1. The document discusses strategies for motivating patients to change unhealthy behaviors through the principles of motivational interviewing. It describes motivational interviewing as a technique that involves expressing empathy, developing discrepancy between current behaviors and goals, rolling with resistance, and supporting self-efficacy.
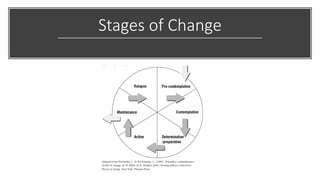
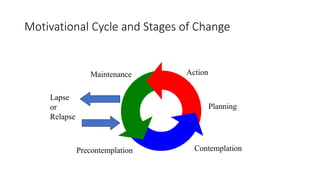
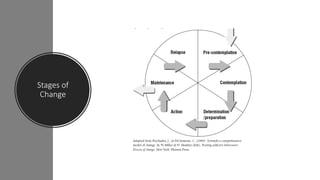
2. Key models of how people change are reviewed, including the stages of change model which identifies pre-contemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, and maintenance as stages in the process of behavior change.
3. Specific strategies are provided to motivate change through setting simple goals, providing education, making community connections, hosting workshops, assigning homework, keeping in touch with patients, and eliminating obstacles to change.