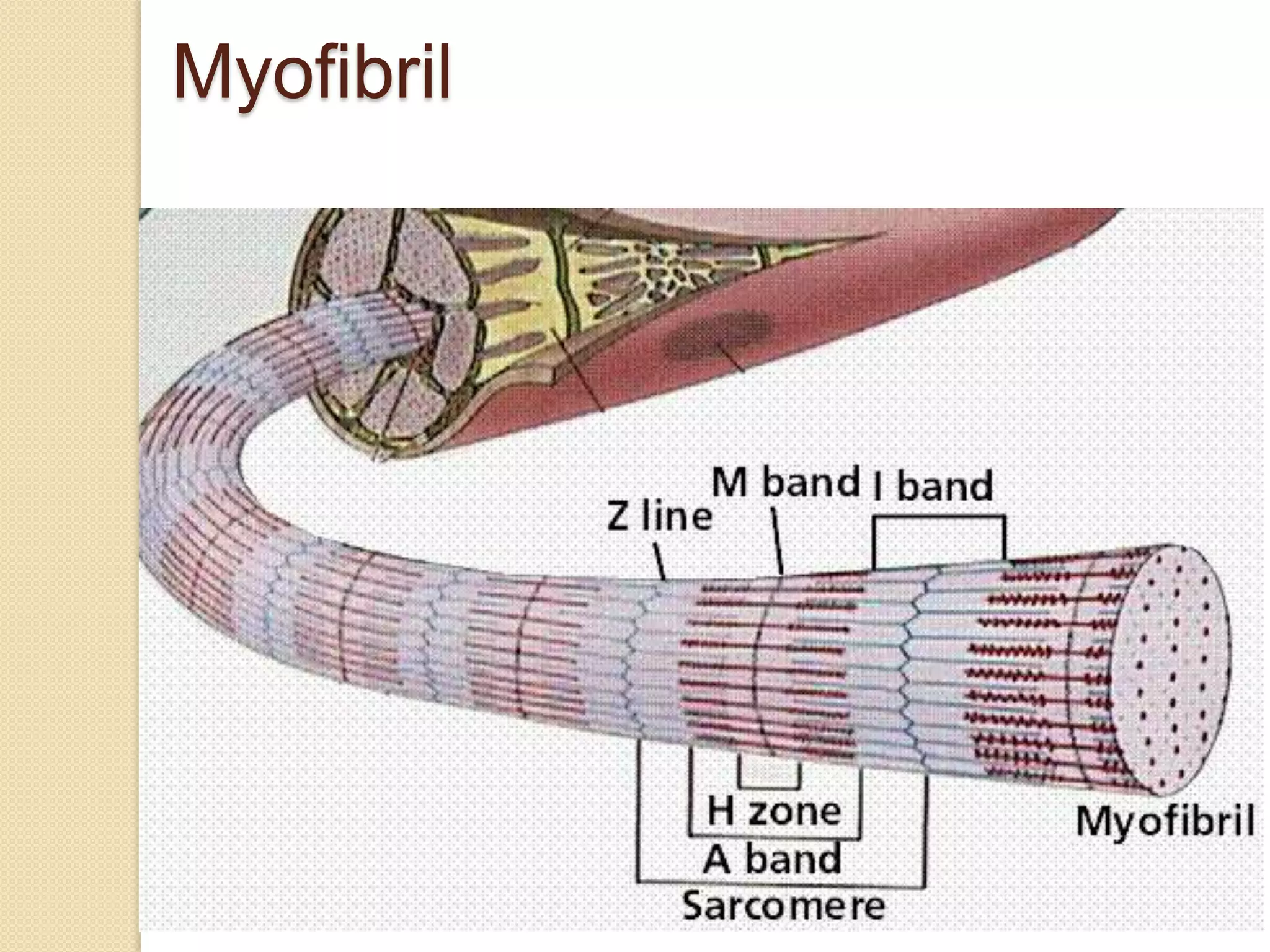
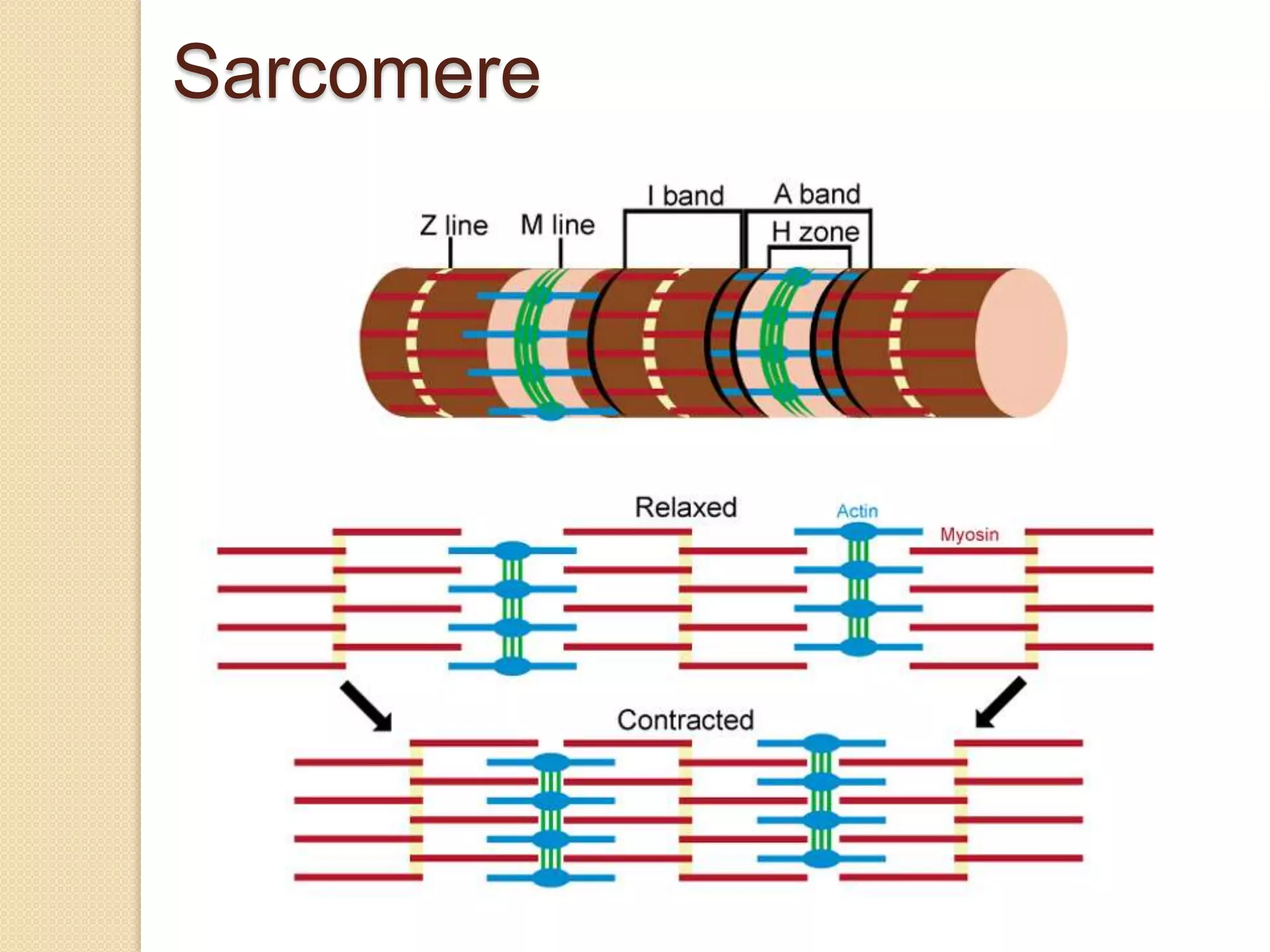
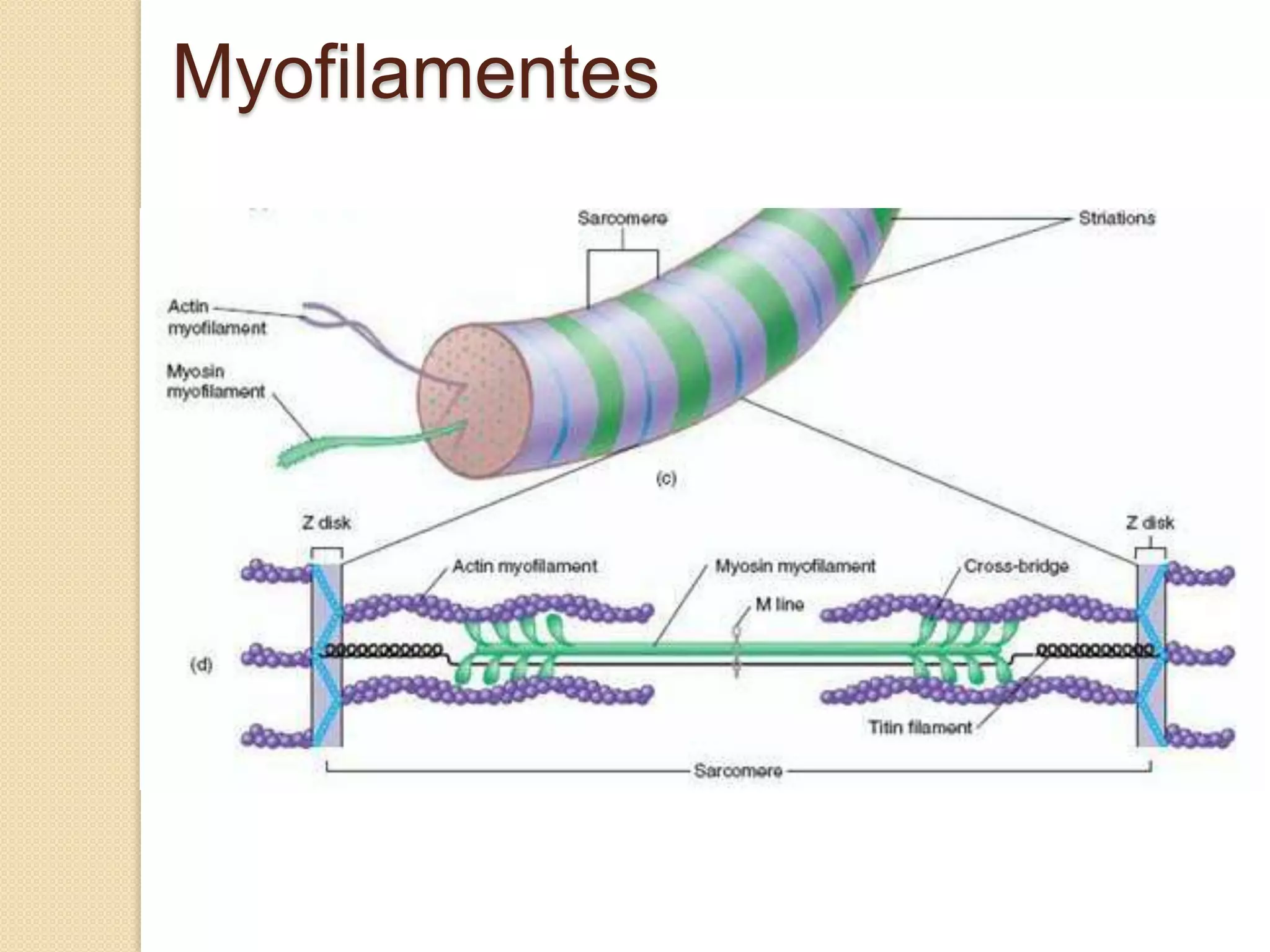
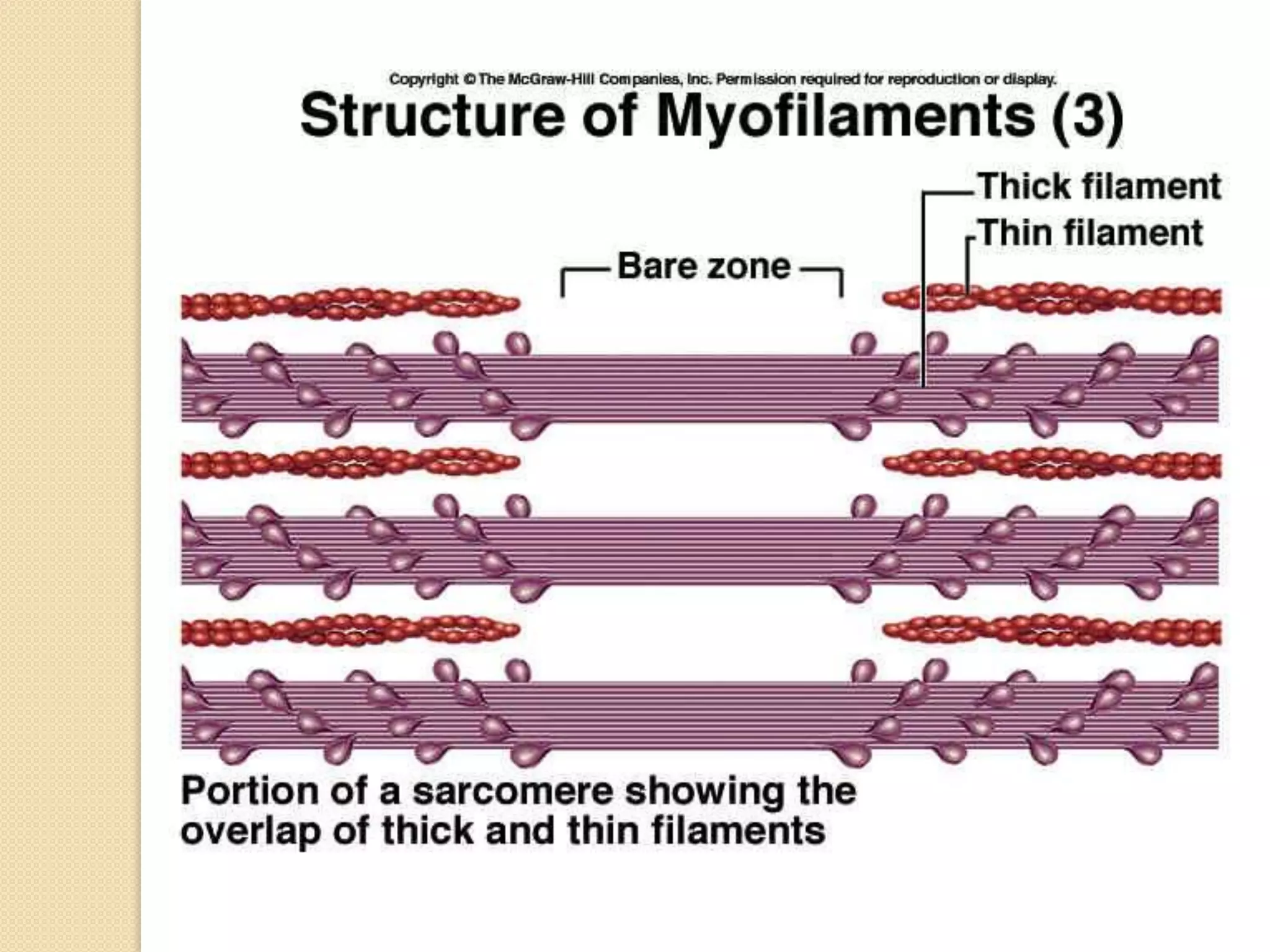
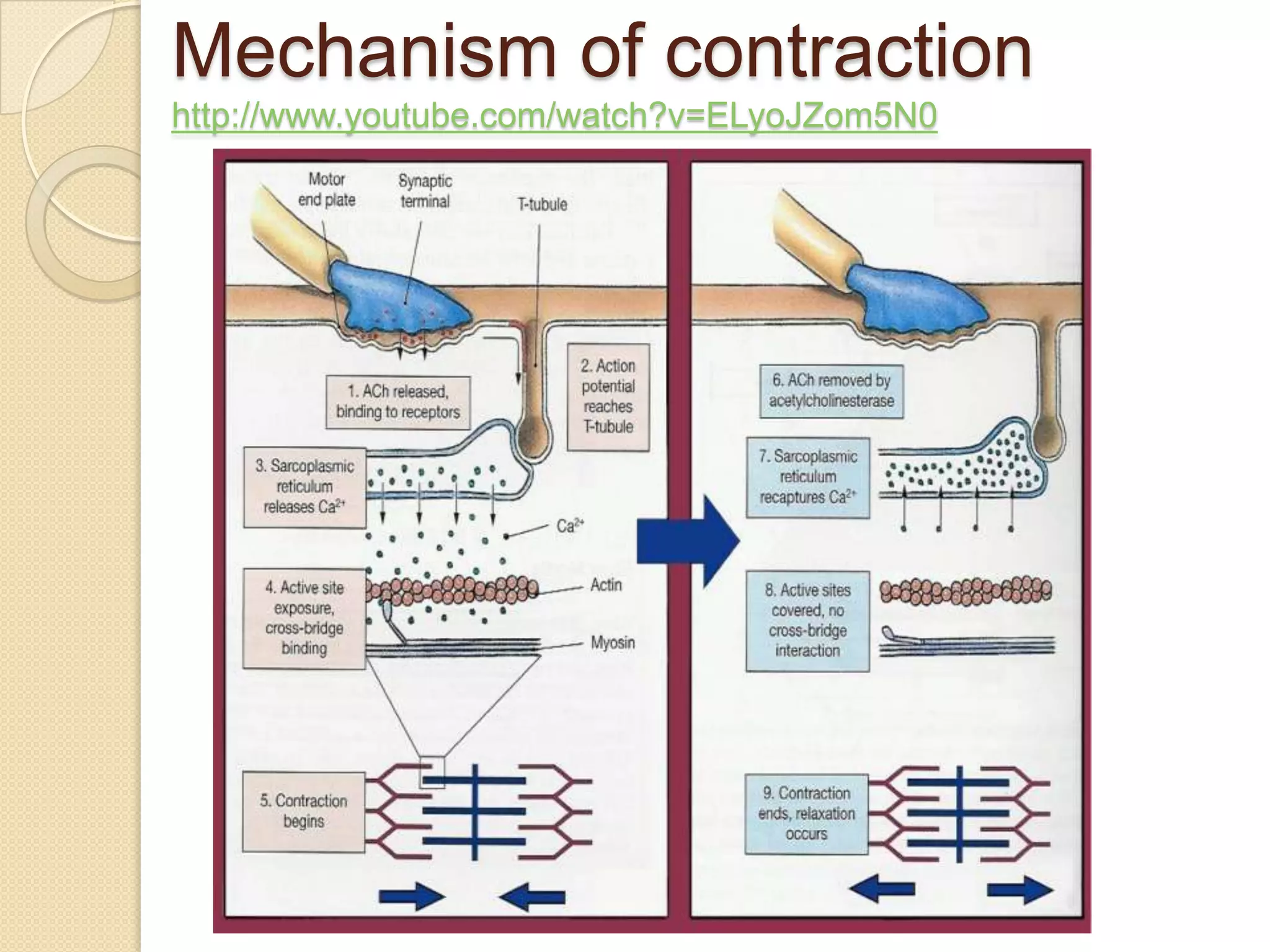
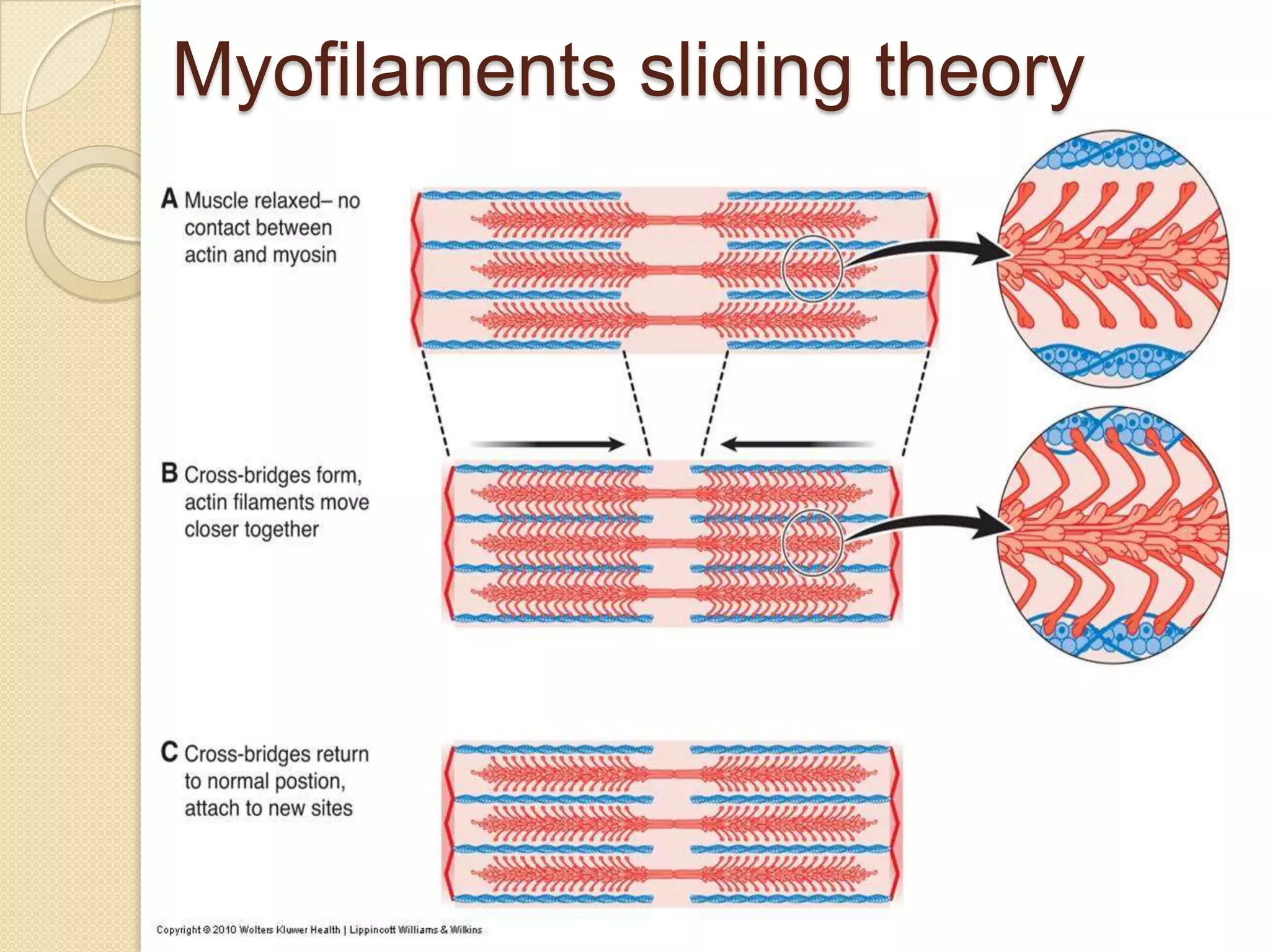
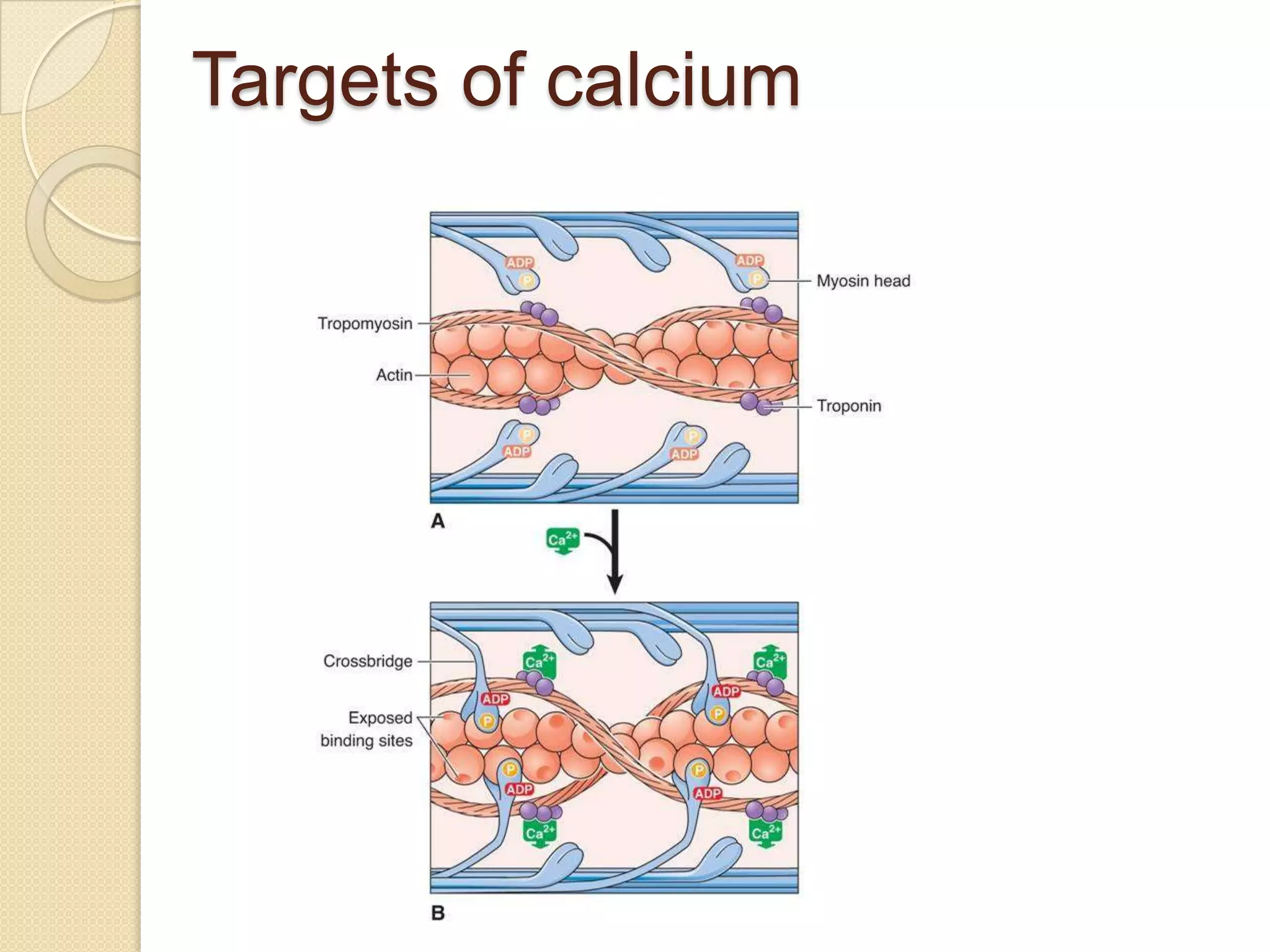
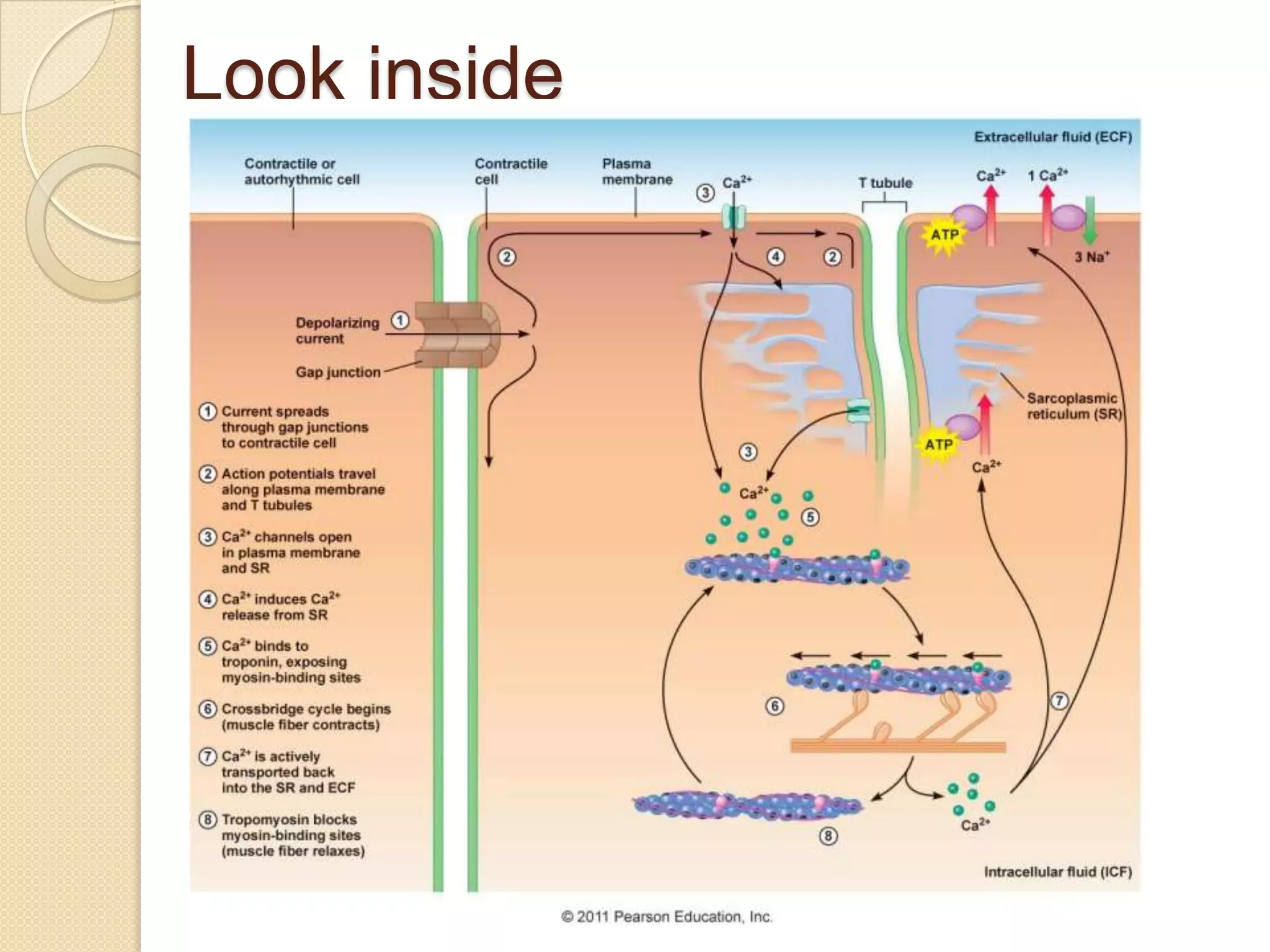
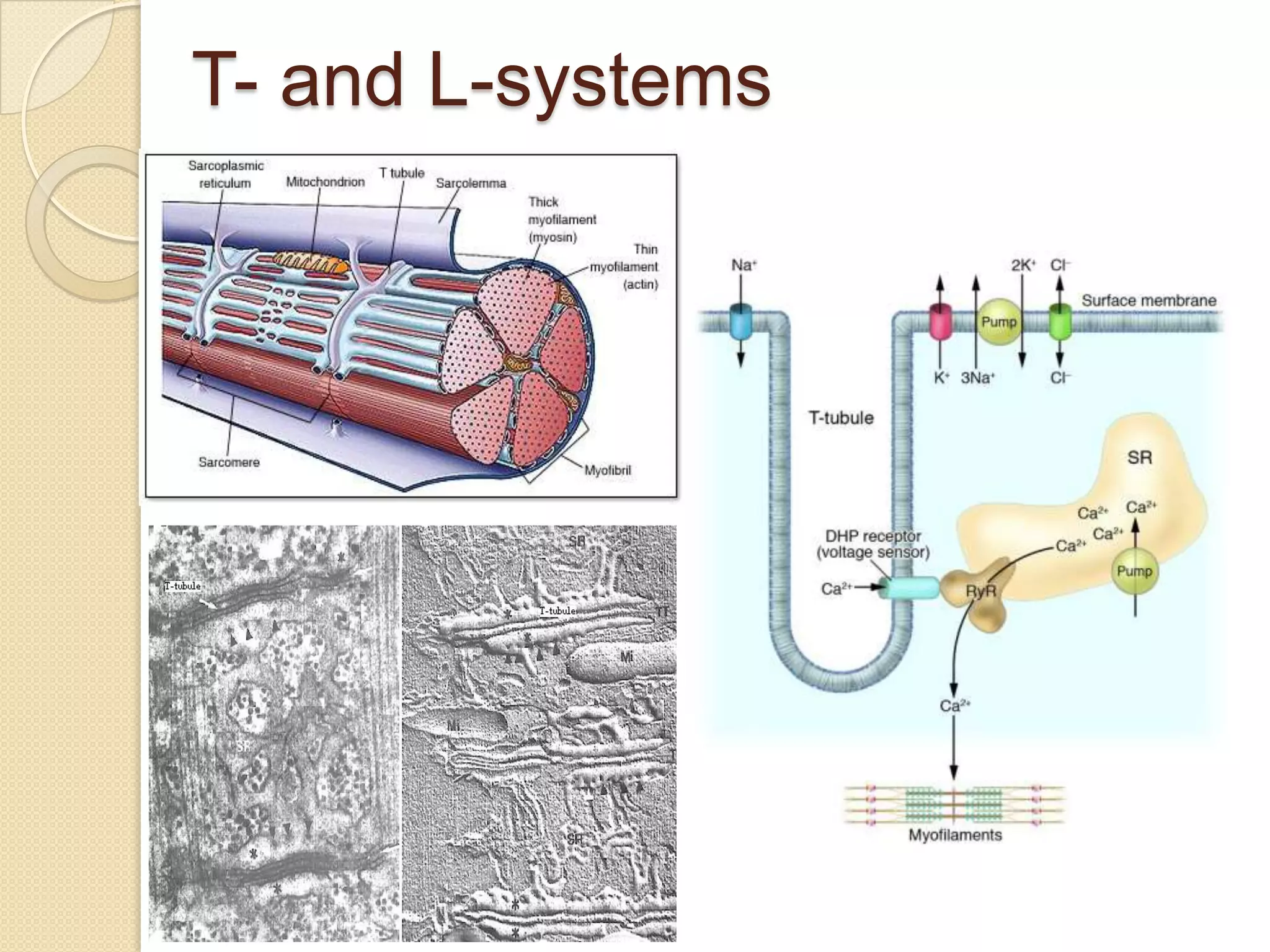
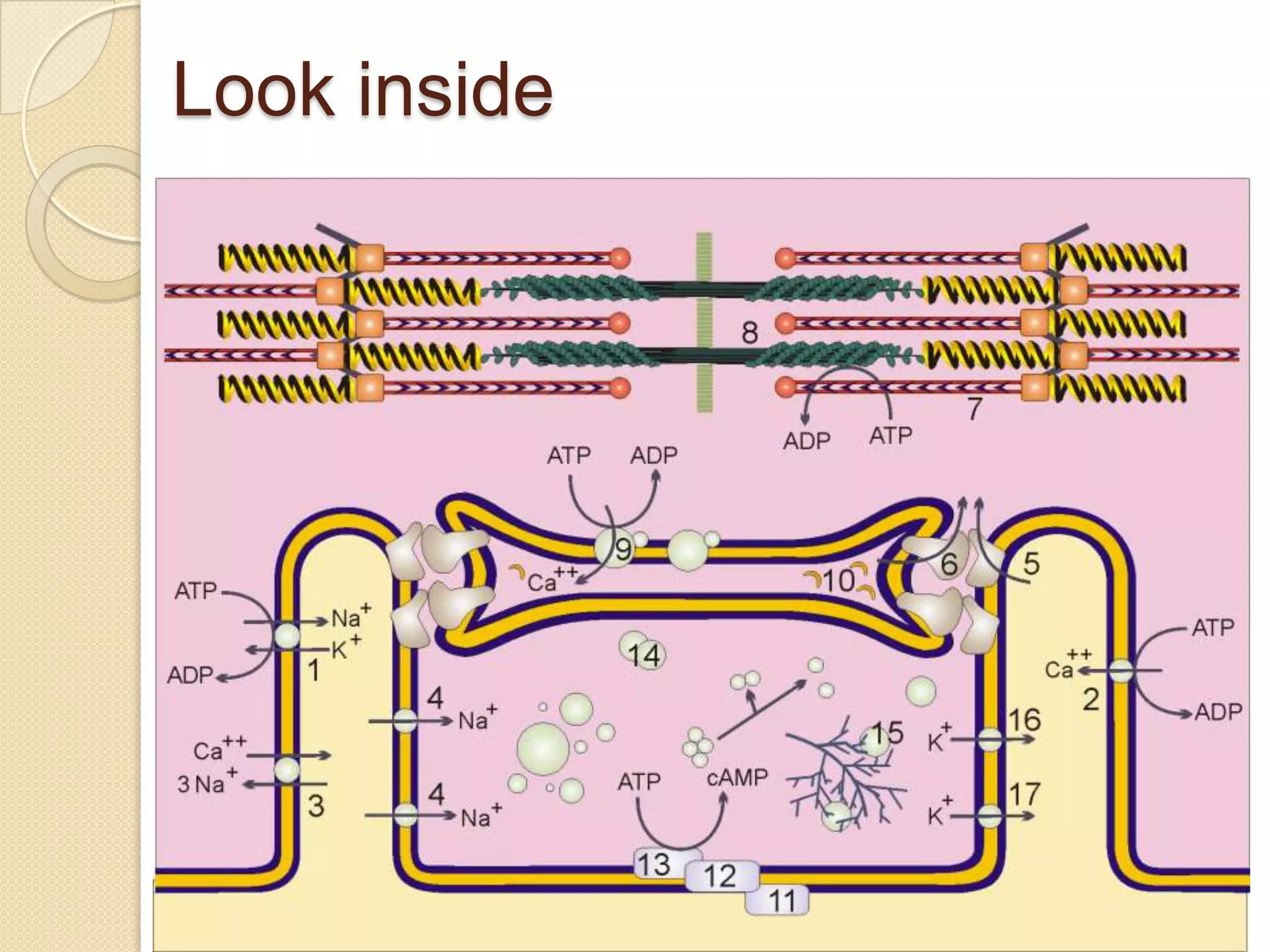
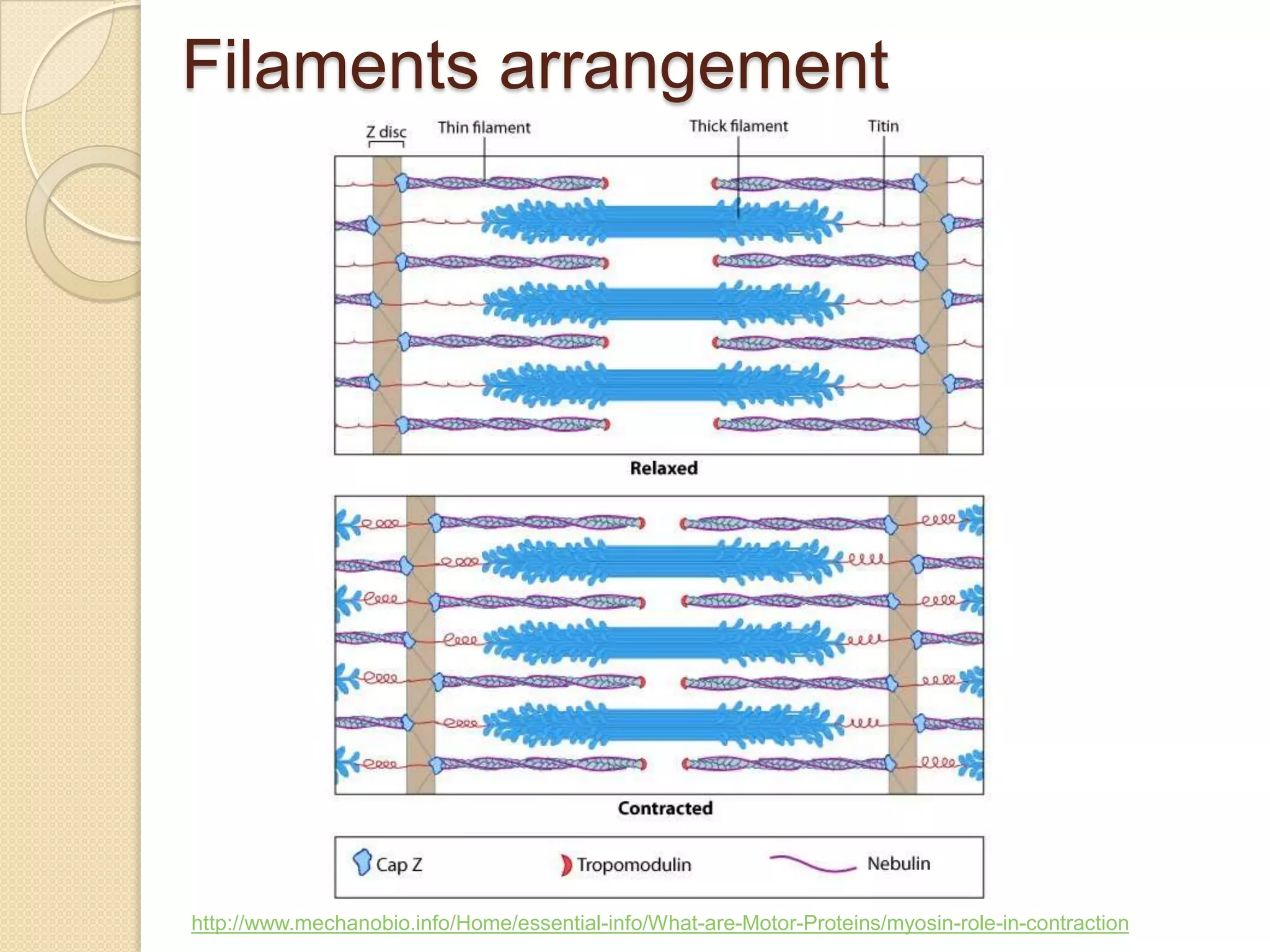
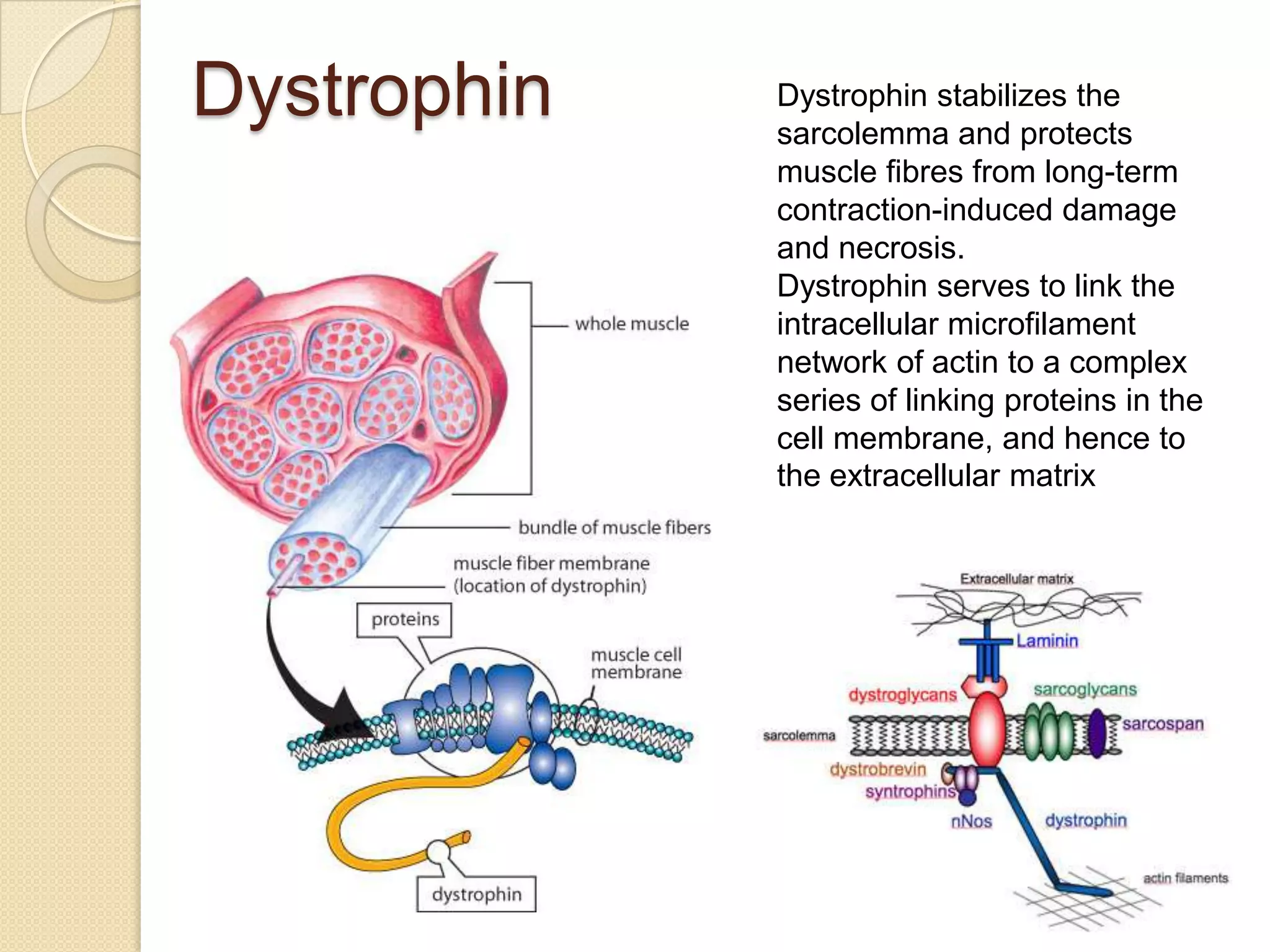
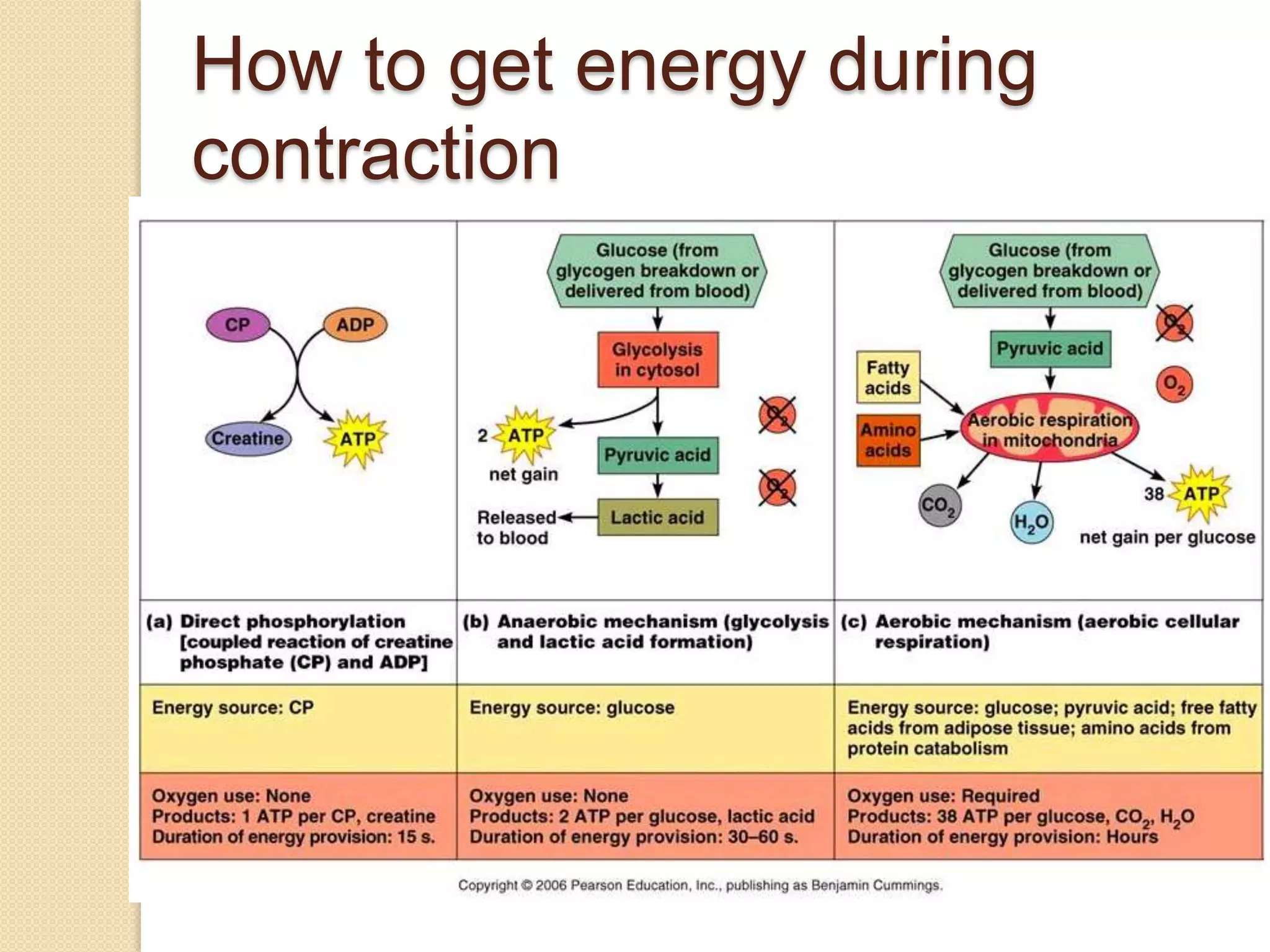
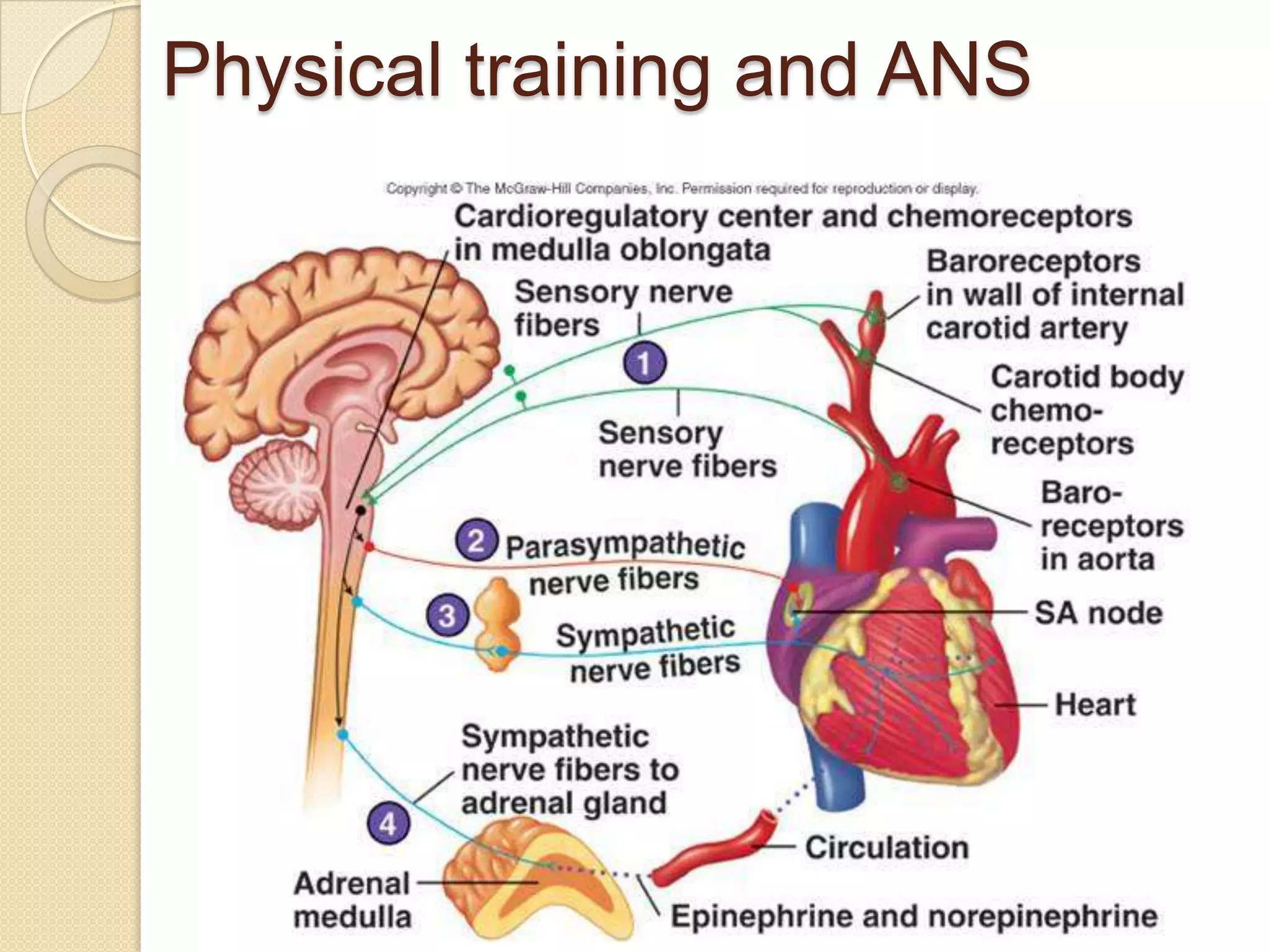
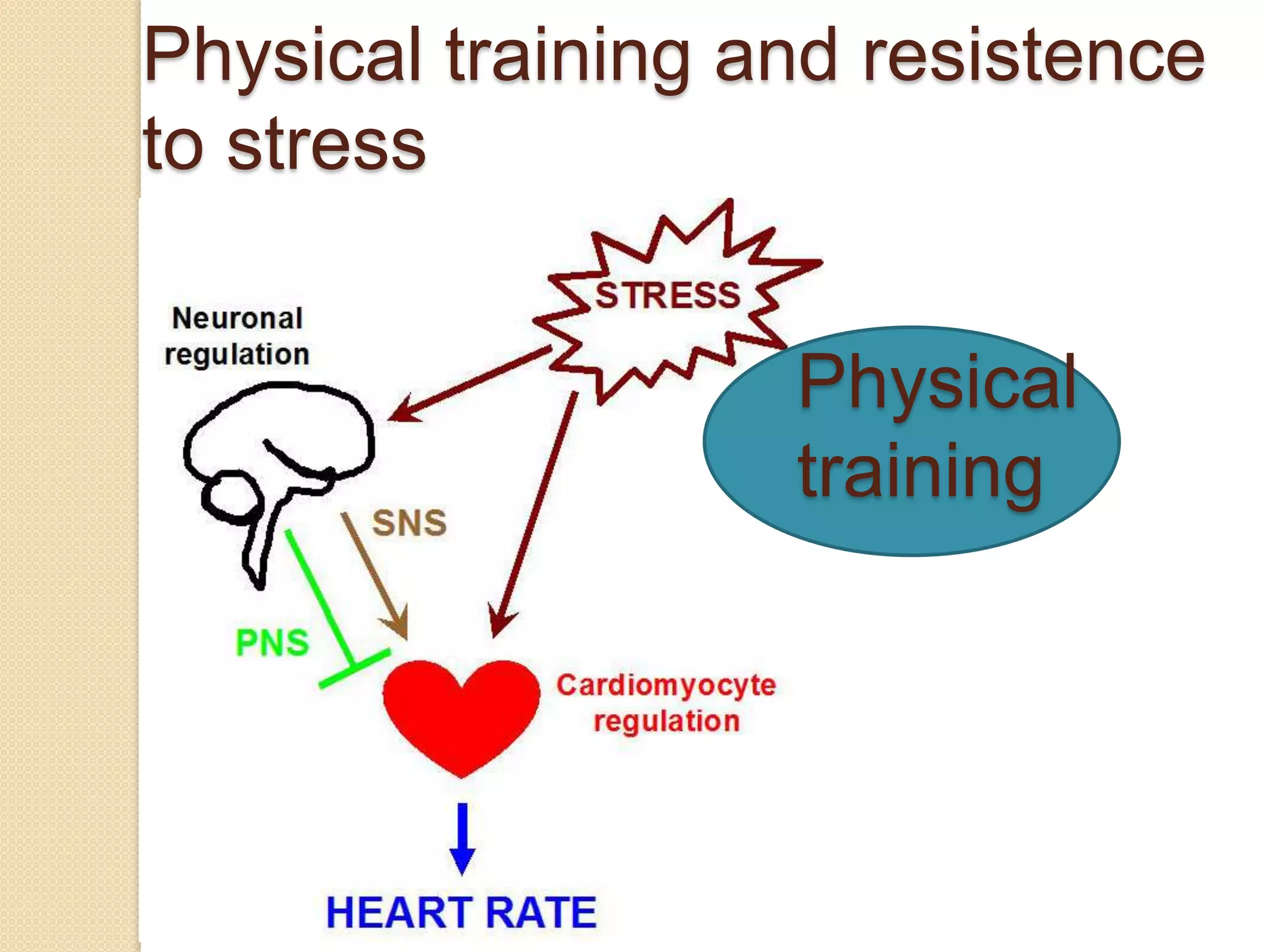
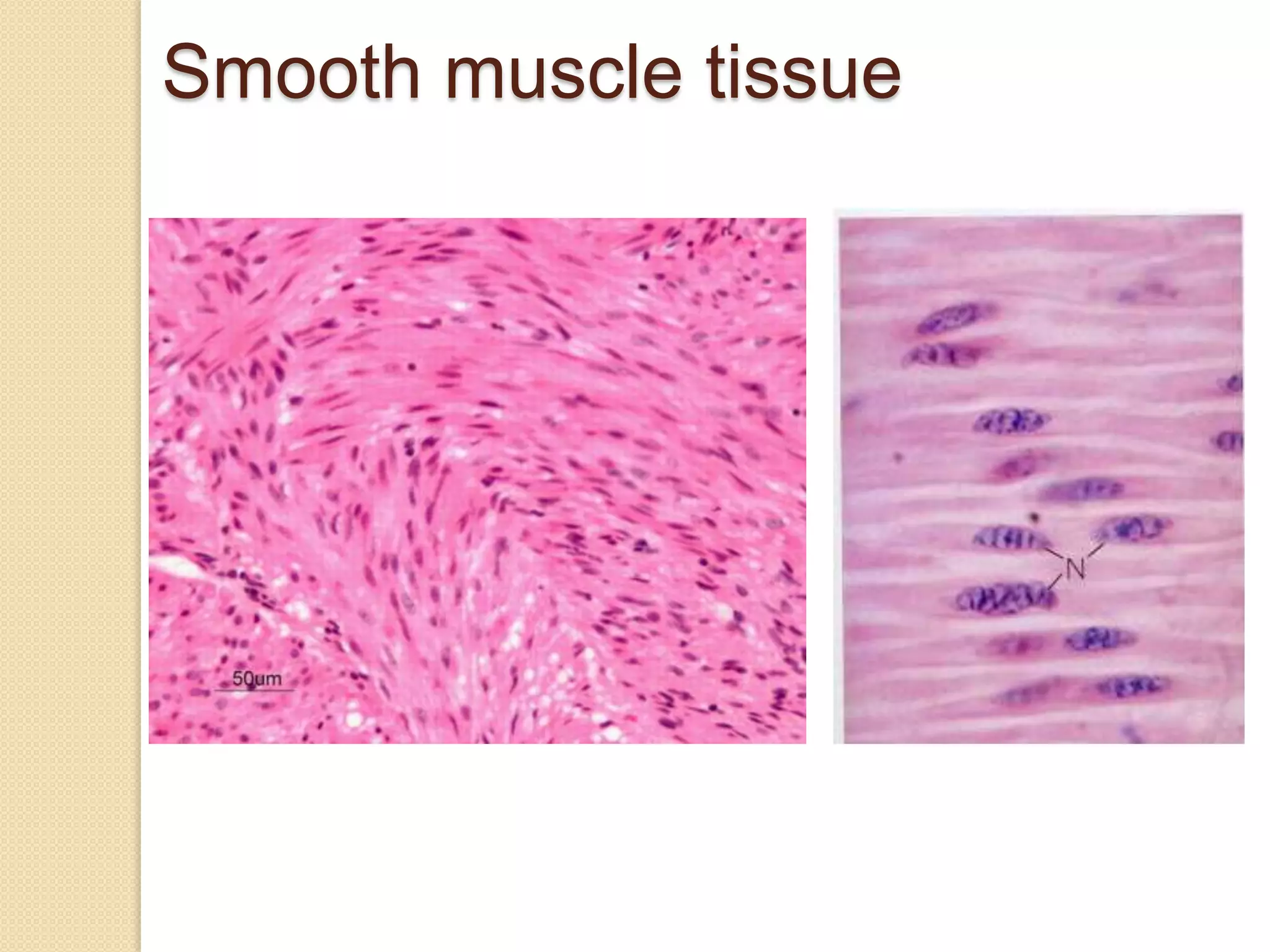
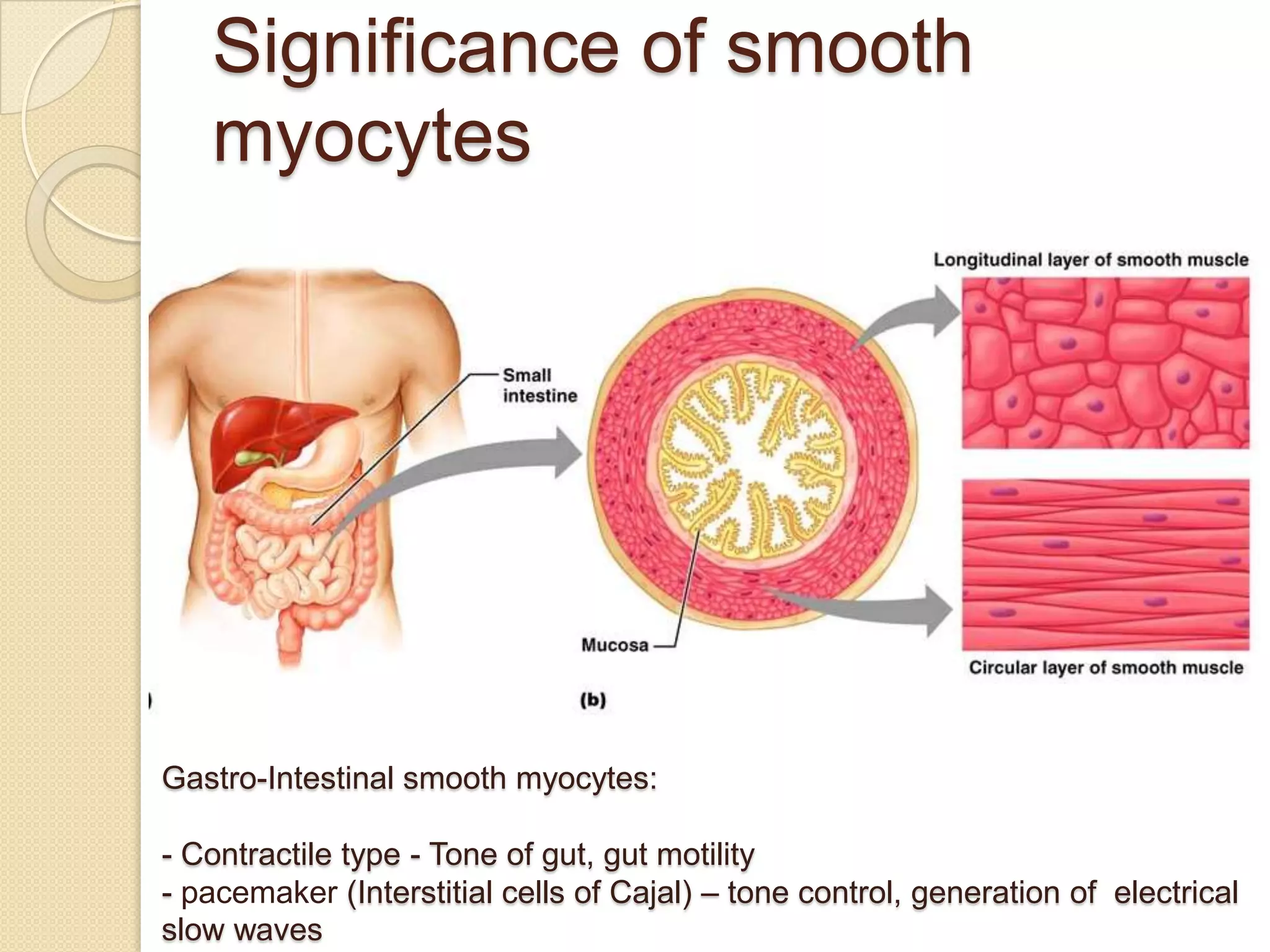
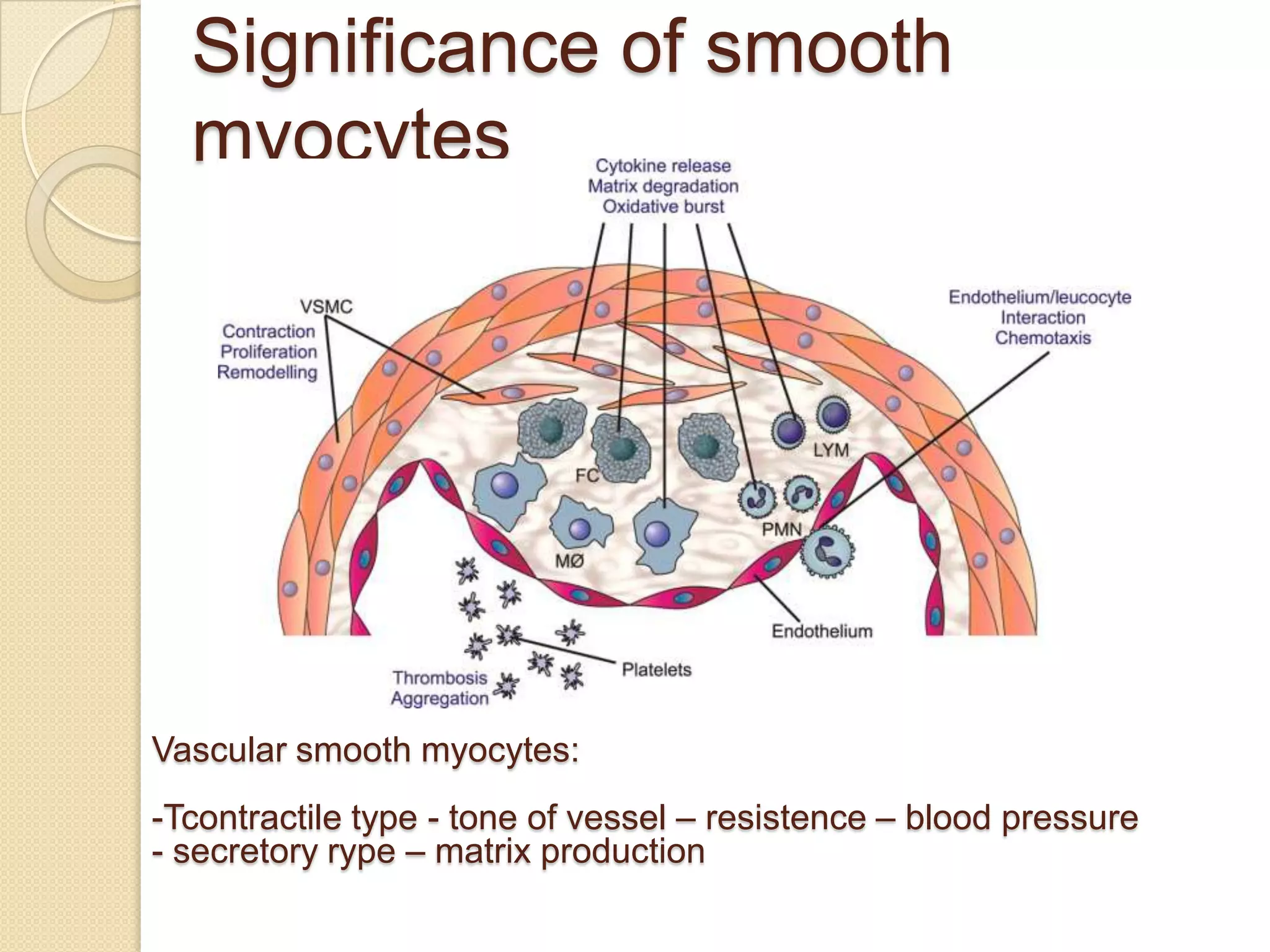
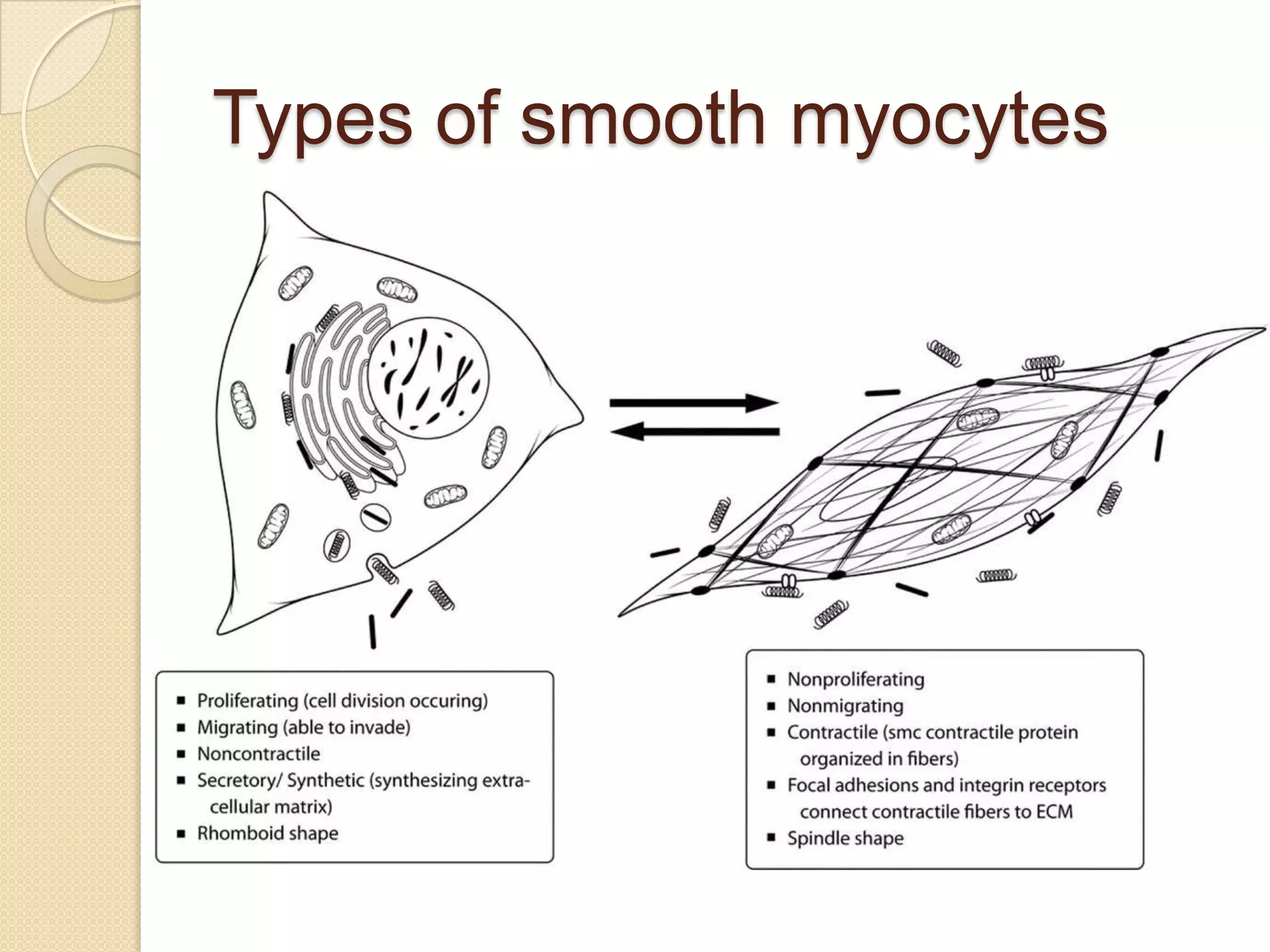
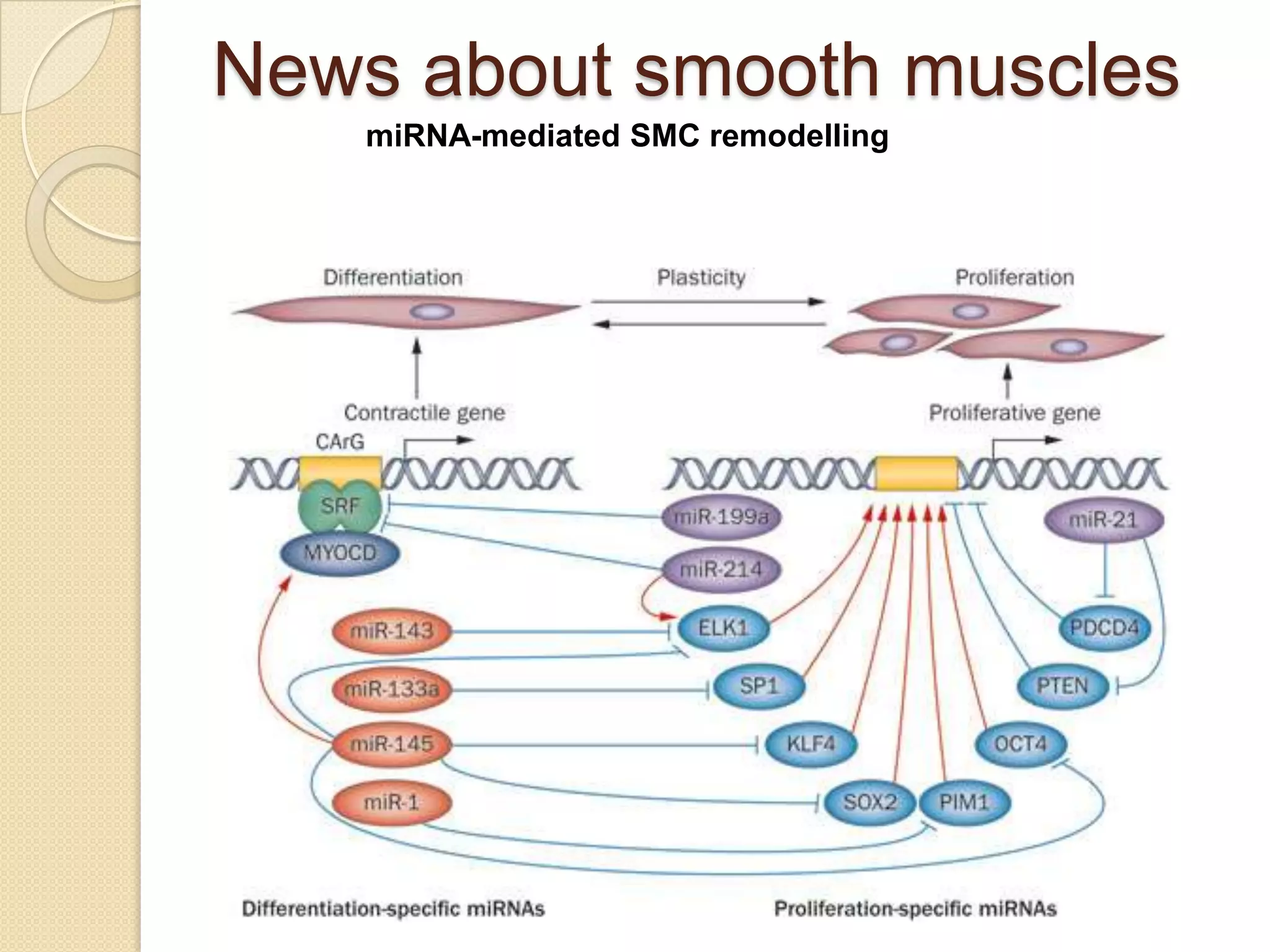
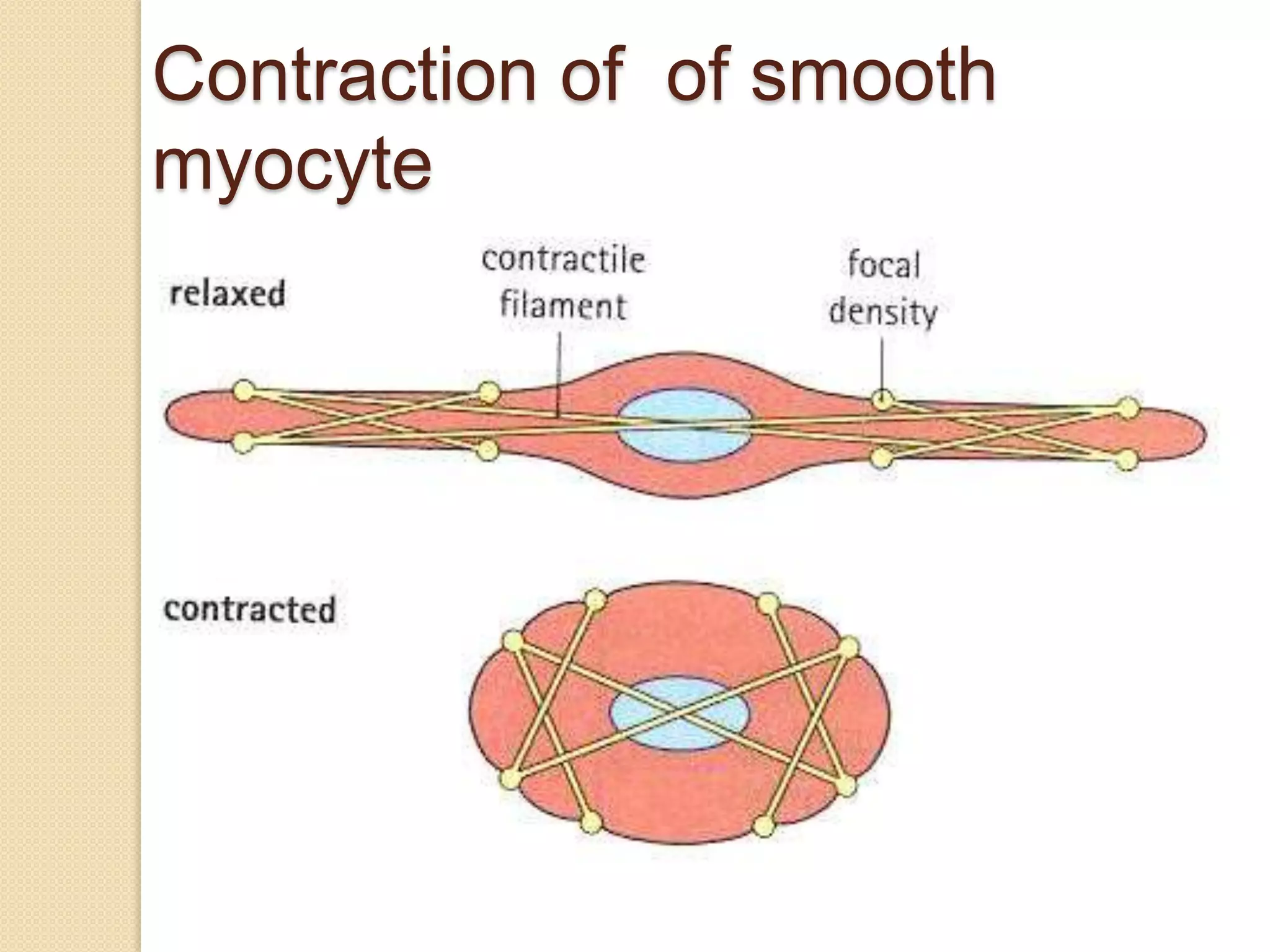
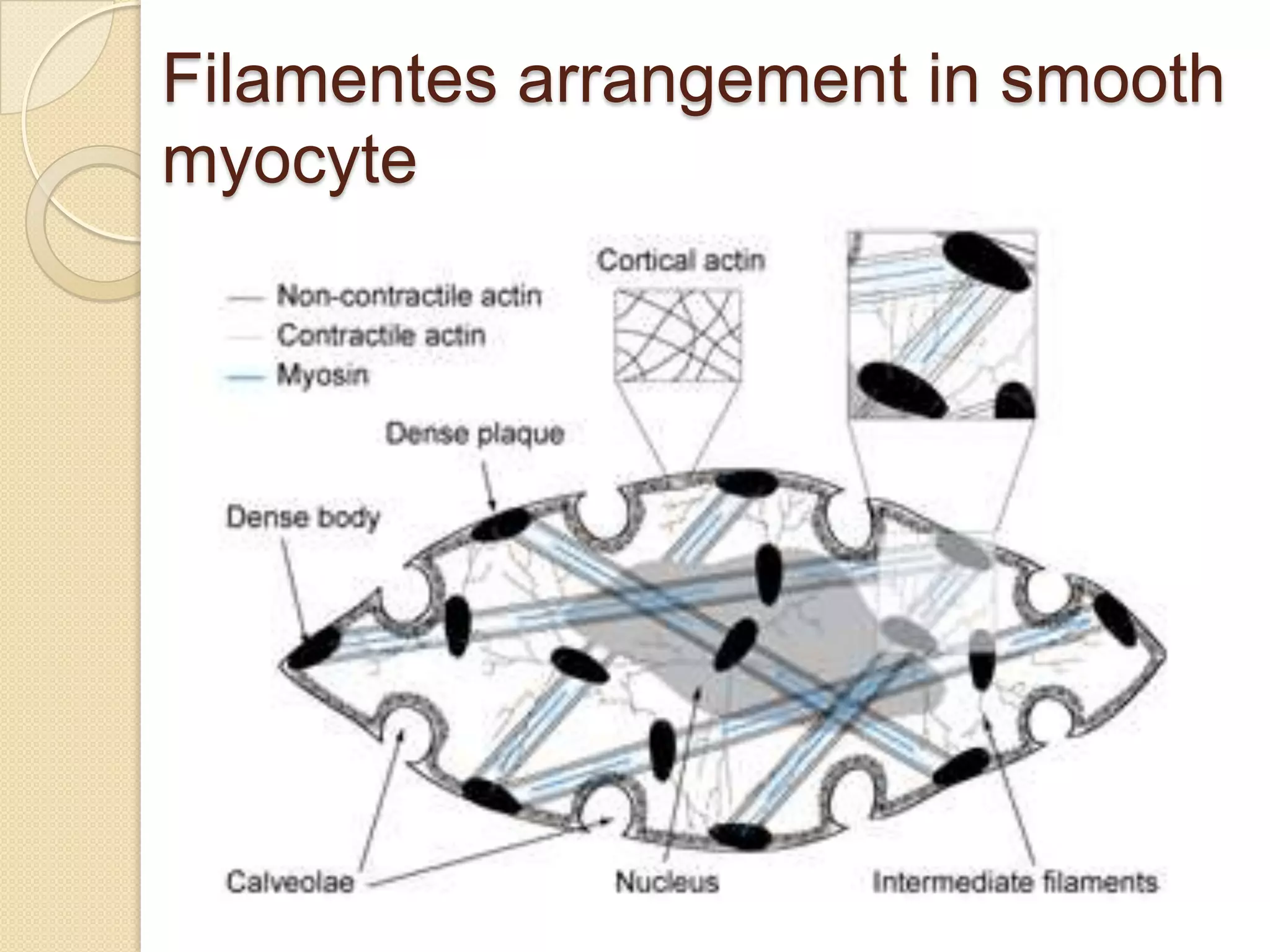
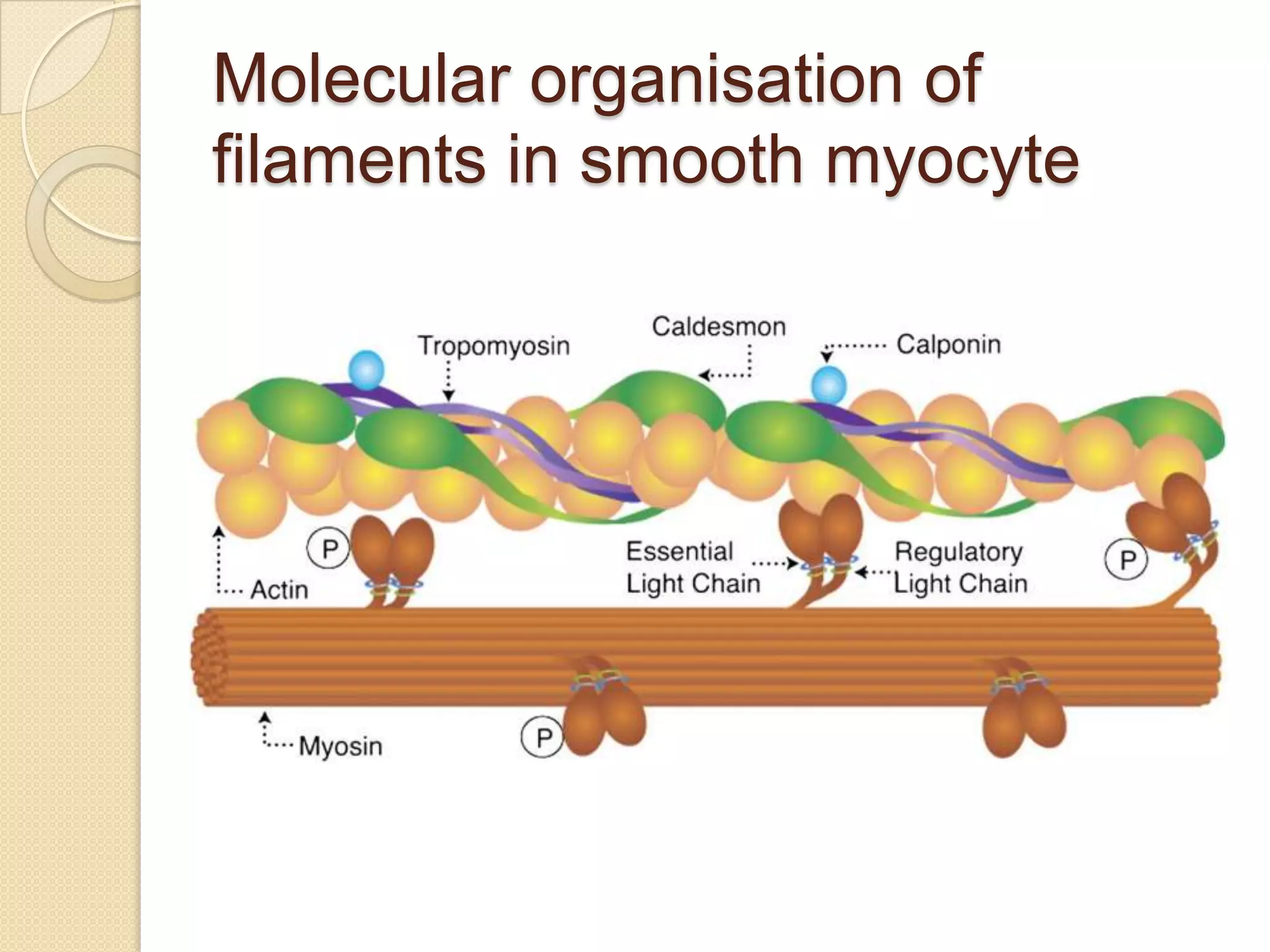
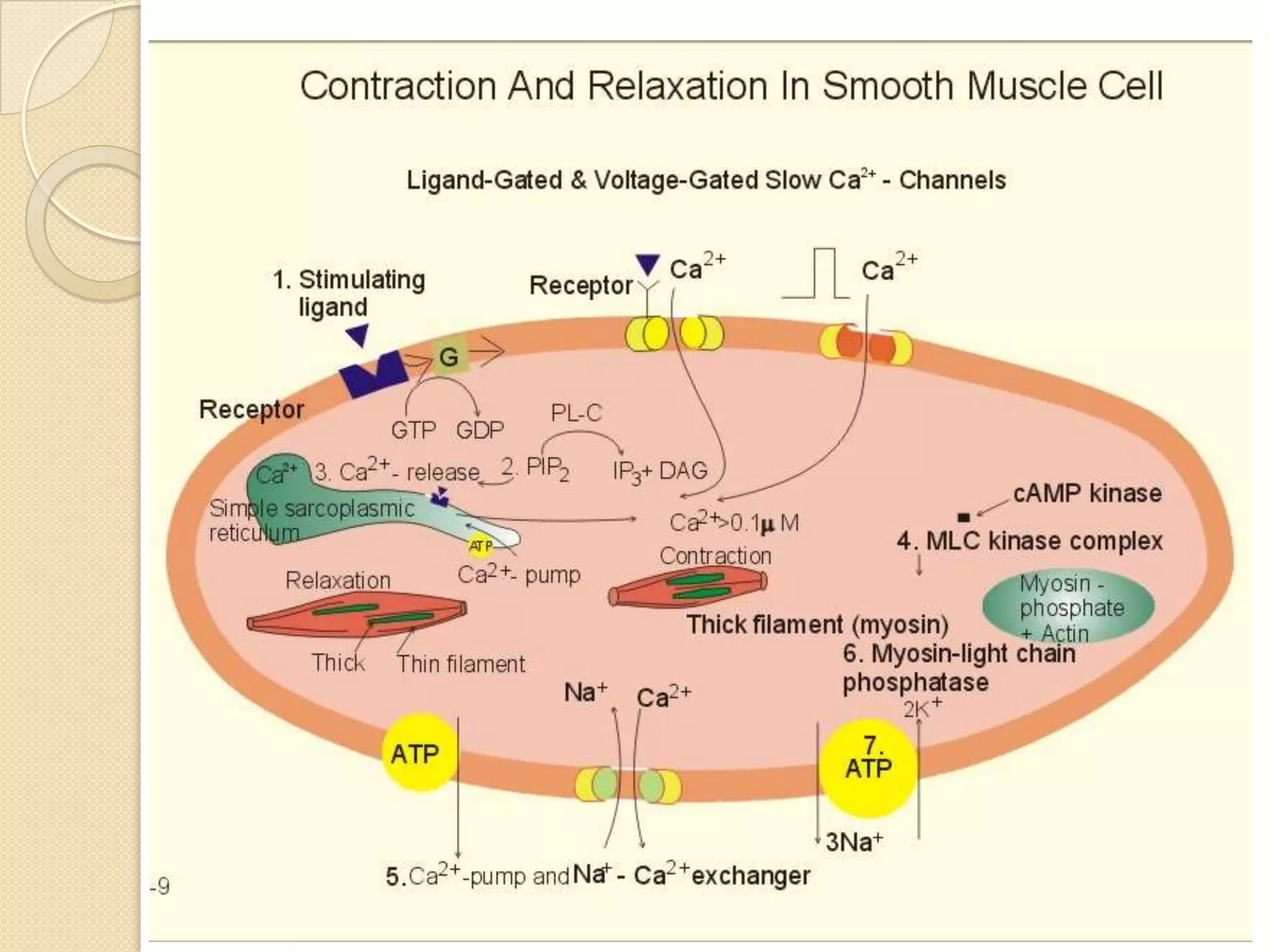
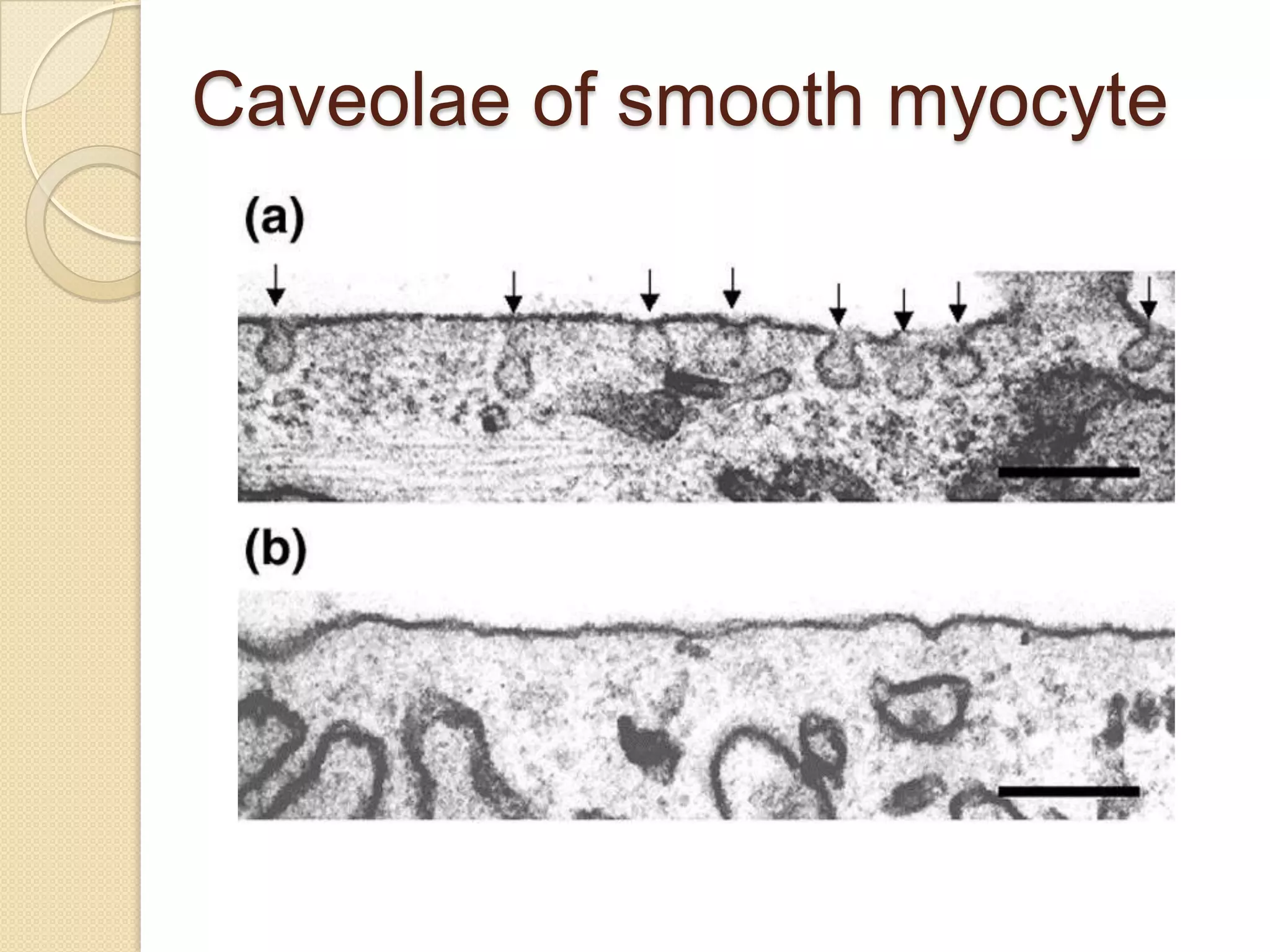
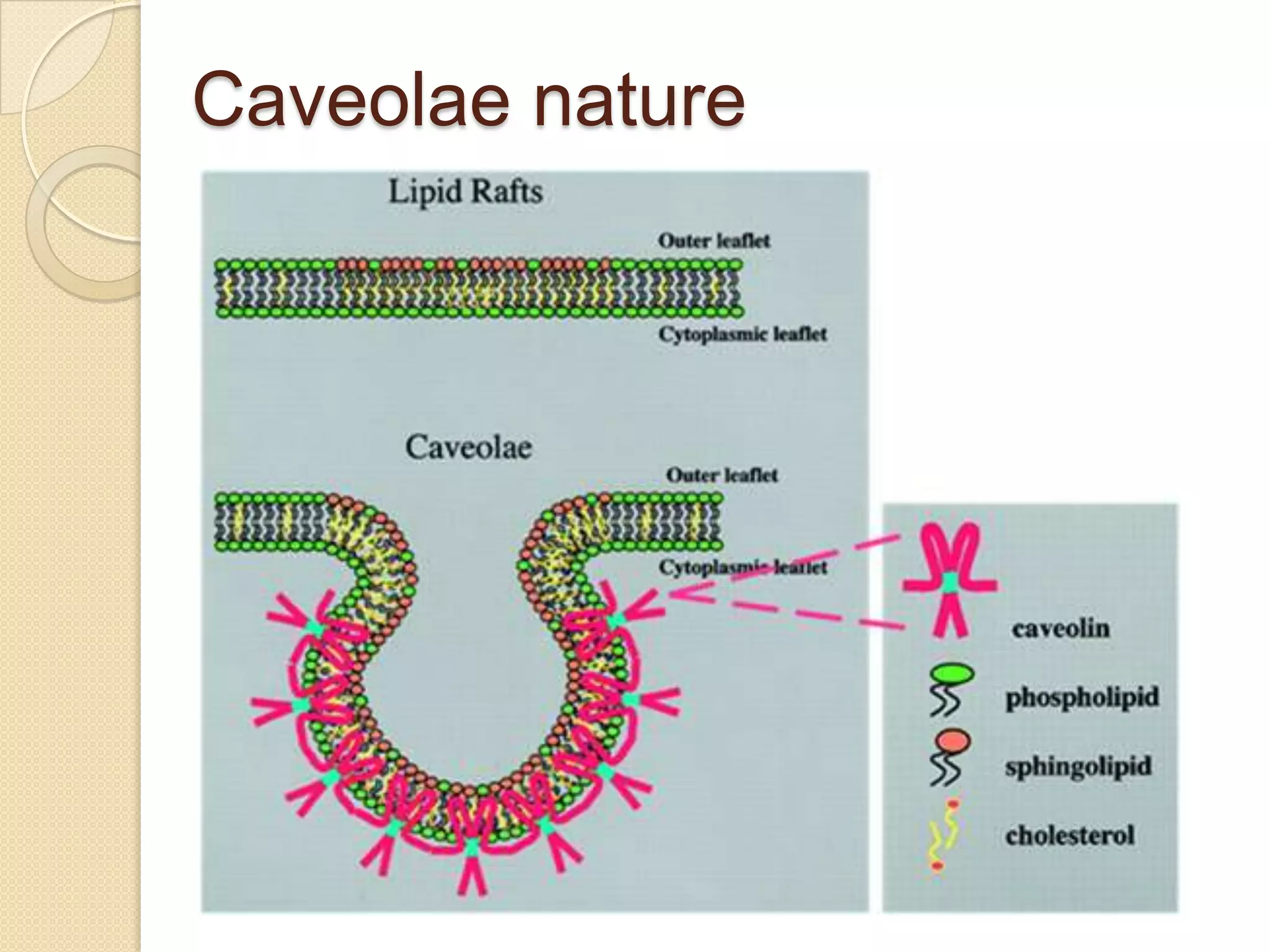
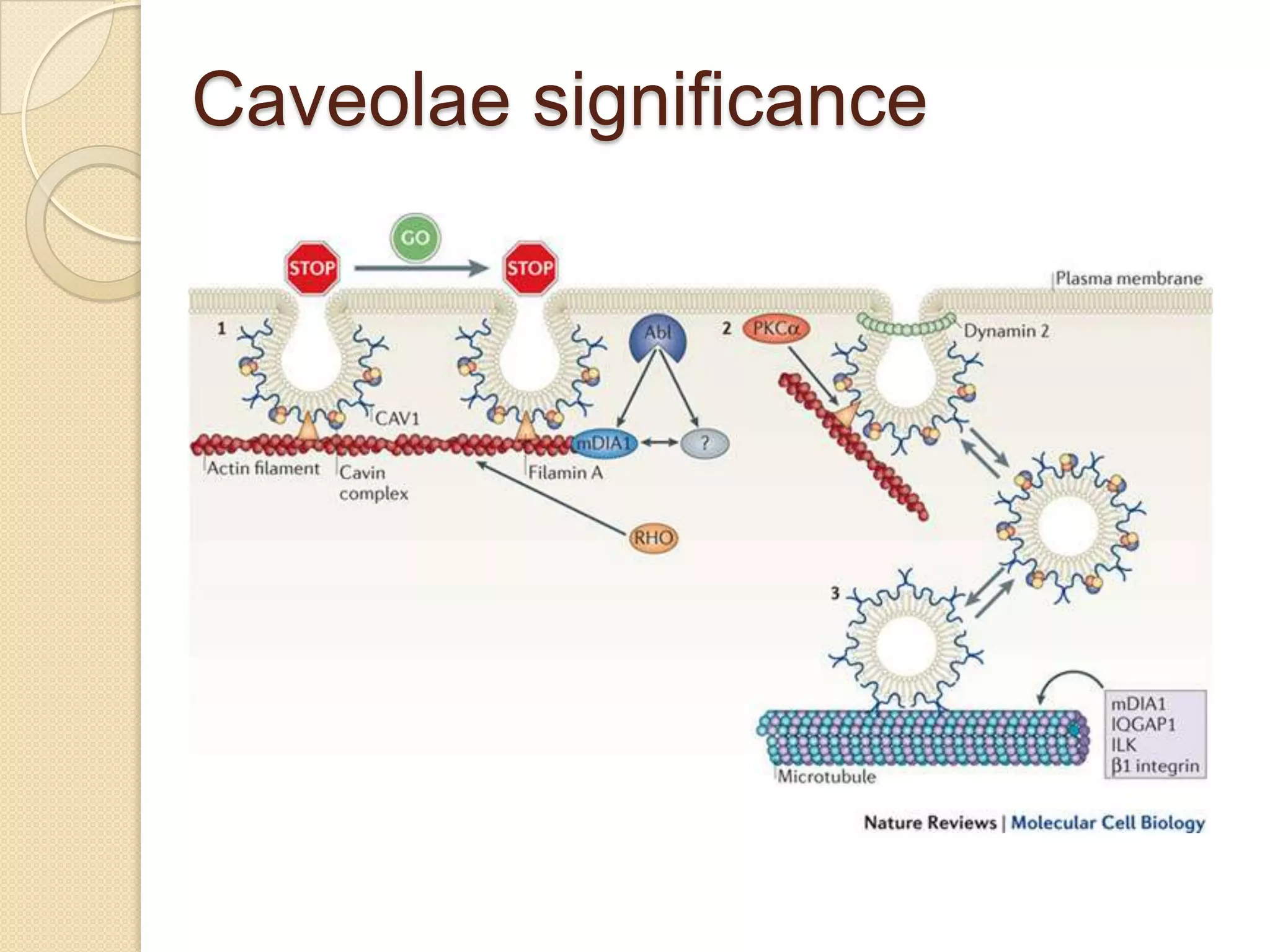
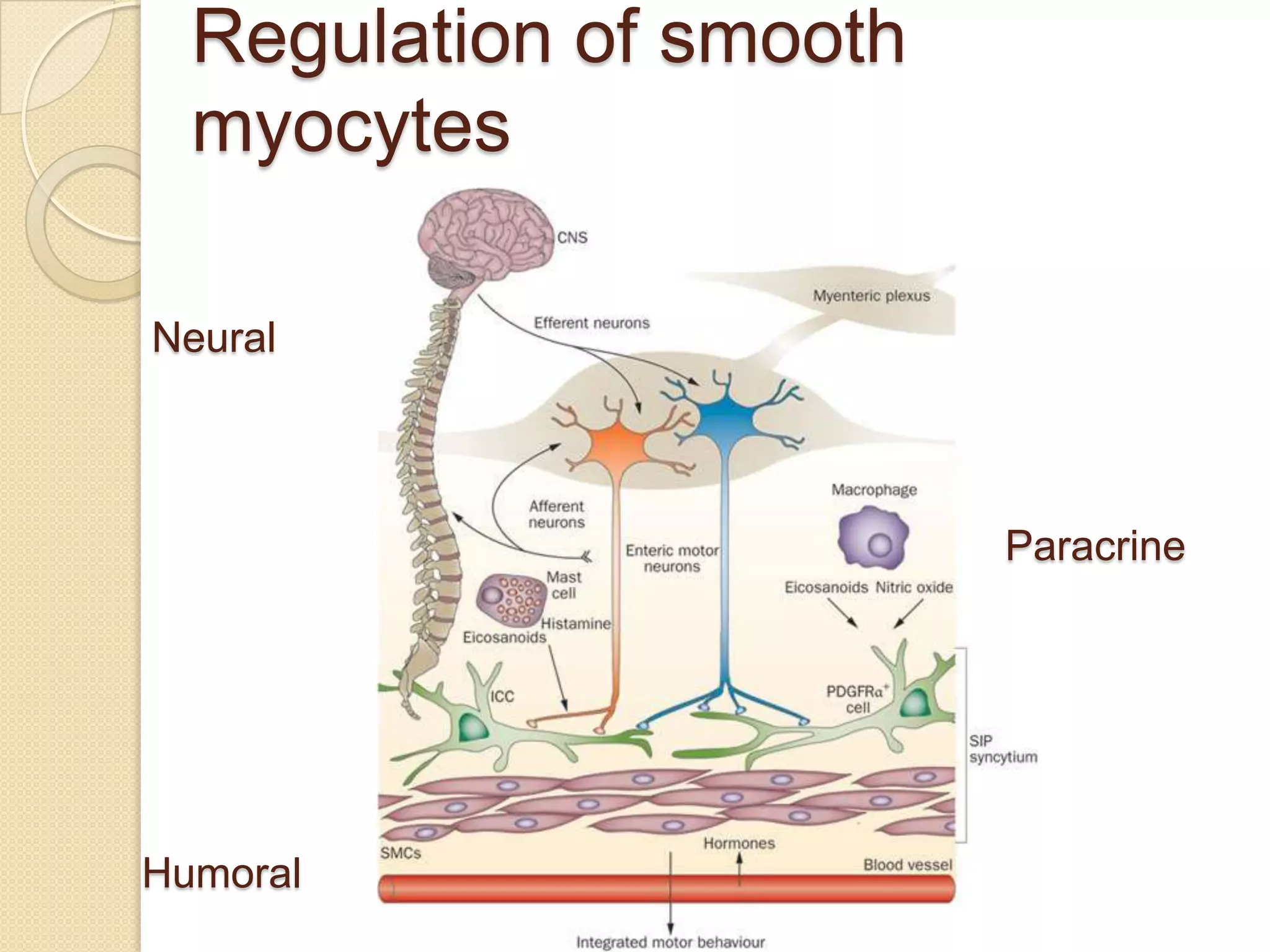
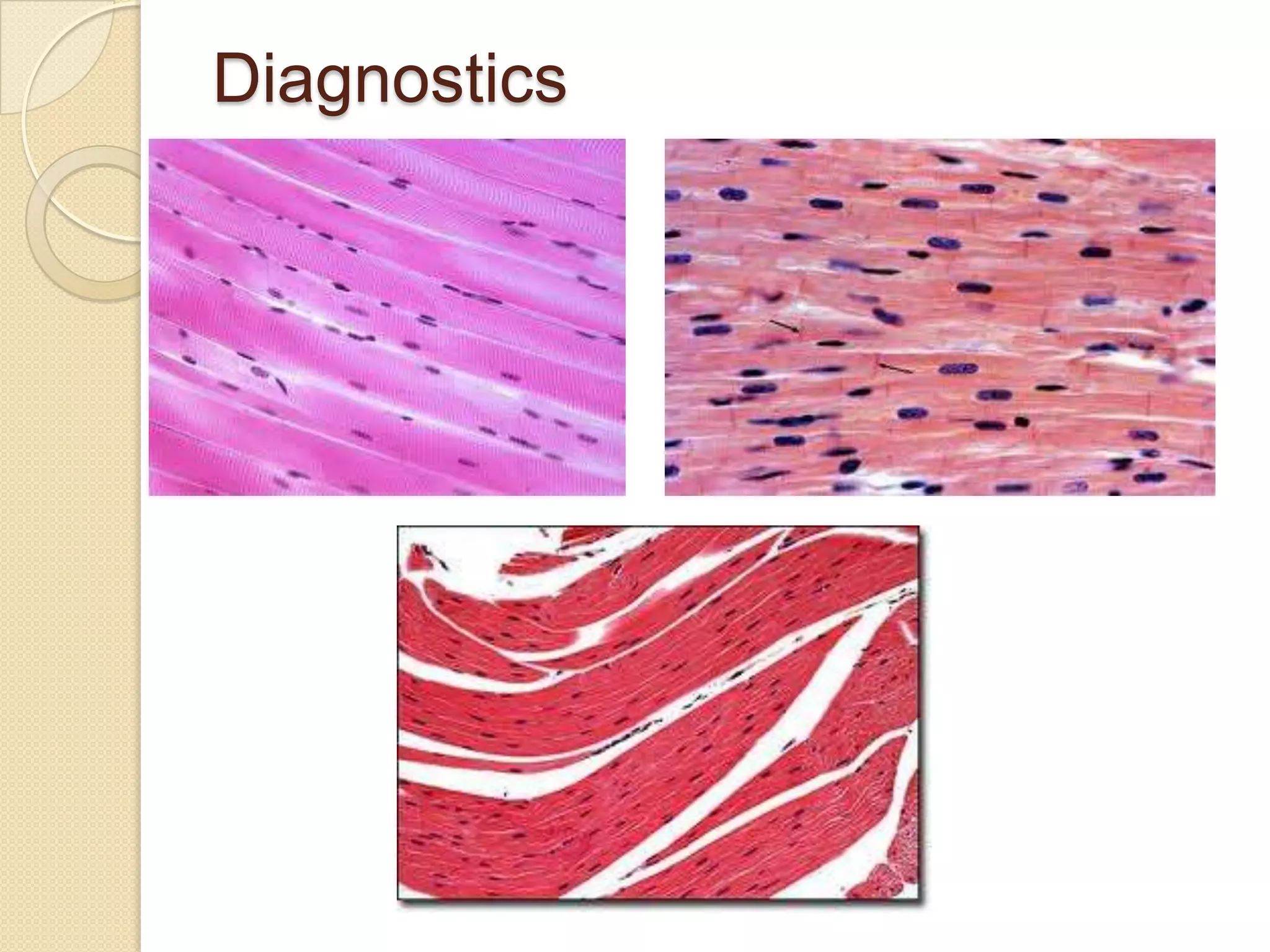
This document provides an overview of muscle tissue histophysiology. It discusses the structural unit of muscle tissue as muscle fibers. It describes the organization of skeletal muscles into myofibrils, sarcomeres, and myofilaments. It explains the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction and how calcium targets activate myofilament sliding. It also discusses dystrophin's role in muscle fiber stability and protection from contraction damage. Smooth muscle tissue types and their roles in organs like the GI tract and blood vessels are outlined. The molecular organization of filaments and caveolae structures in smooth muscle are briefly touched on.