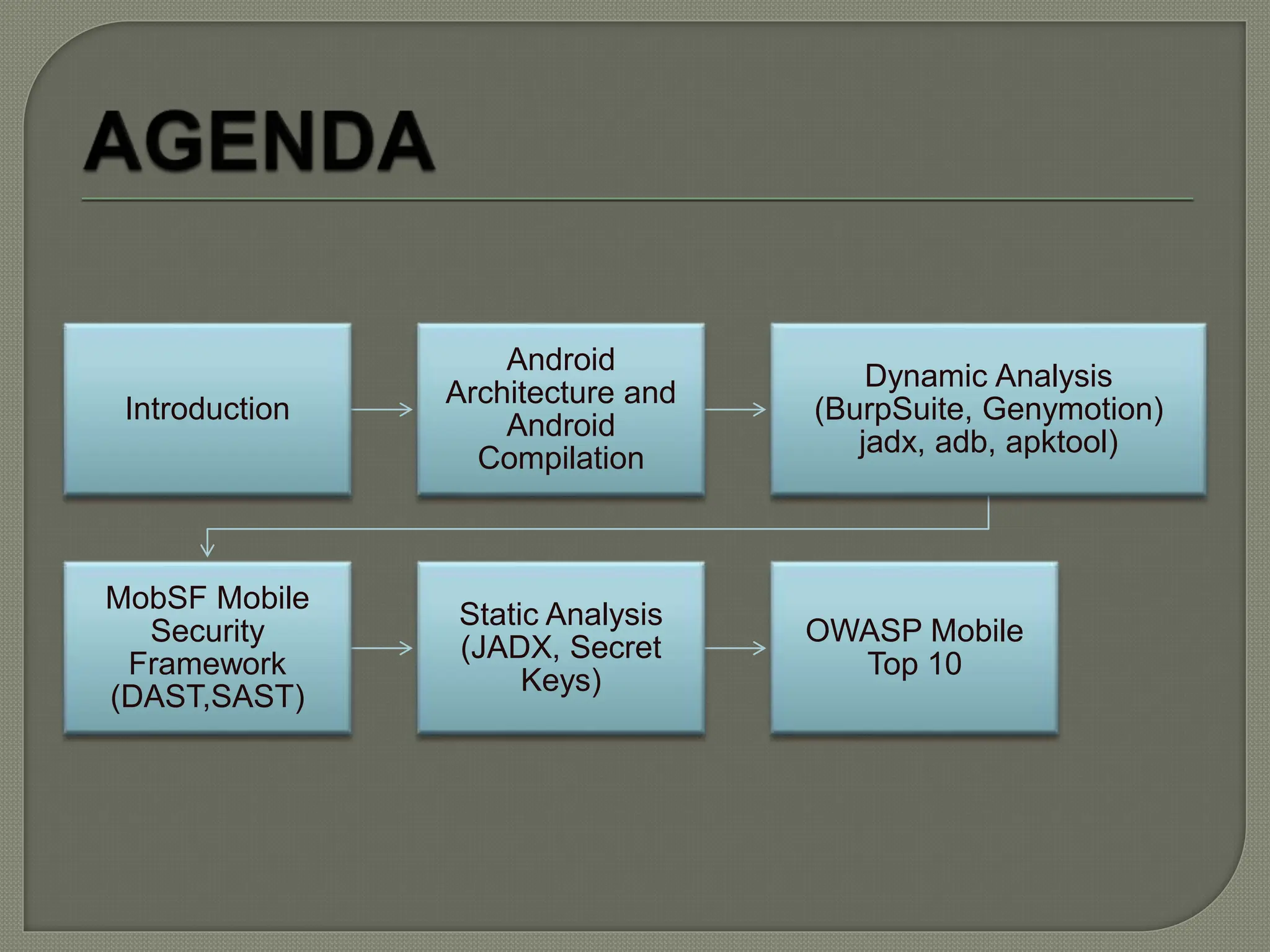
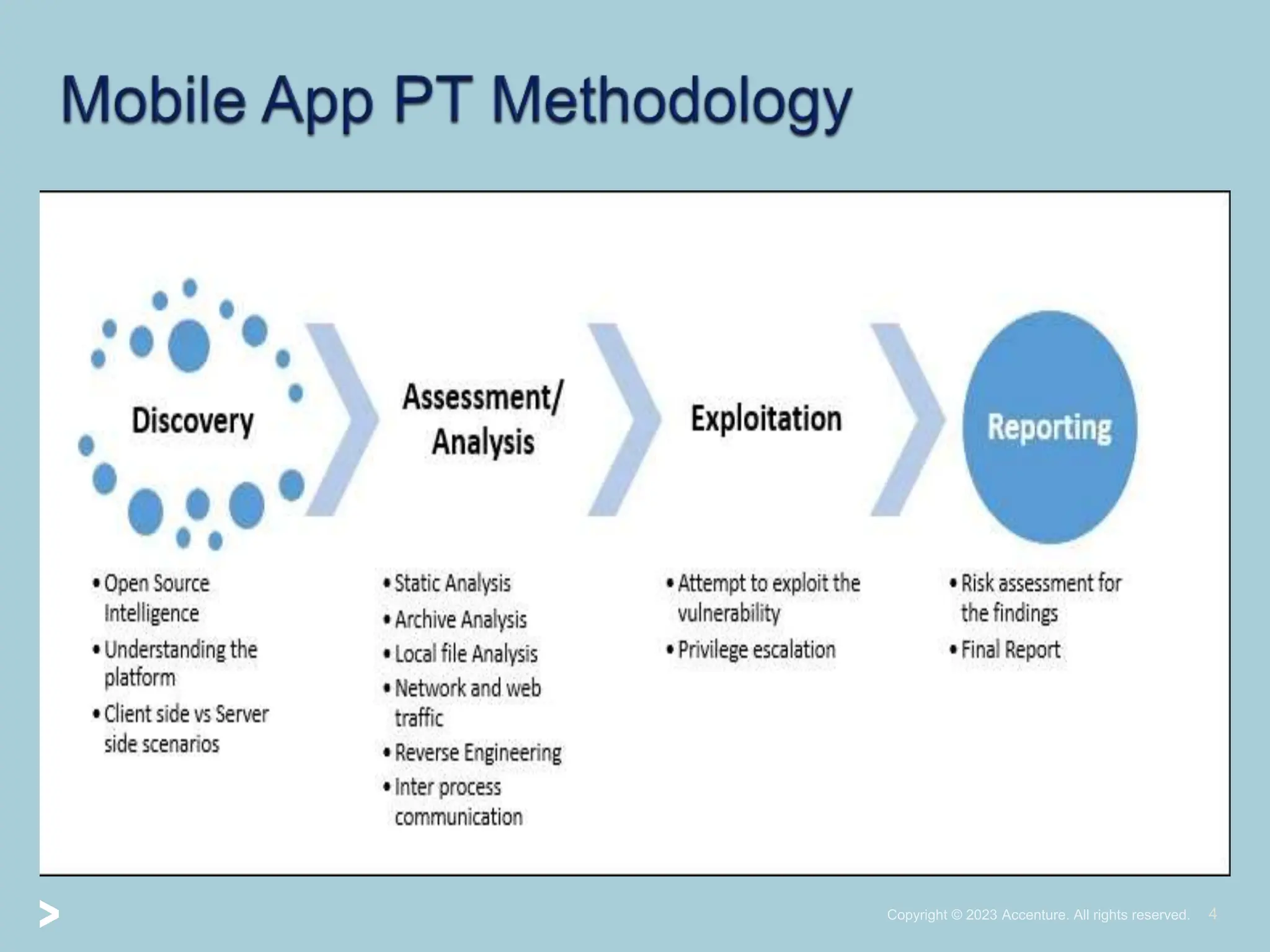
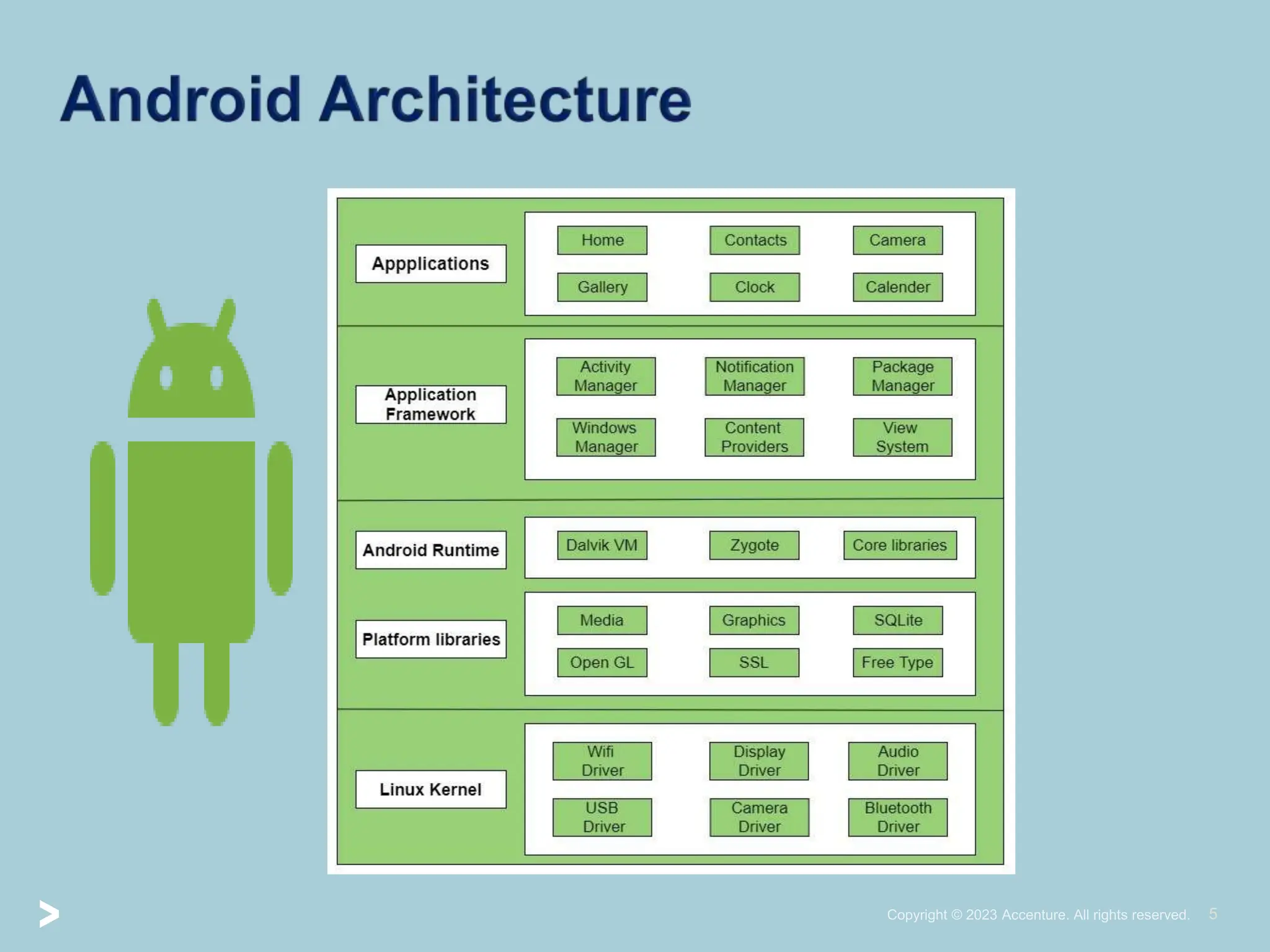
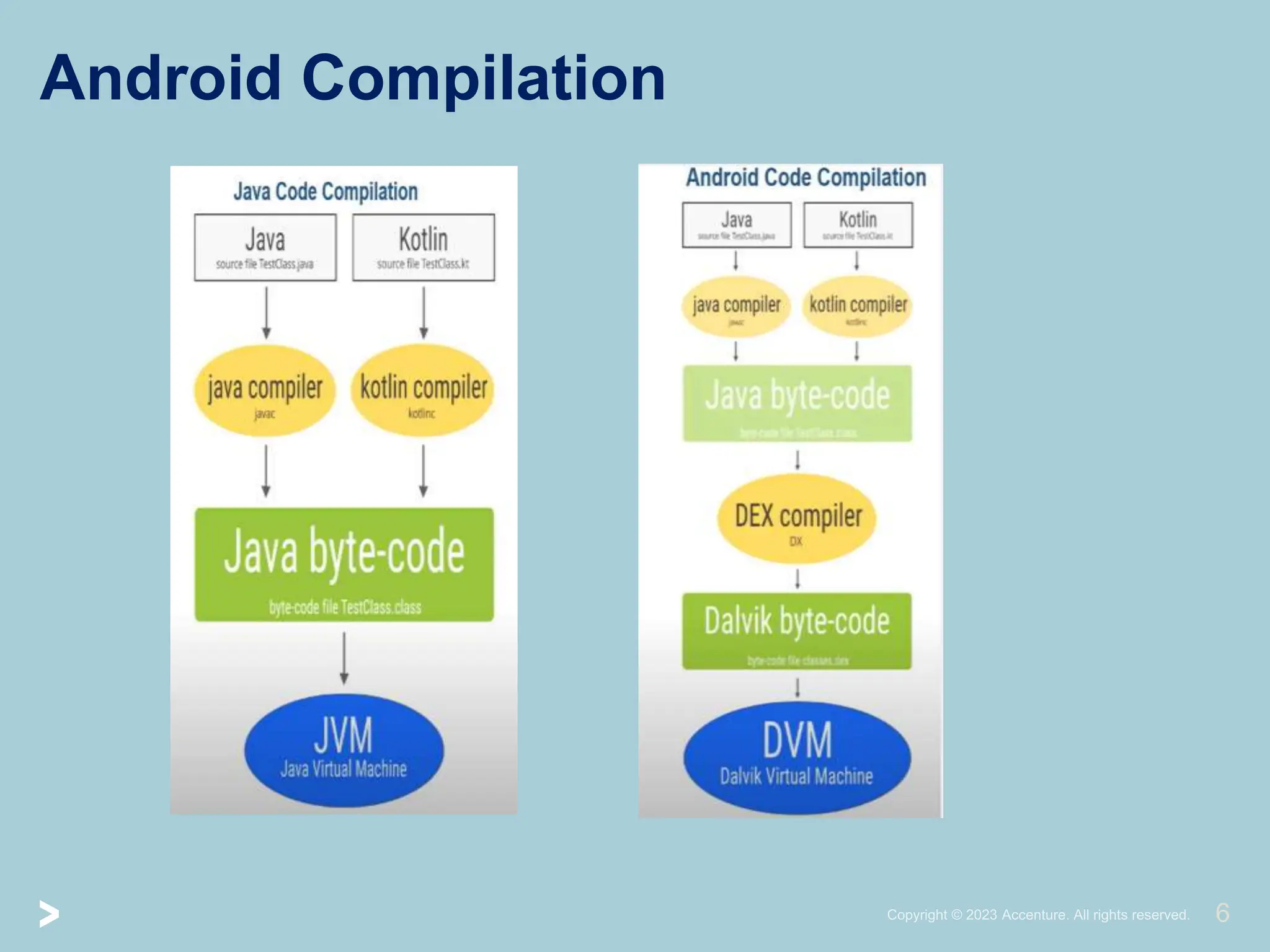
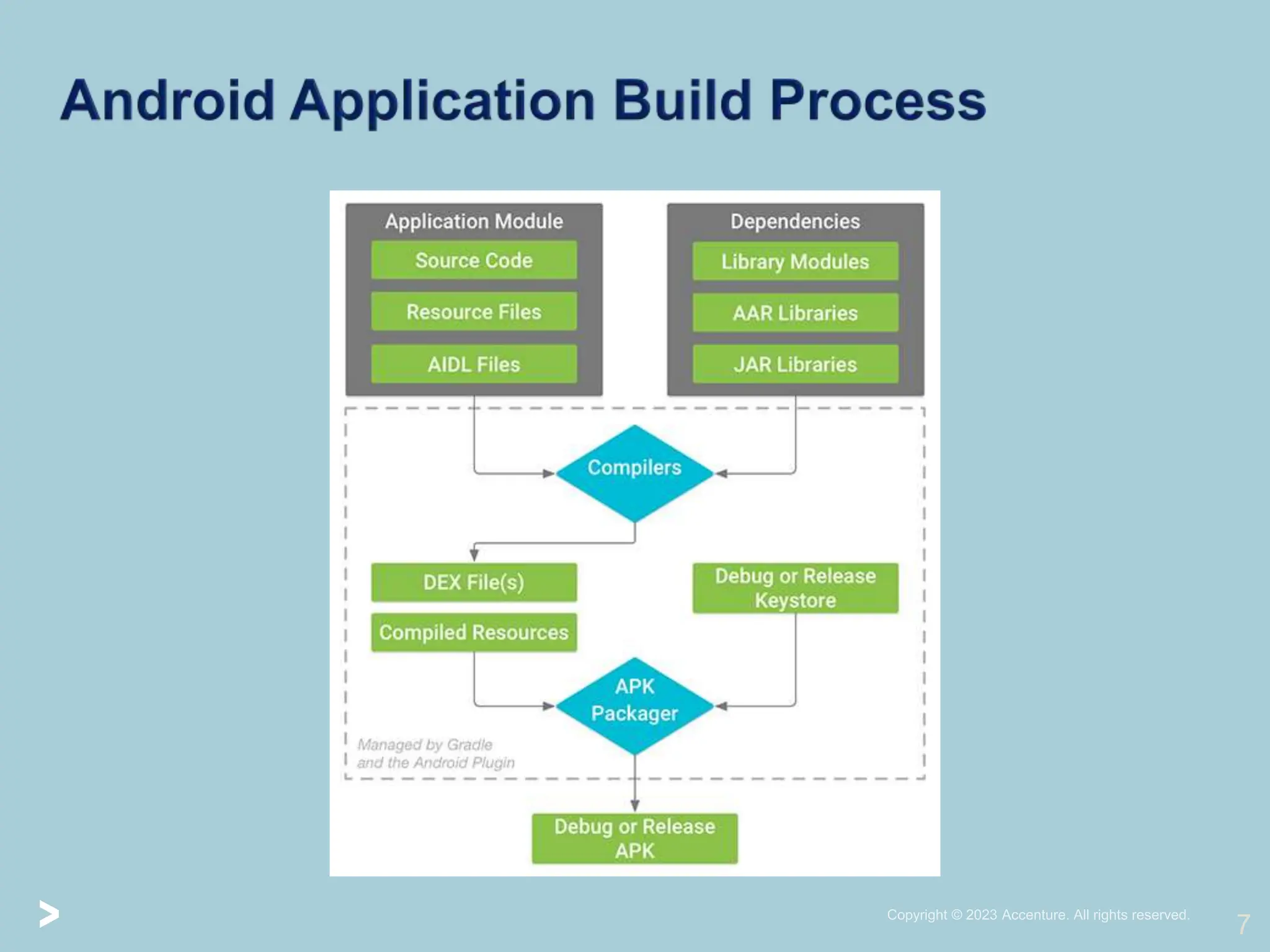
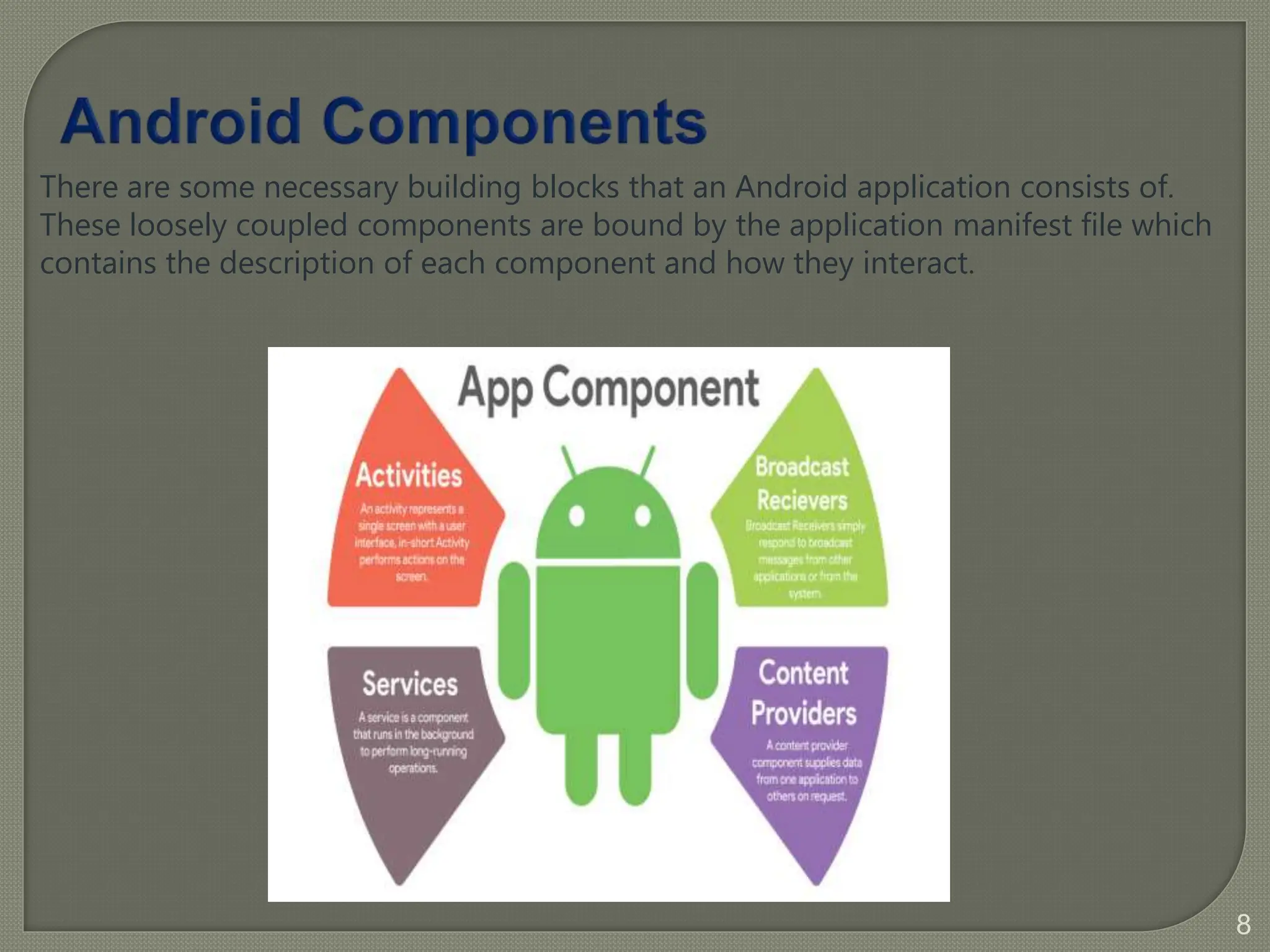
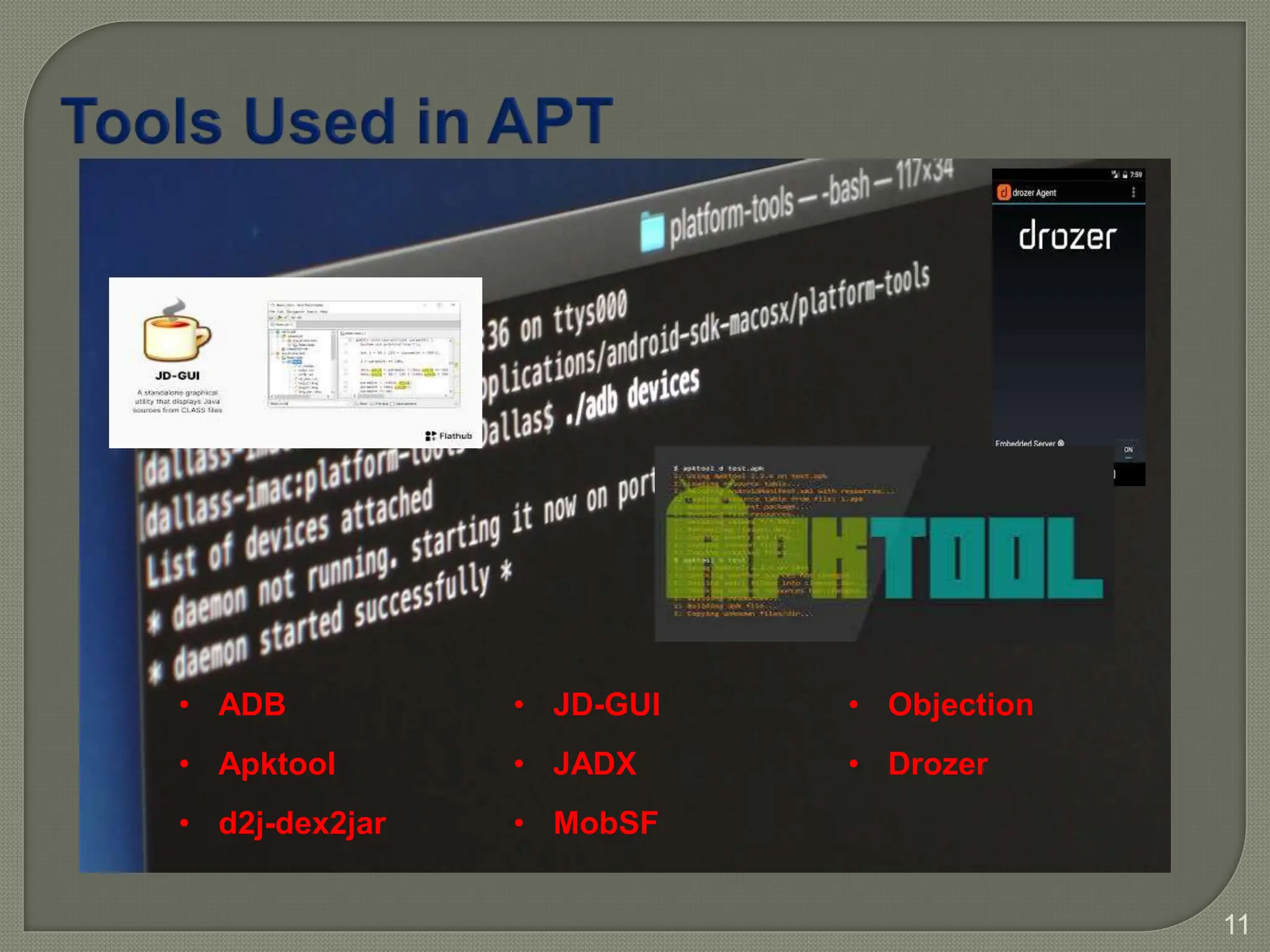
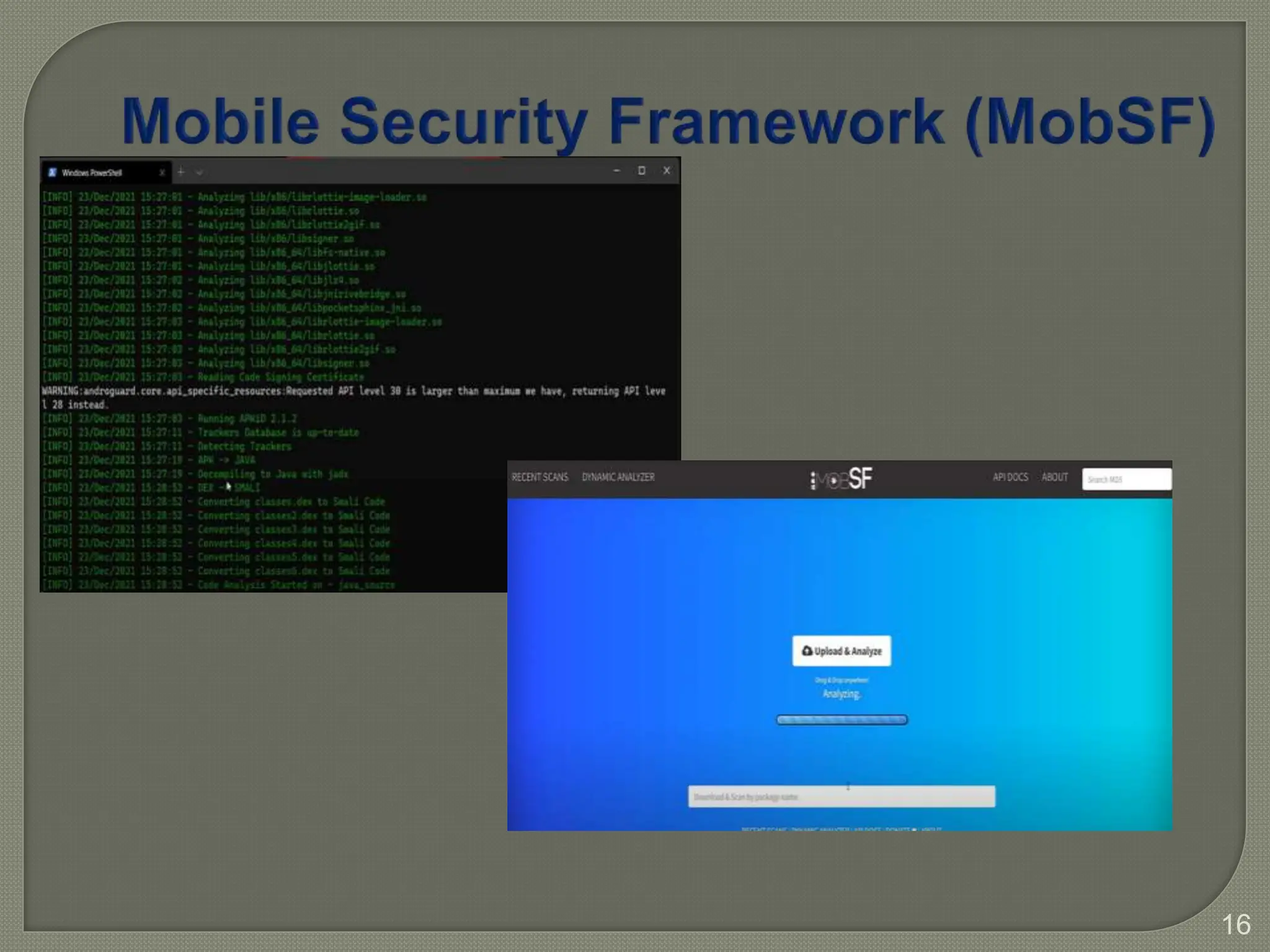
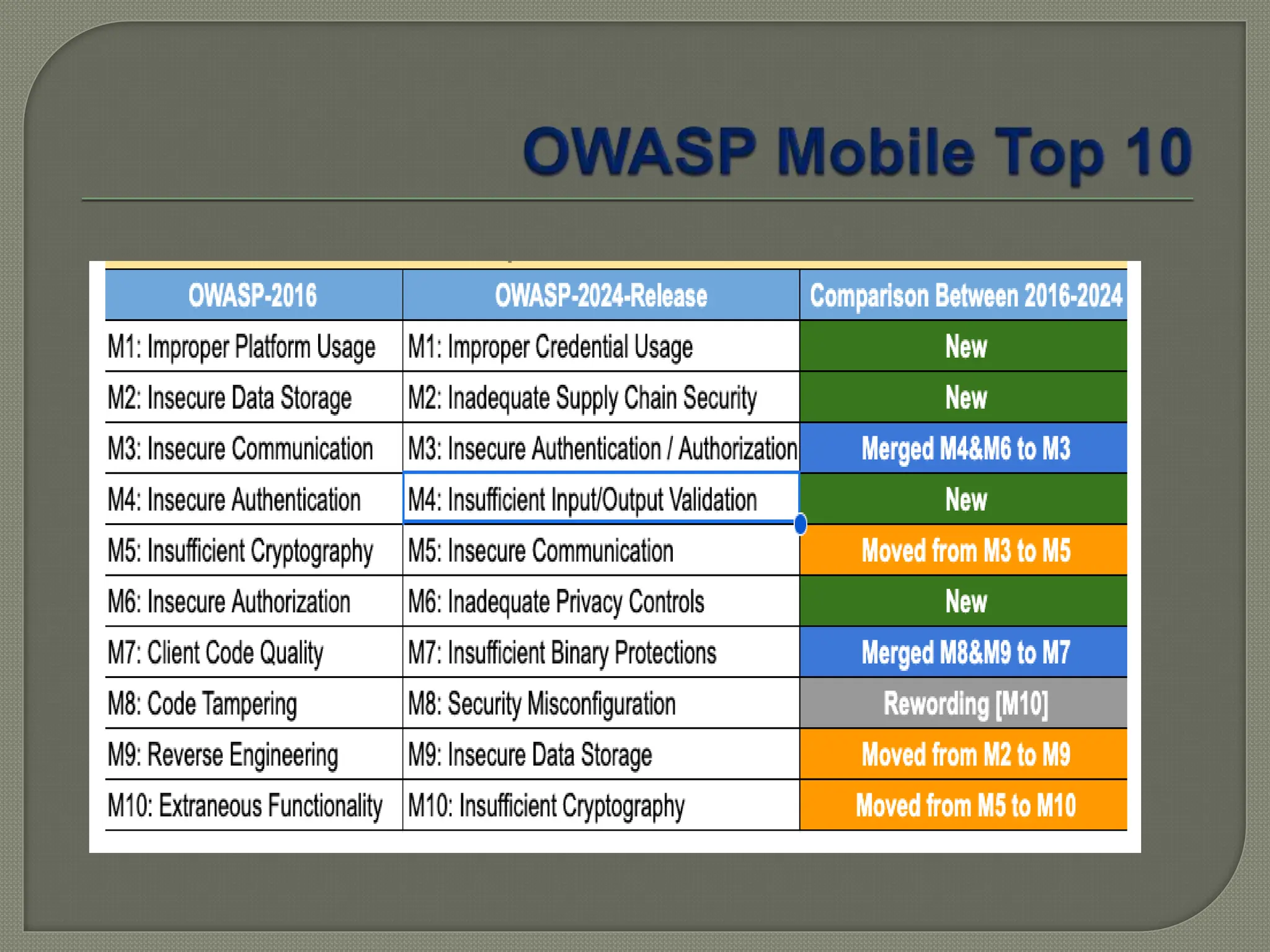
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to Android application security, focusing on architecture, compilation, and penetration testing. It outlines important components of Android applications, tools utilized for analysis (like ADB, Burp Suite, and MobSF), and explains the purpose and goals of Android penetration testing in identifying security flaws. Additionally, it covers key elements such as APK structure and dynamic/static analysis methods.