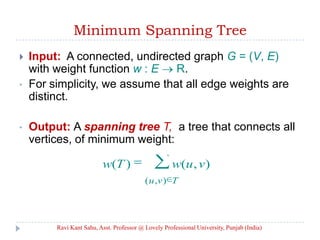
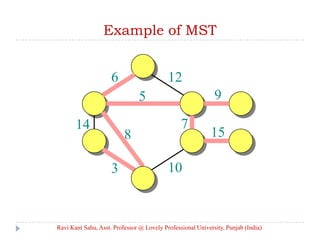
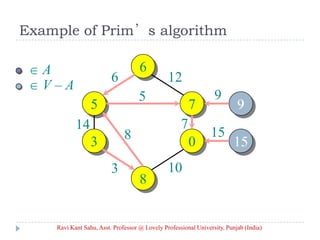
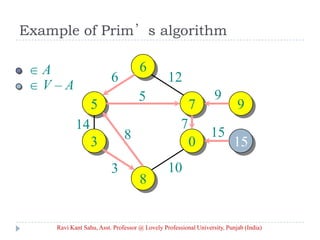
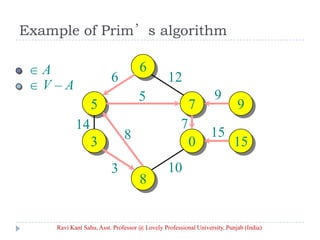
The document discusses minimum spanning trees (MST) in graph theory, detailing Prim's and Kruskal's algorithms for finding MSTs in connected, undirected graphs with distinct edge weights. Prim's algorithm uses a priority queue to maintain the minimum weight edges, while Kruskal's algorithm builds a forest and combines trees using a union-find structure. Both algorithms have a complexity of O(e log v).


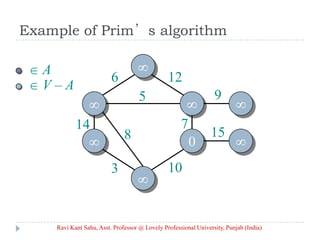
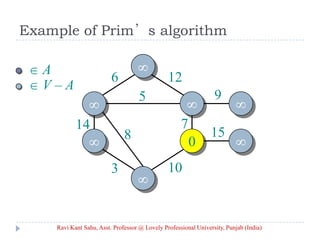
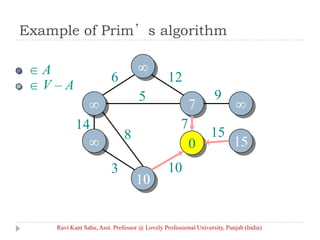
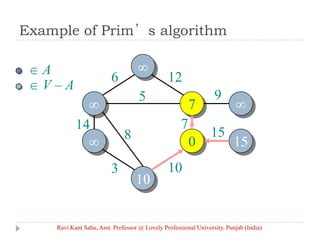
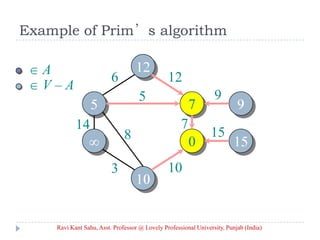
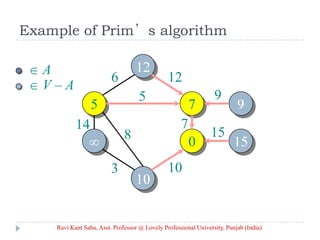
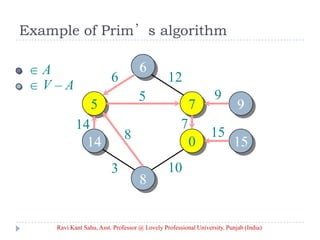
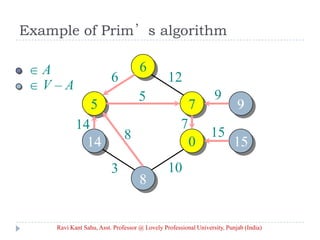
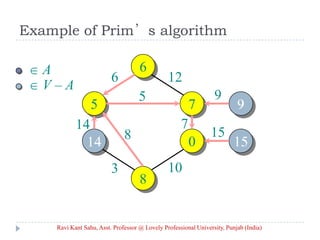
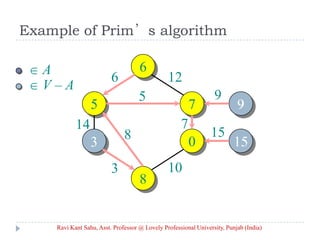
![Prim’s Algorithm
IDEA: Maintain V – A as a priority queue Q. Key
each vertex in Q with the weight of the least-
weight edge connecting it to a vertex in A.
Q V
key[v] for all v V
key[s] 0 for some arbitrary s V
while Q
do u EXTRACT-MIN(Q)
for each v Adj[u]
do if v Q and w(u, v) < key[v]
then key[v] w(u, v) ⊳ DECREASE-KEY
[v] u
Ravi Kant Sahu, Asst. Professor @ Lovely Professional University, Punjab (India)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/minimum-20spanning-20tree-140416091422-phpapp01/85/Minimum-spanning-tree-5-320.jpg)


![Kruskal’s Algorithm
1. A
2. for each vertex v V[G]
3.do MAKE-SET(v)
4.short the edges of E into non-decreasing order
by weight.
5.for each edge (u, v) E, taken in non-decreasing order
by weight.
6.do if FIND-SET(u) != FIND-SET(v)
7. then, A A U {(u, v)}
8. UNION(u, v)
9.return A
Ravi Kant Sahu, Asst. Professor @ Lovely Professional University, Punjab (India)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/minimum-20spanning-20tree-140416091422-phpapp01/85/Minimum-spanning-tree-21-320.jpg)

