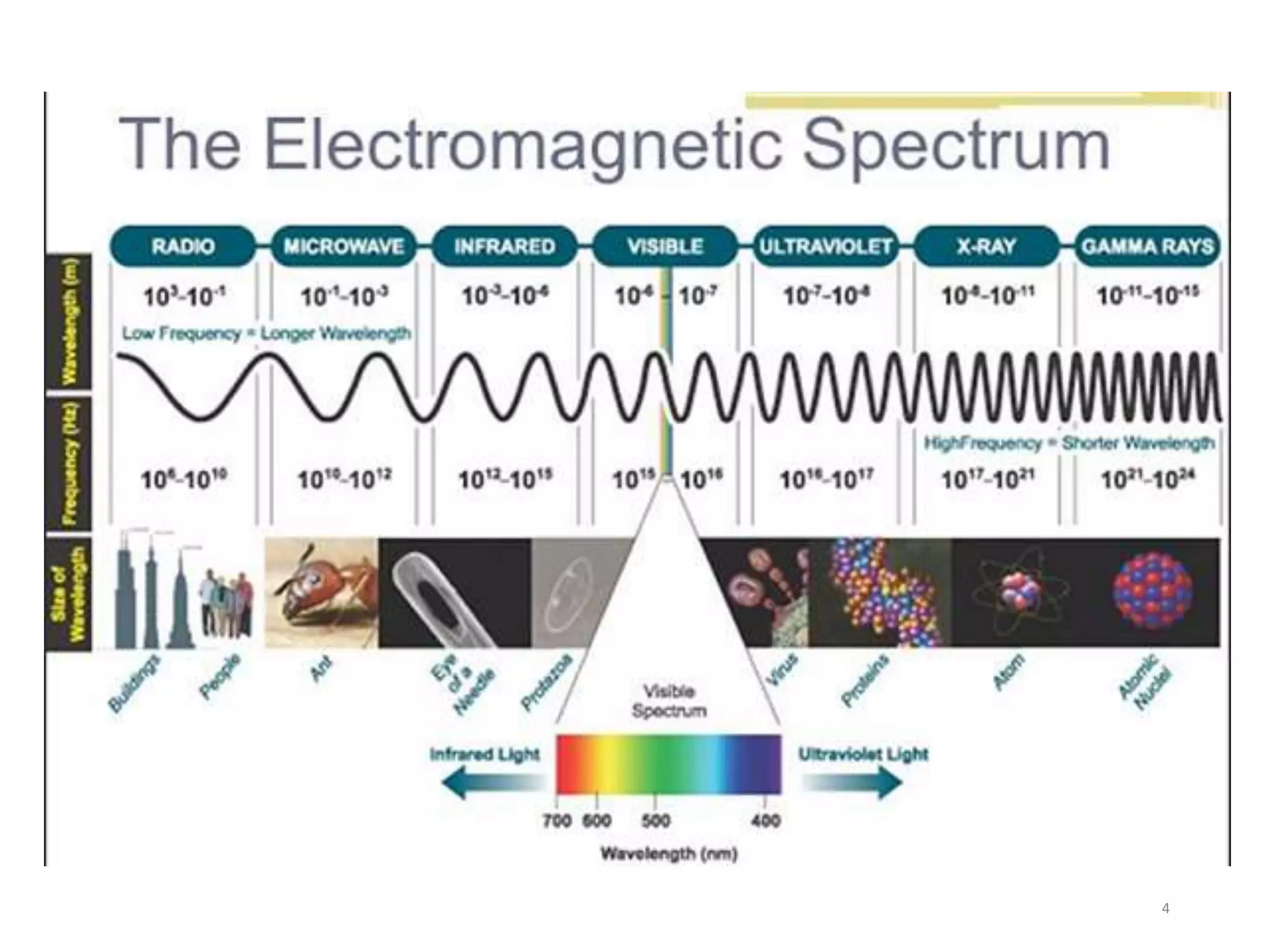
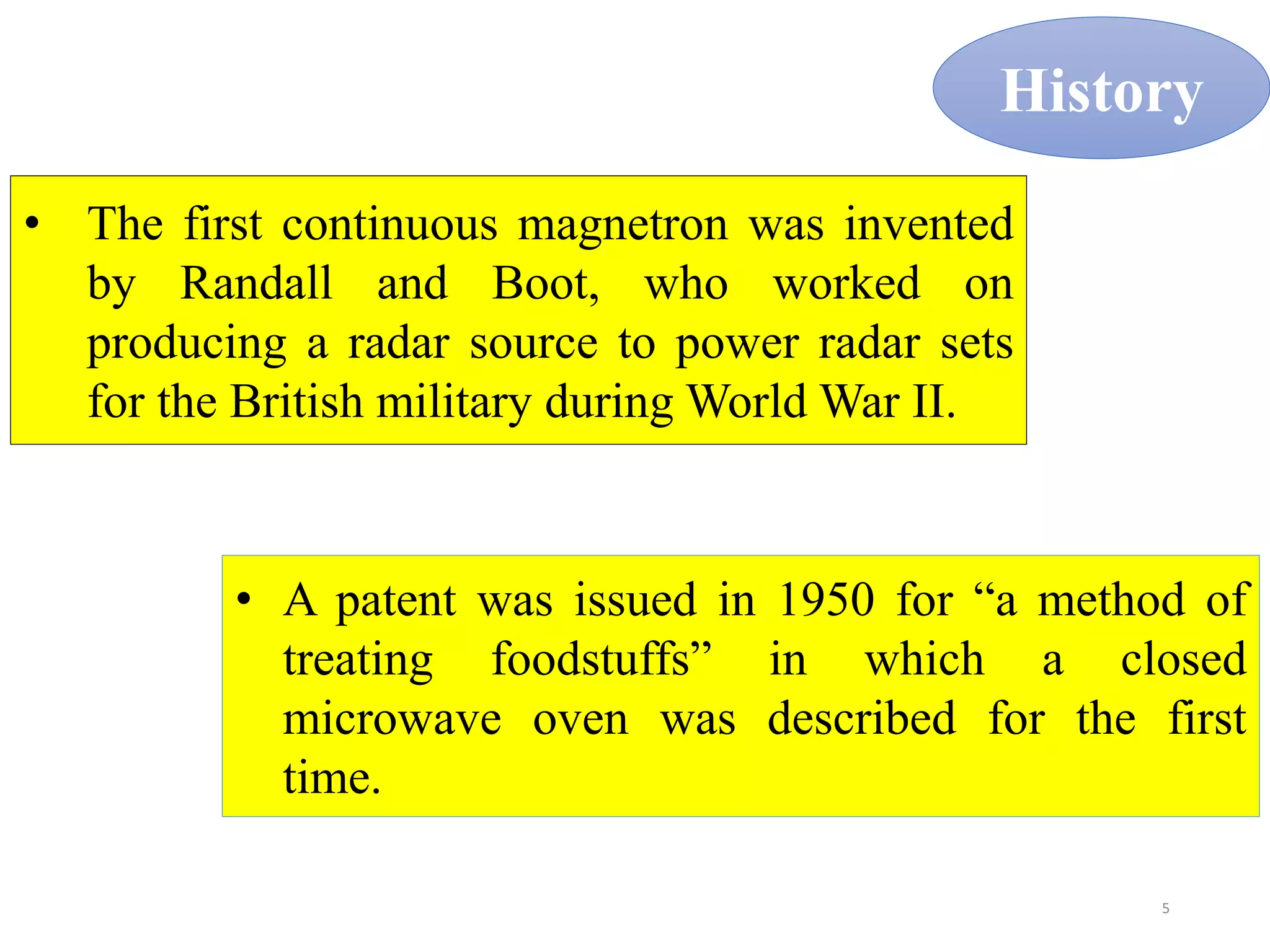
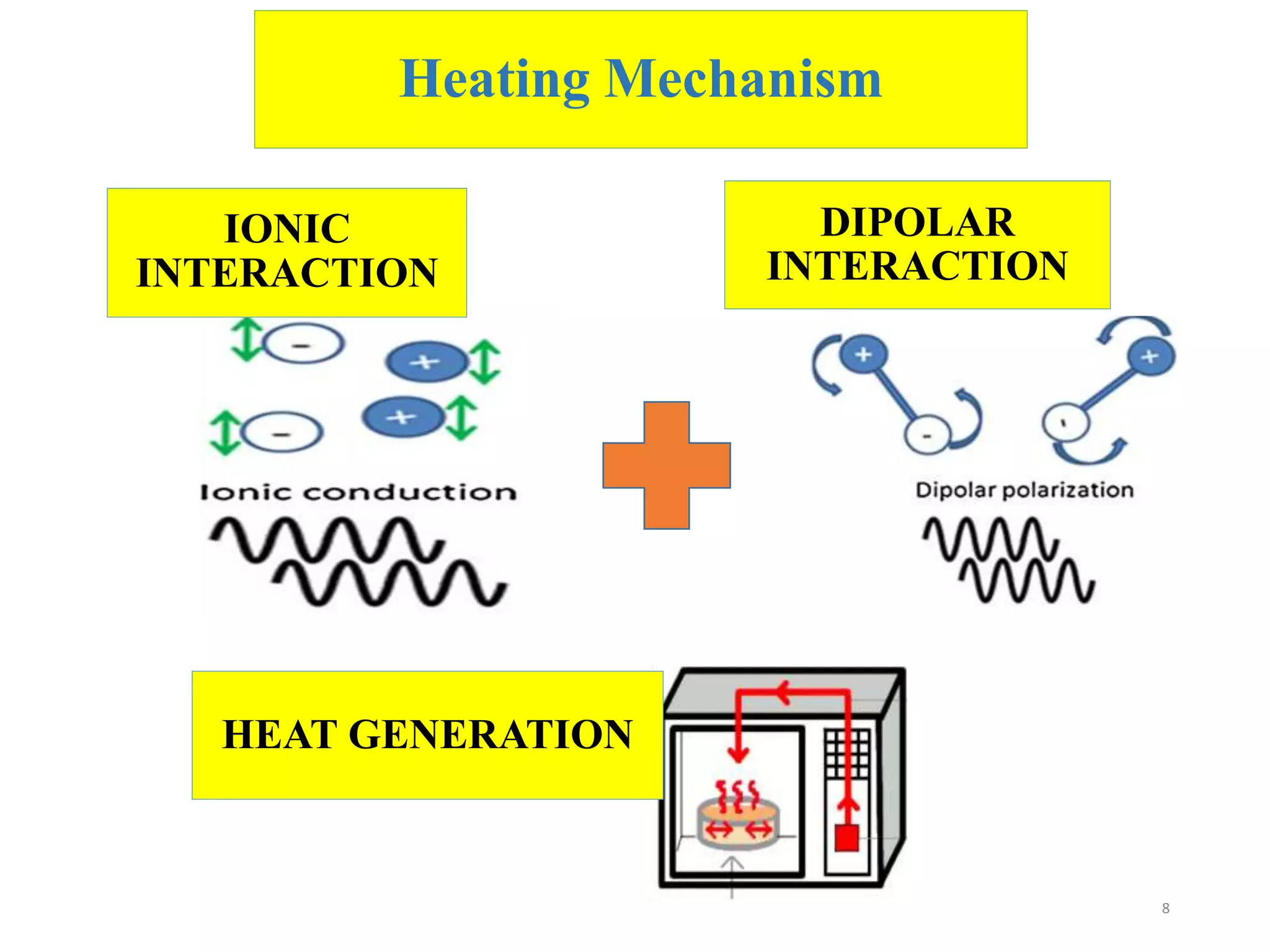
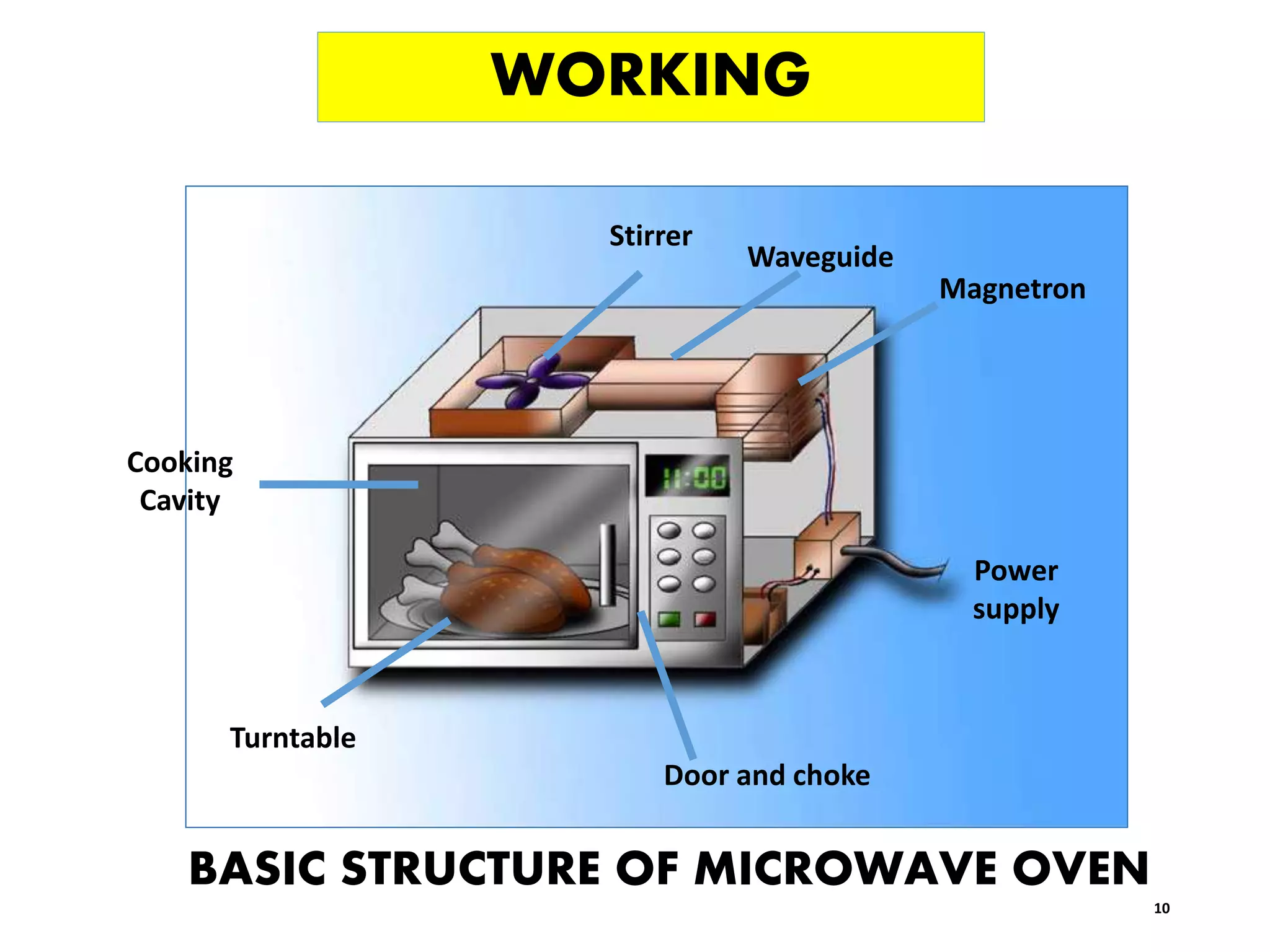
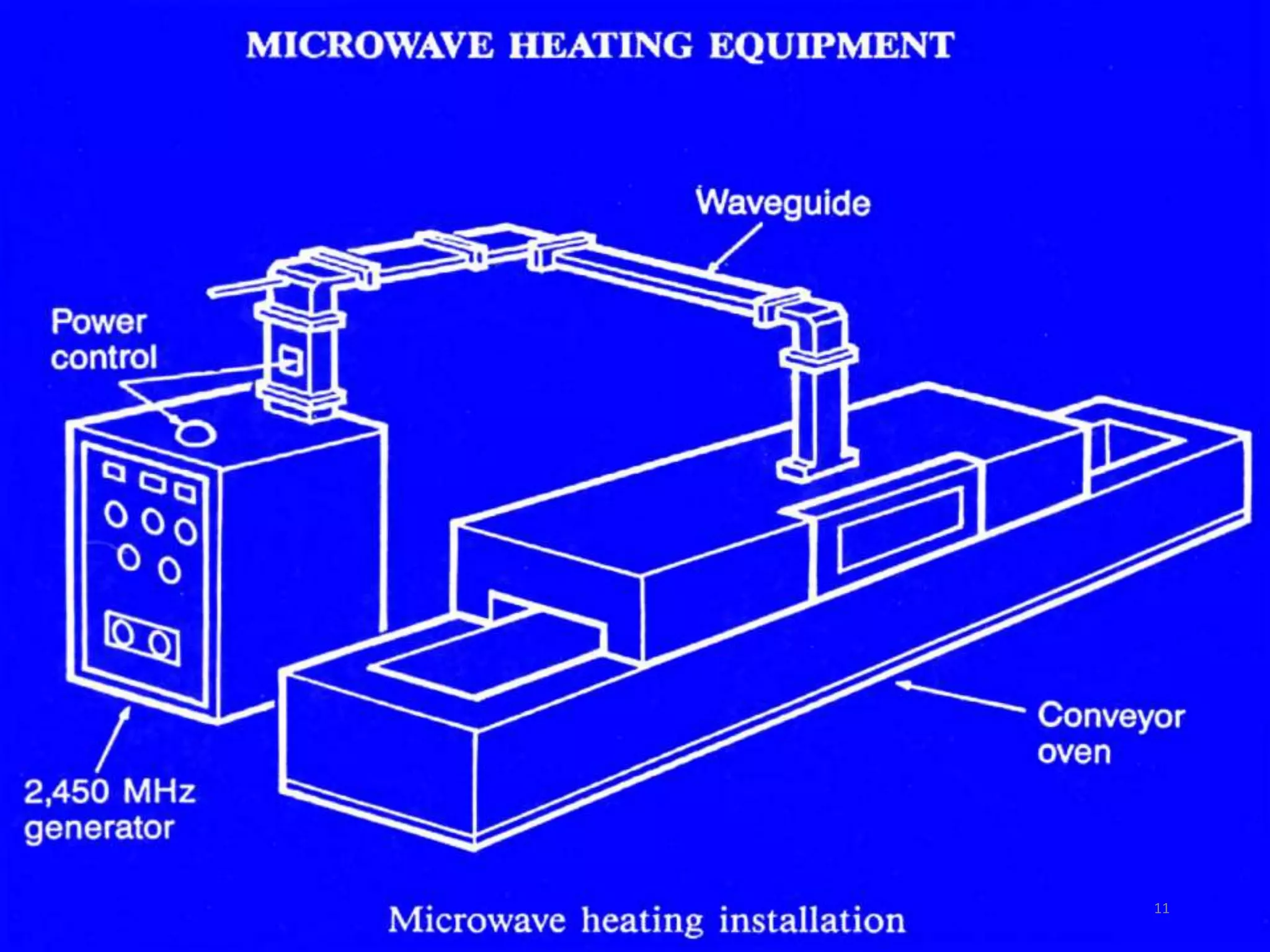
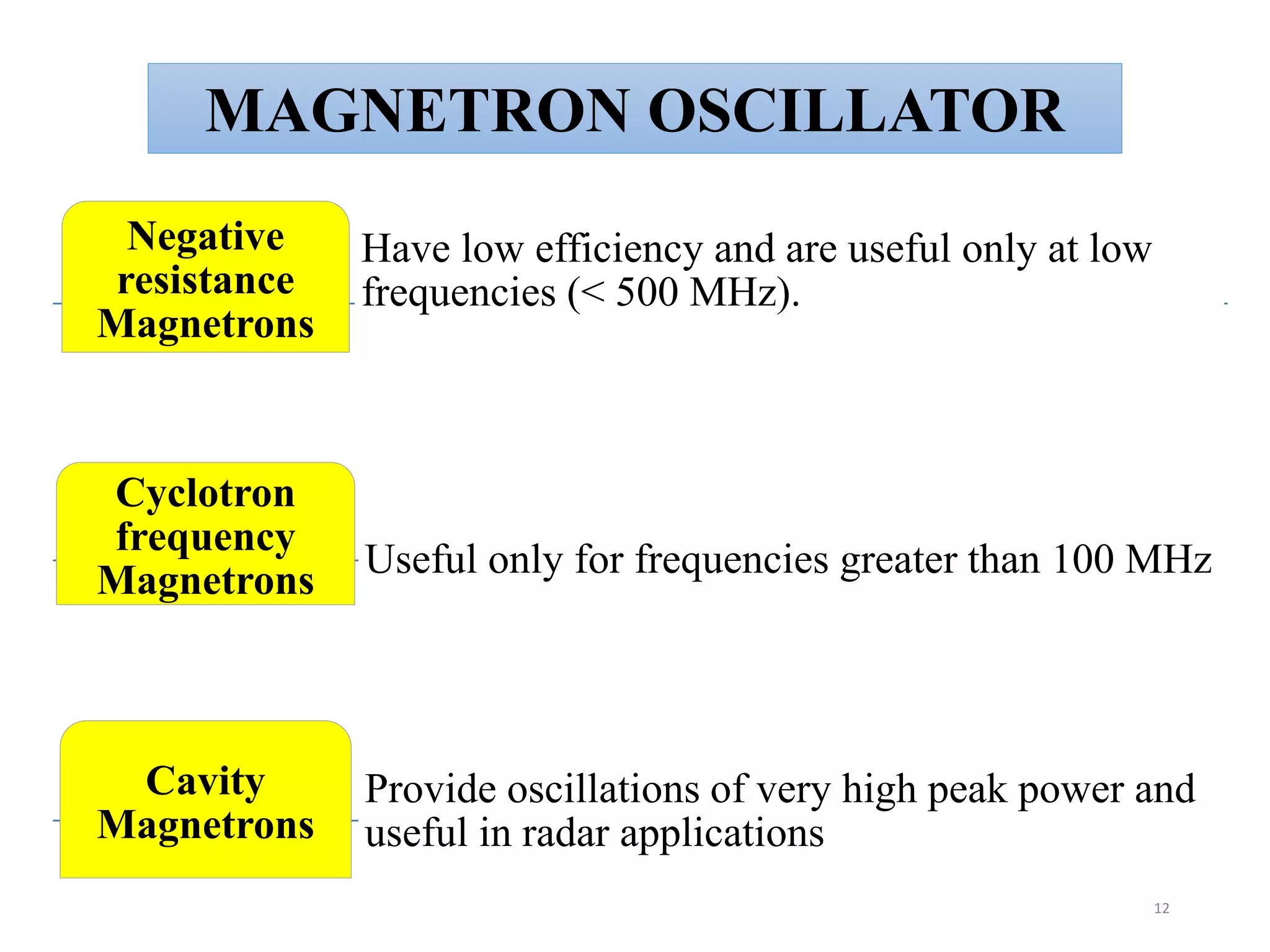
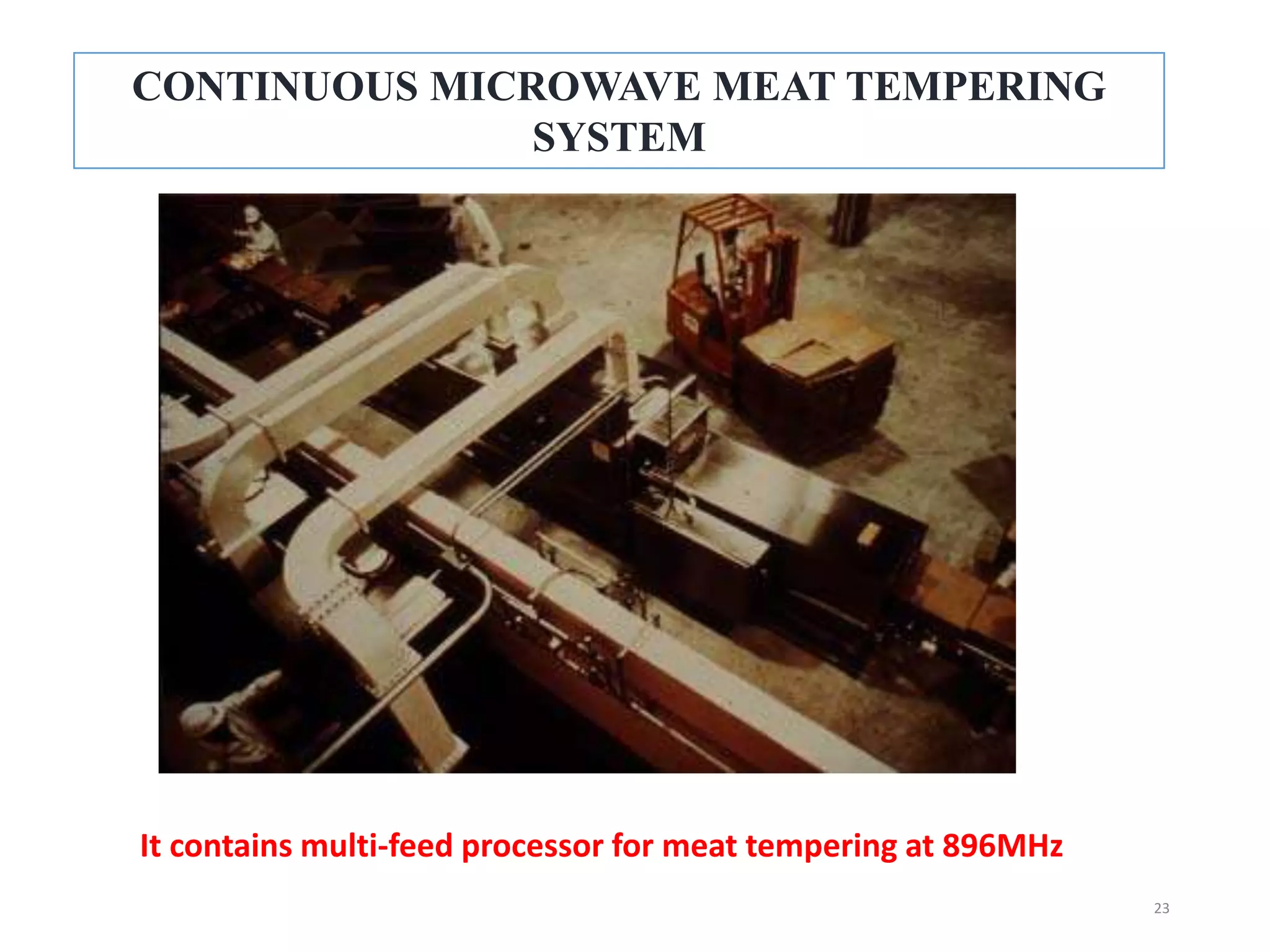
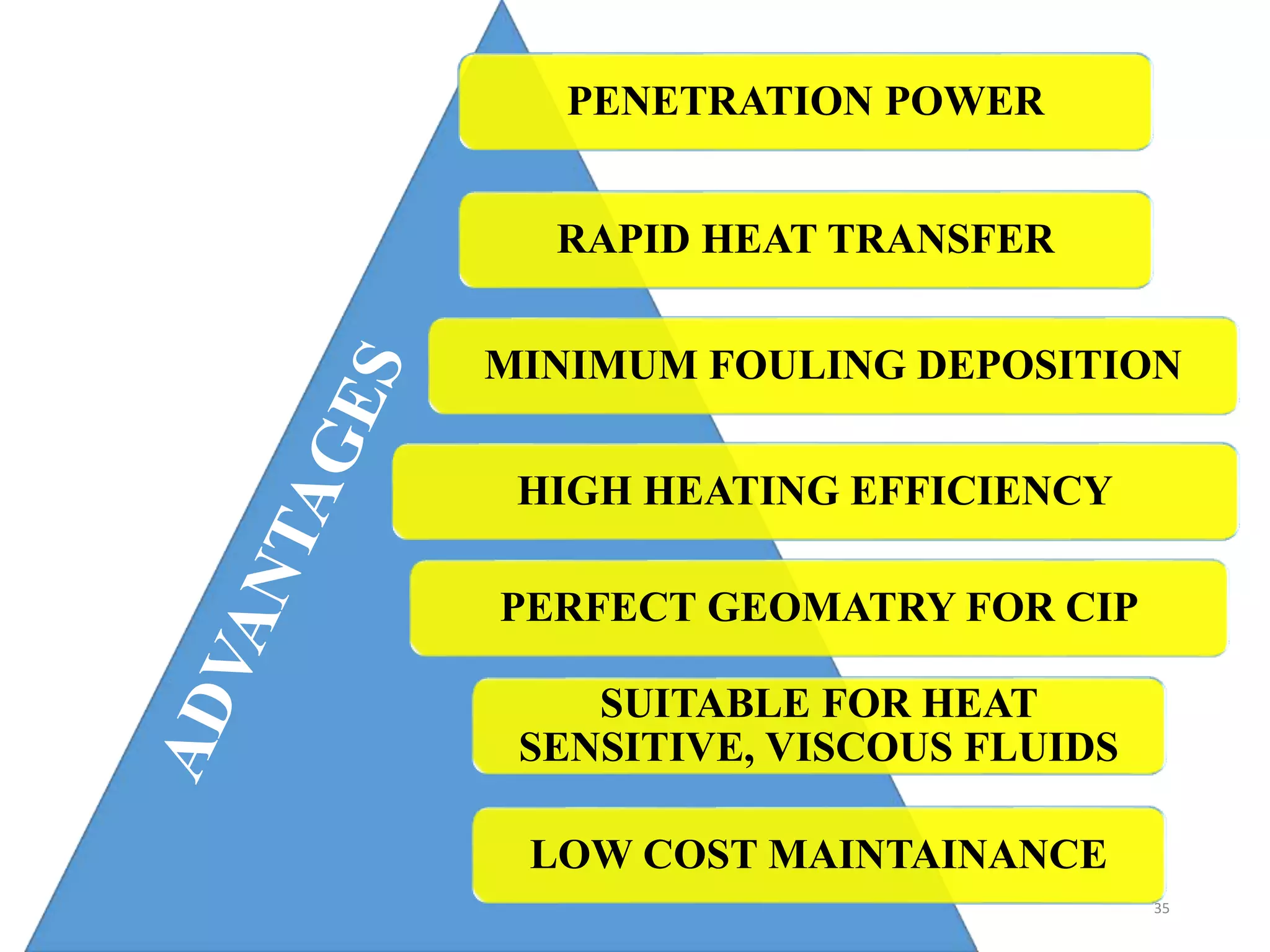
Microwave processing is a technique that uses electromagnetic waves to heat and cook food. Microwaves work by causing water and other polar molecules in food to vibrate rapidly, generating heat. A typical microwave oven contains a magnetron that generates microwaves which pass into a cooking cavity to heat food. Microwave heating is more energy efficient than conventional heating as it heats food directly rather than heating the surrounding air. Common applications of microwave processing in the food industry include cooking, baking, thawing, tempering, drying, blanching, pasteurization and sterilization. However, some controversies exist around the effects of microwaves on food quality and potential health impacts from leakage.