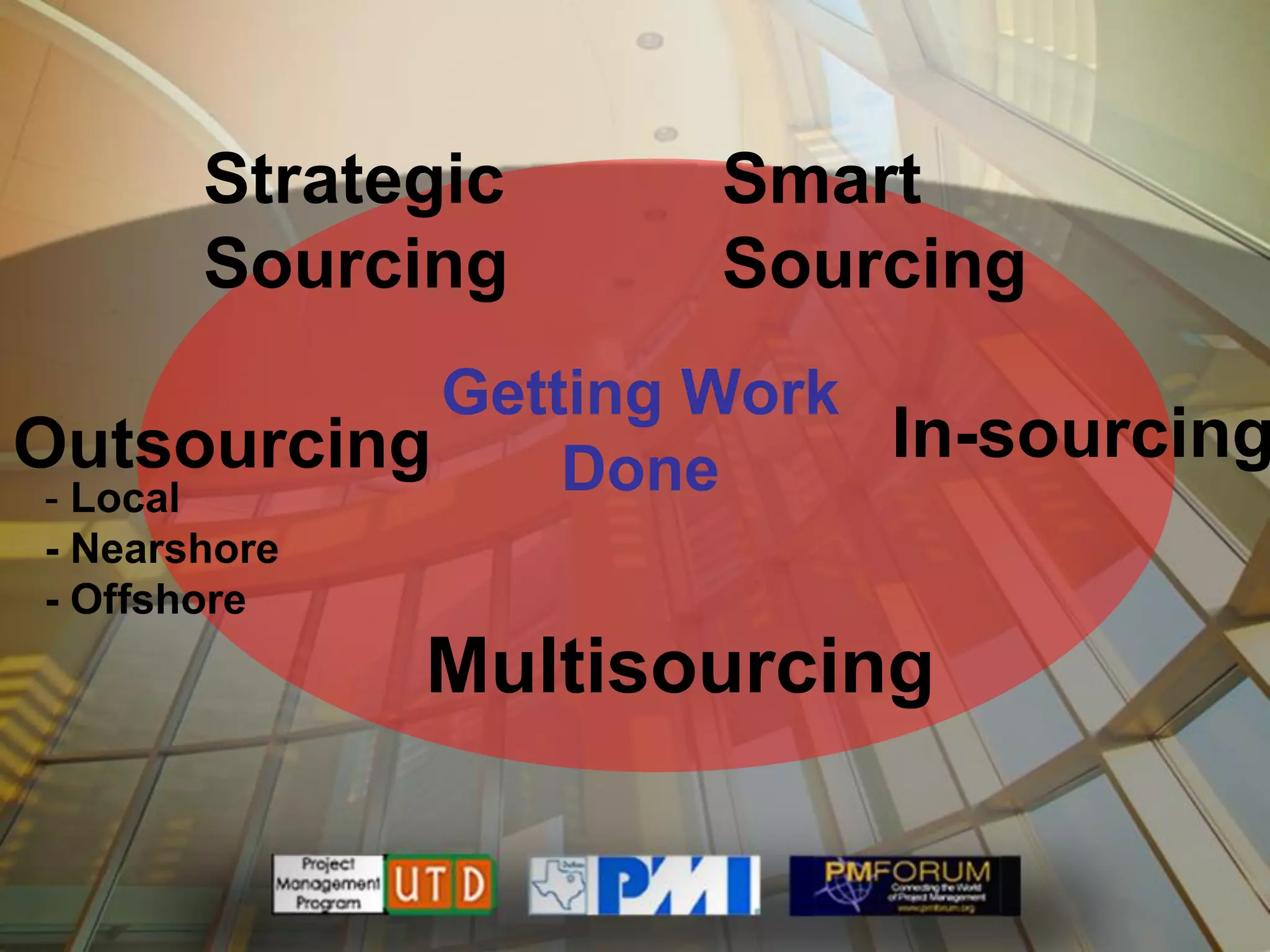
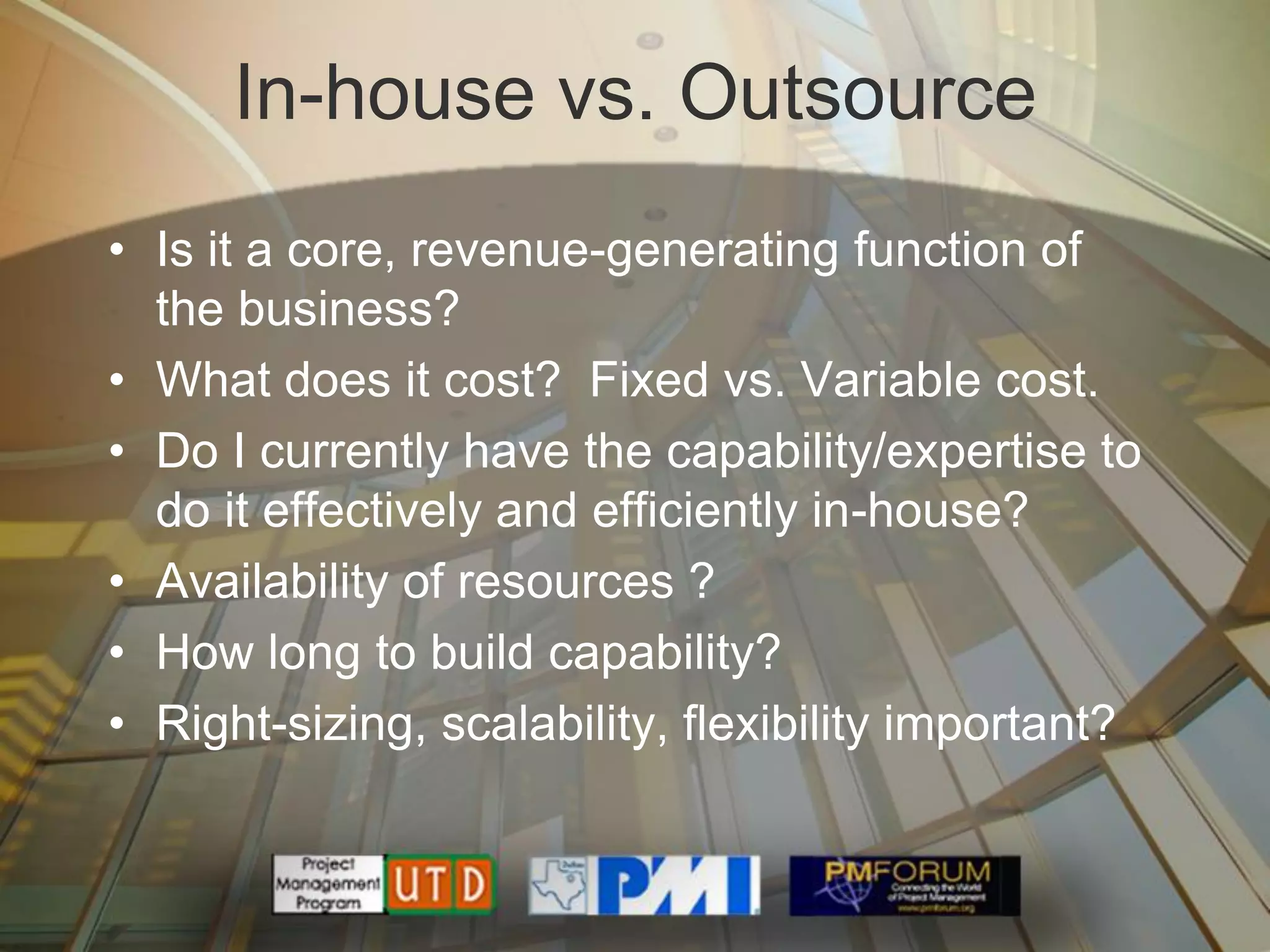
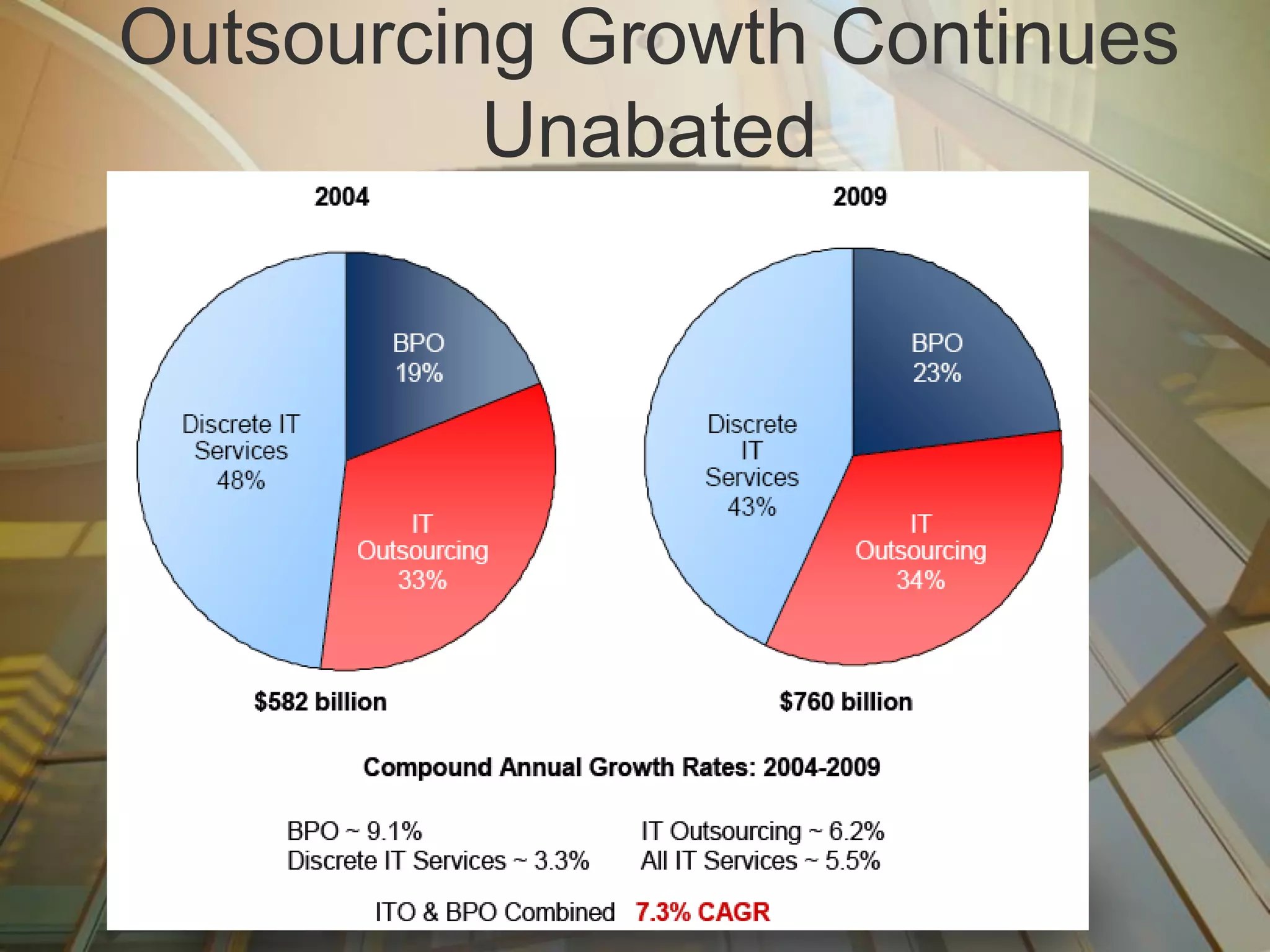
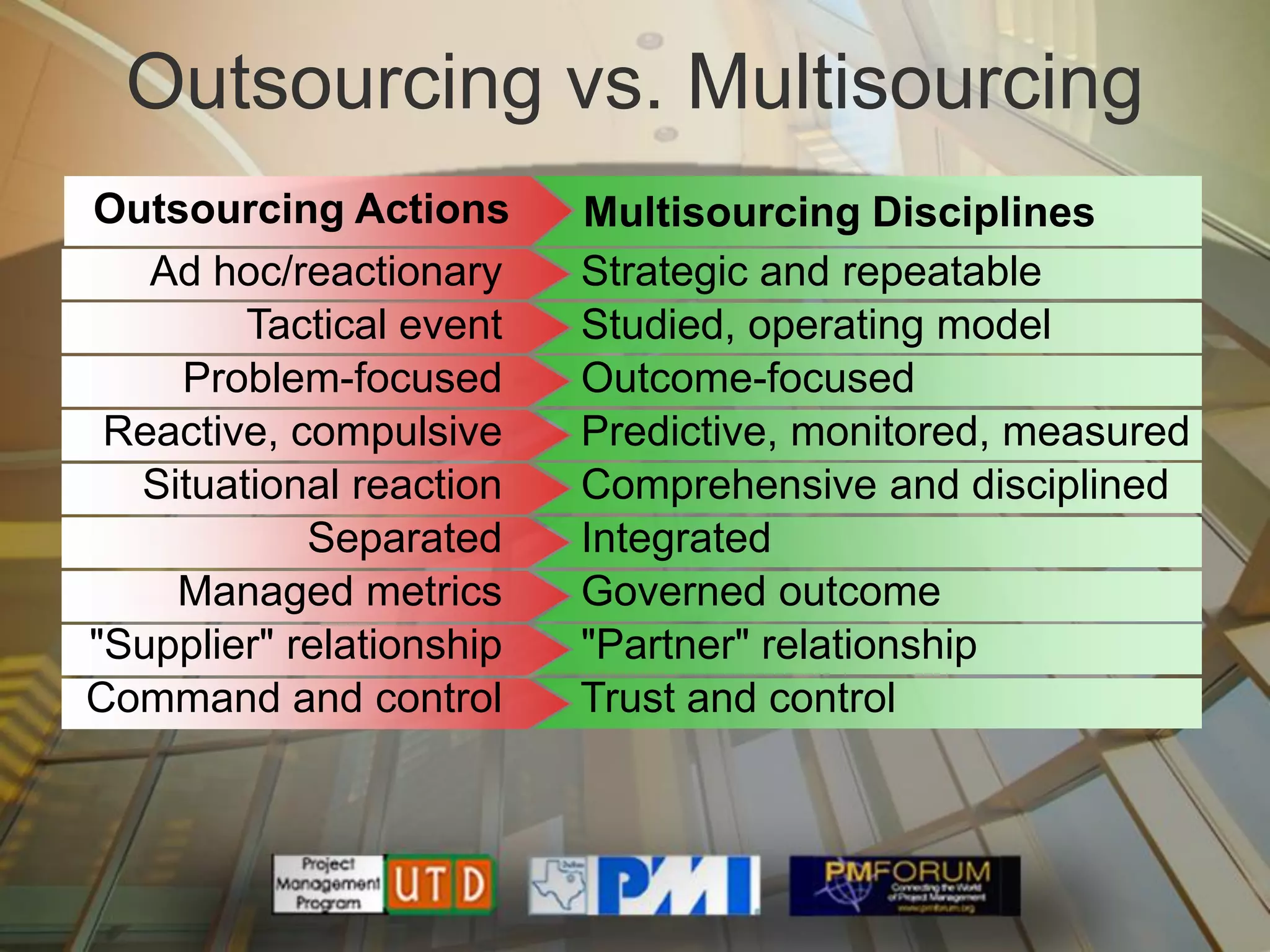
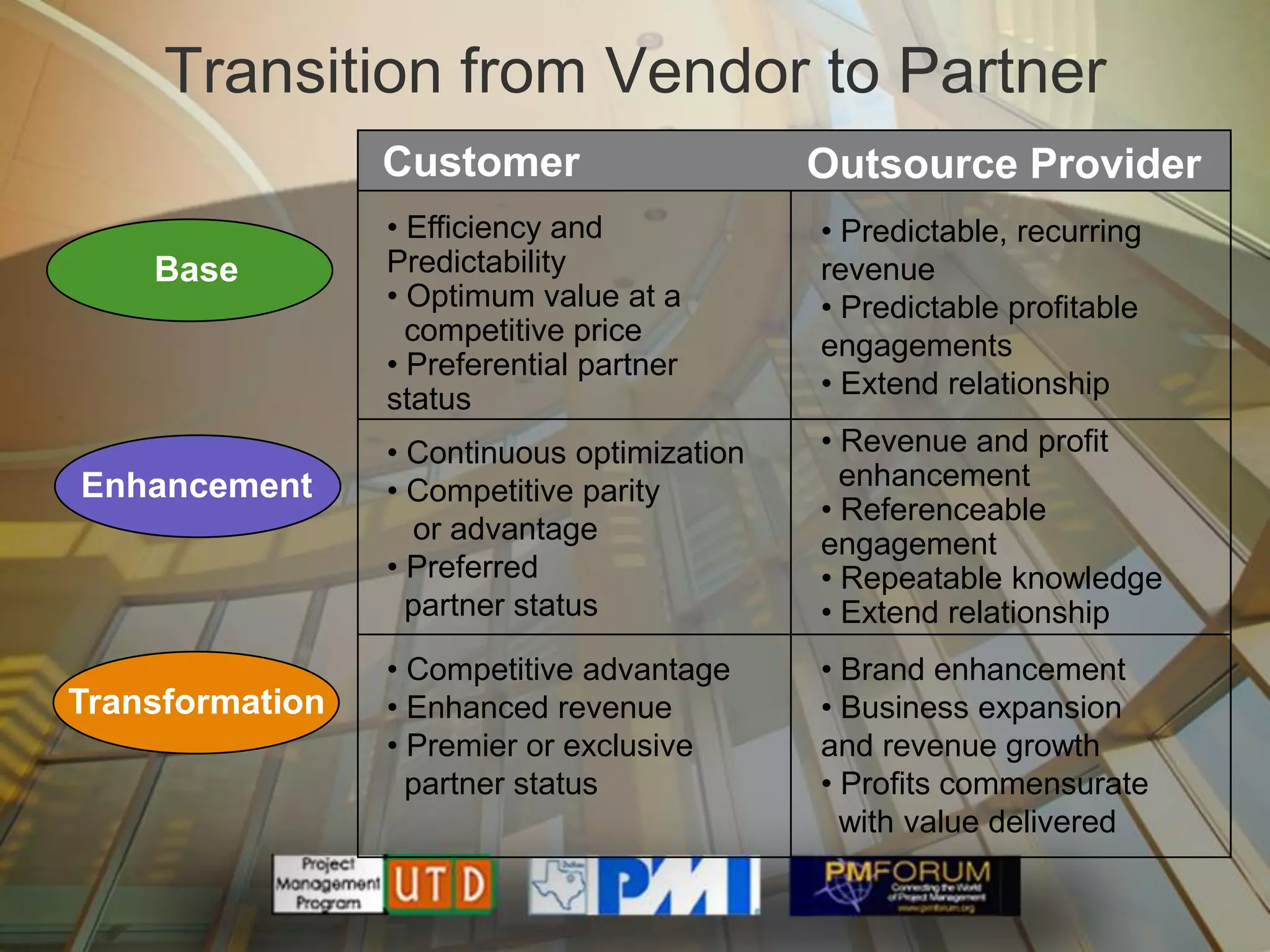
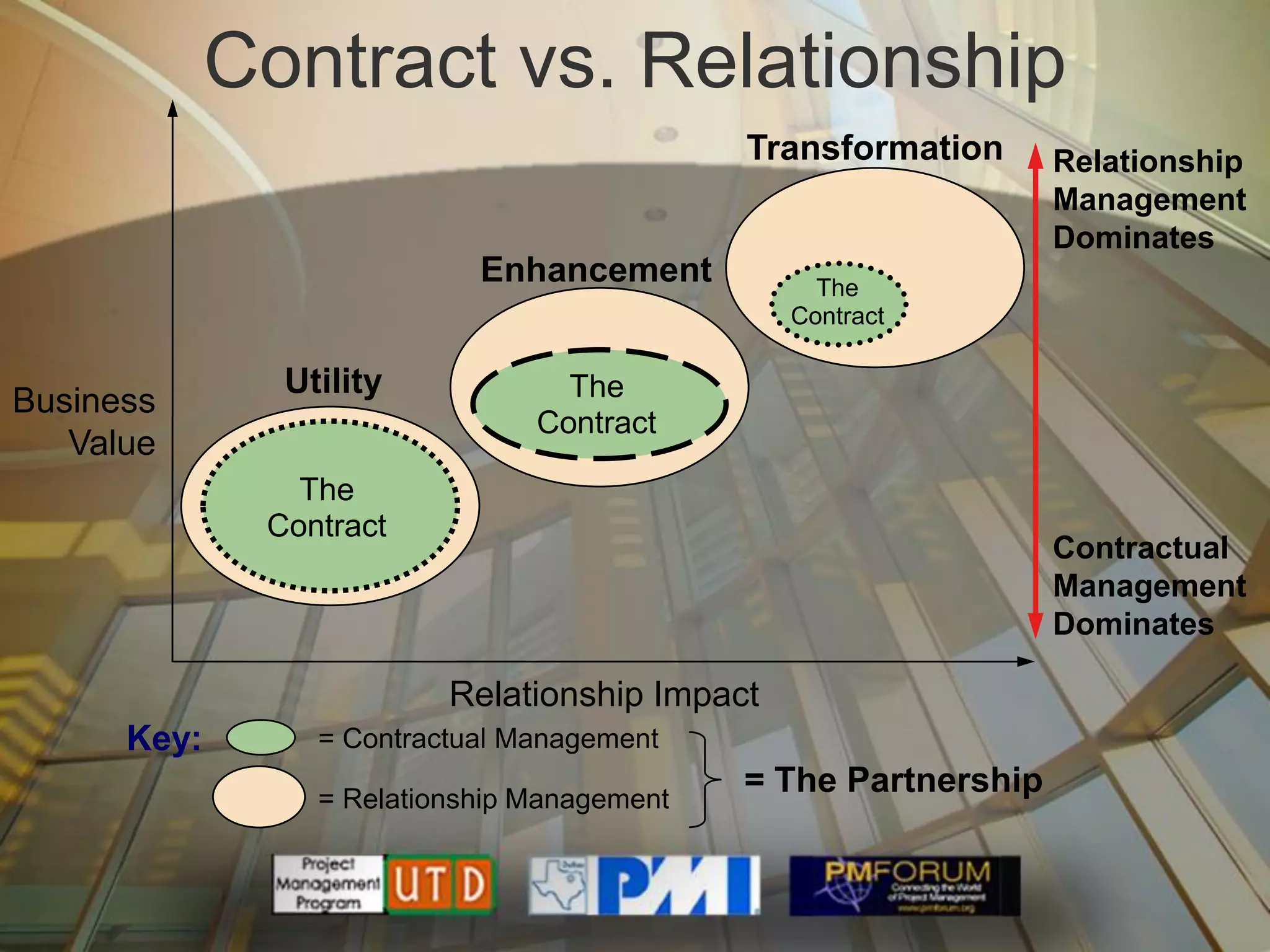
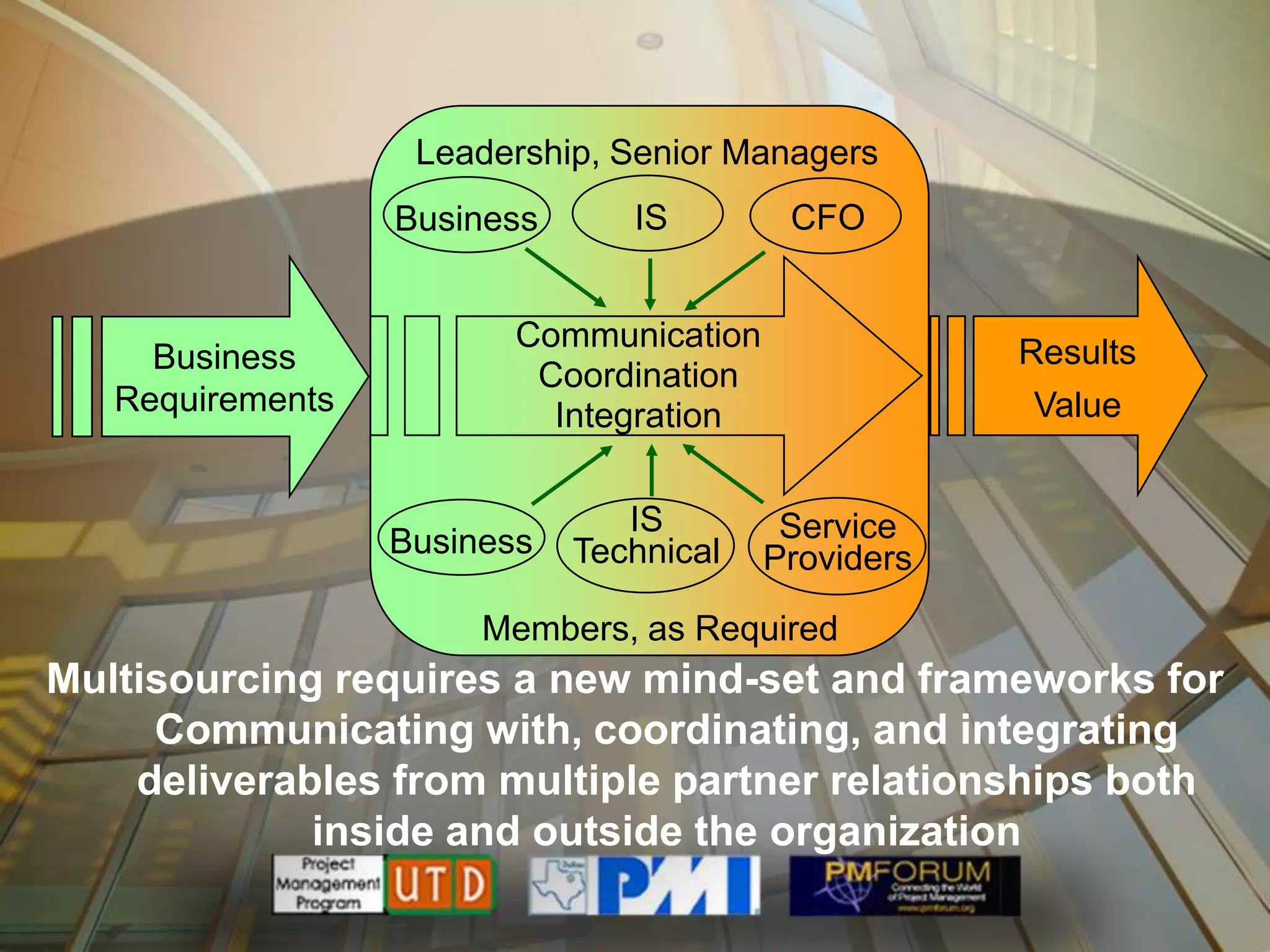
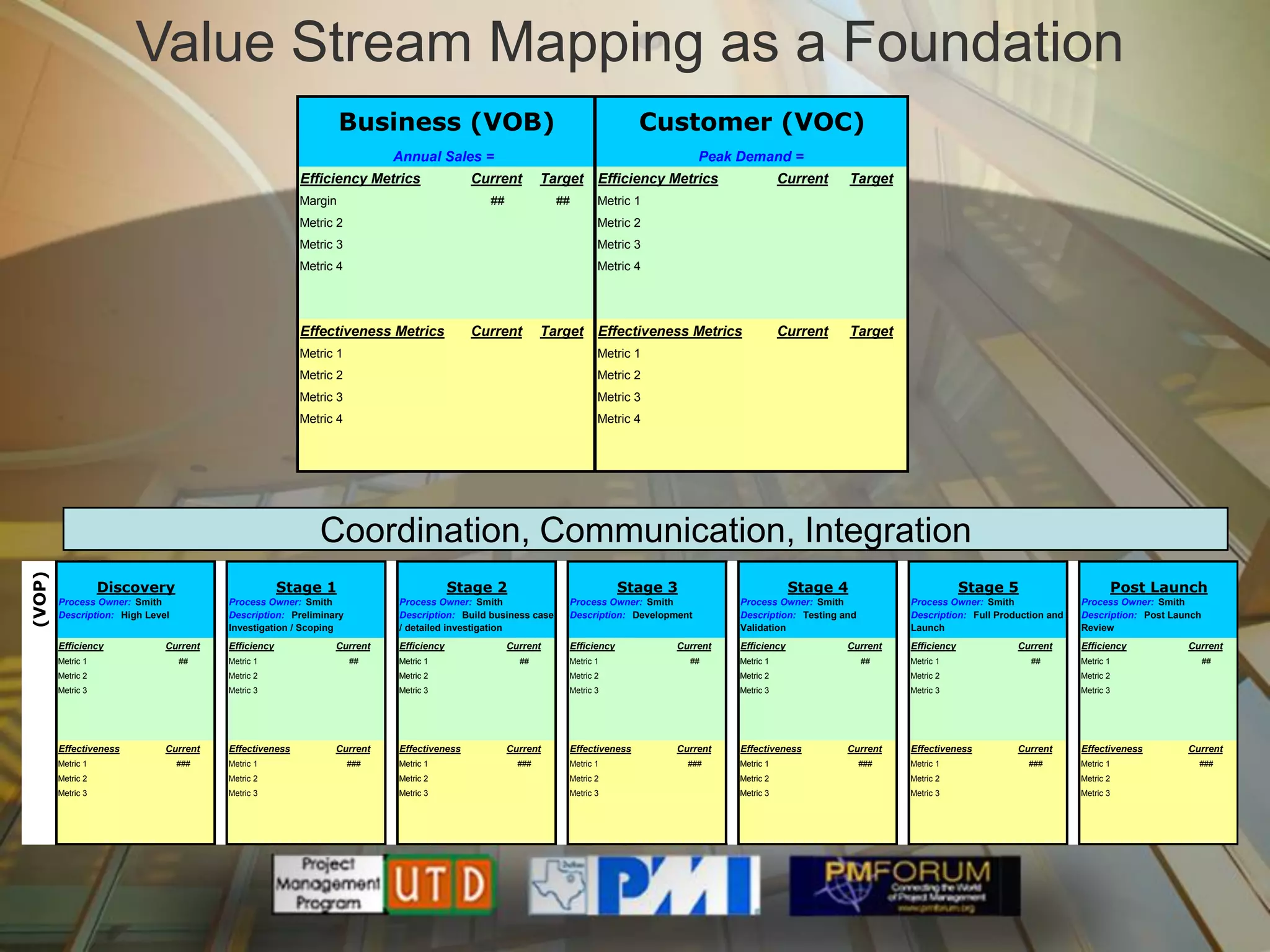
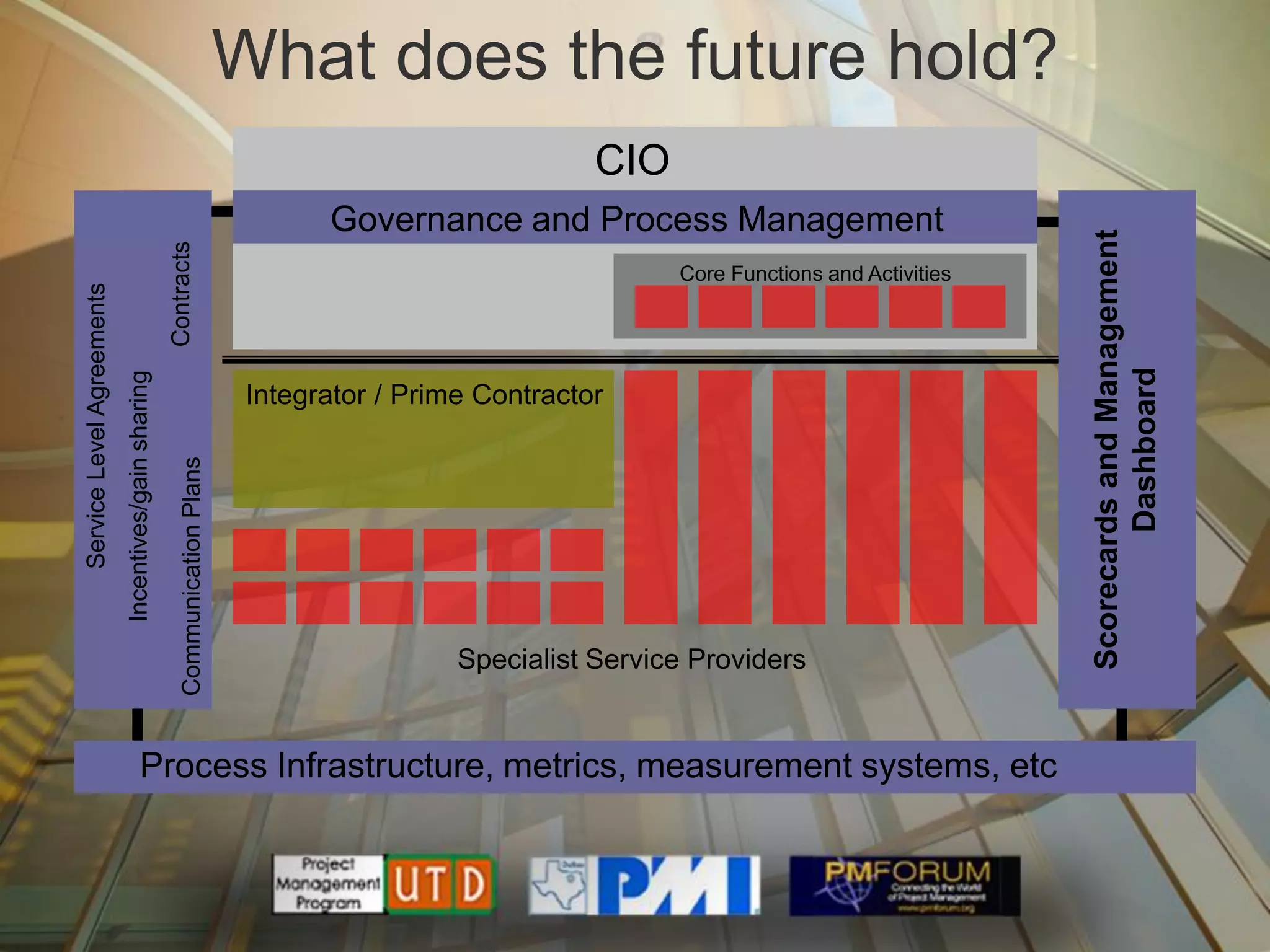
Multisourcing is a new global trend that involves blending services from internal and external providers to pursue business goals. It leverages multiple specialist teams to improve quality, costs, and time-to-market over traditional outsourcing approaches. Critical success factors include having a clear strategy and governance model, managing relationships rather than transactions, and implementing measurements to manage complexity. Making multisourcing work requires visibility, coordination, and integration across partner boundaries.