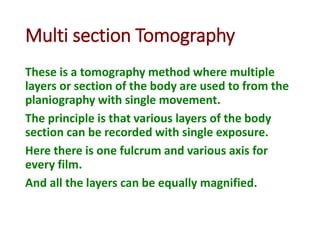
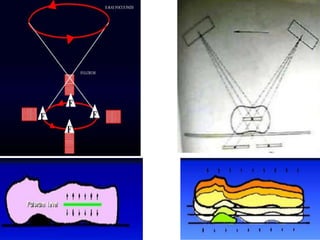
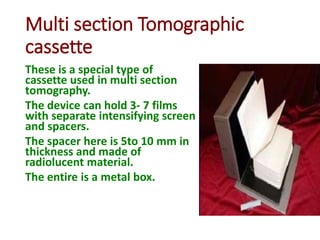
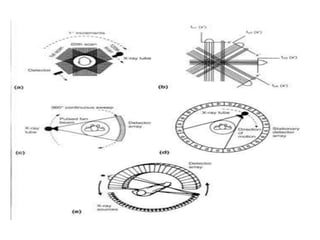
1) Multi-section tomography allows for multiple layers or sections of the body to be imaged simultaneously using a single exposure, reducing scan time and radiation dose compared to traditional tomography.
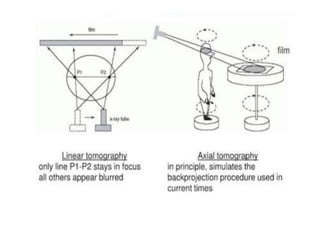
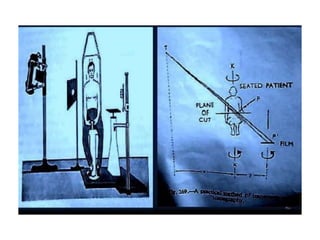
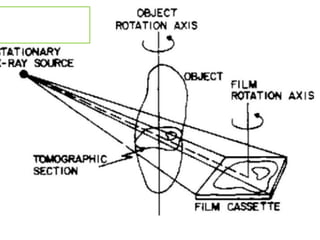
2) Transaxial tomography images sections of the body transversely using a rotating chair and stationary x-ray tube, allowing for coronal and sagittal plane images.
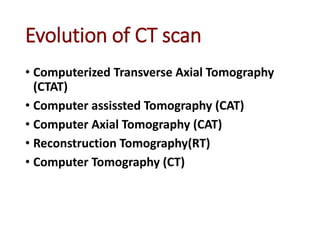
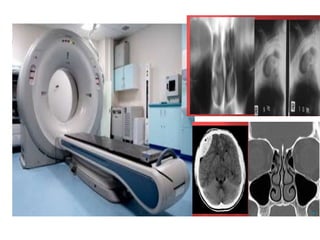
3) Computerized tomography (CT) evolved from early tomography techniques through advances in reconstruction techniques, pioneered by researchers including Radon, Bracewell, Oldendorf, Cormack, and Hounsfield.