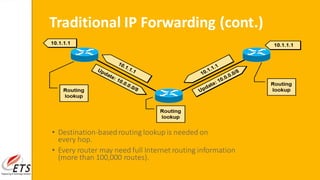
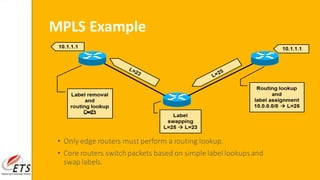
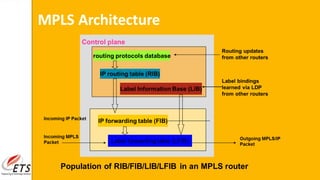
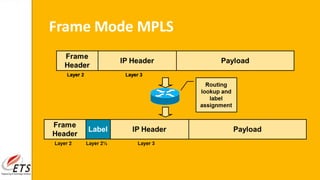
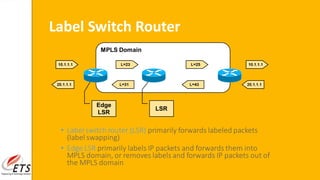
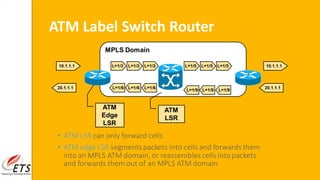
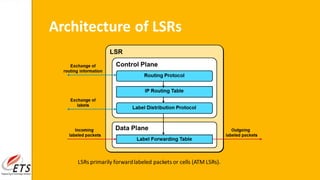
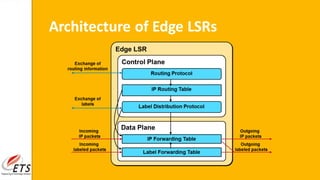
This document provides an introduction to MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching). It discusses the drawbacks of traditional IP routing, including destination-based routing lookups needed on every hop. It then describes basic MPLS concepts, including forwarding packets based on labels rather than IP addresses. The MPLS architecture uses a control plane to exchange routing information and labels, and a data plane for simple label-based forwarding. MPLS can operate in frame mode, inserting labels between layers 2 and 3. Label switch routers perform label swapping in the data plane.