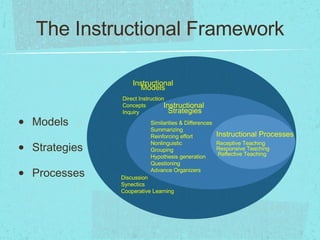
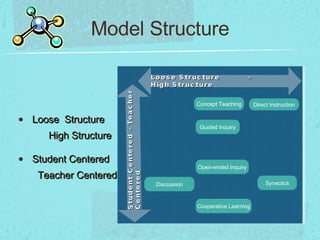
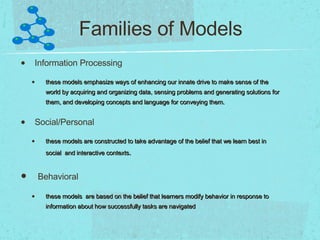
The document discusses instructional models and strategies that teachers can use. It describes three categories of instructional models: information processing models that emphasize data acquisition and problem solving; social/personal models that promote learning through social interaction; and behavioral models based on modifying behavior through feedback. Example models listed include direct instruction, concept development, guided inquiry, and collaborative learning. The document also discusses instructional strategies like questioning, grouping, and summarizing; and instructional processes of receptive, responsive, and reflective teaching.