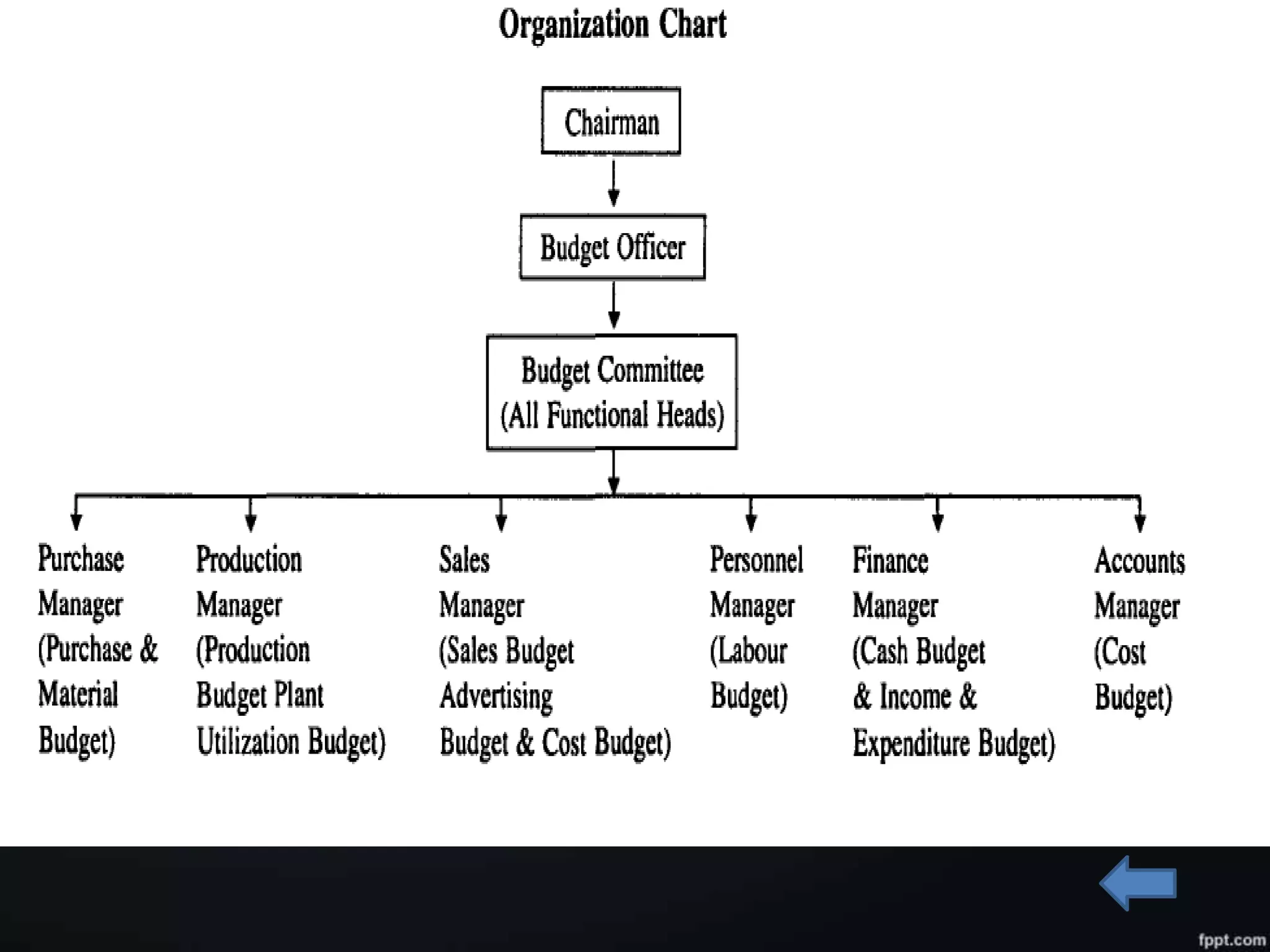
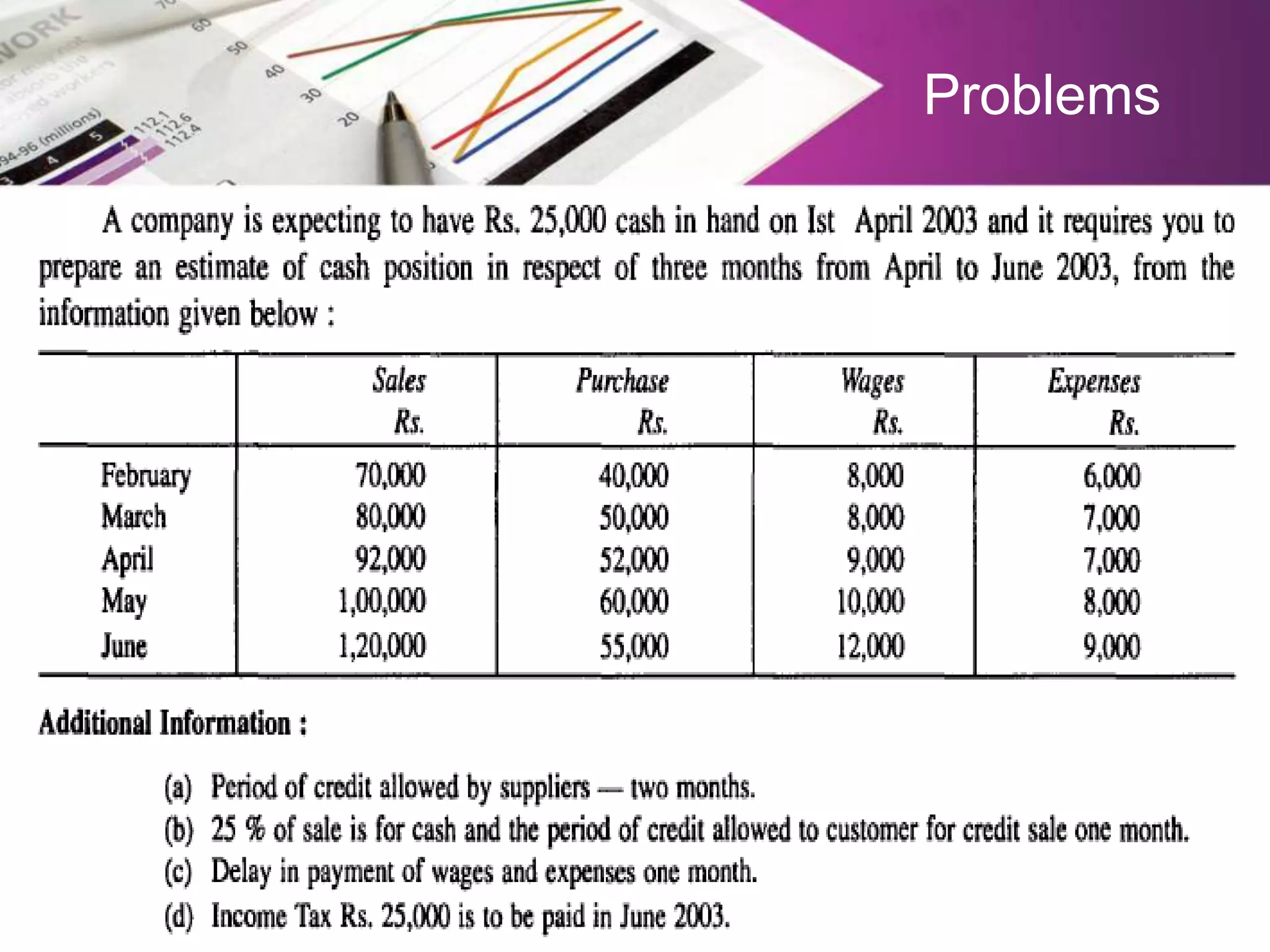
Budgetary control system involves creating budgets for financial planning and control. It includes:
- Defining a budget as a financial plan for expenses and revenues over a period of time.
- Describing features of budgets like being for a specific period and including definite numbers.
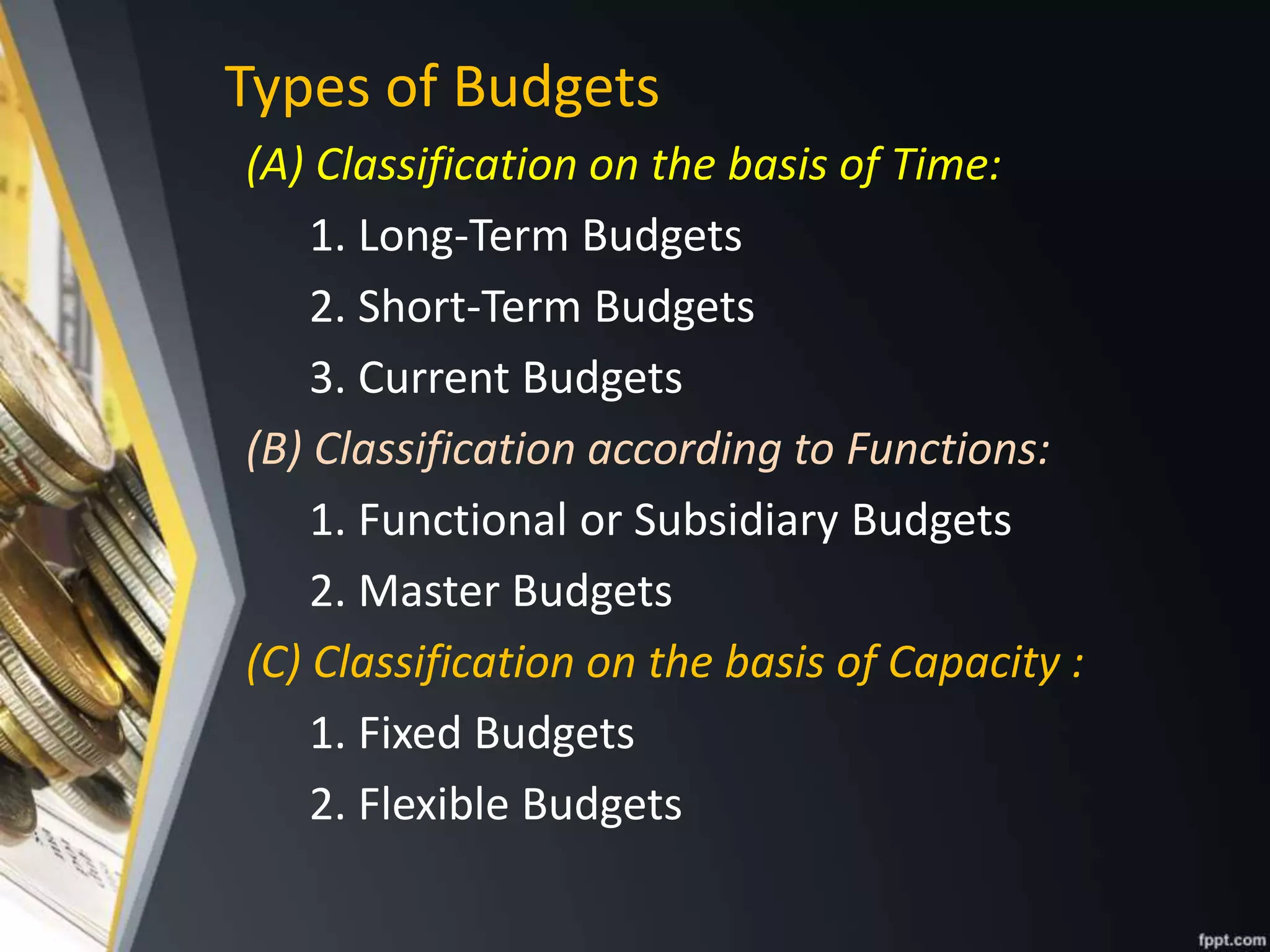
- Explaining types of budgets like short-term vs long-term and functional vs master budgets.
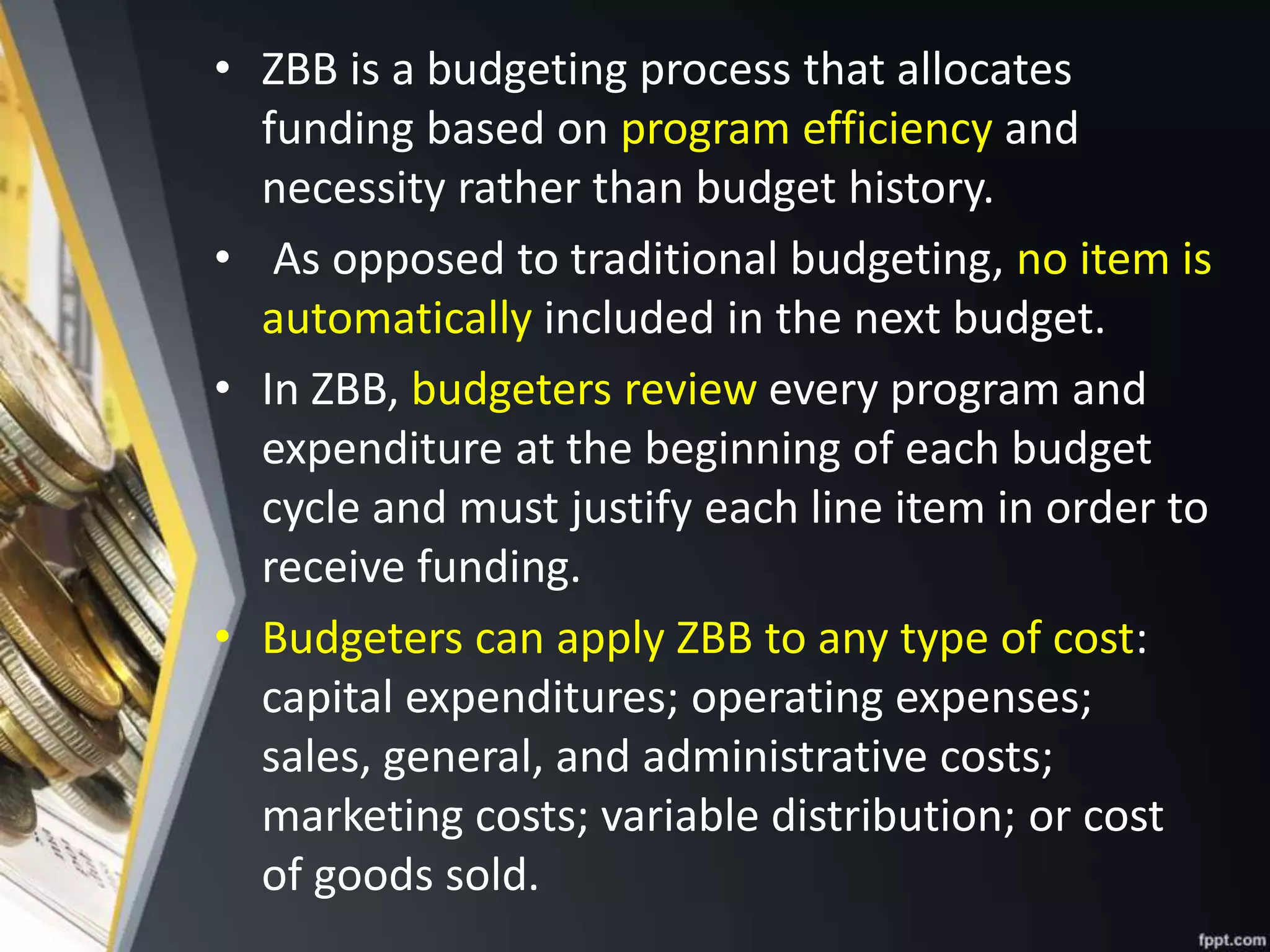
- Detailing approaches like zero-based budgeting, which requires justifying all spending, and performance budgeting, which relates costs to performance outcomes.
- Noting the importance of flexible budgets that can adapt to different activity levels for planning and control.