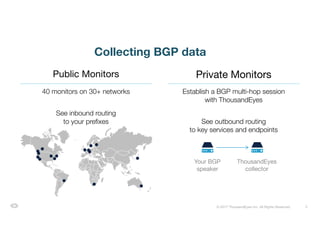
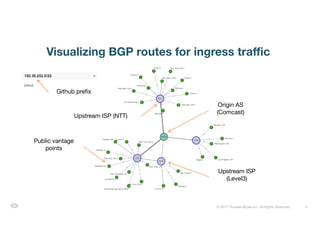
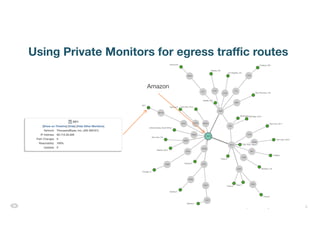
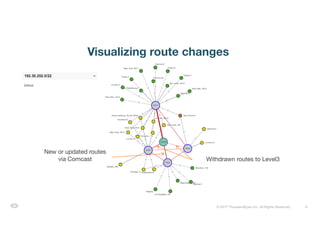
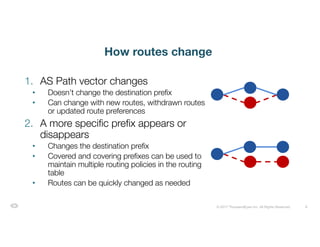
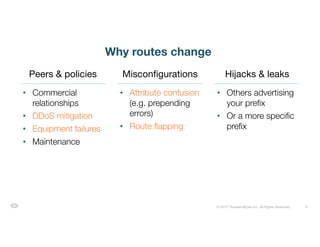
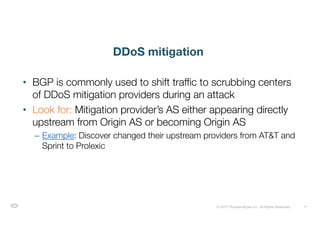
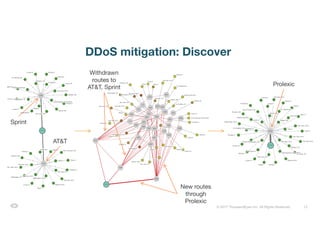
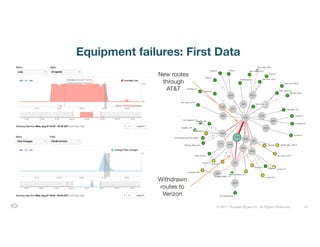
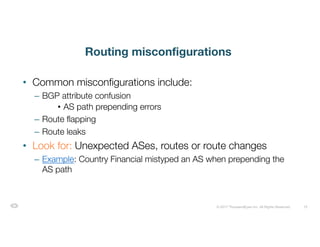
The document discusses ThousandEyes' network intelligence platform, focusing on monitoring BGP route changes and their impact on network performance. It highlights key metrics for analyzing routing behaviors, common reasons for route changes, and methods for improving BGP alert tuning. Additionally, it outlines best practices for managing DDoS mitigation and addressing equipment failures and routing misconfigurations.