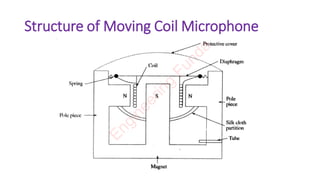
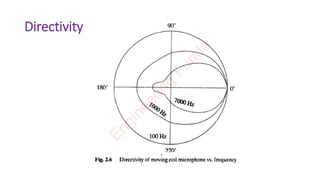
The document discusses the moving coil microphone. It describes the basic structure and working principle of the moving coil microphone. The moving coil microphone uses electromagnetic induction - sound pressure moves a coil within a magnetic field, changing the magnetic flux and producing an electric signal. It has an omnidirectional pickup pattern. Key features include robust construction, ability to be spoken into from a distance, and relatively low cost compared to other microphone types. Common applications include PA systems and broadcast studios.