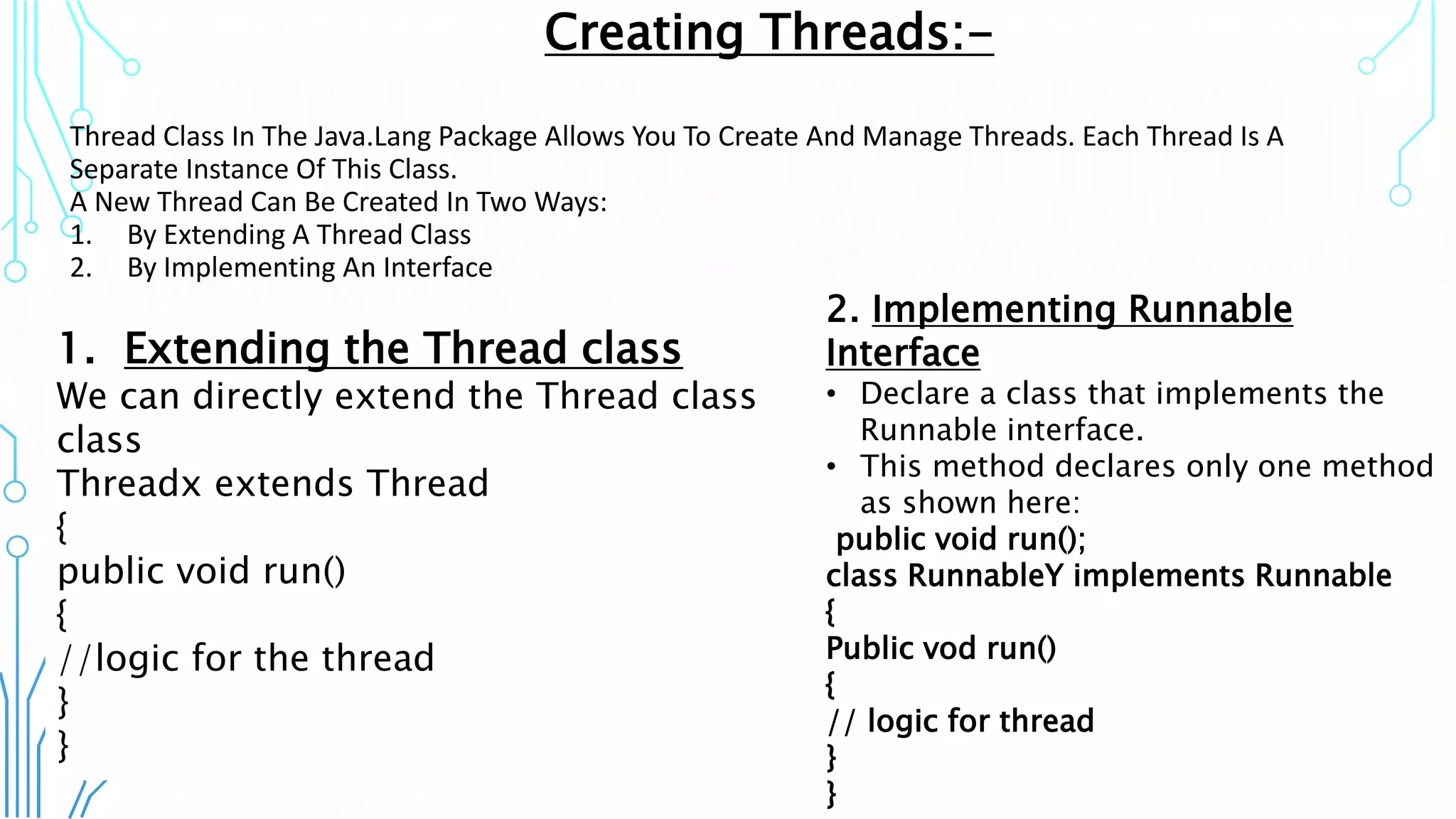
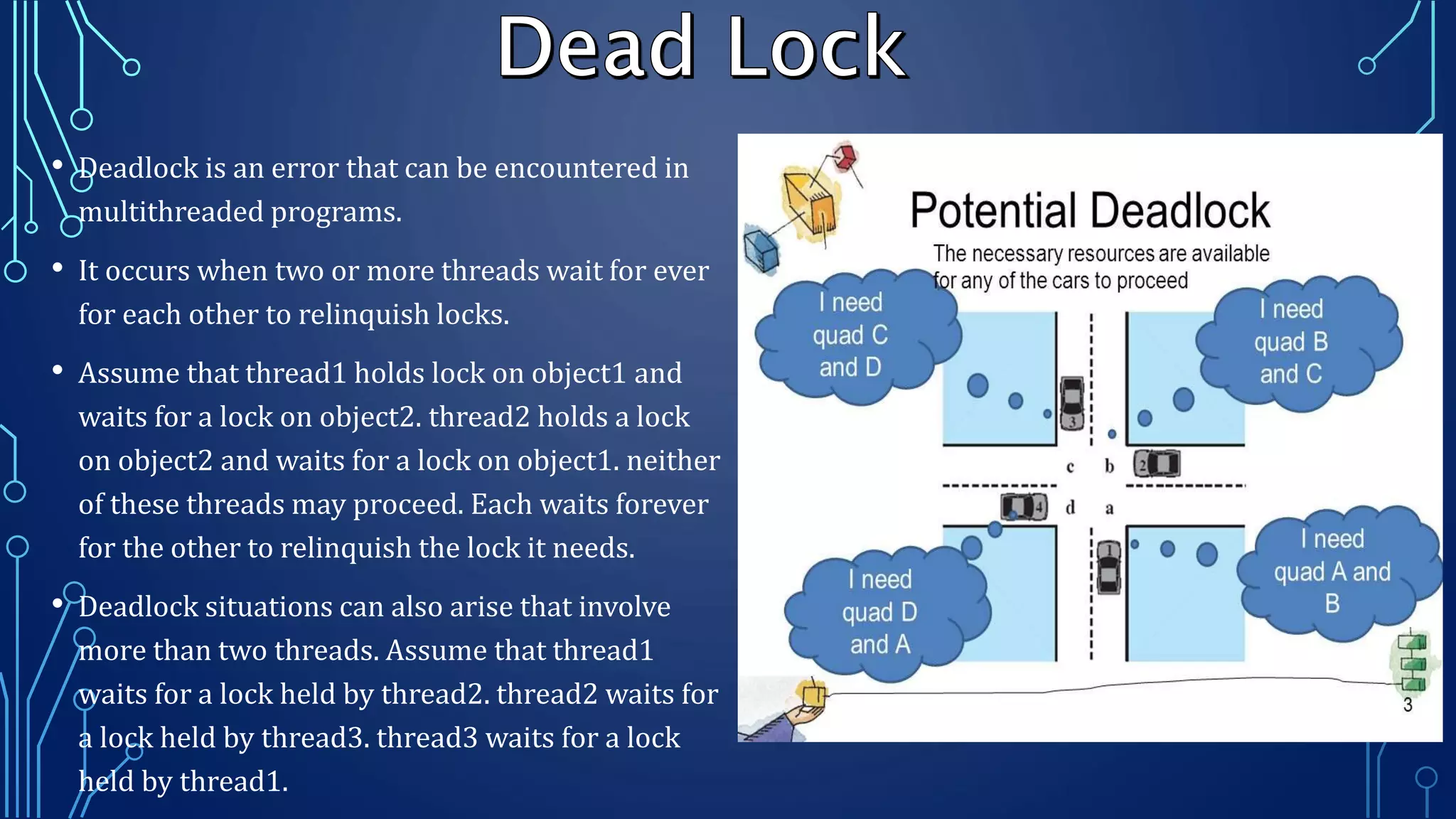
This document provides an overview of multithreading in 3 sentences or less:
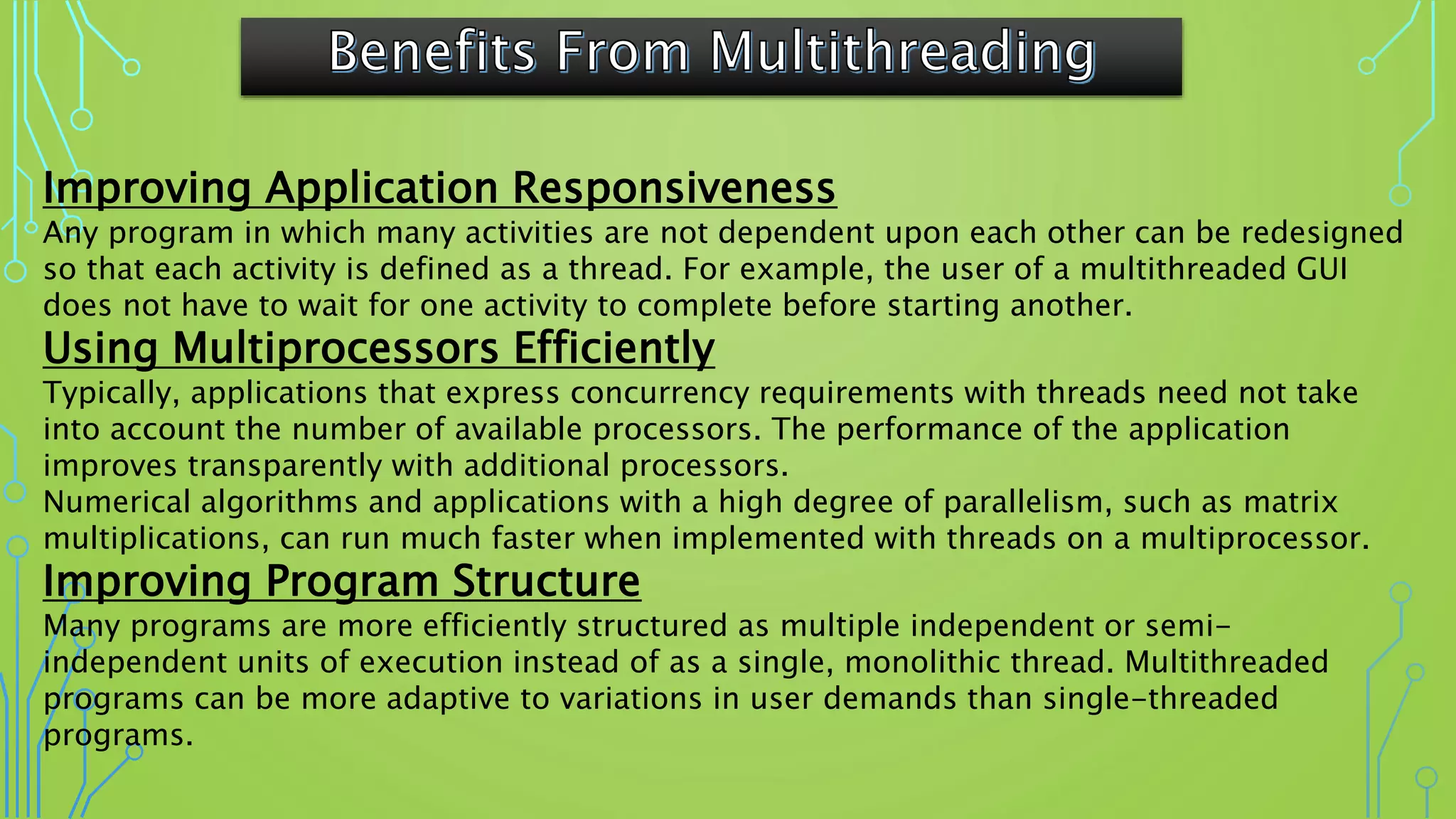
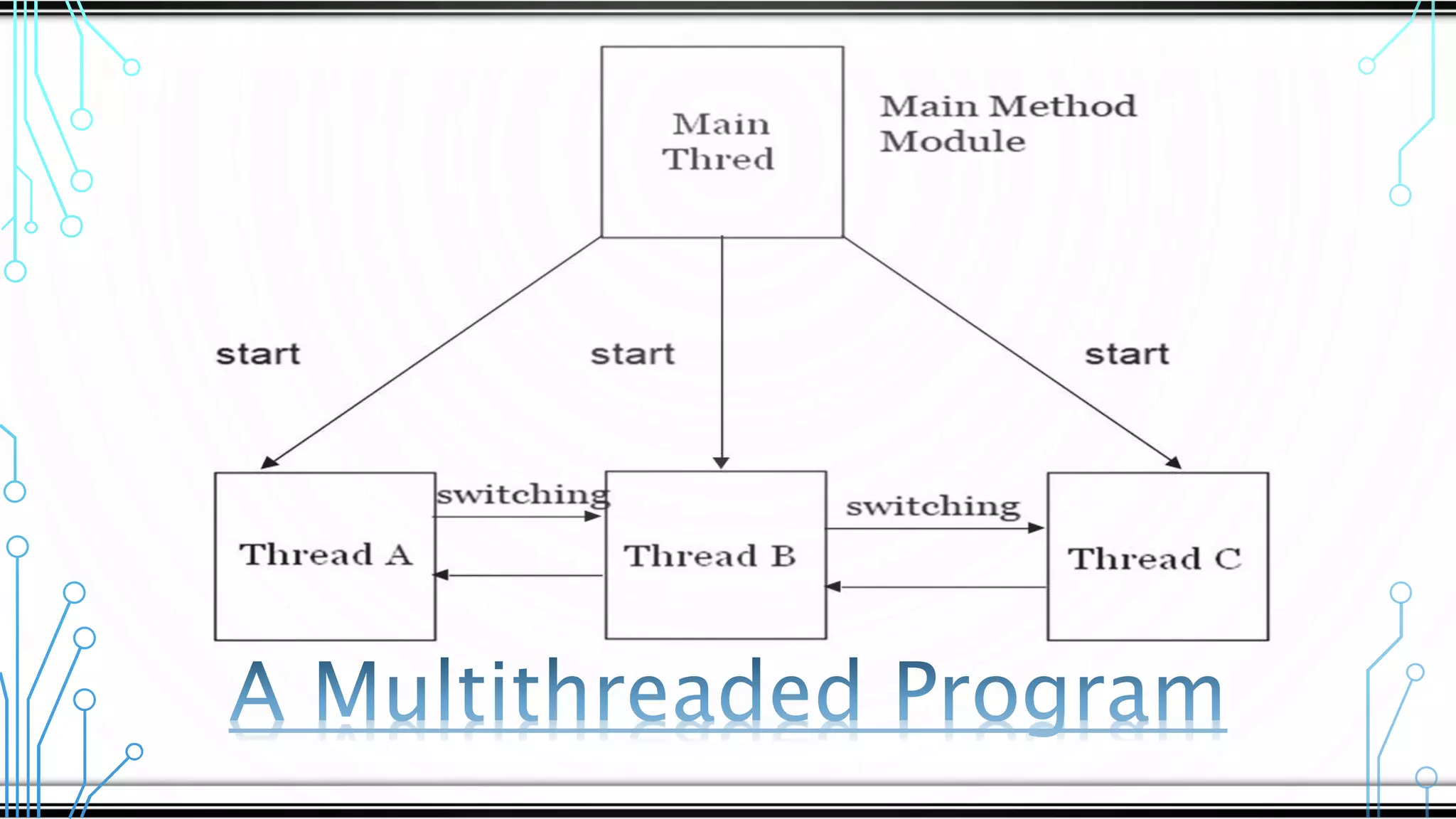
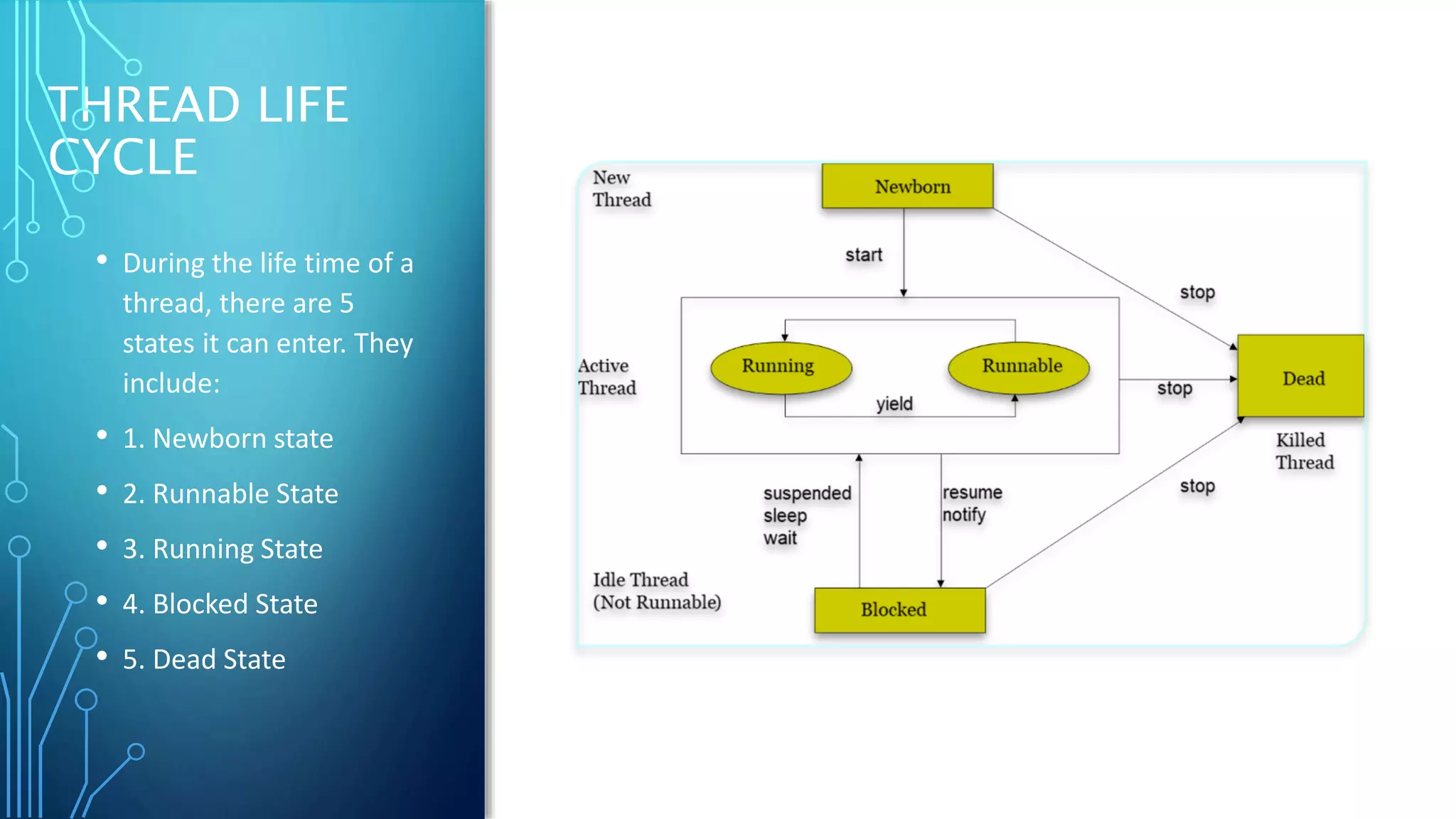
Multithreading allows a program to split into multiple threads that can run simultaneously, improving responsiveness, utilizing multiprocessors efficiently, and structuring programs more effectively. Threads transition between different states like new, runnable, running, blocked, and dead over their lifetime. Common threading techniques include setting thread priority, enabling communication between threads, and avoiding deadlocks when multiple threads depend on each other's locks.