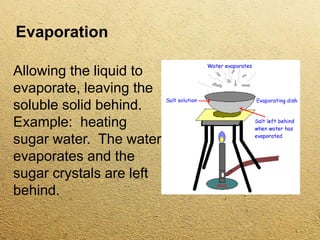
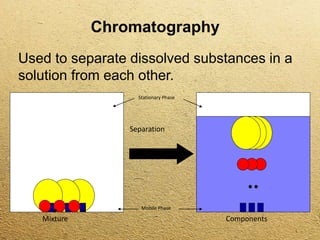
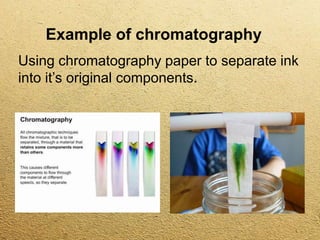
This document discusses different methods for separating mixtures without chemical reactions. It defines a mixture as multiple substances mixed without combining chemically. Various physical separation techniques are then described, including magnetism, hand separation, filtration, sieving, extraction and evaporation, and chromatography. Examples are provided to illustrate each technique.