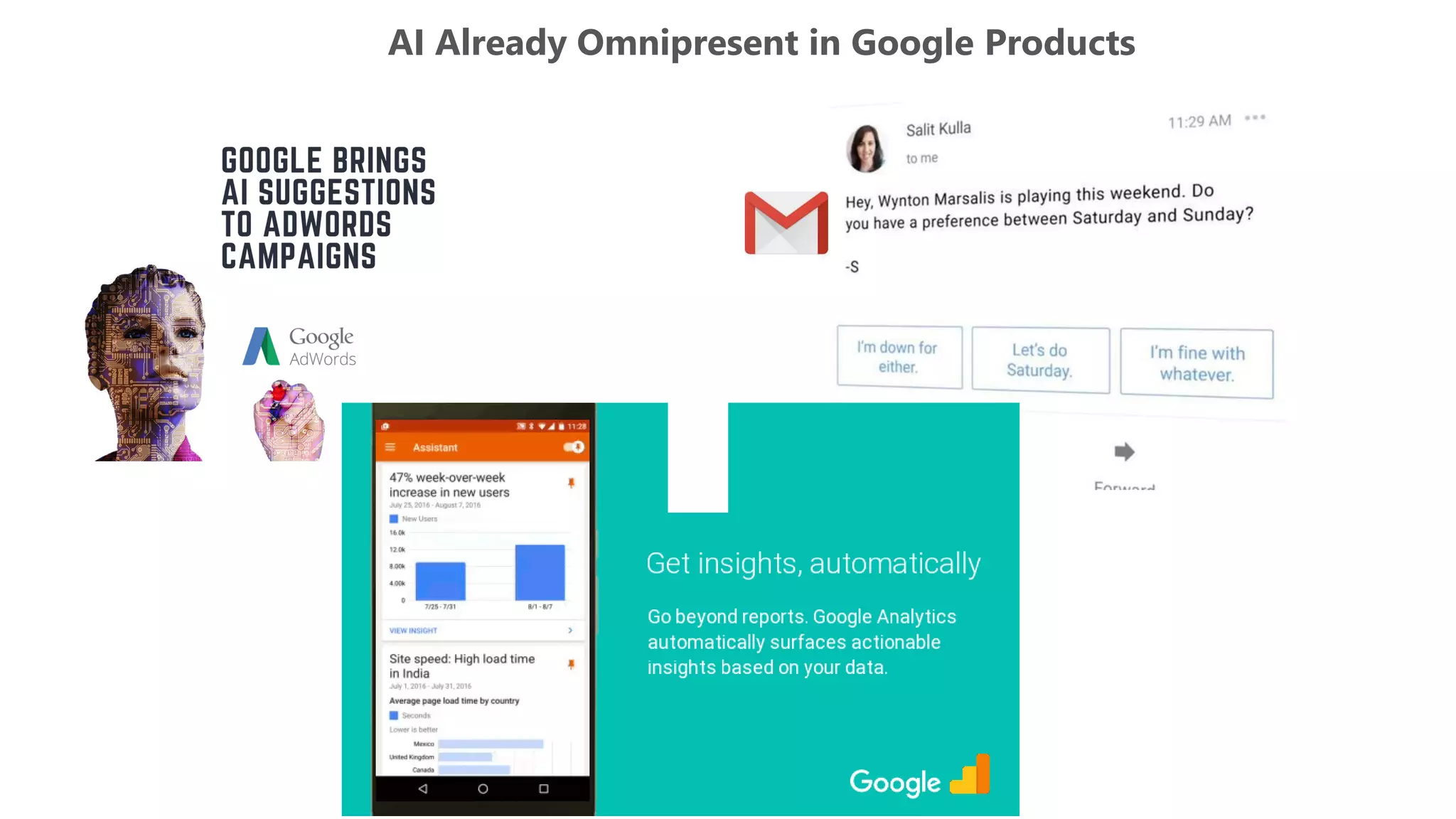
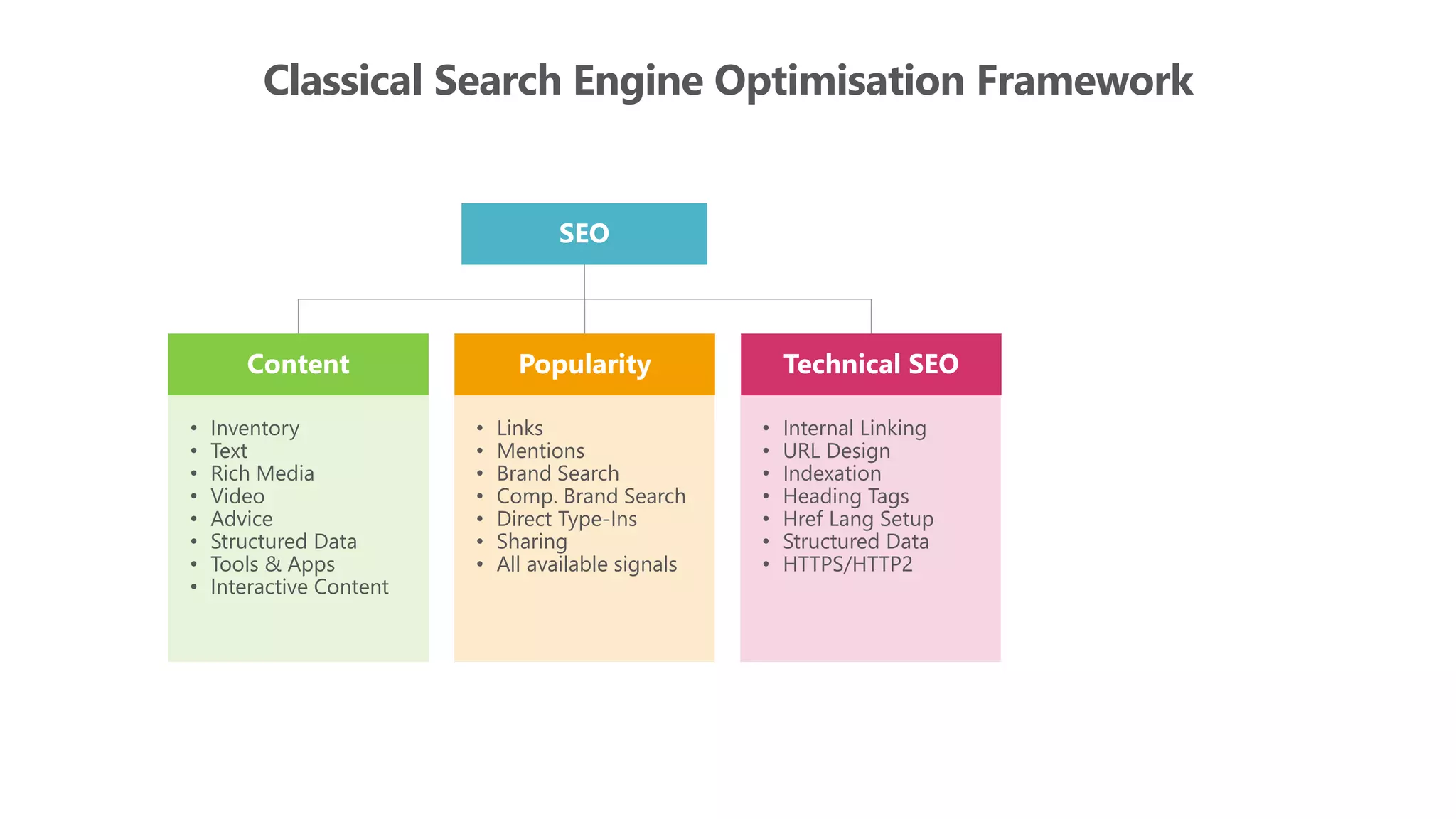
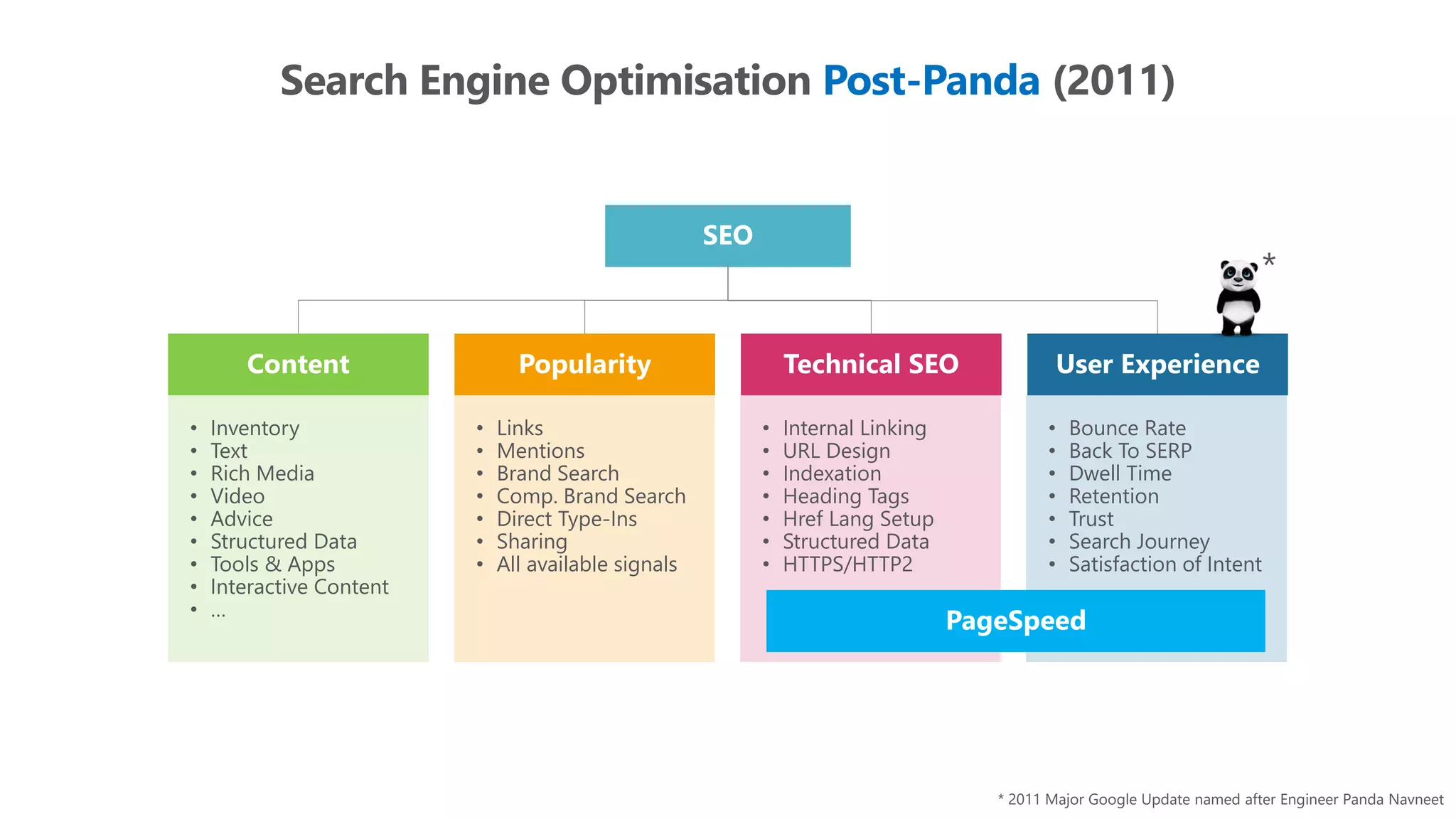
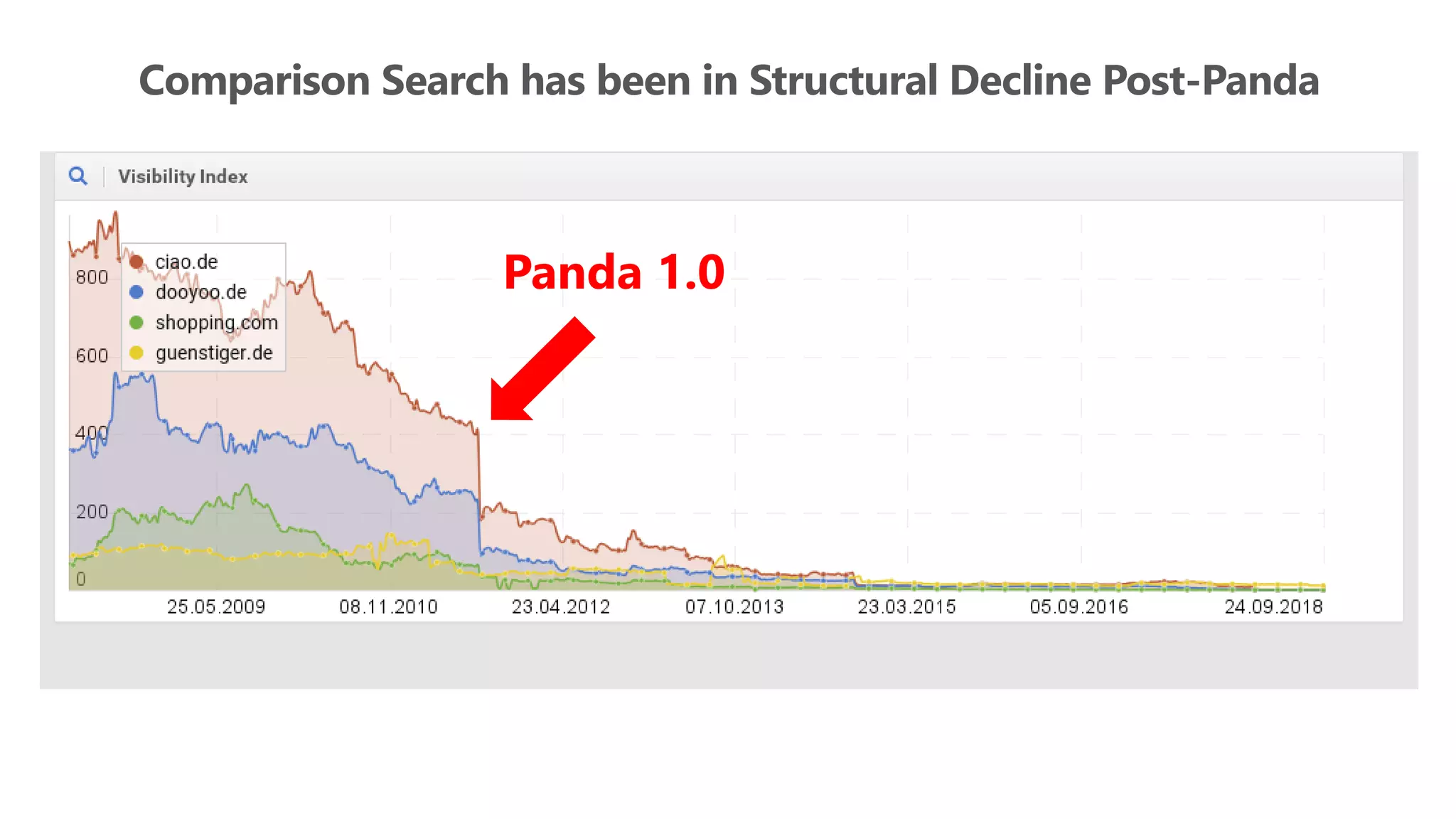
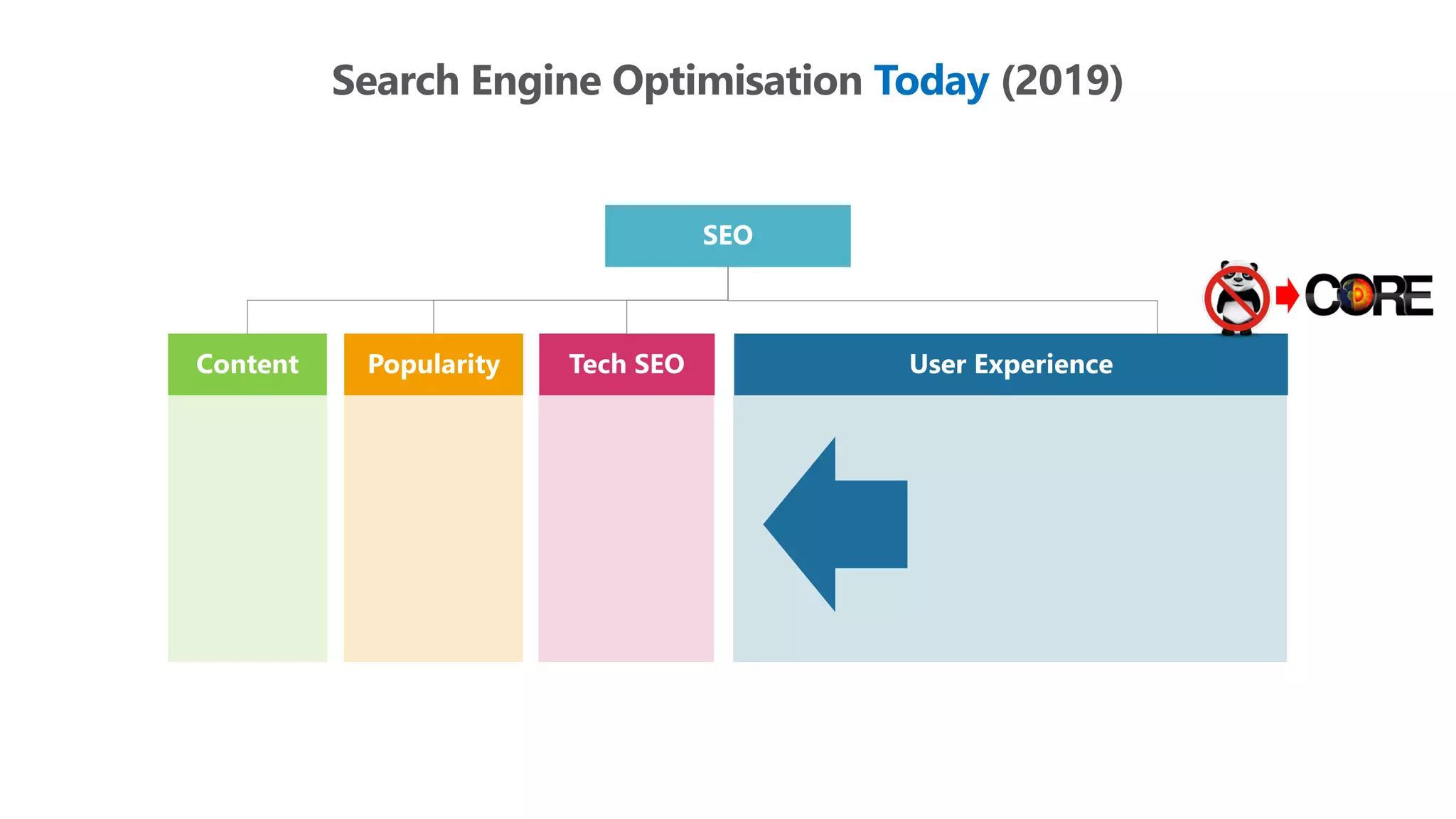
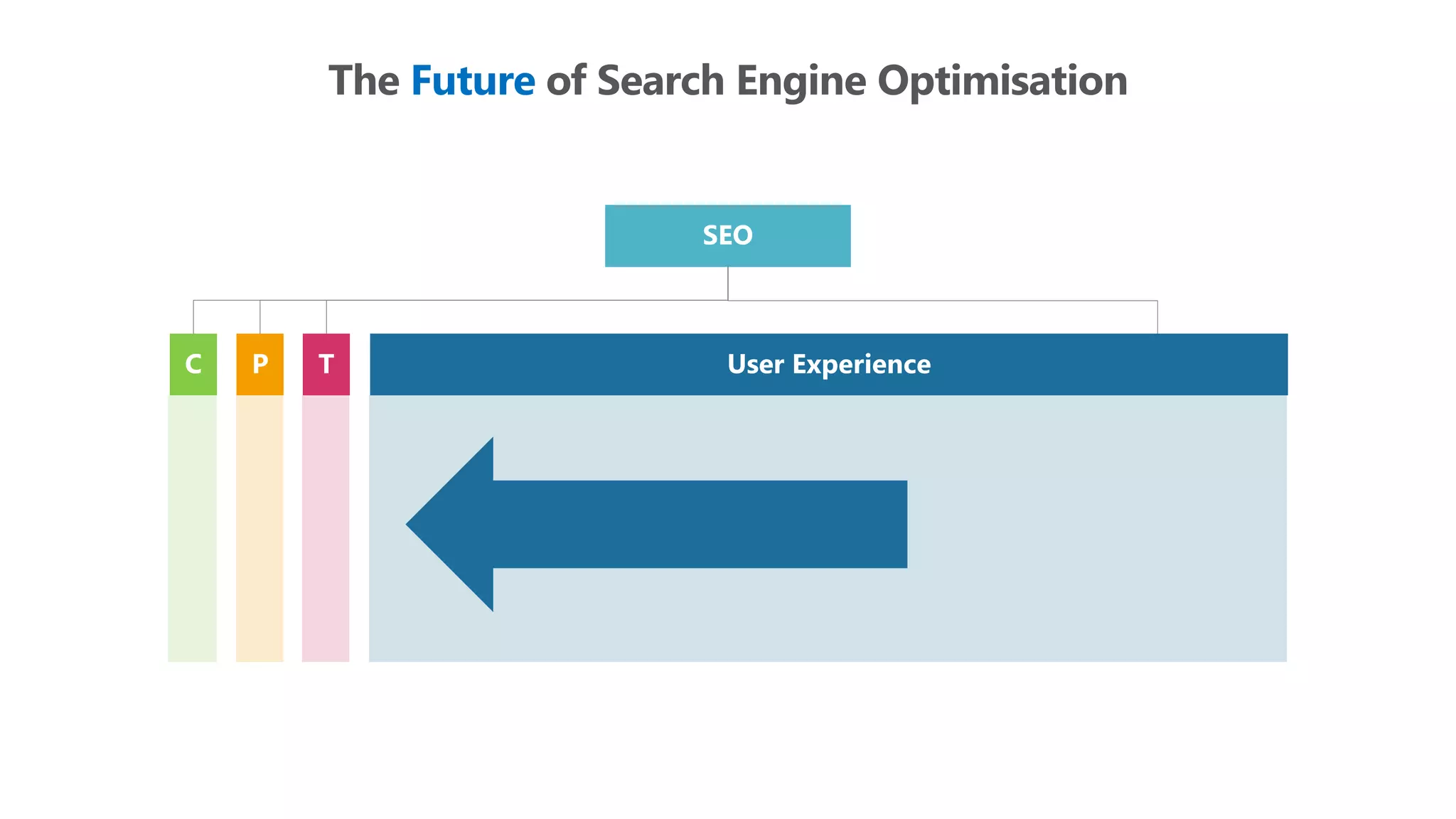
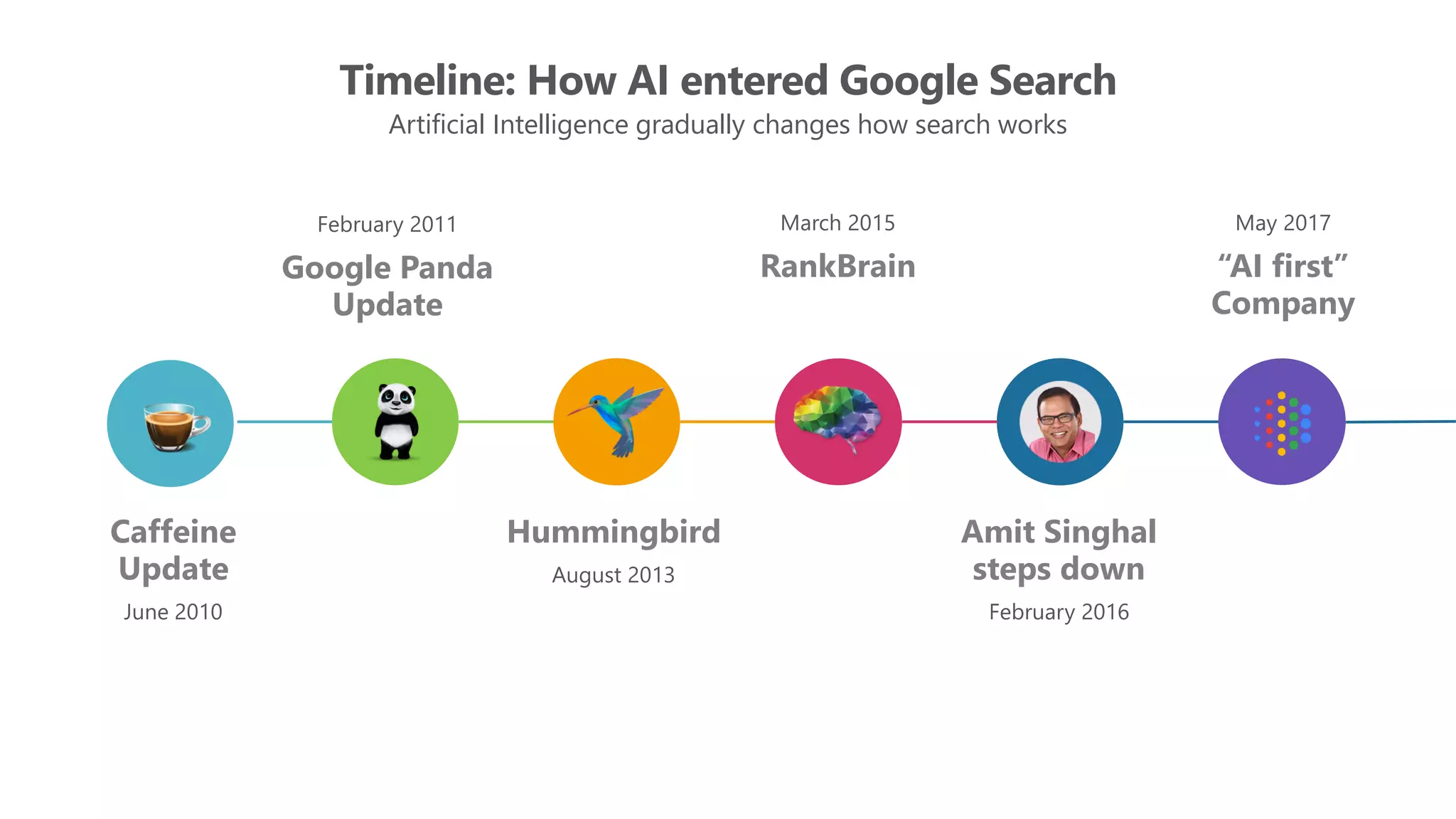
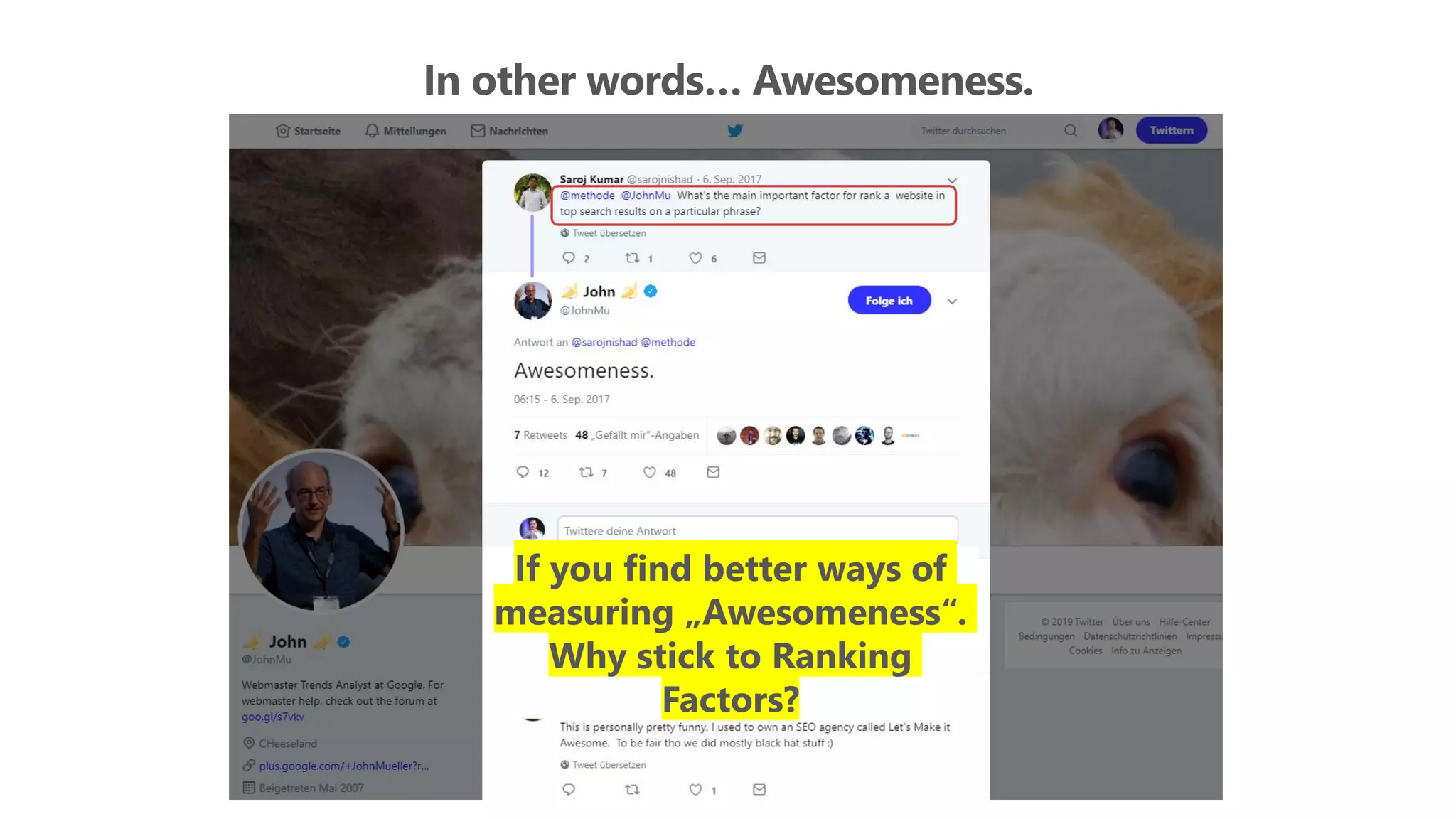
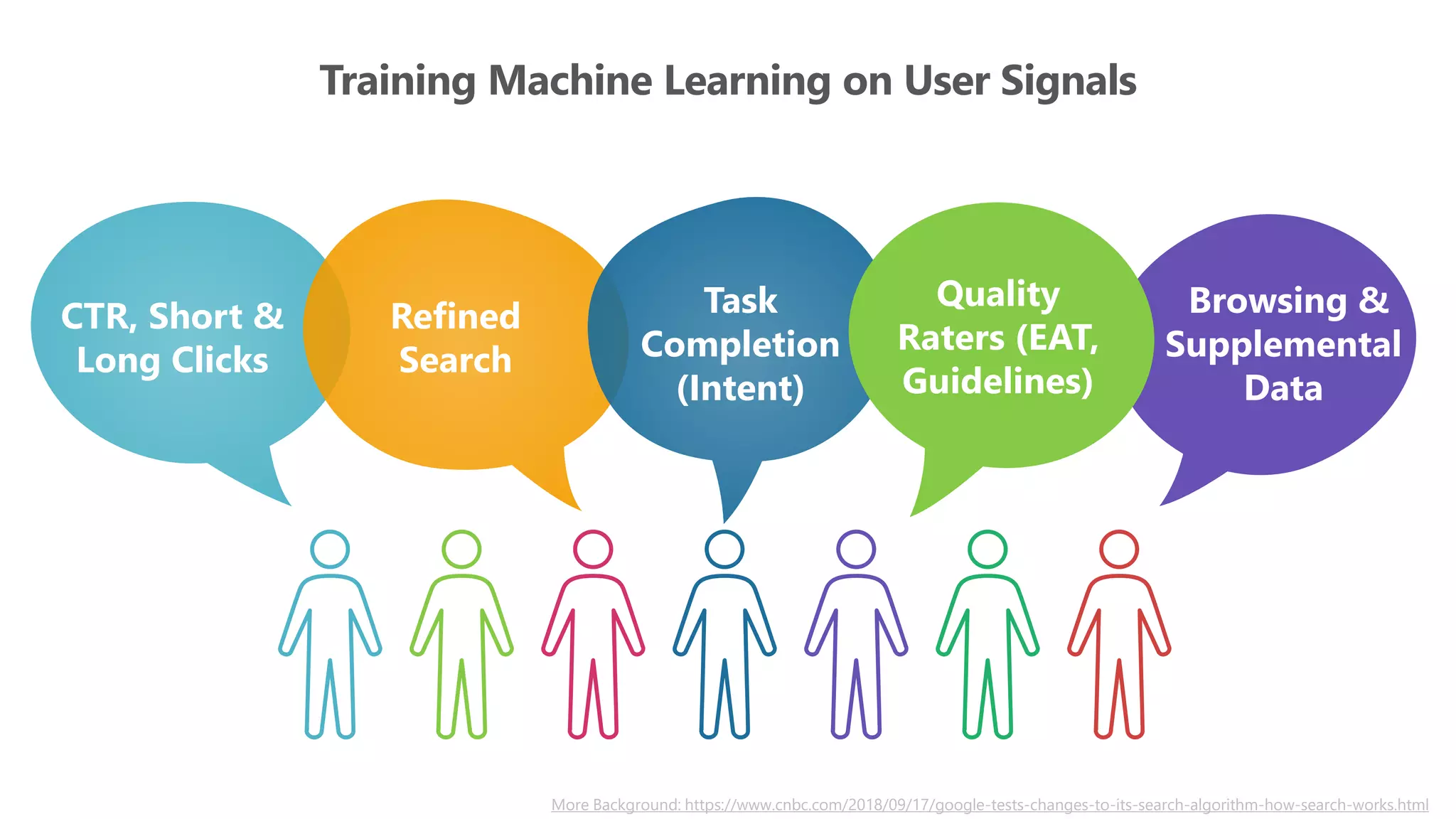
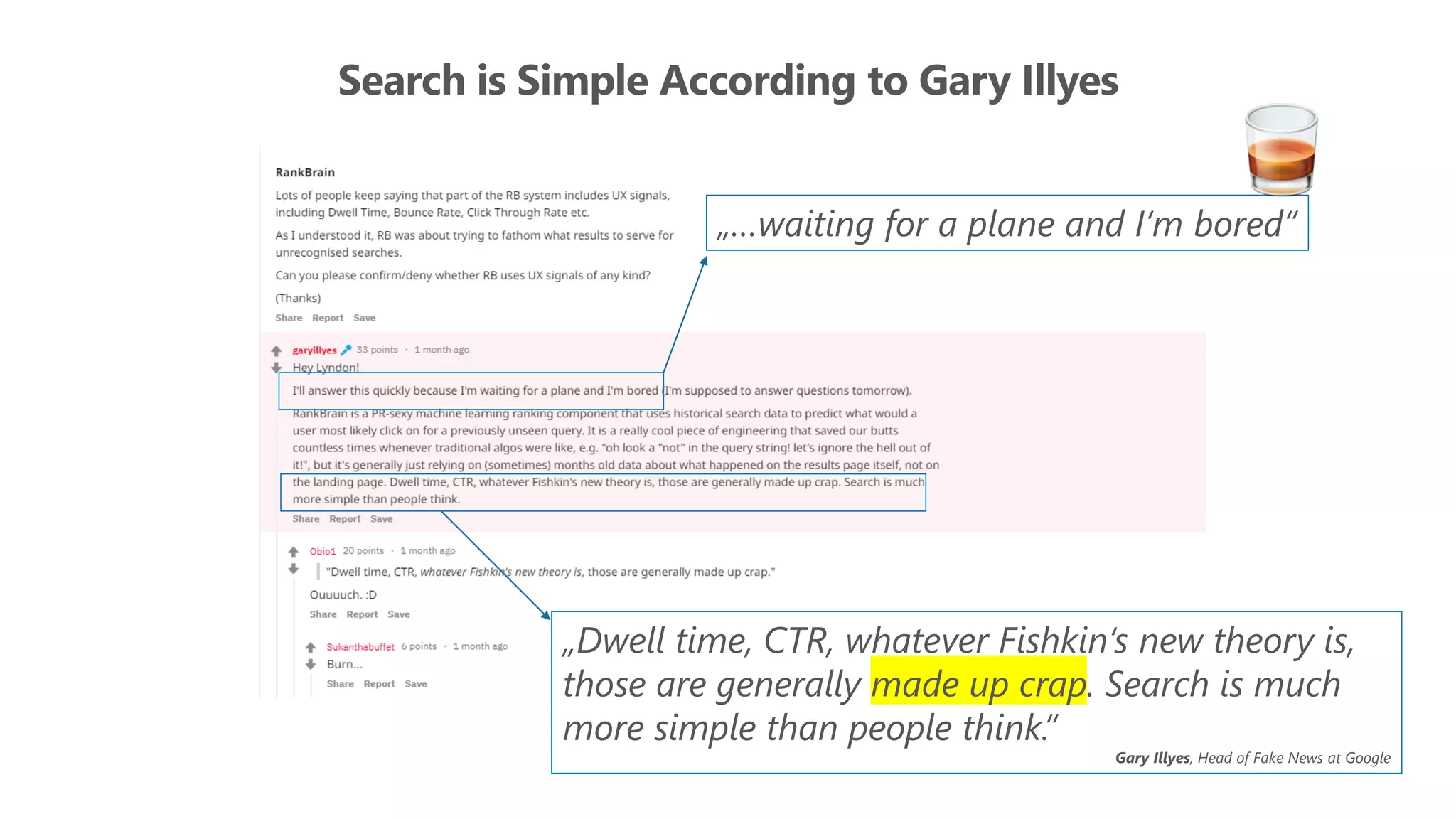
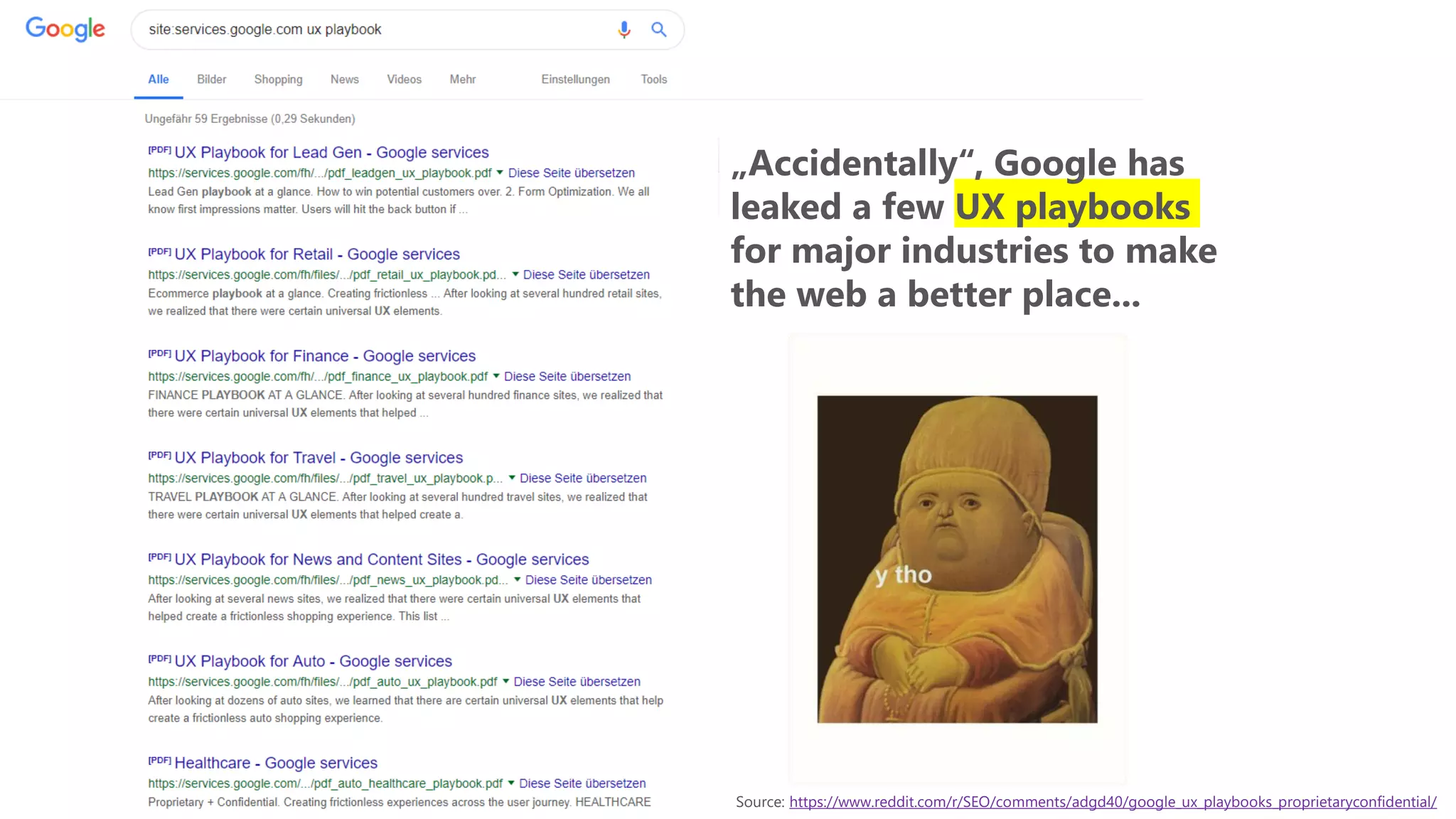
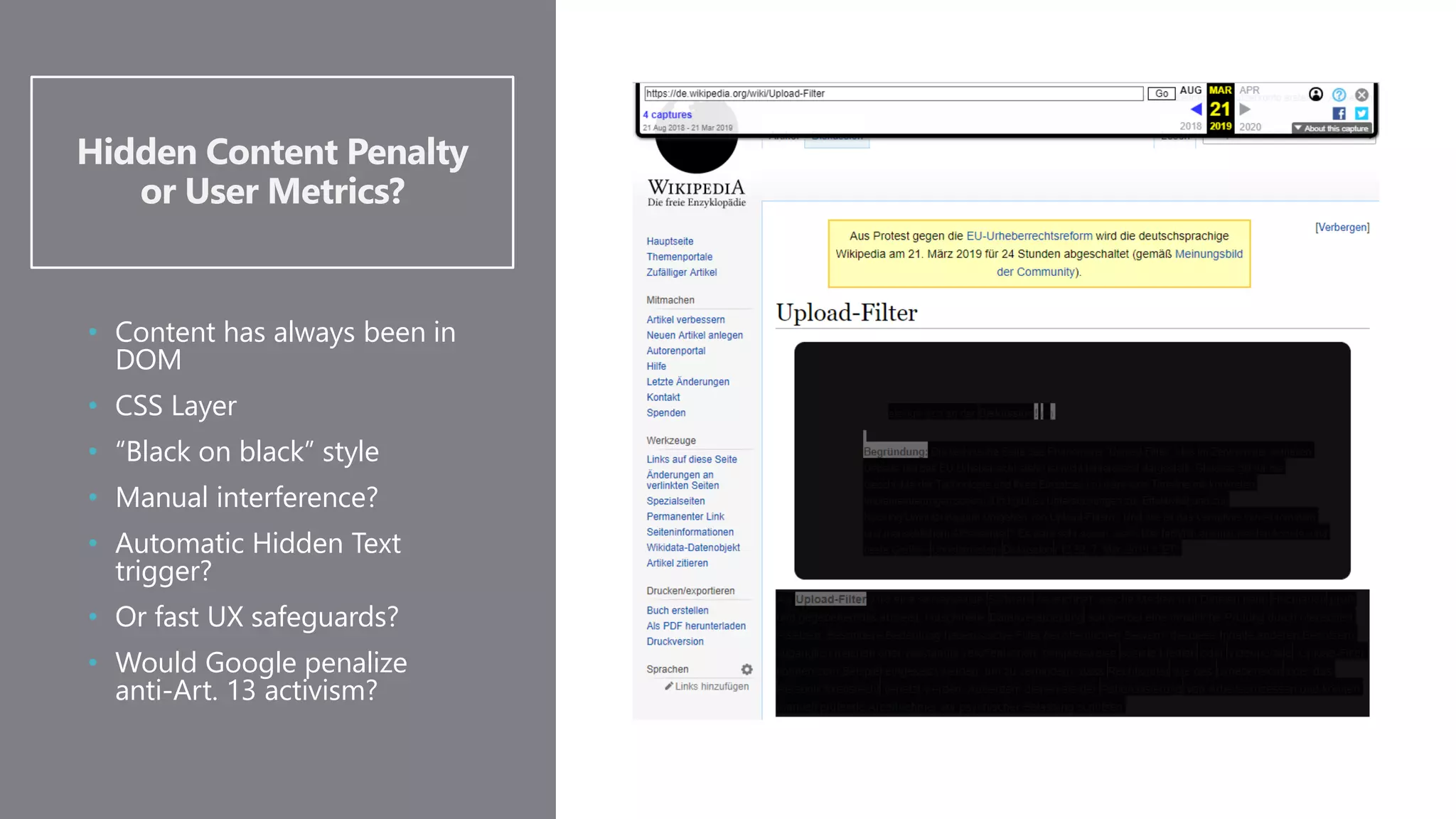
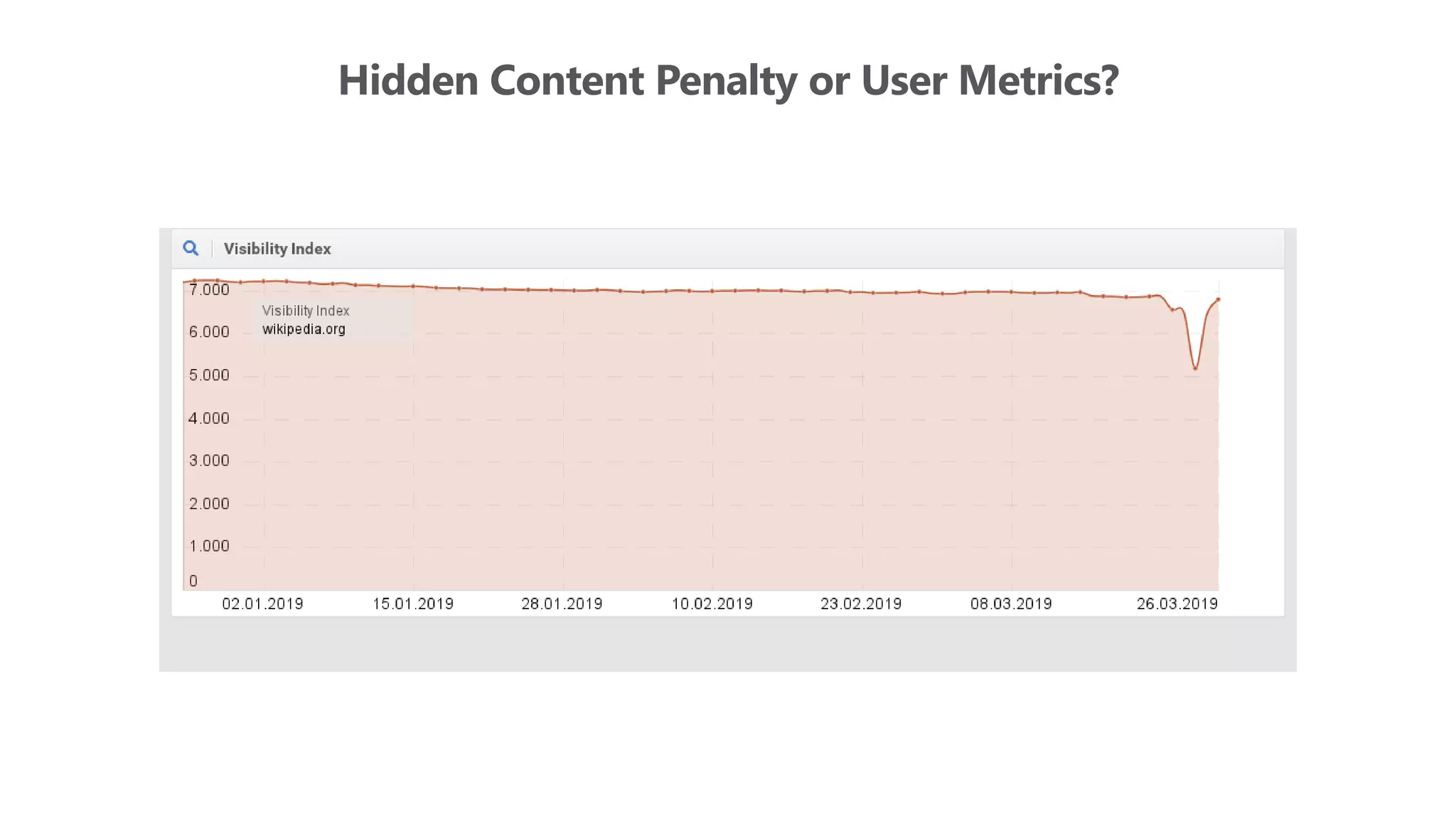
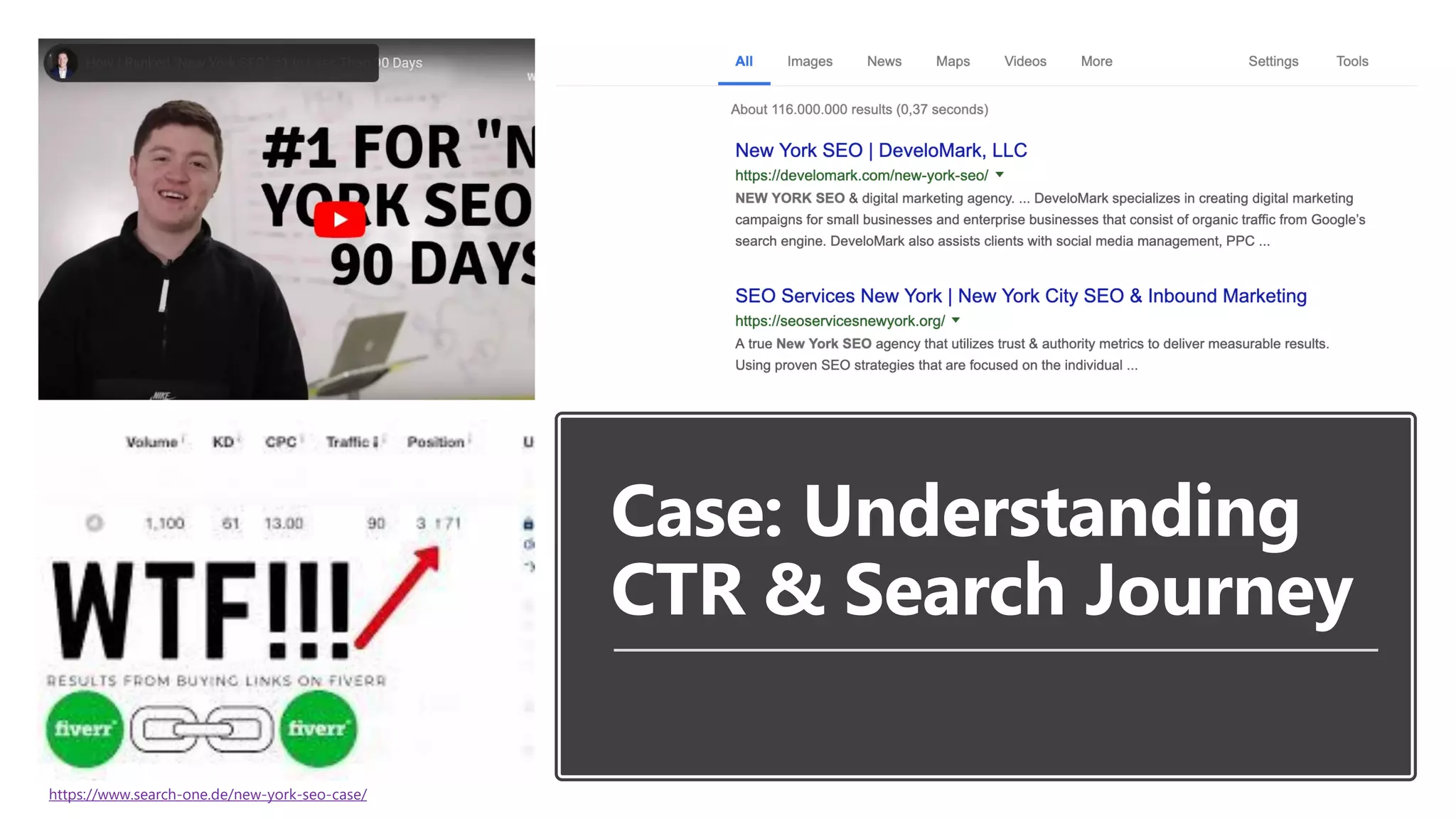
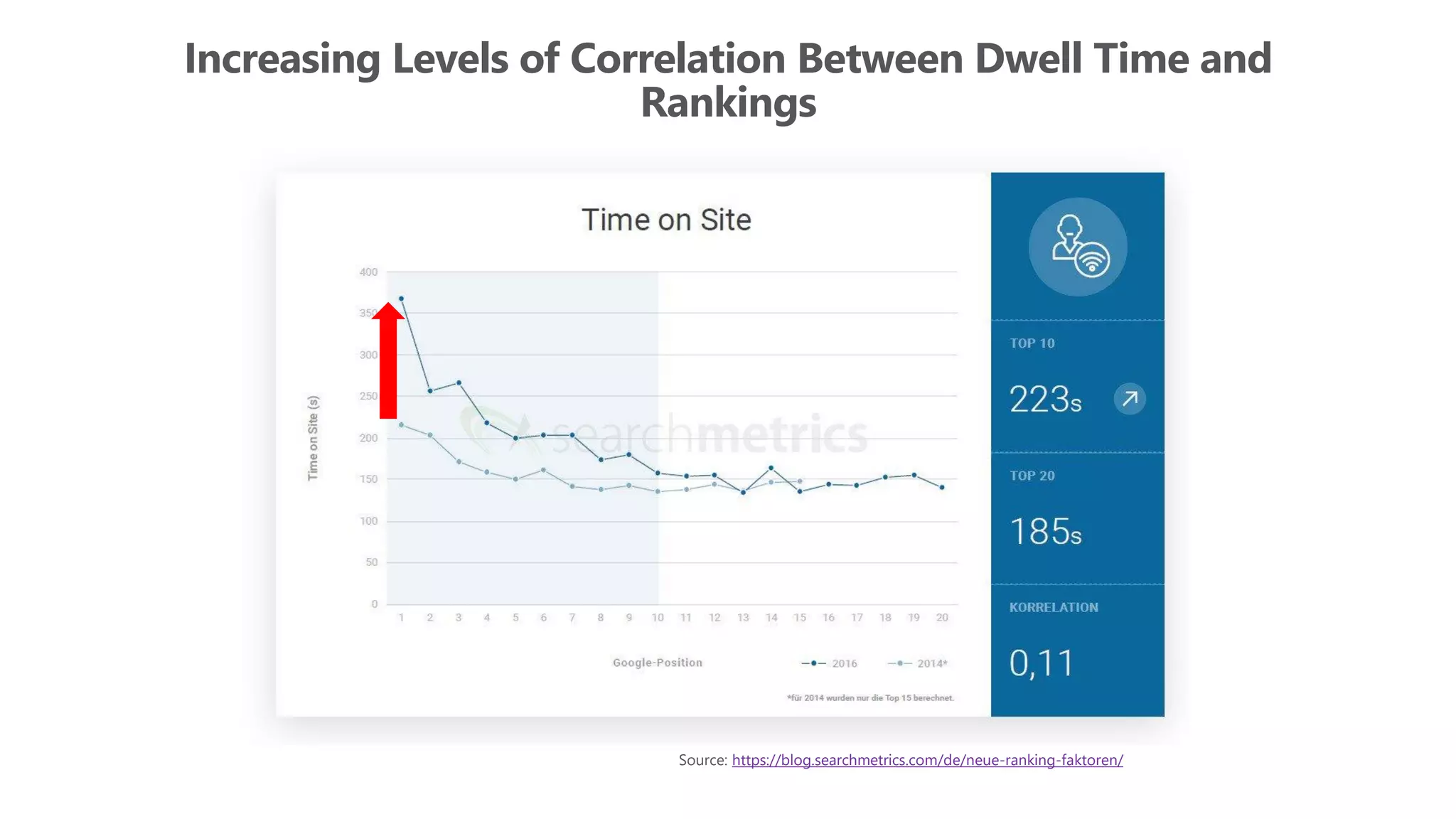
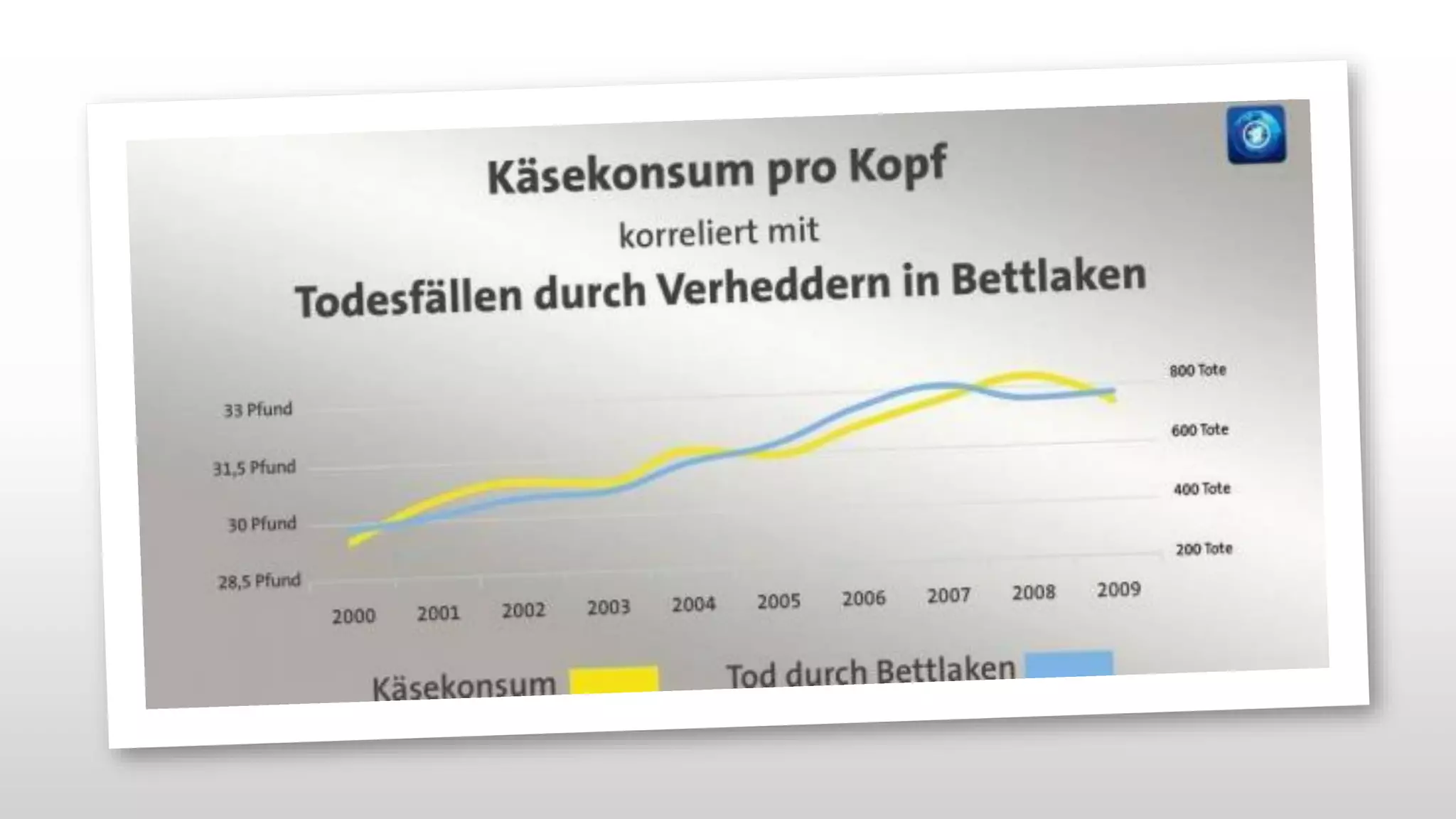
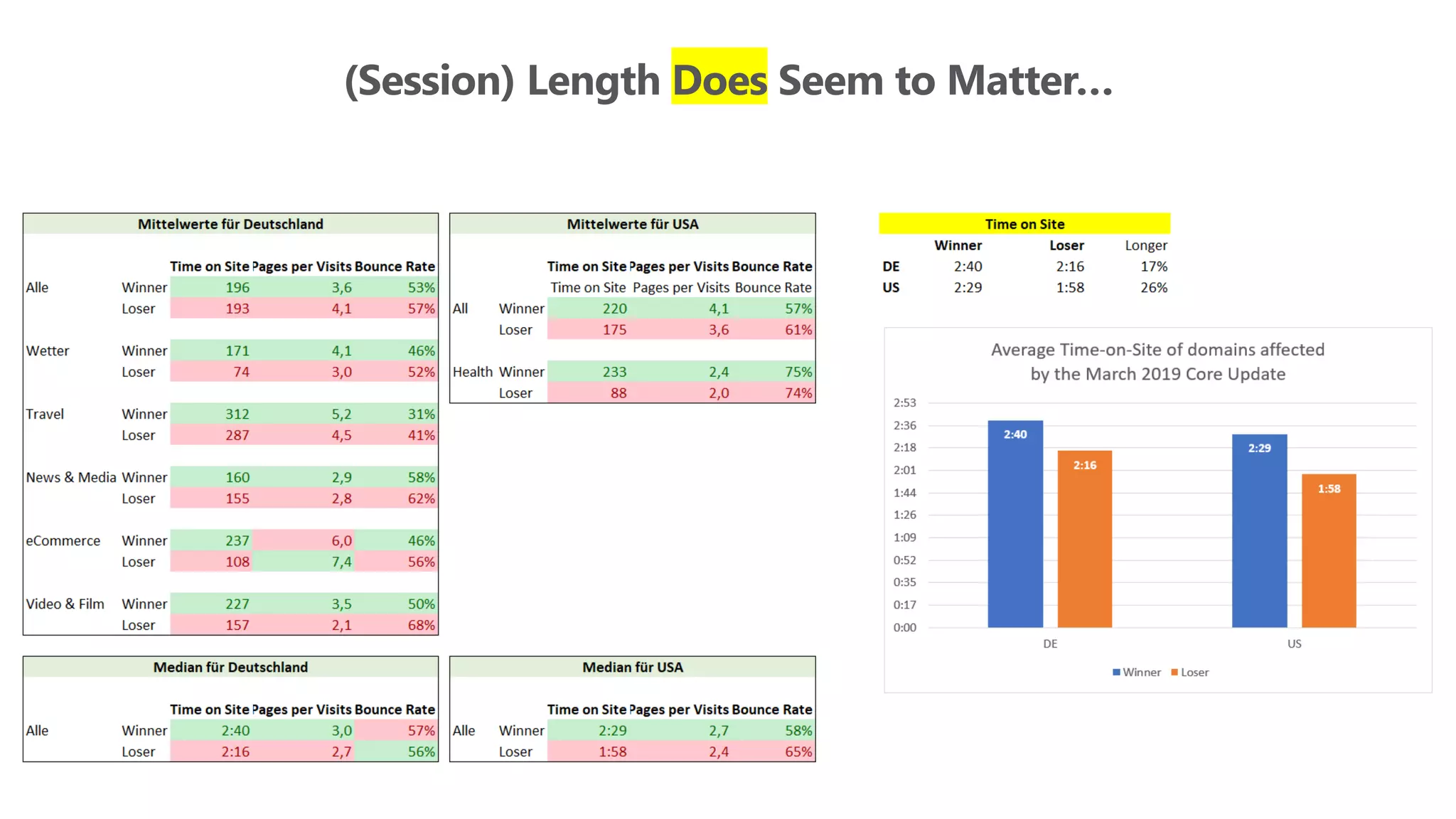
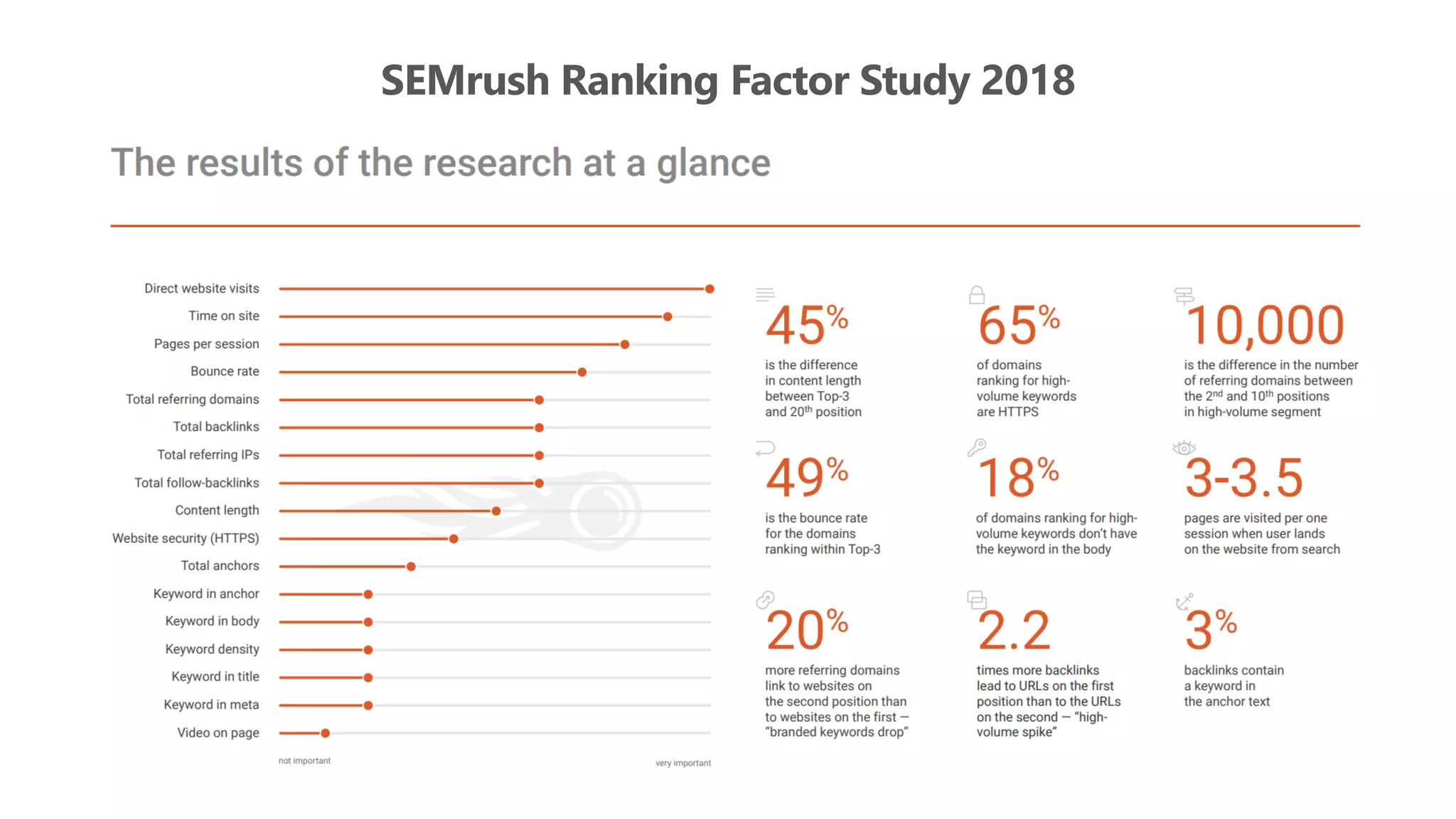
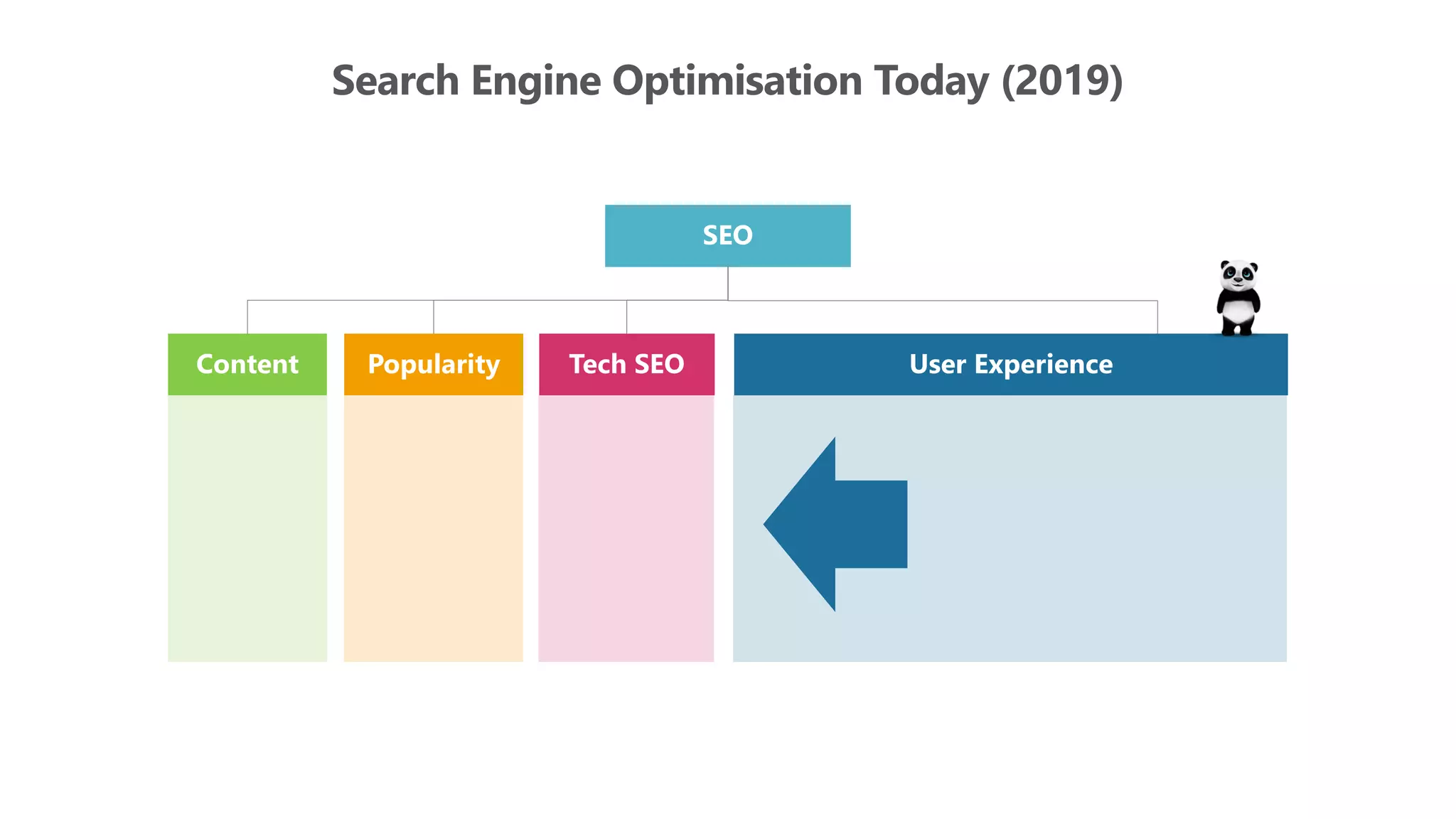
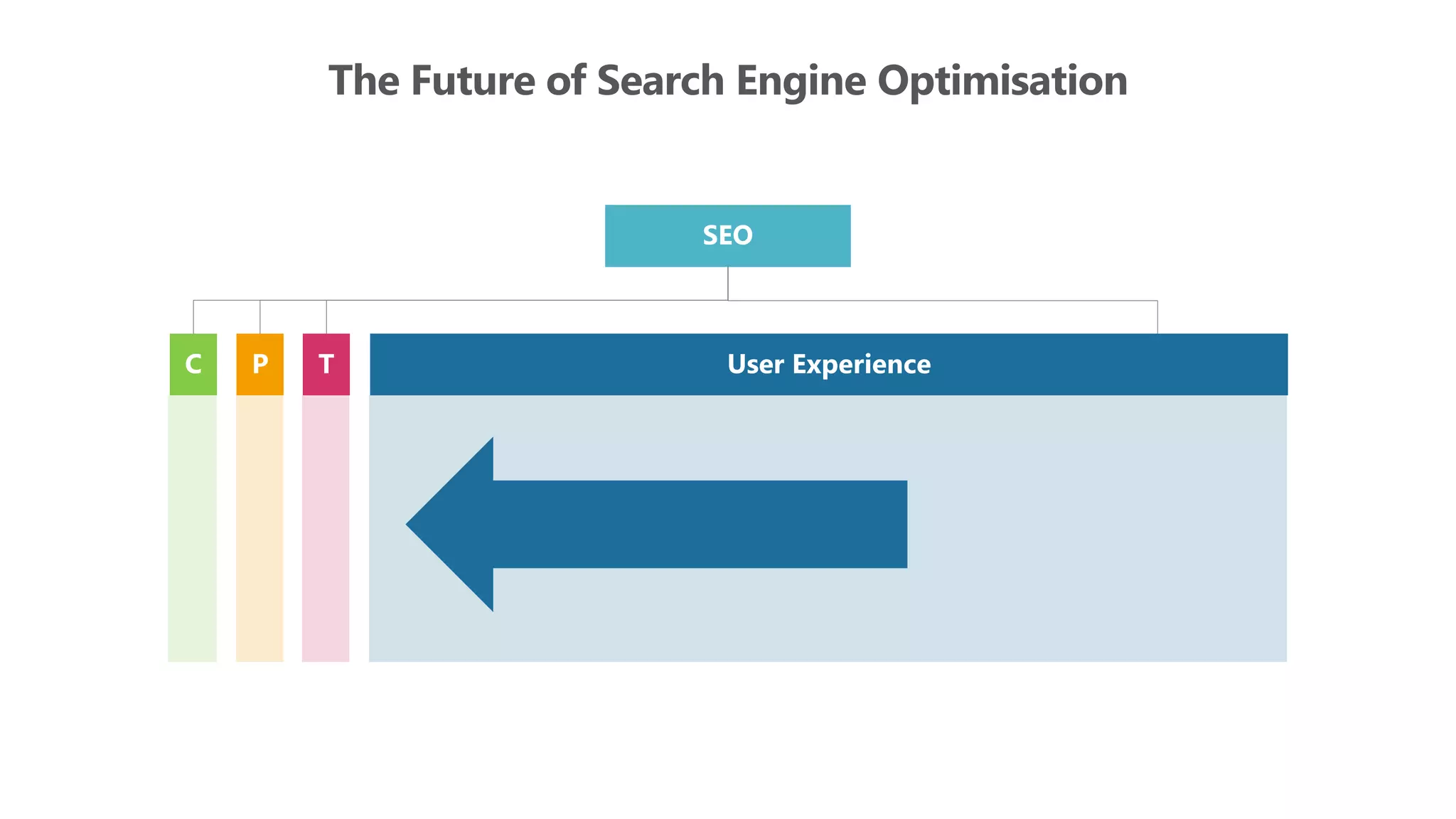
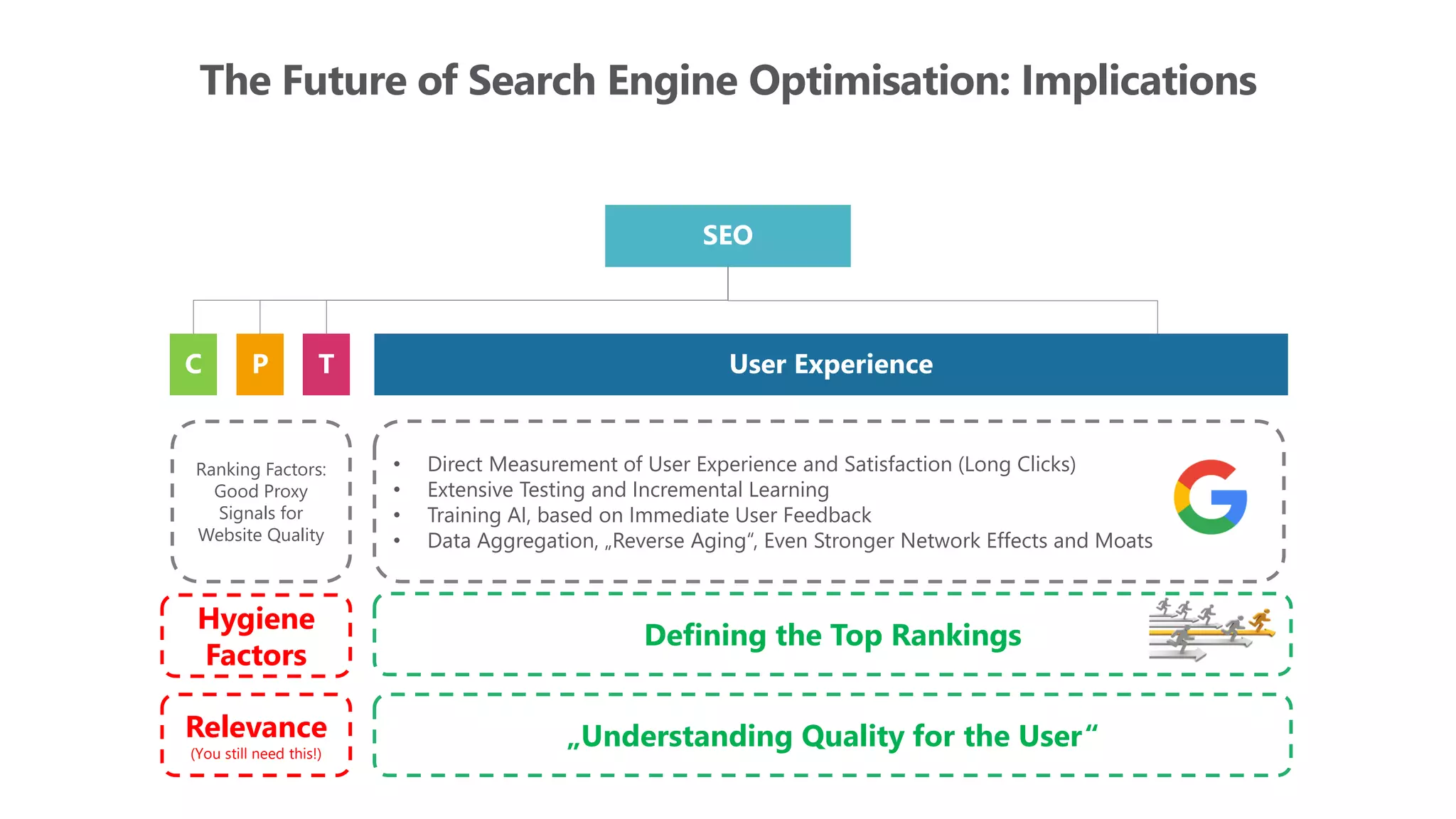
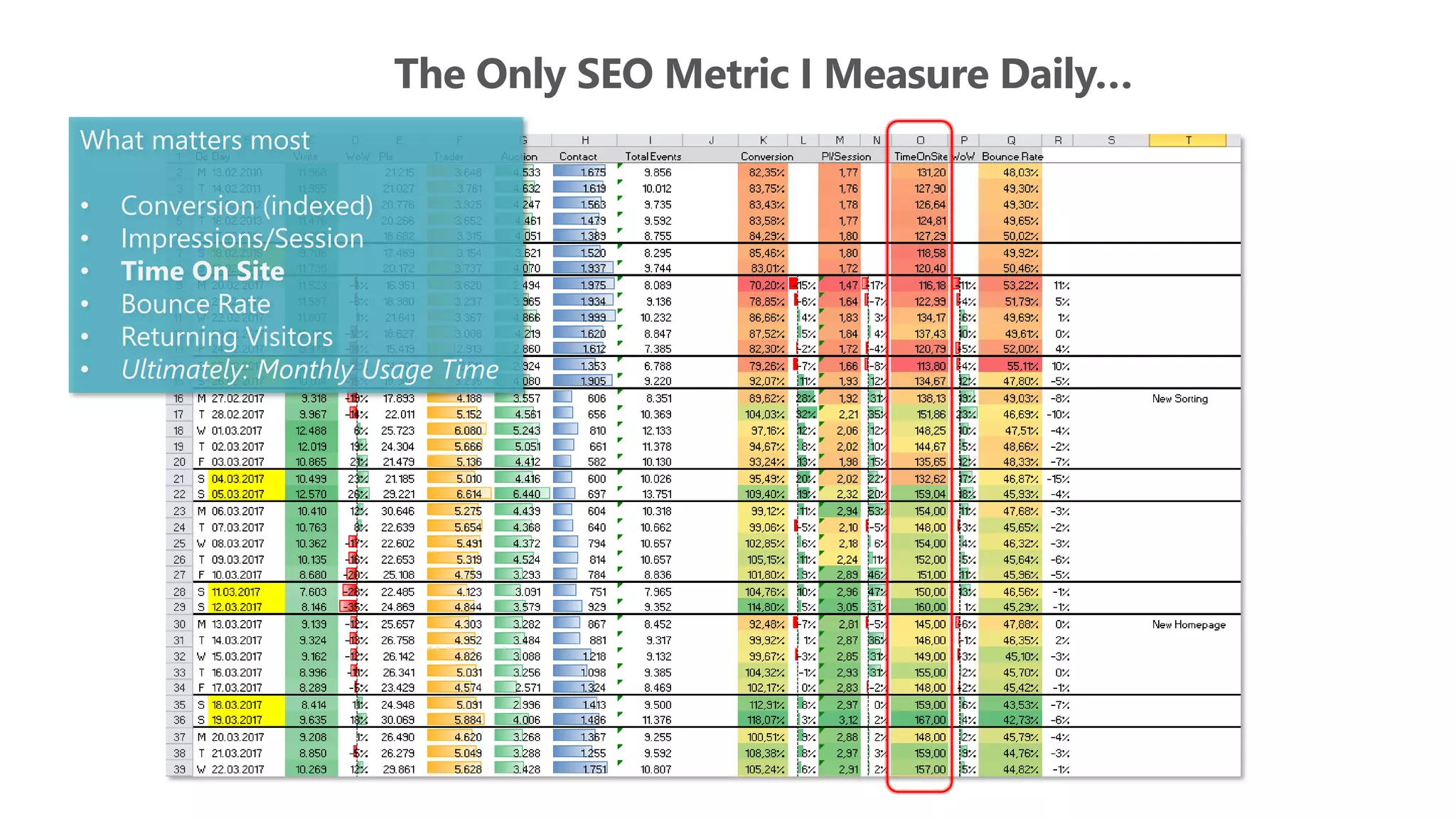
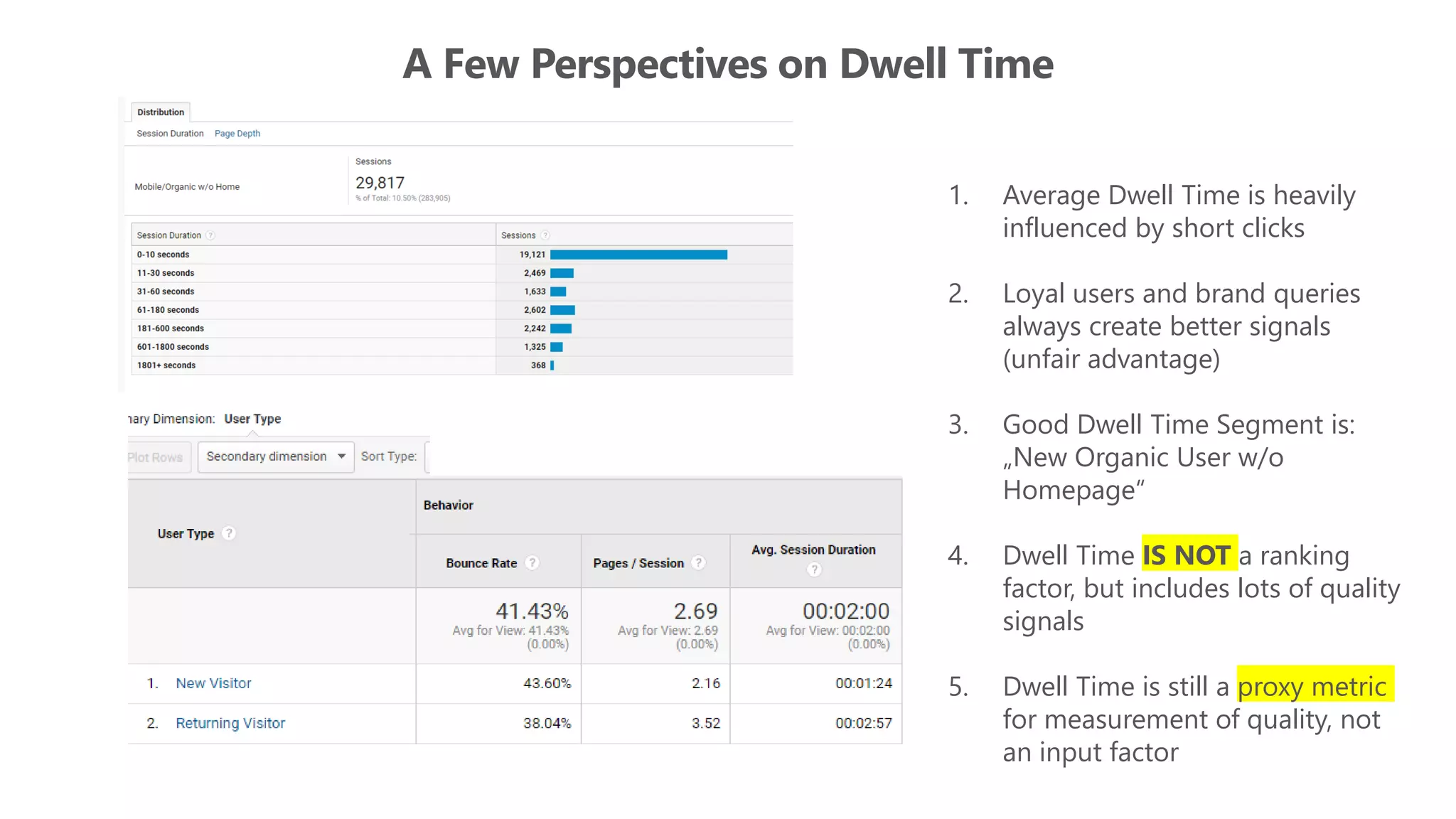
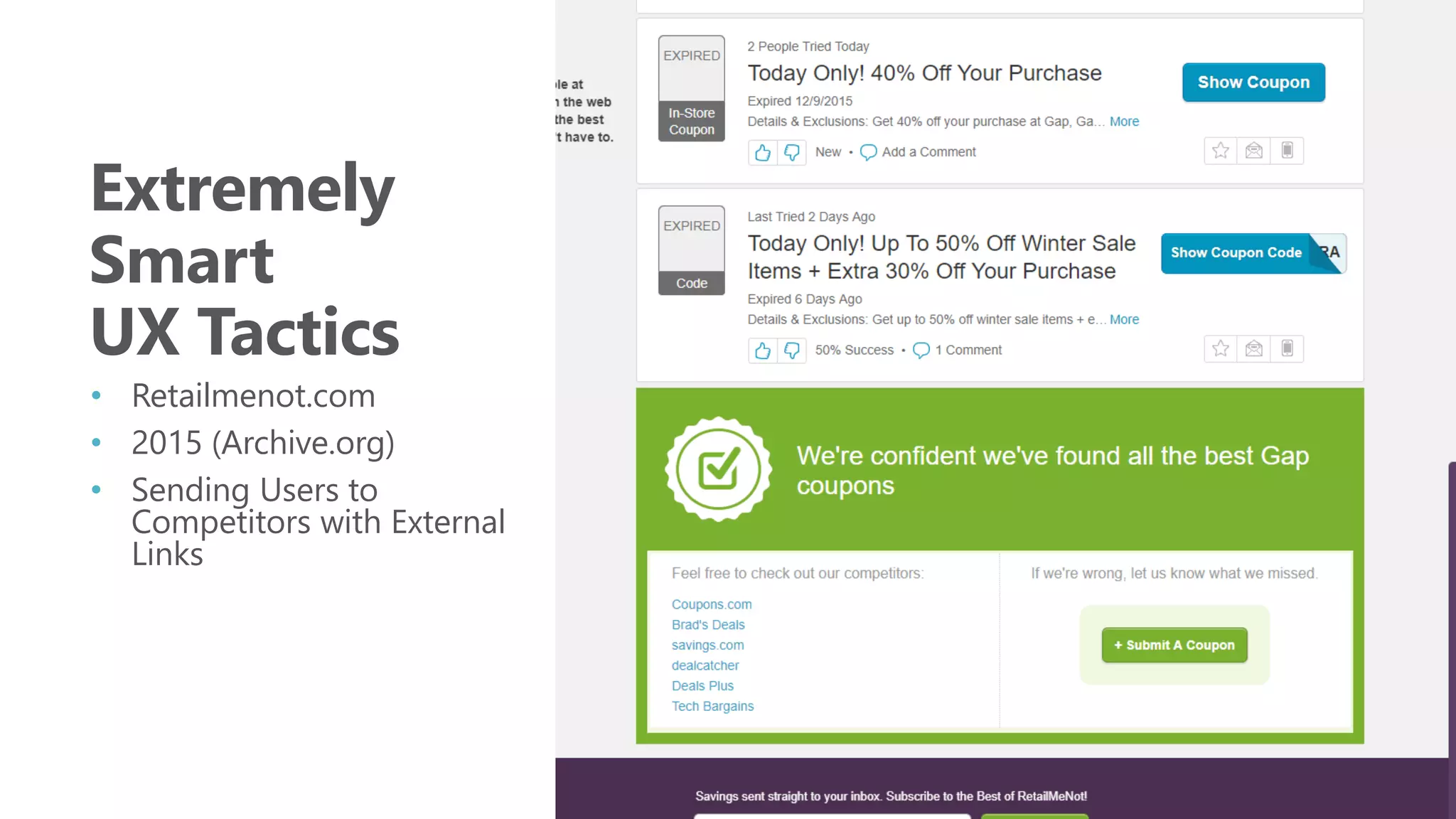
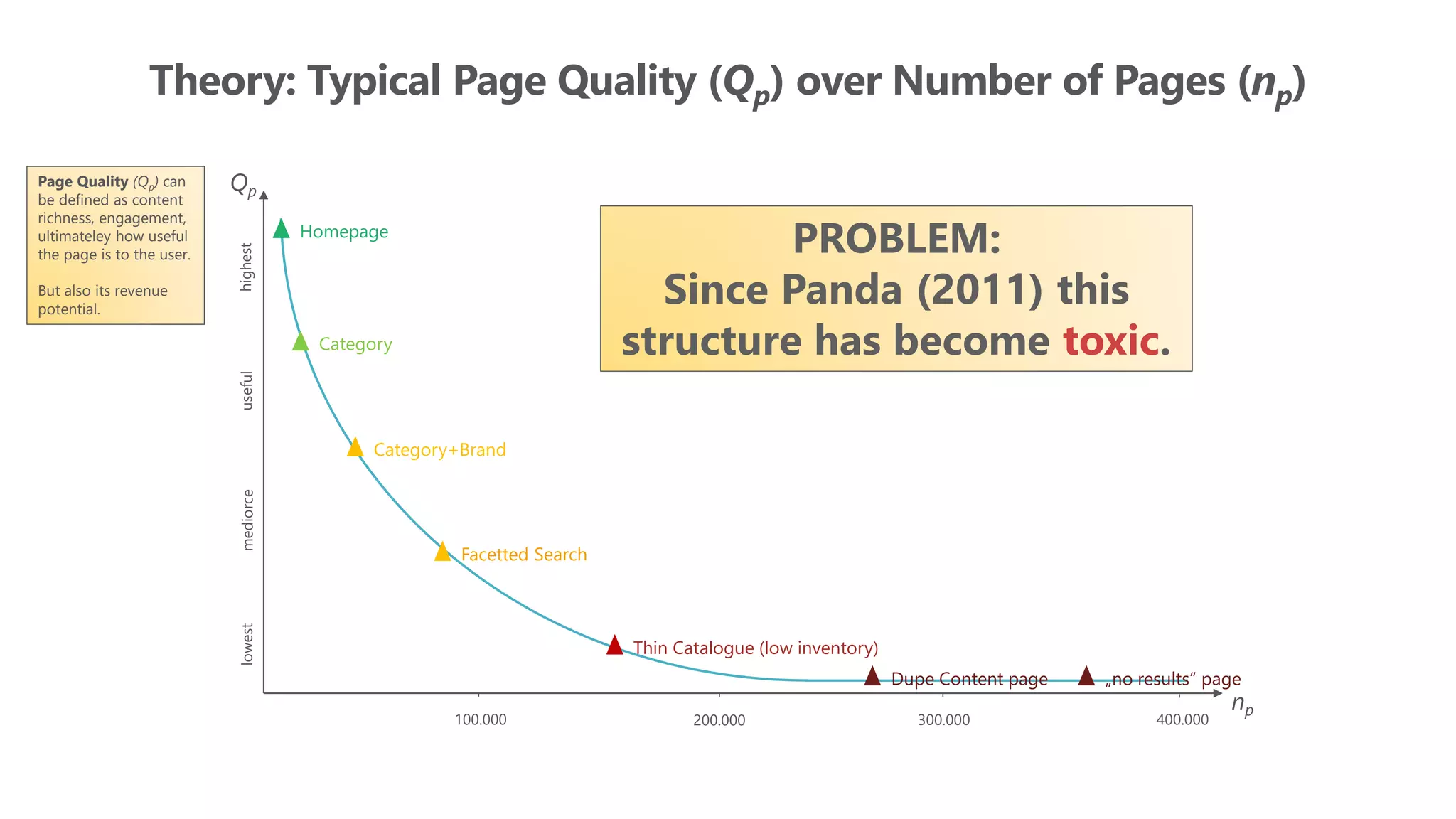
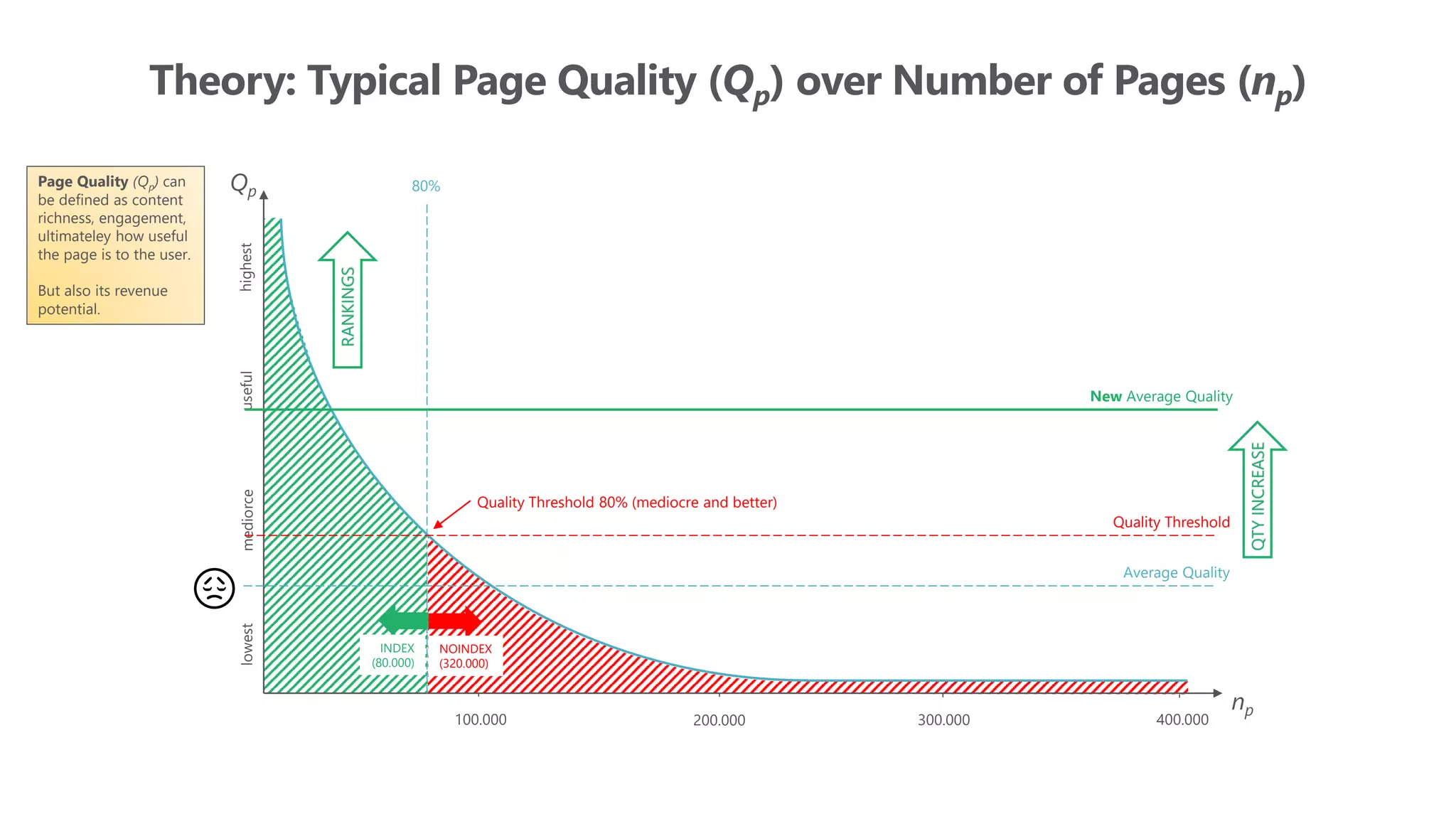
The document outlines the transition from traditional search engine optimization (SEO) to an AI-driven approach, emphasizing the importance of user experience and engagement metrics, particularly dwell time. It discusses the implications of Google's AI advancements on website ranking factors and how SEO practices must adapt to prioritize content quality and user satisfaction. The presentation also highlights the challenges and future prospects for SEO in light of evolving technology and user behavior.