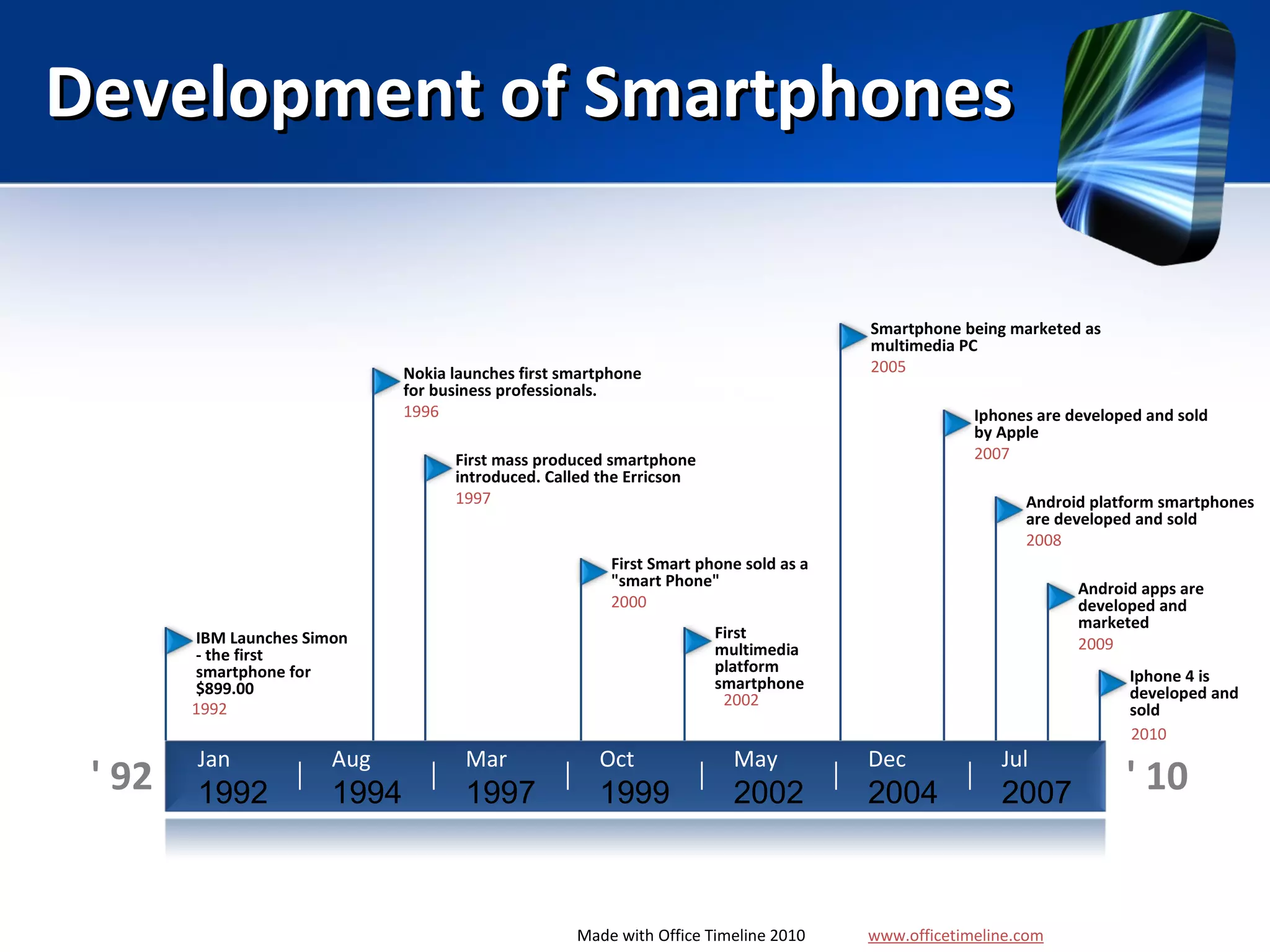
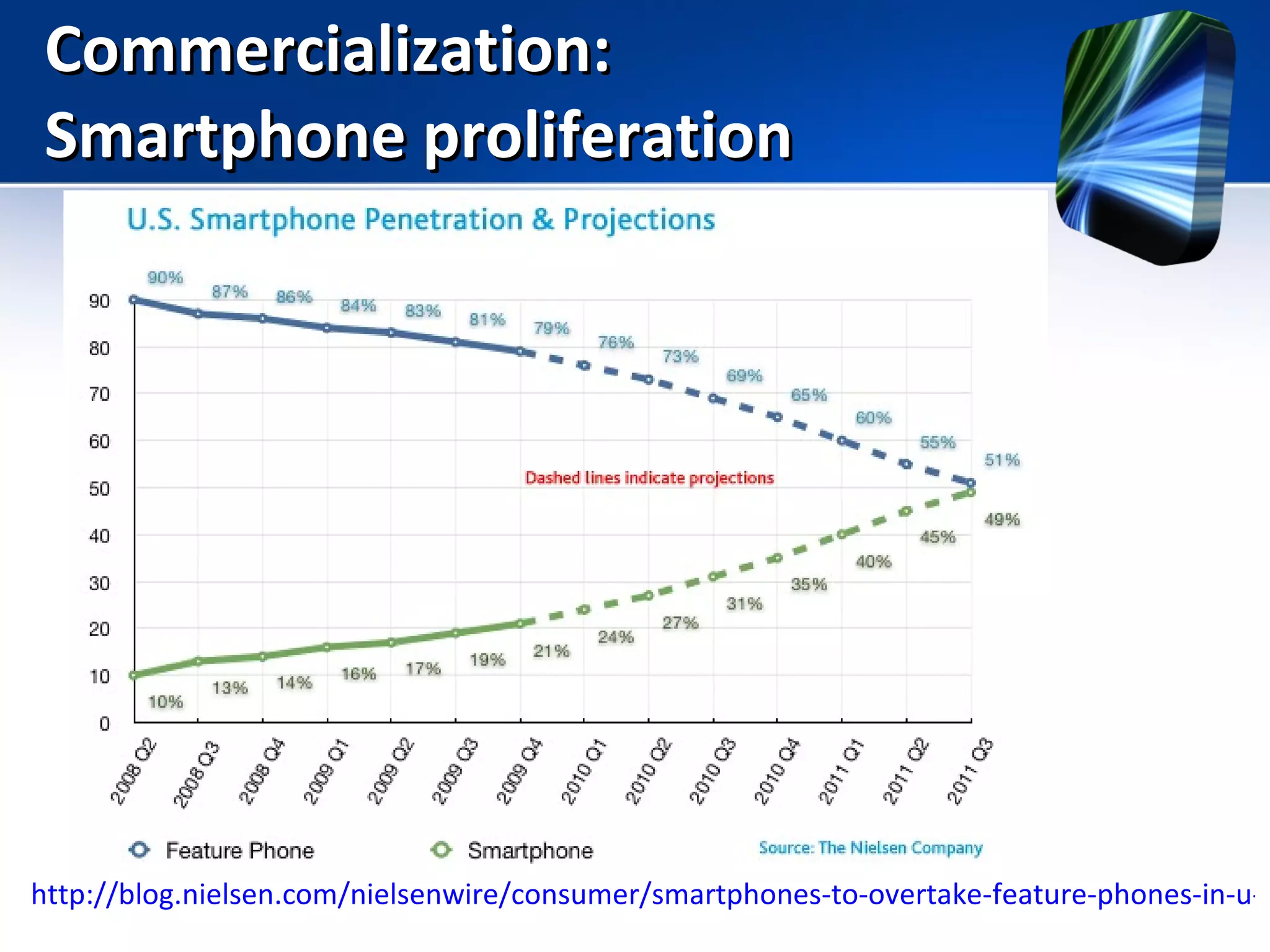
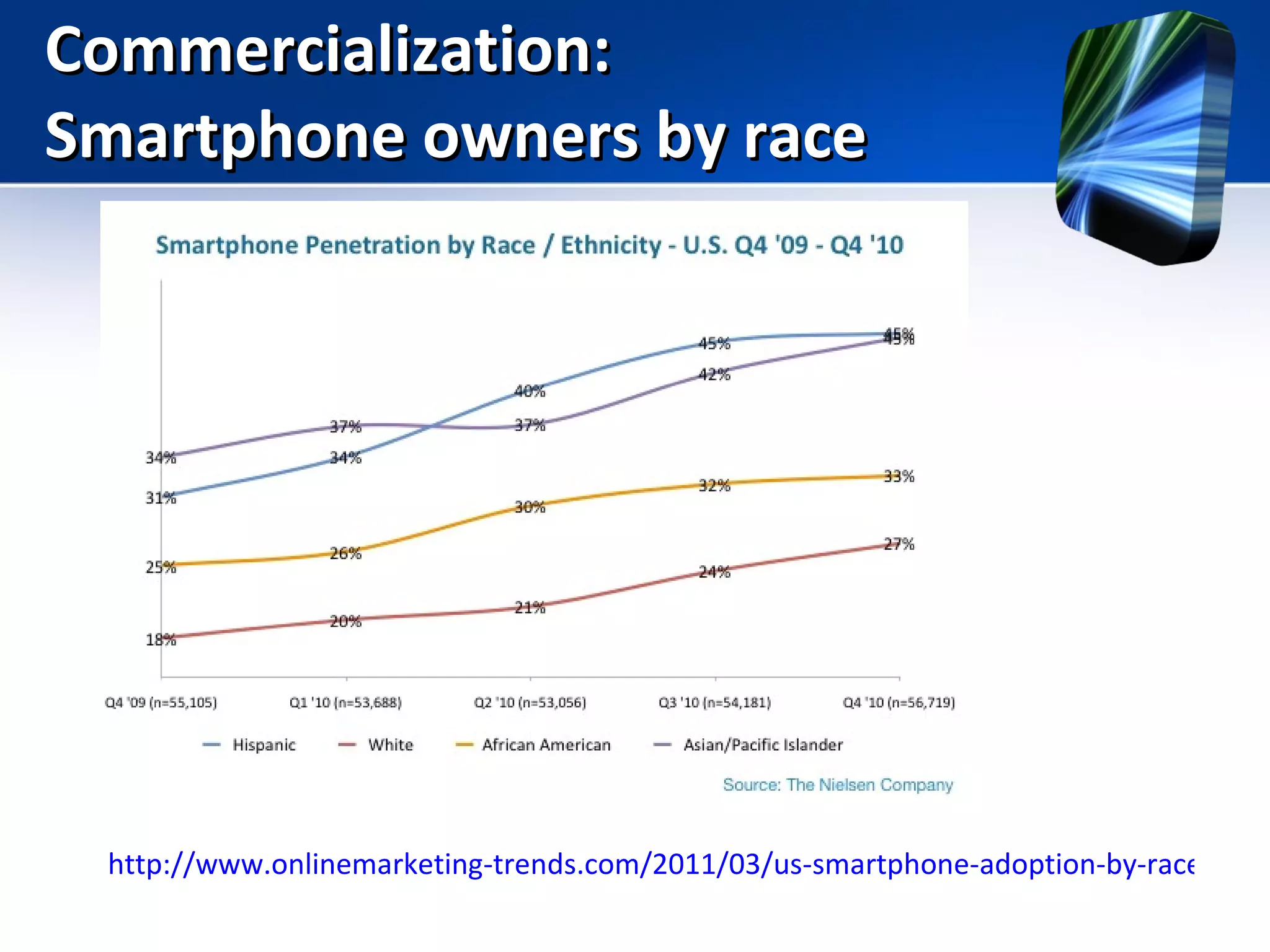
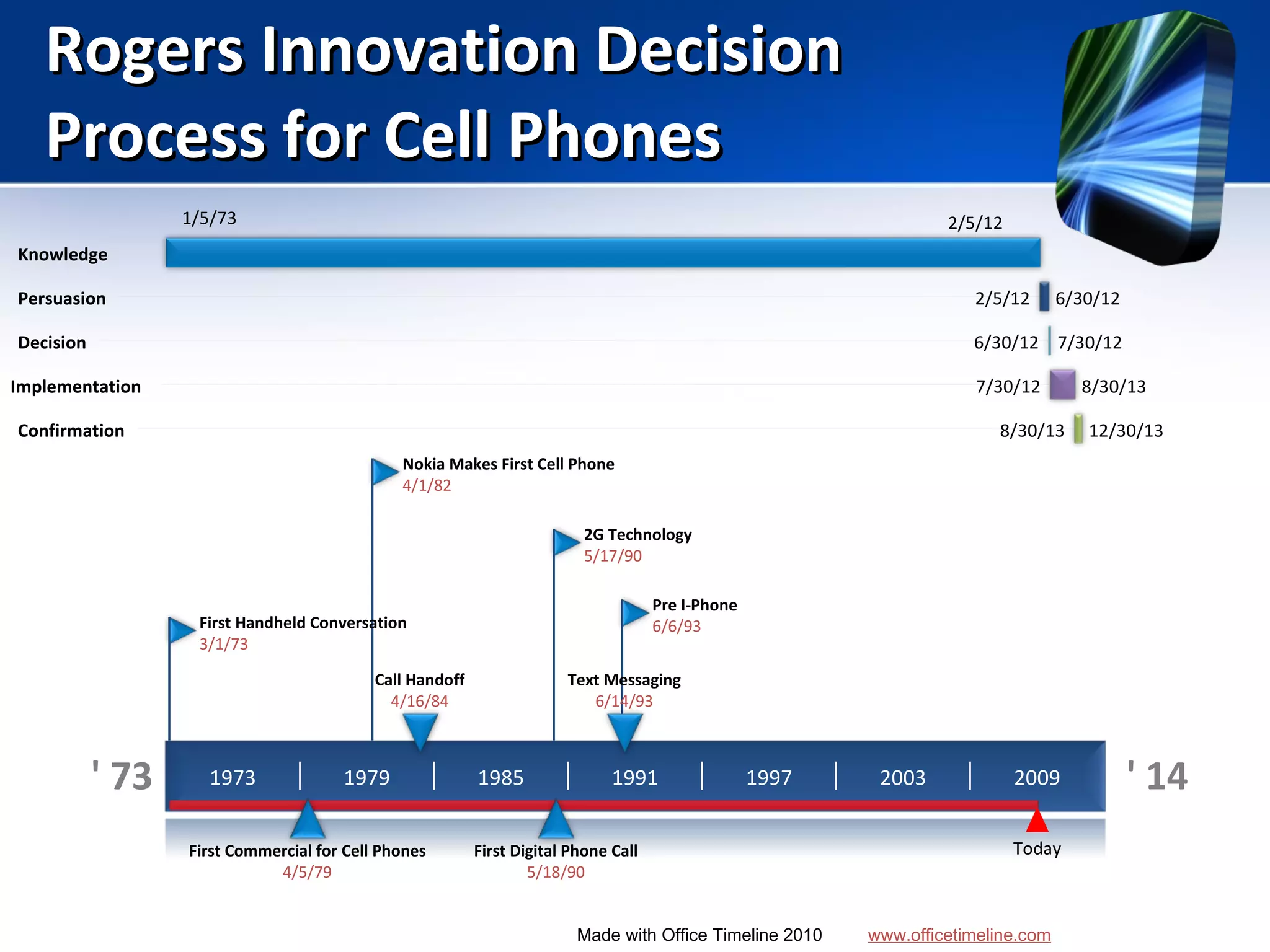
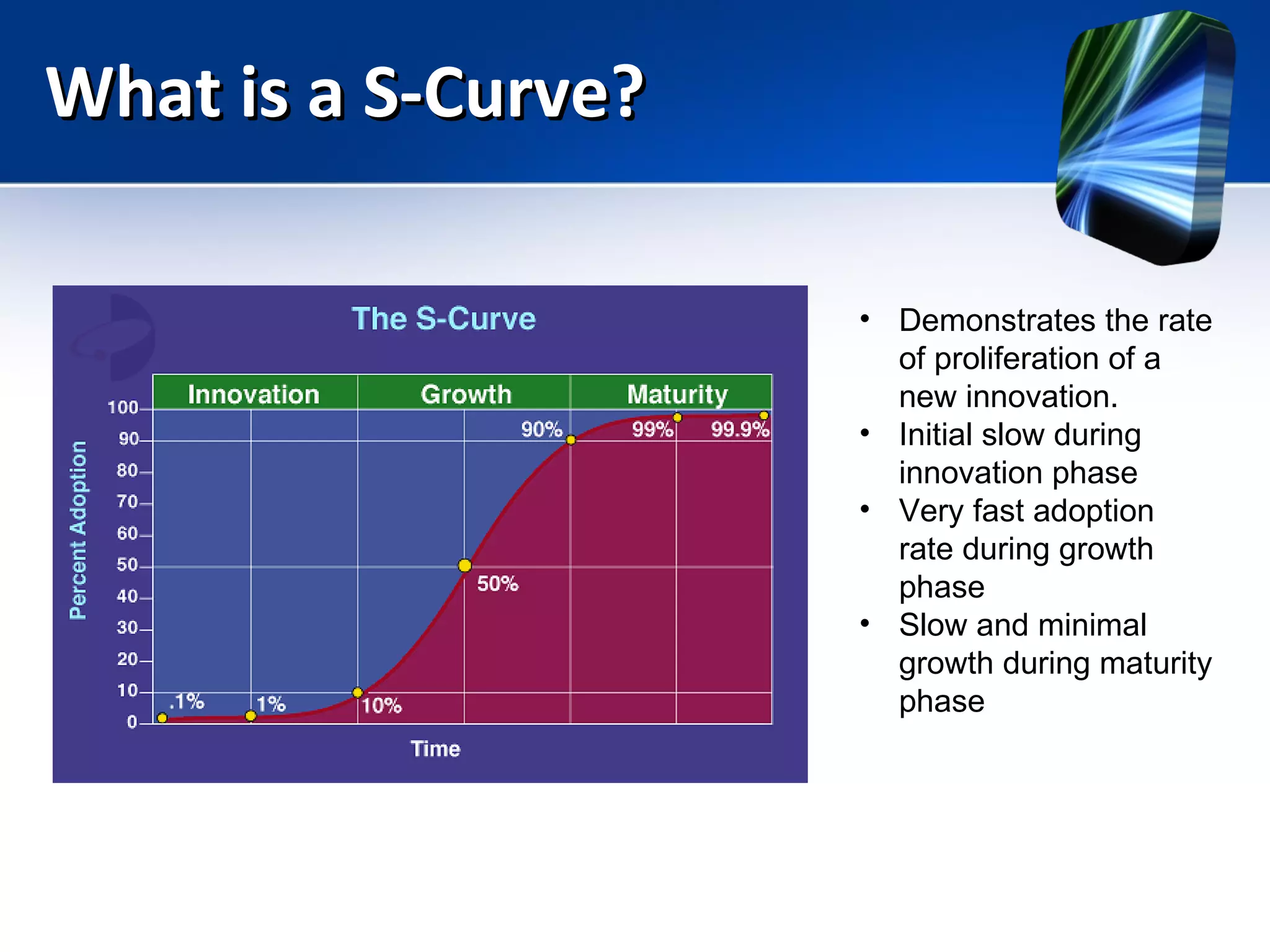
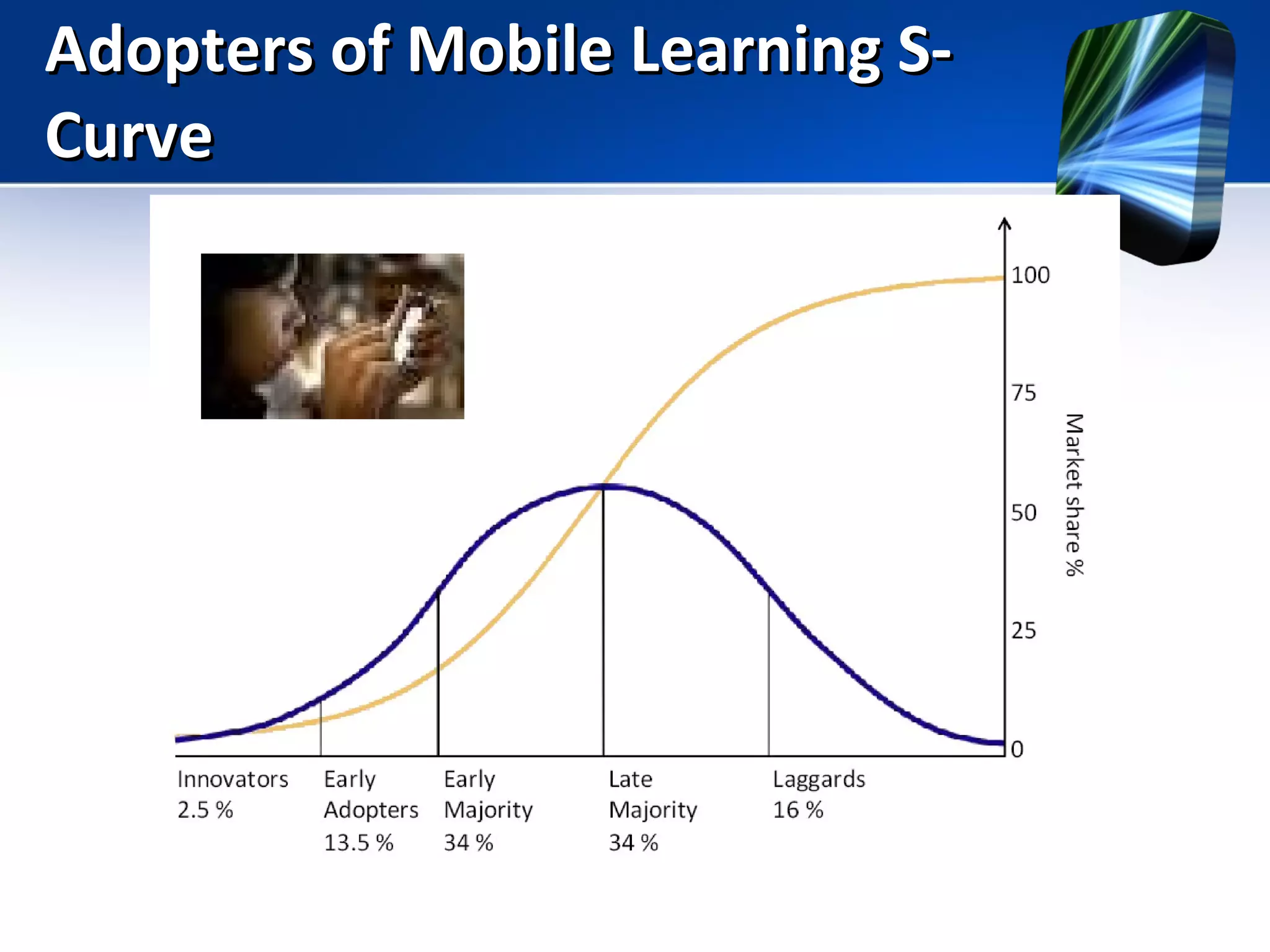
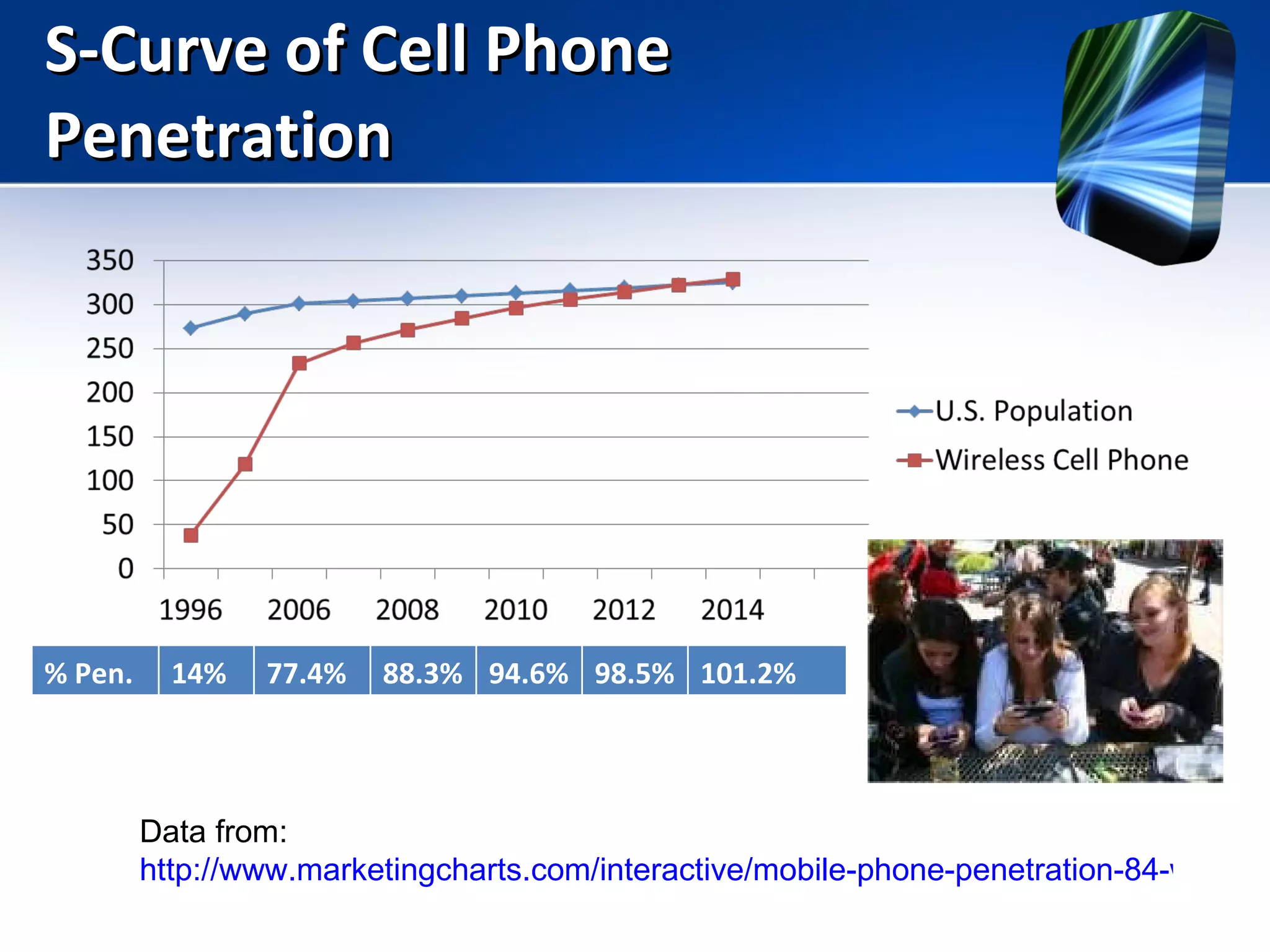
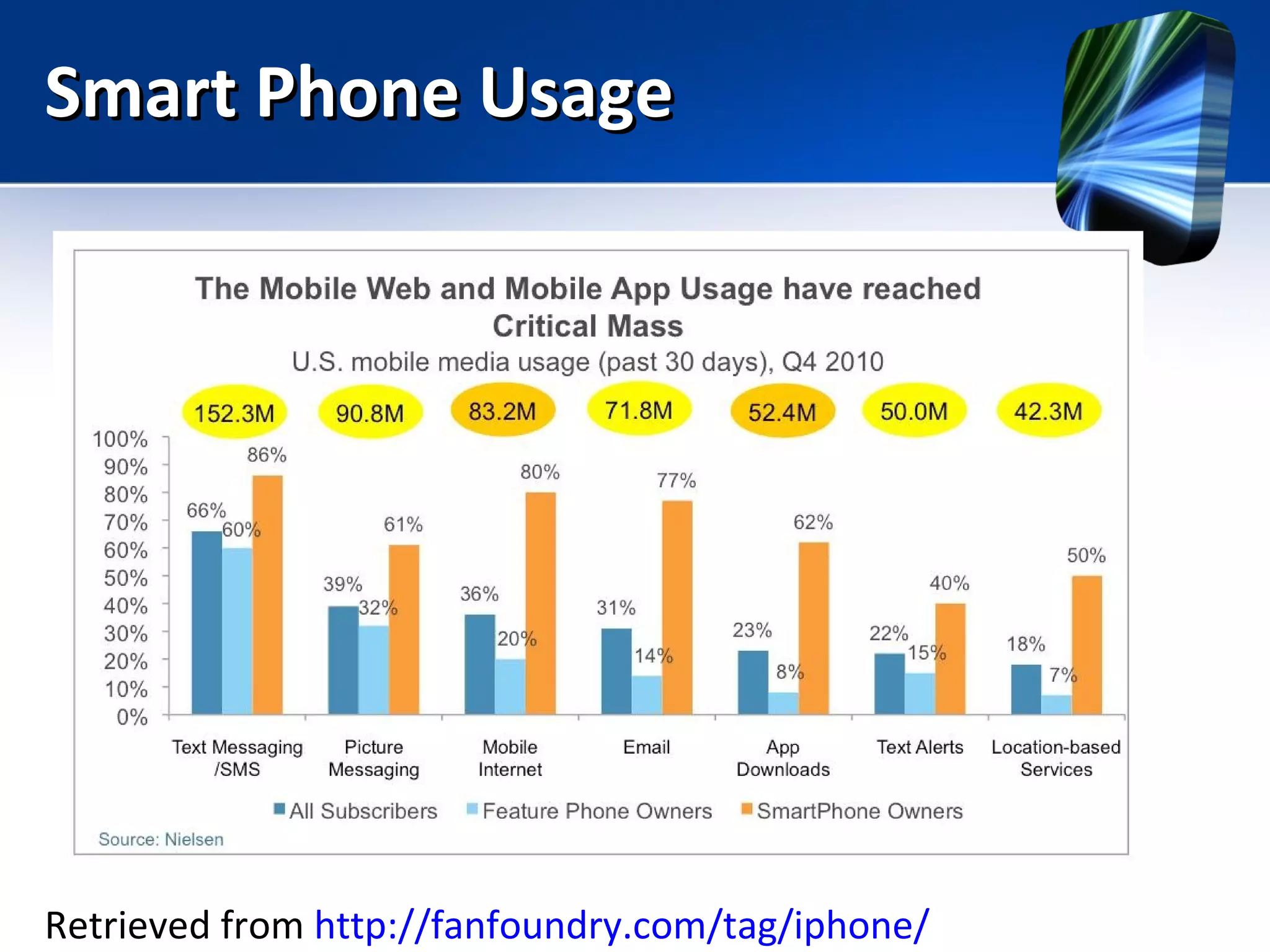
Mobile learning allows students to learn anywhere at any time through their smartphones. Research shows mobile learning has positive impacts on education by making it more personalized and technology-focused. As smartphones became more advanced after 2010, their use in education increased. For mobile learning to be widely adopted, it must be implemented gradually starting with innovators and early adopters before reaching critical mass. Change agents like teachers and administrators can encourage adoption by demonstrating mobile learning's benefits.