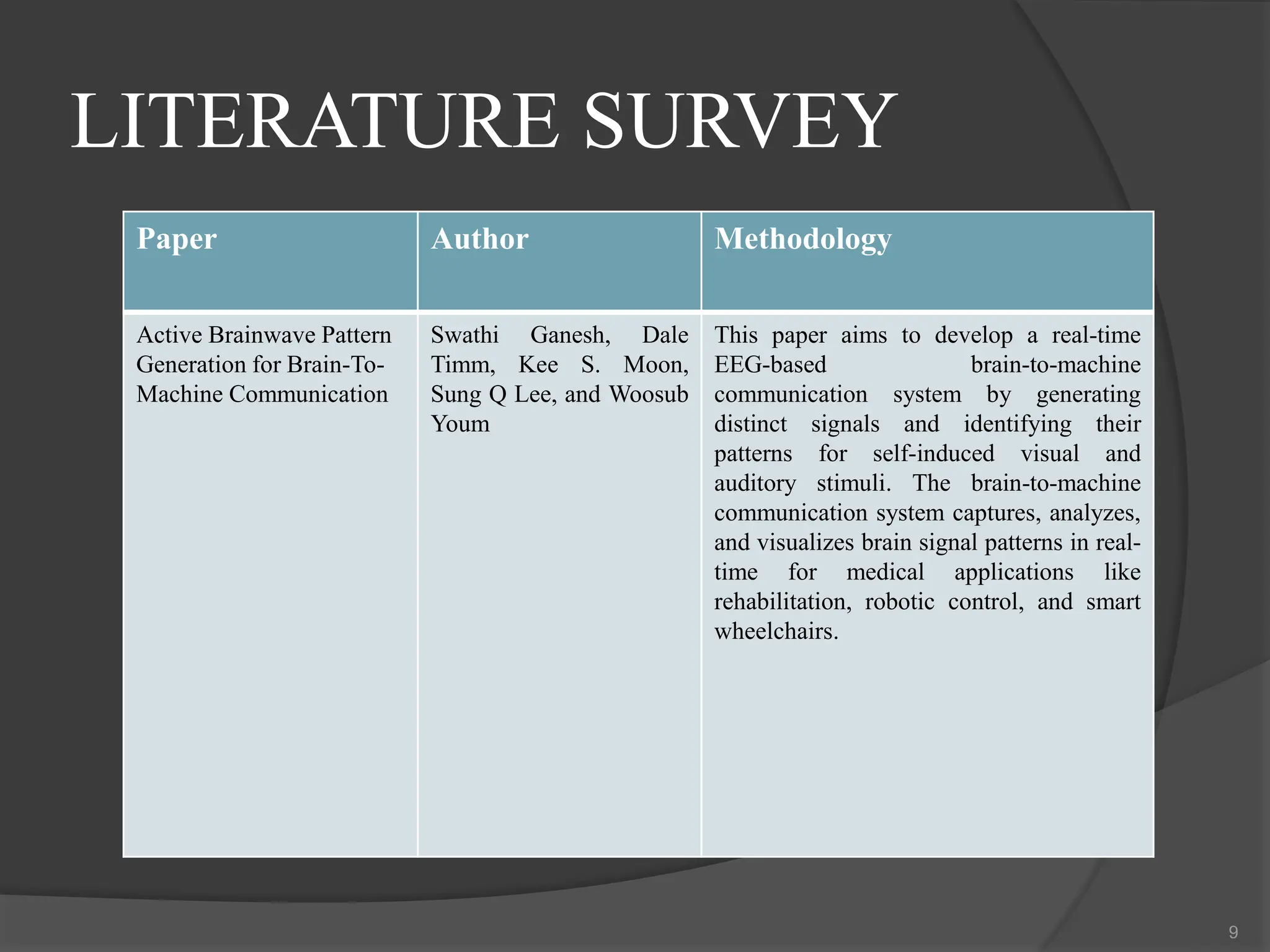
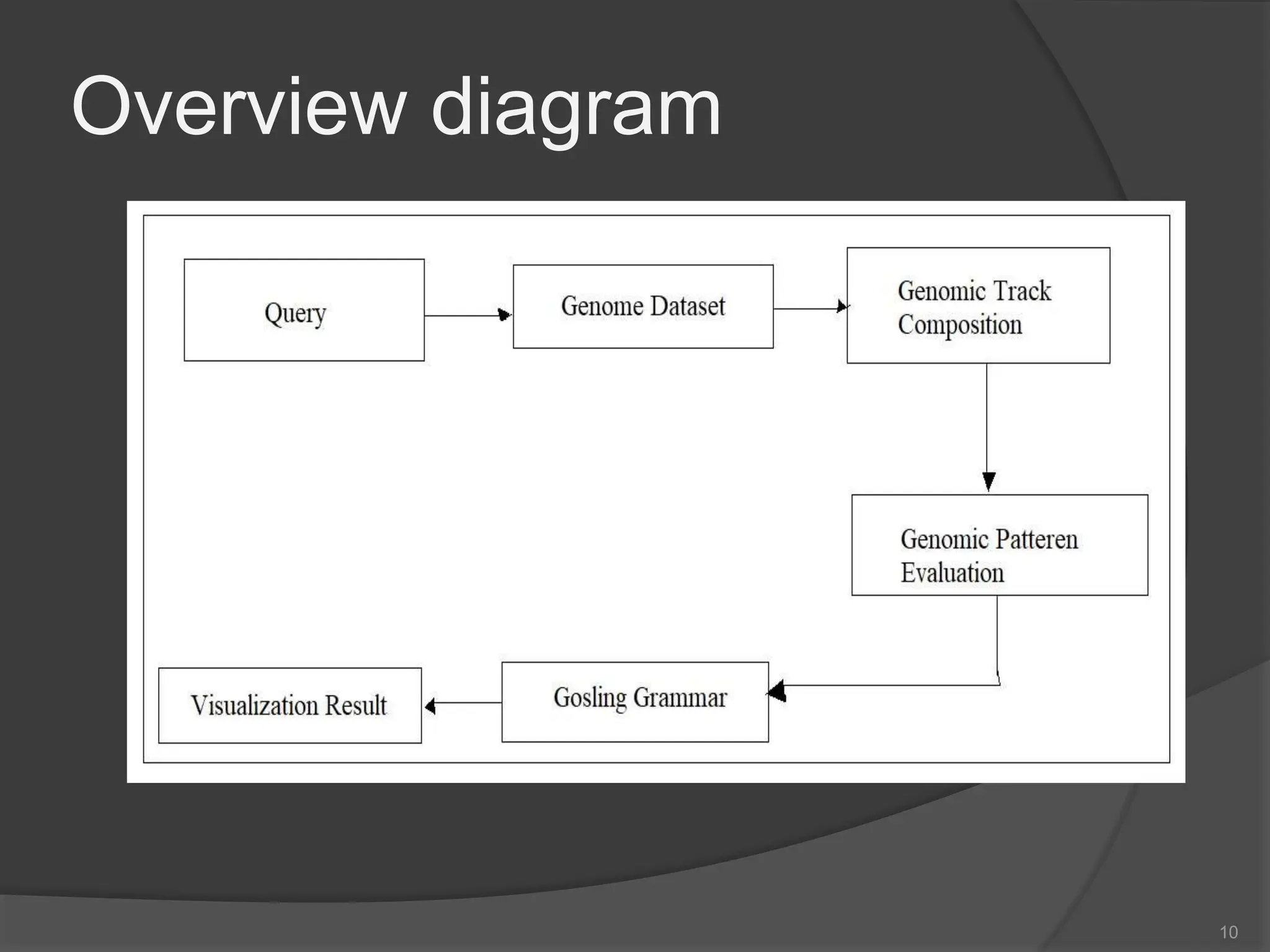
The document presents a seminar on multi-view design patterns and responsive visualization for genomics data, detailing its importance in clinical trials and the challenges in understanding genome patterns. It highlights the use of gosling grammar to enhance genome data visualization and includes a literature survey of existing methodologies in responsive genomics visualizations. The document also outlines the objectives of pre-processing data, enhancing models, and identifying multi-patterns in genome tracks.