This document provides instructions for installing MongoDB on Windows and CentOS. It outlines 5 steps for installing on Windows which include downloading MongoDB, creating a data folder, extracting the download package, connecting to MongoDB using mongo.exe, and testing with sample data. It also outlines 5 steps for installing on CentOS that mirror the Windows steps. The document then discusses additional MongoDB concepts like connecting to databases, creating collections and inserting documents, using cursors, querying for specific documents, and core CRUD operations.


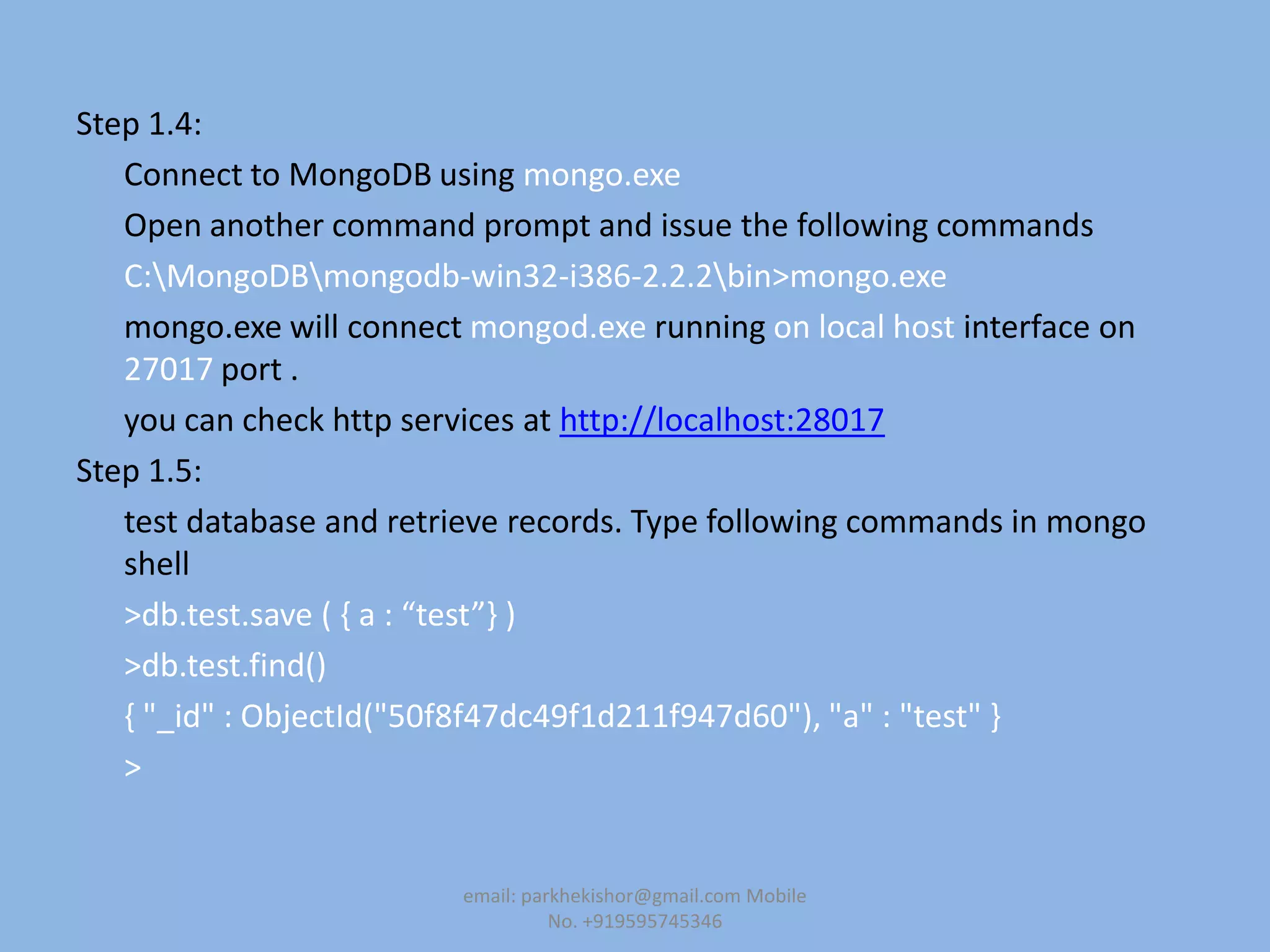

![Step 1.4:
Connect to MongoDB using mongo.exe
Open another command prompt and issue the following commands
[root@HMCLUSTER2 /]# cd mongodb-linux-x86_64-2.0.6/bin
[root@HMCLUSTER2 bin]# ./mongo
mongo.rpm will connect mongod.rpm running on local host interface on 27017
port .
you can check http services at http://localhost:28017
Step 1.5:
test database and retrieve records. Type following commands in mongo shell
>db.test.save ( , a : “test”- )
>db.test.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("50f8f47dc49f1d211f947d60"), "a" : "test" }
>
email: parkhekishor@gmail.com Mobile
No. +919595745346](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbbasicinstallation-130526143911-phpapp02/75/Mongo-db-basic-installation-7-2048.jpg)

![Implementing Curser
1. When you querying, MongoDB return curser object that contain result of
query.
2. Iterating over the curser with loop
var curser= db.blog.find();
while( curser.hasnext() ){
printjson( curser.next() );
}
3. Use array operation with curser
curser[4];
email: parkhekishor@gmail.com Mobile
No. +919595745346](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbbasicinstallation-130526143911-phpapp02/75/Mongo-db-basic-installation-10-2048.jpg)








![Querying Array
Example suppose array is a list of colors,
1 like this:
> db.user.insert({colors : [ "red" , "white" ,"green", "black"]})
the following query:
> db.user.find({colors : "red"})
Out put:
{ "_id" : ObjectId("50ff83f9c5d2a43b68806829"), "colors" : [
"red", "white", "green", "black" ] }
2 if you need to match array more than on element the you use $all,
> db.user.find(,colors : ,$all : *"red“ , “ black " +--)
{ "_id" : ObjectId("50ff83f9c5d2a43b68806829"), "colors" : [
"red", "white", "green", "black" ] }
email: parkhekishor@gmail.com Mobile
No. +919595745346](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbbasicinstallation-130526143911-phpapp02/75/Mongo-db-basic-installation-19-2048.jpg)

!["$slice" can also return pages in the middle of the results by taking an
offset and the number of elements to return:
> db.blog.posts.findOne(criteria, {"comments" : {"$slice" : [23, 10]}})
this would keep first 23 elements and return 24th to 34th.
email: parkhekishor@gmail.com Mobile
No. +919595745346](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbbasicinstallation-130526143911-phpapp02/75/Mongo-db-basic-installation-21-2048.jpg)
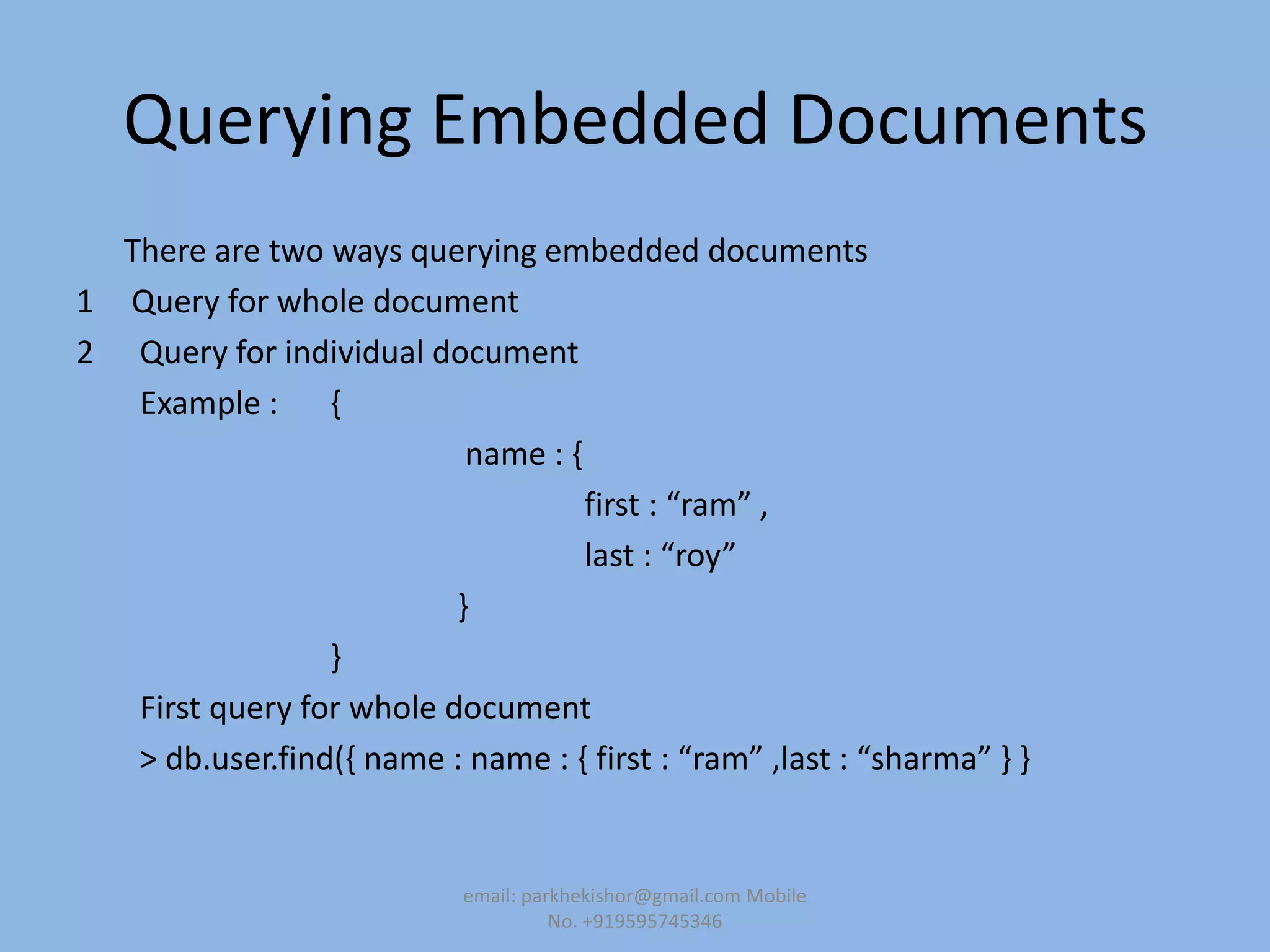
![Query for just a specific key or keys of an embedded document.
>db.user.find( , “name.first” : “ram”-)
Example
{
"content" : “what is MongoDB? ",
"comments" : [
{
"author" : “ram",
"score" : 3,
"comment" : "nice post"
},
{
"author" : “sham",
"score" : 6,
"comment" : "terrible post"
}
]
}
email: parkhekishor@gmail.com Mobile
No. +919595745346](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbbasicinstallation-130526143911-phpapp02/75/Mongo-db-basic-installation-23-2048.jpg)
