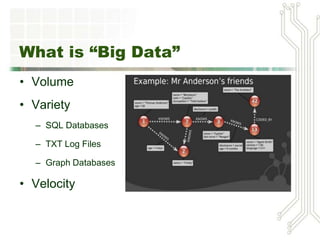
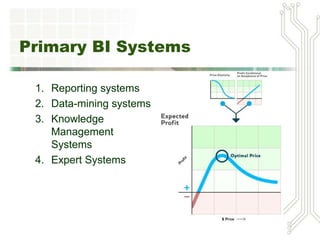
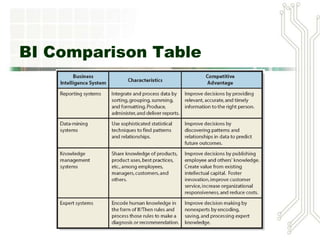
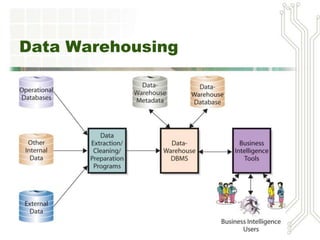
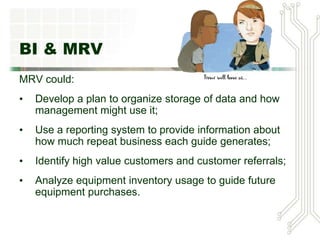
This document discusses big data and business intelligence. It defines big data as large volumes of varied data that is collected and processed rapidly. It outlines different types of primary BI systems including reporting systems, data mining systems, knowledge management systems, and expert systems. It also discusses challenges with raw data and the need for data warehousing to extract, clean, and prepare data from different sources for BI processing and analysis. Finally, it provides an example of how a mountain resort (MRV) could use BI and data warehousing to develop a data storage plan, generate reports on repeat business, identify high-value customers, and analyze equipment usage.