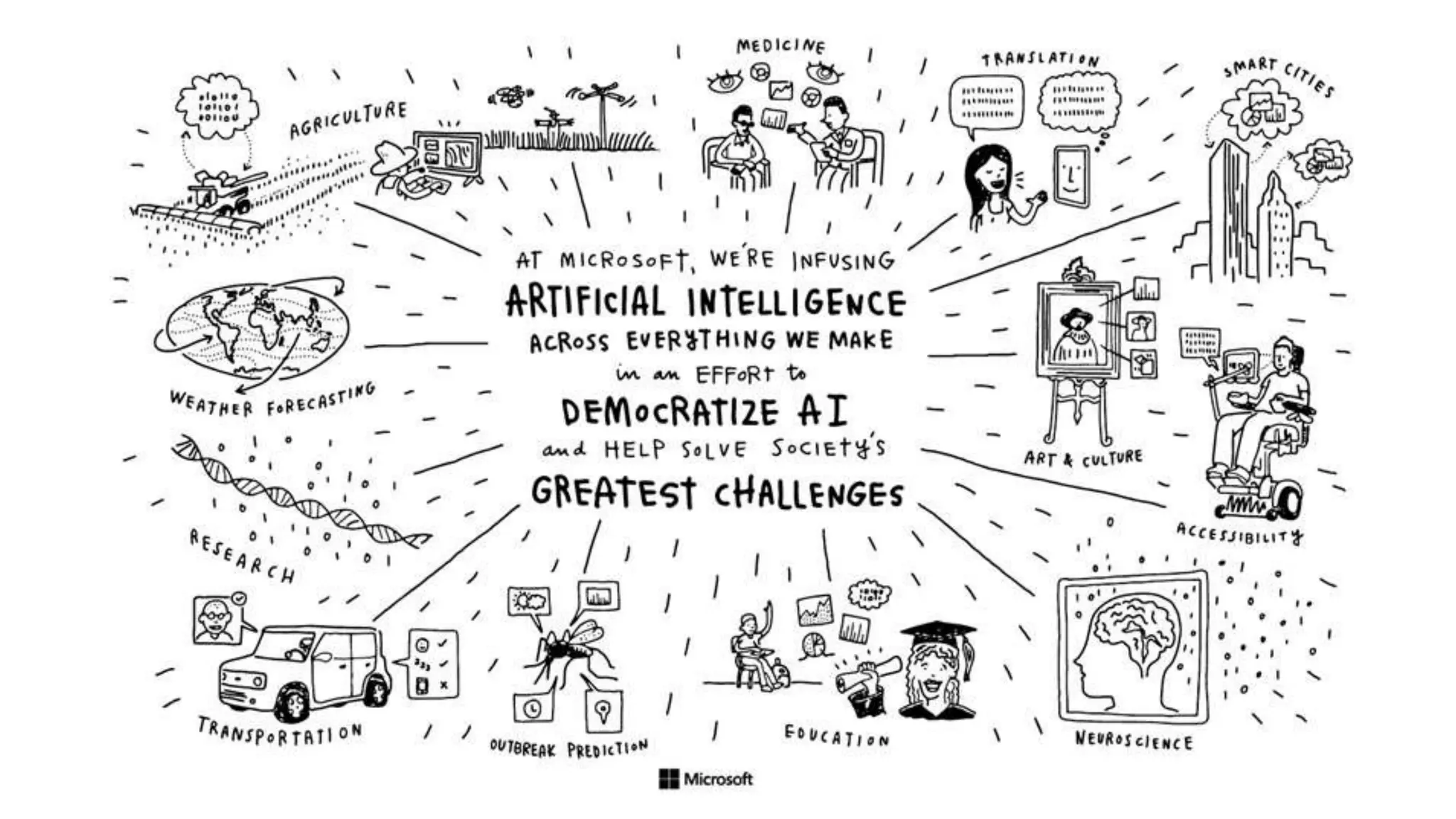
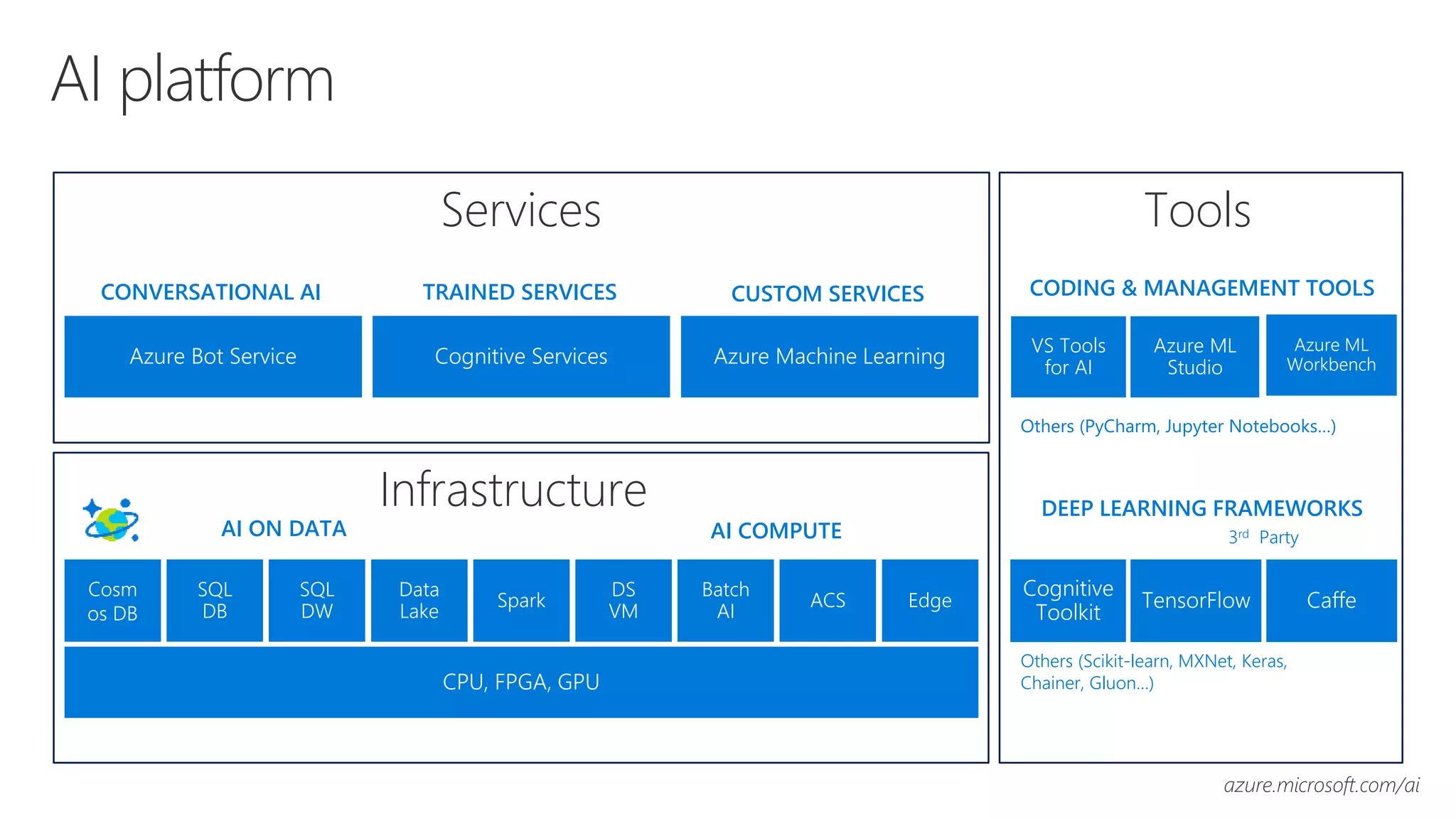
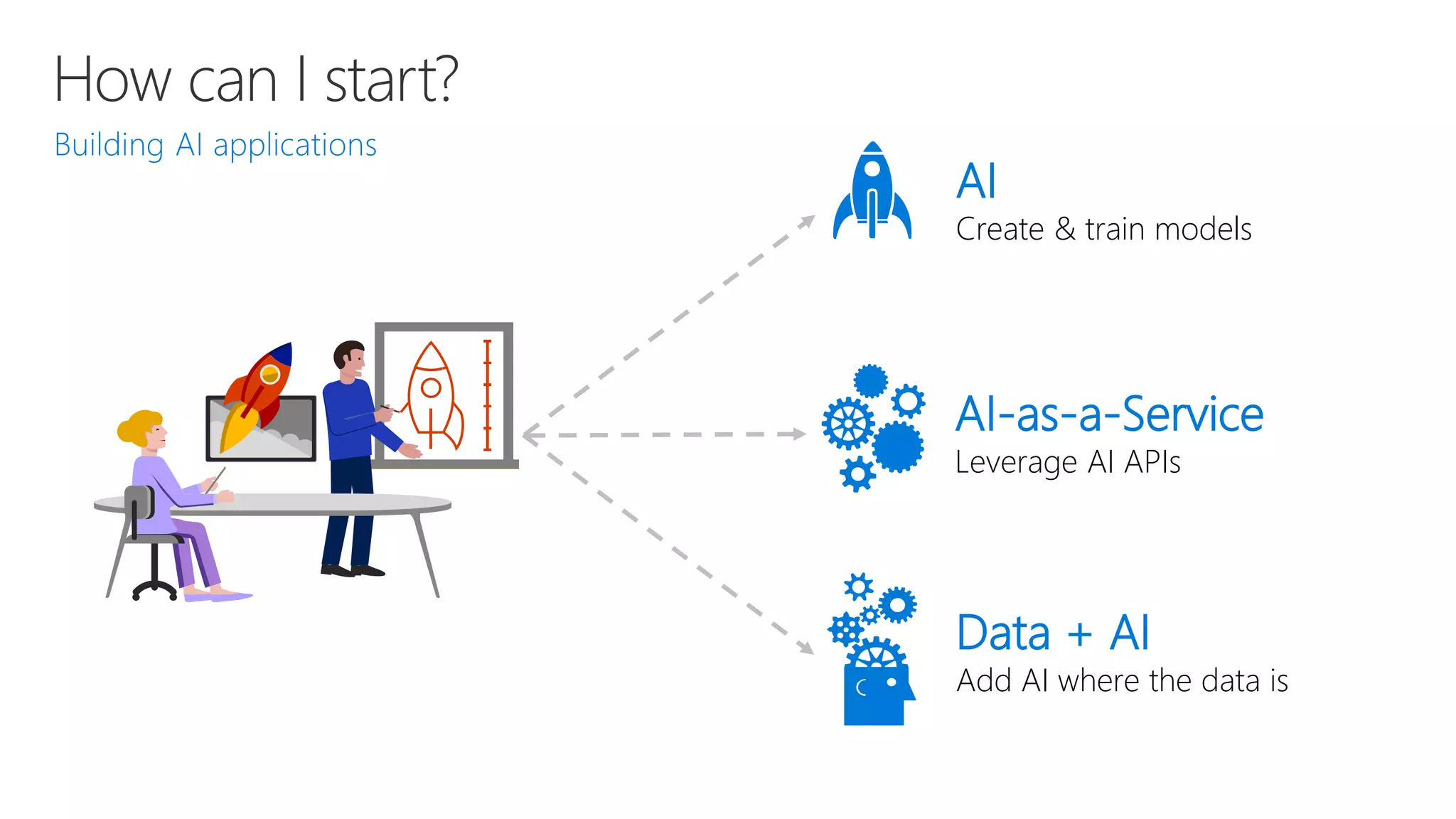
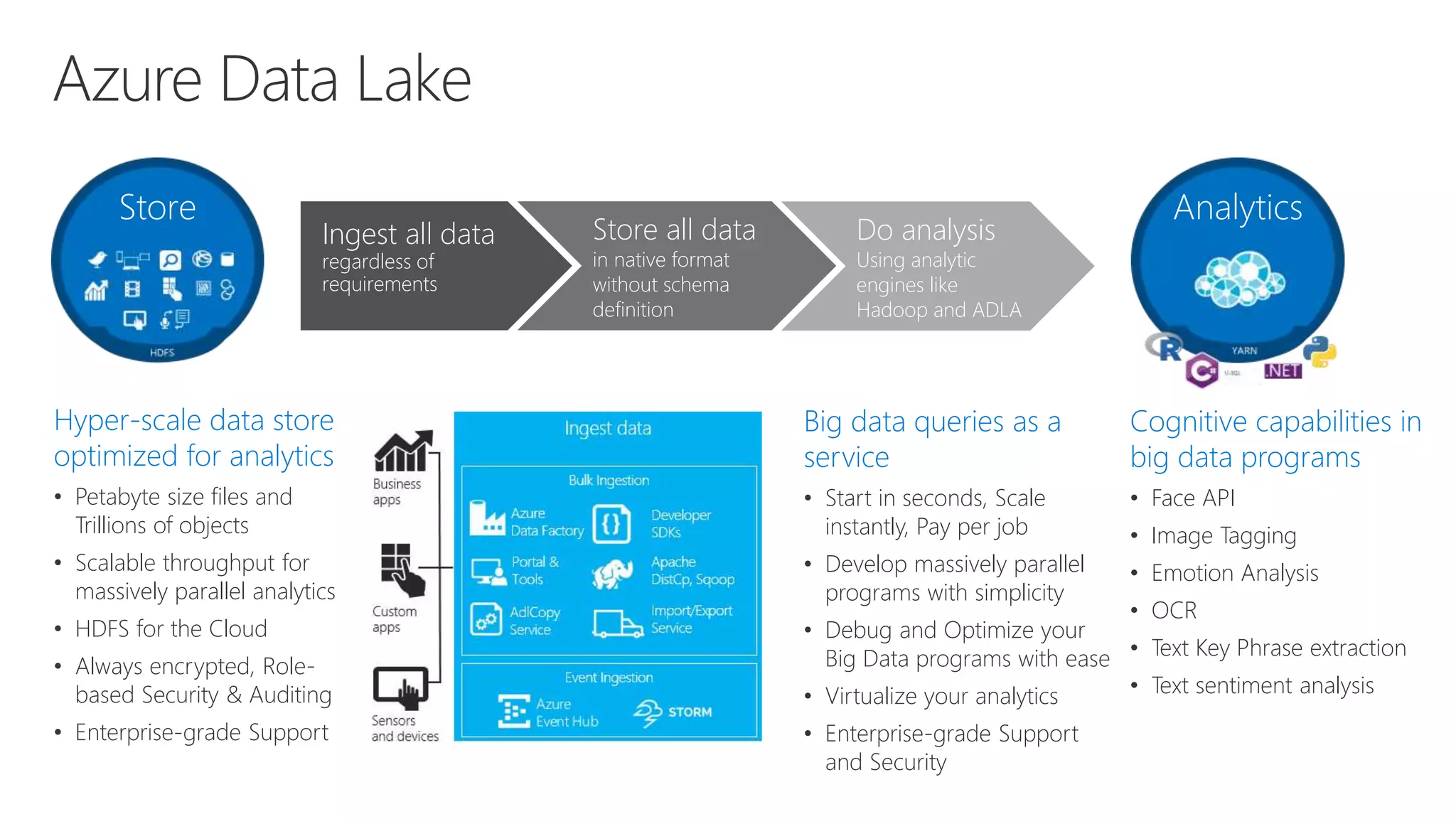
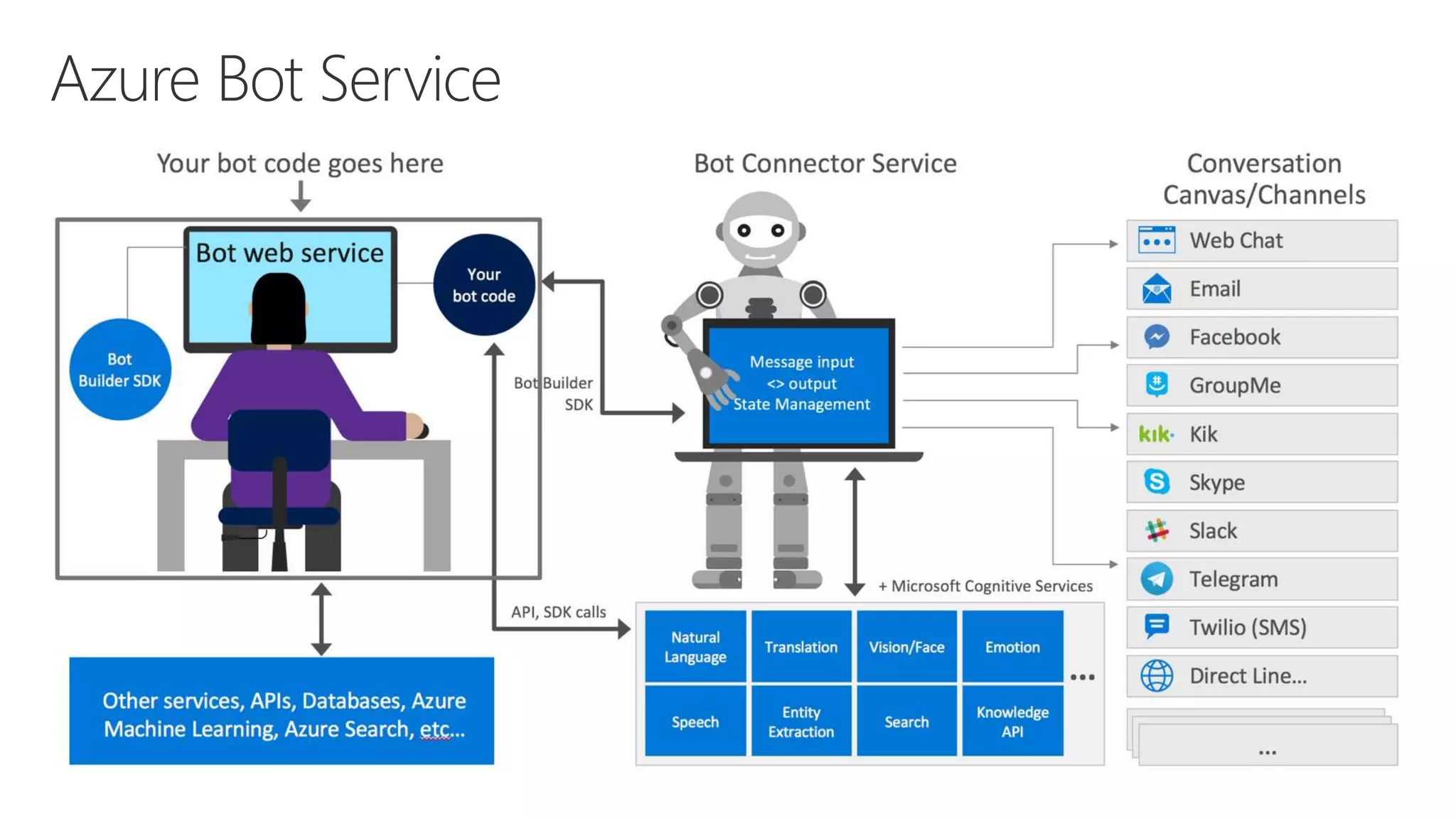
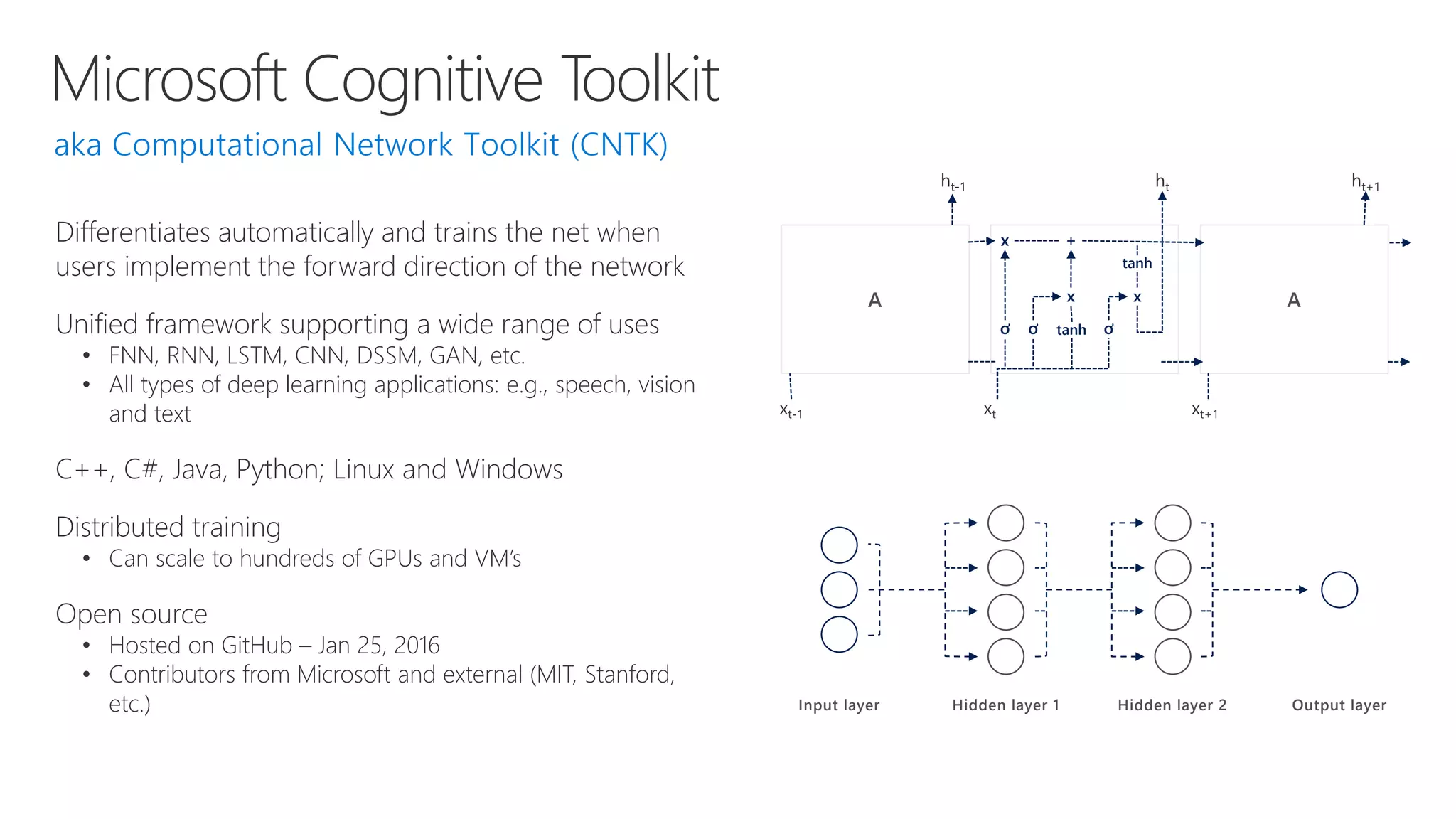
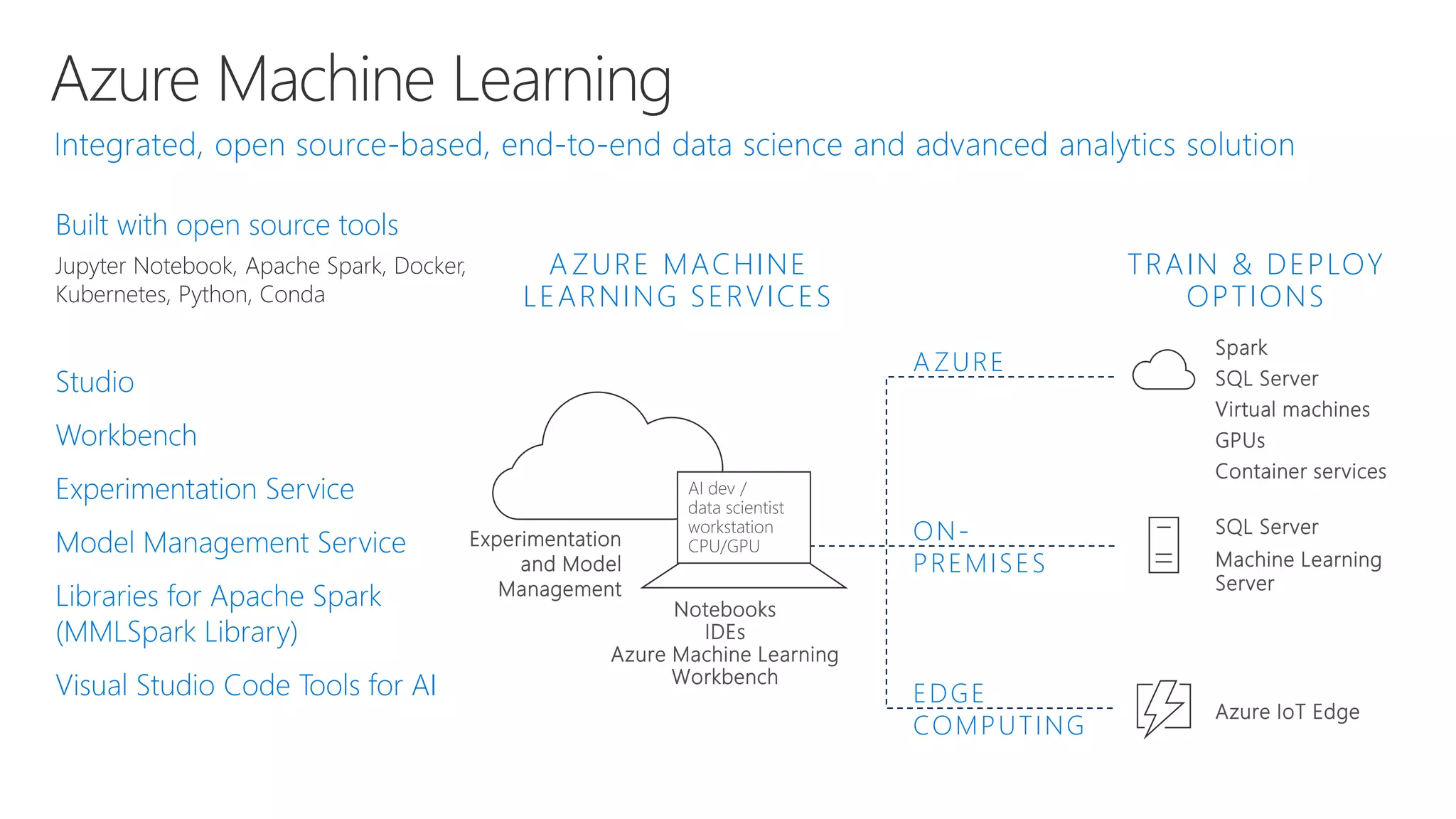
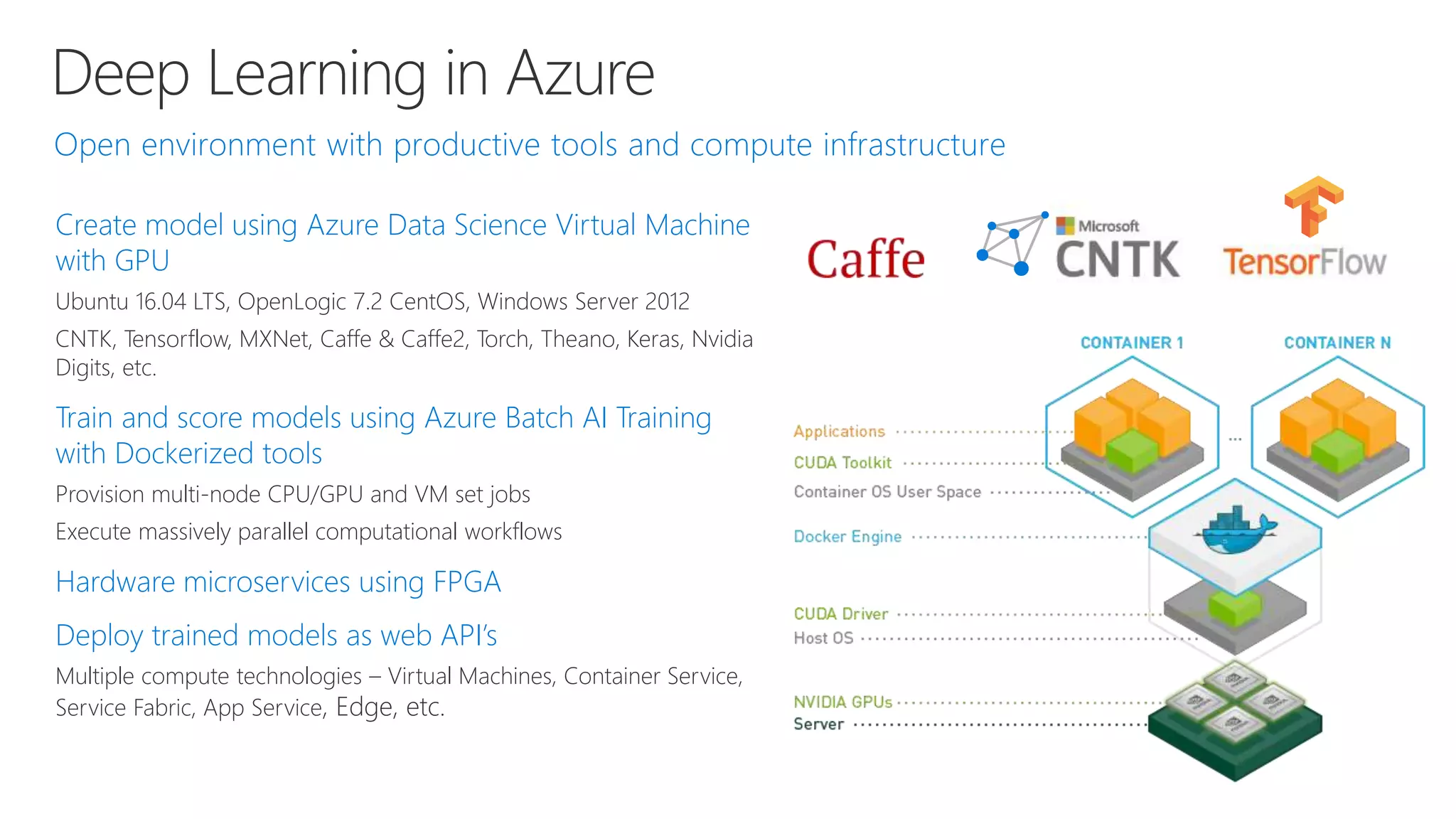
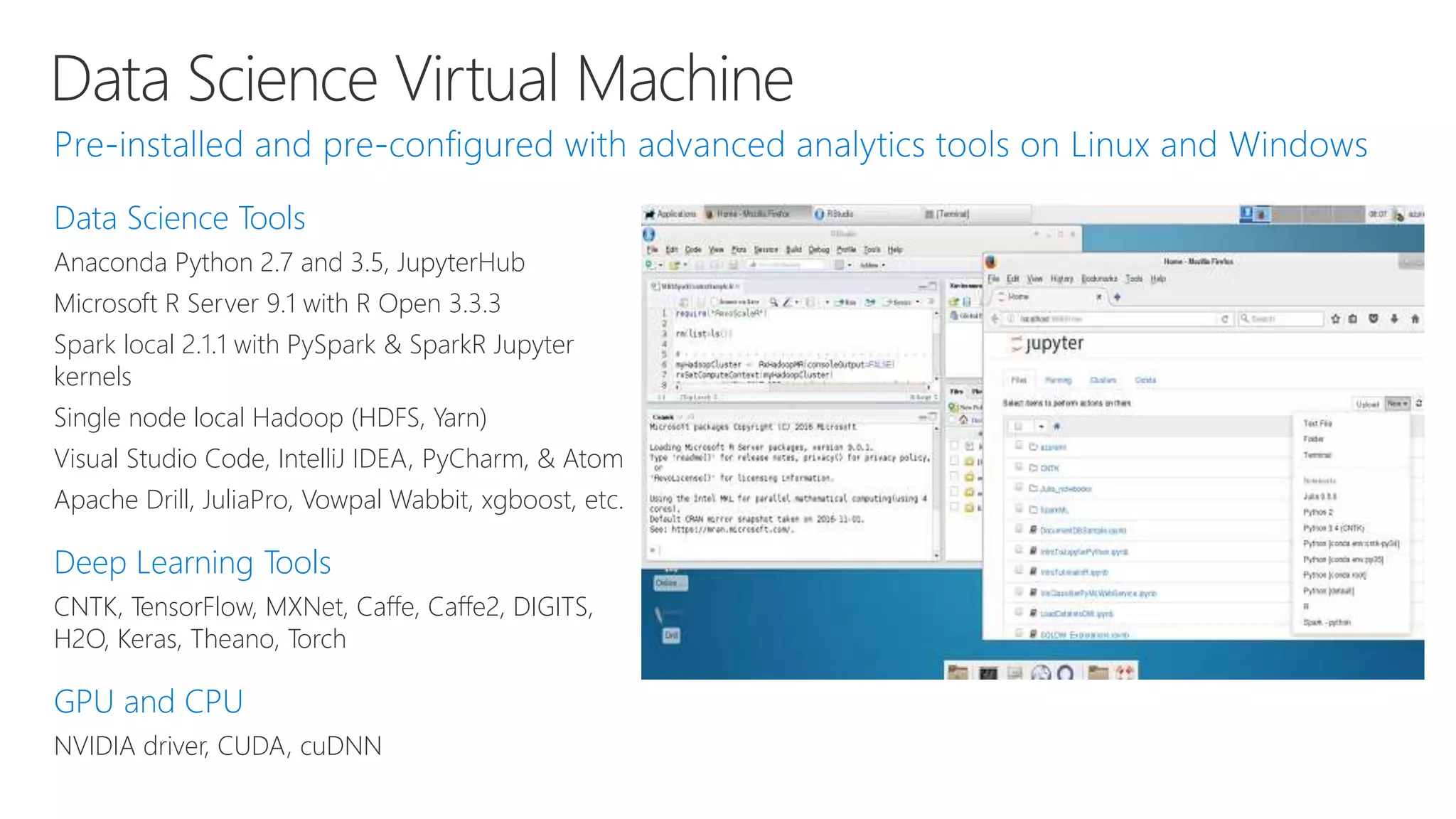
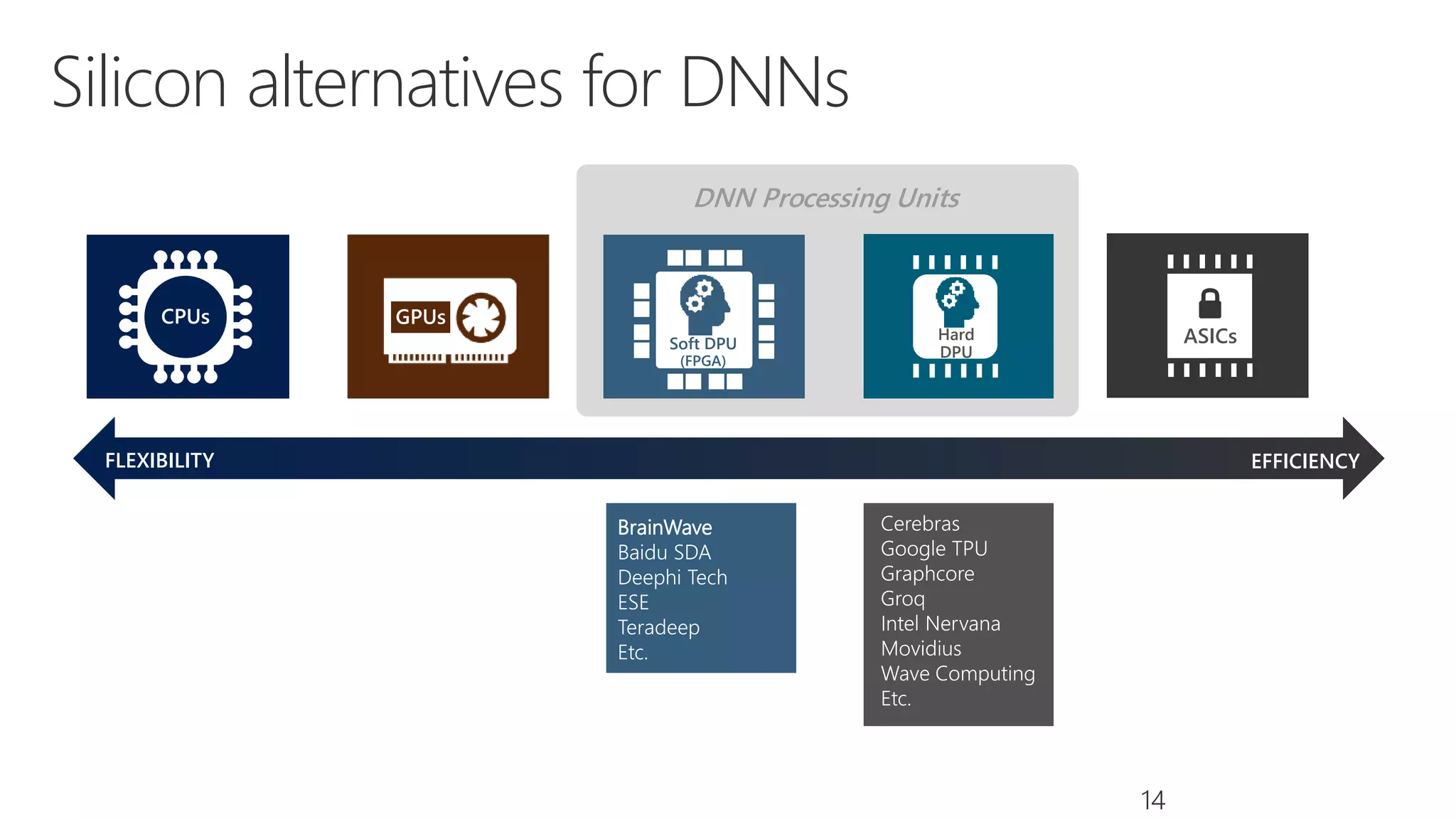
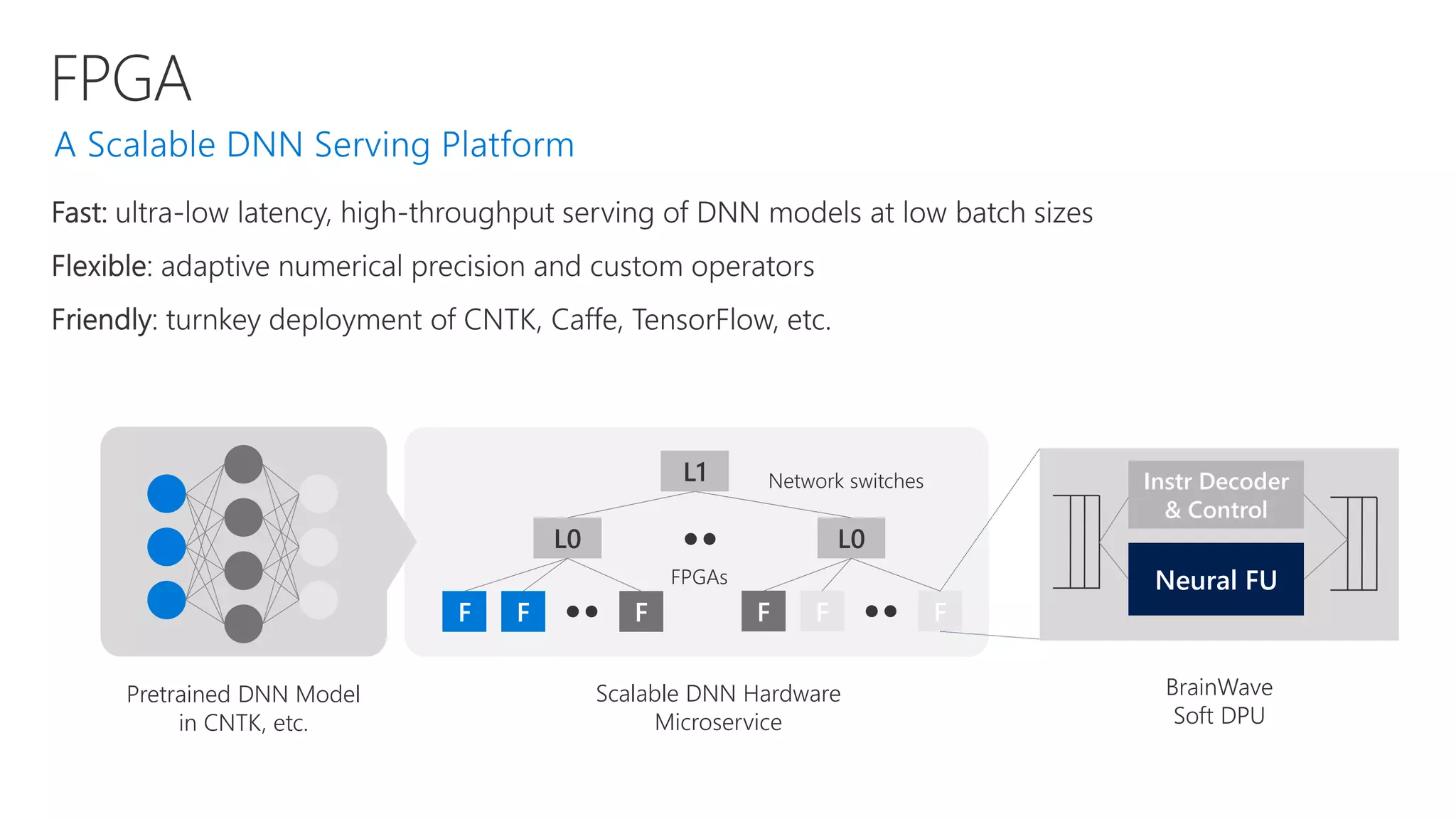
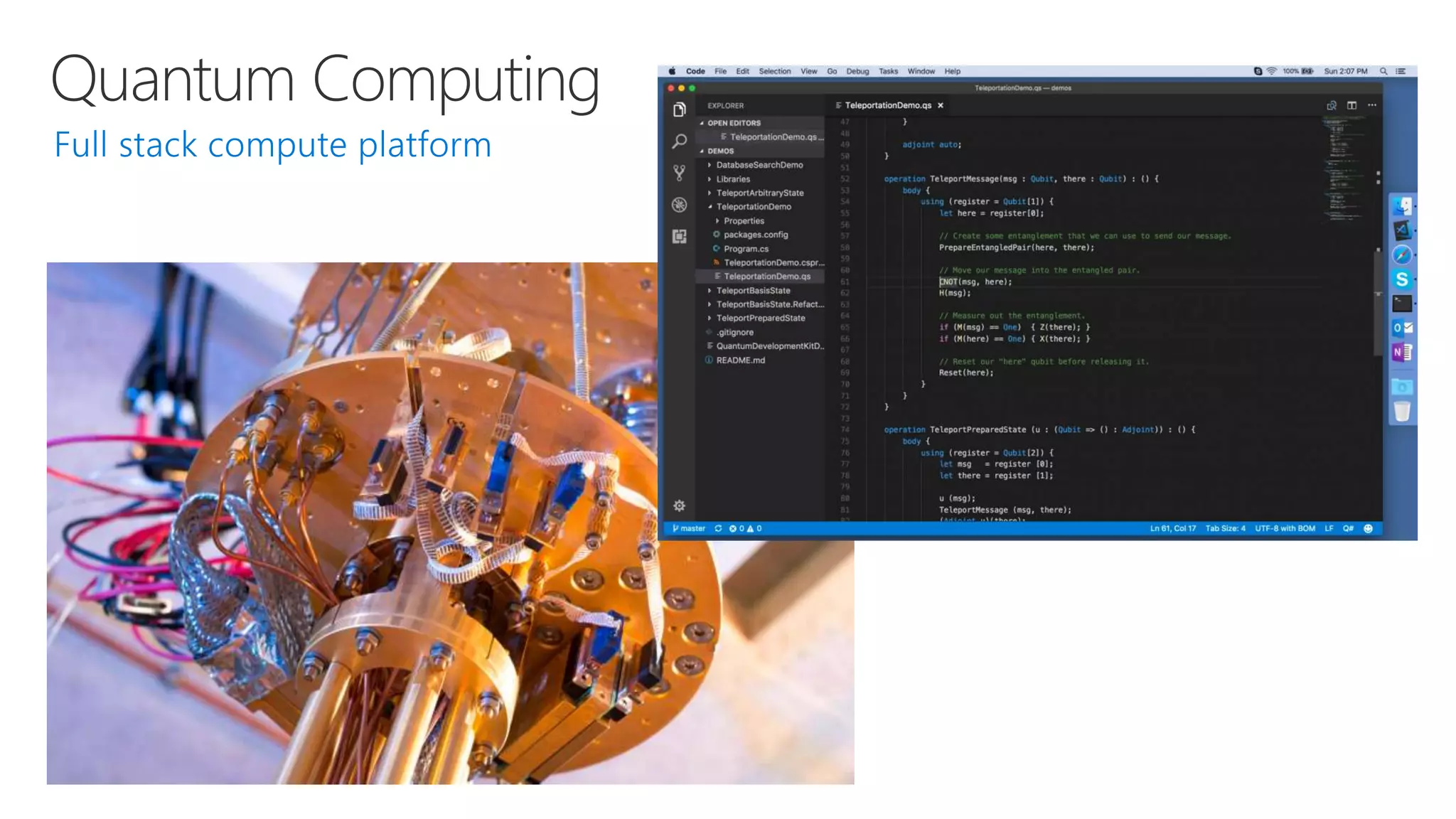
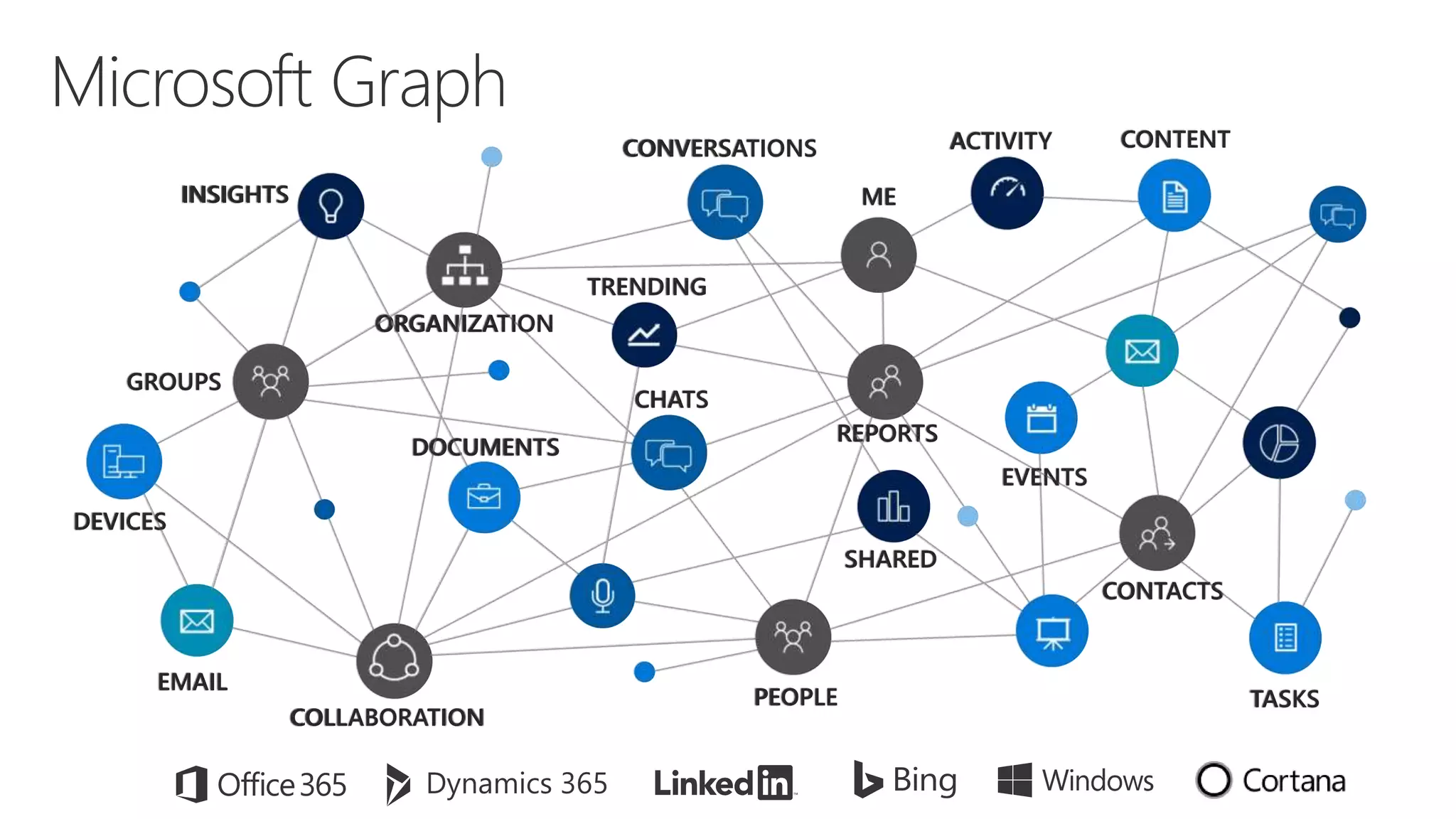
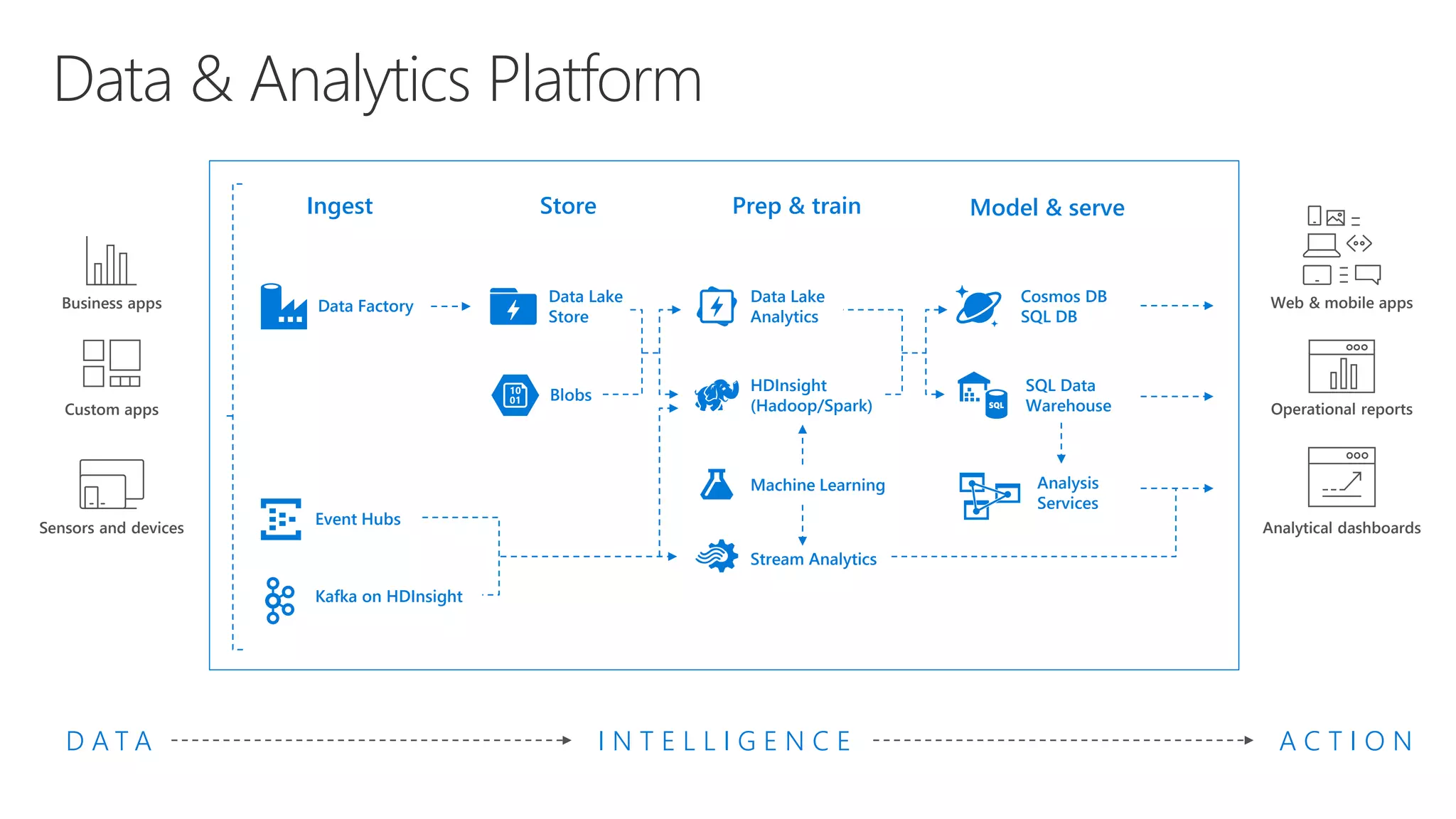
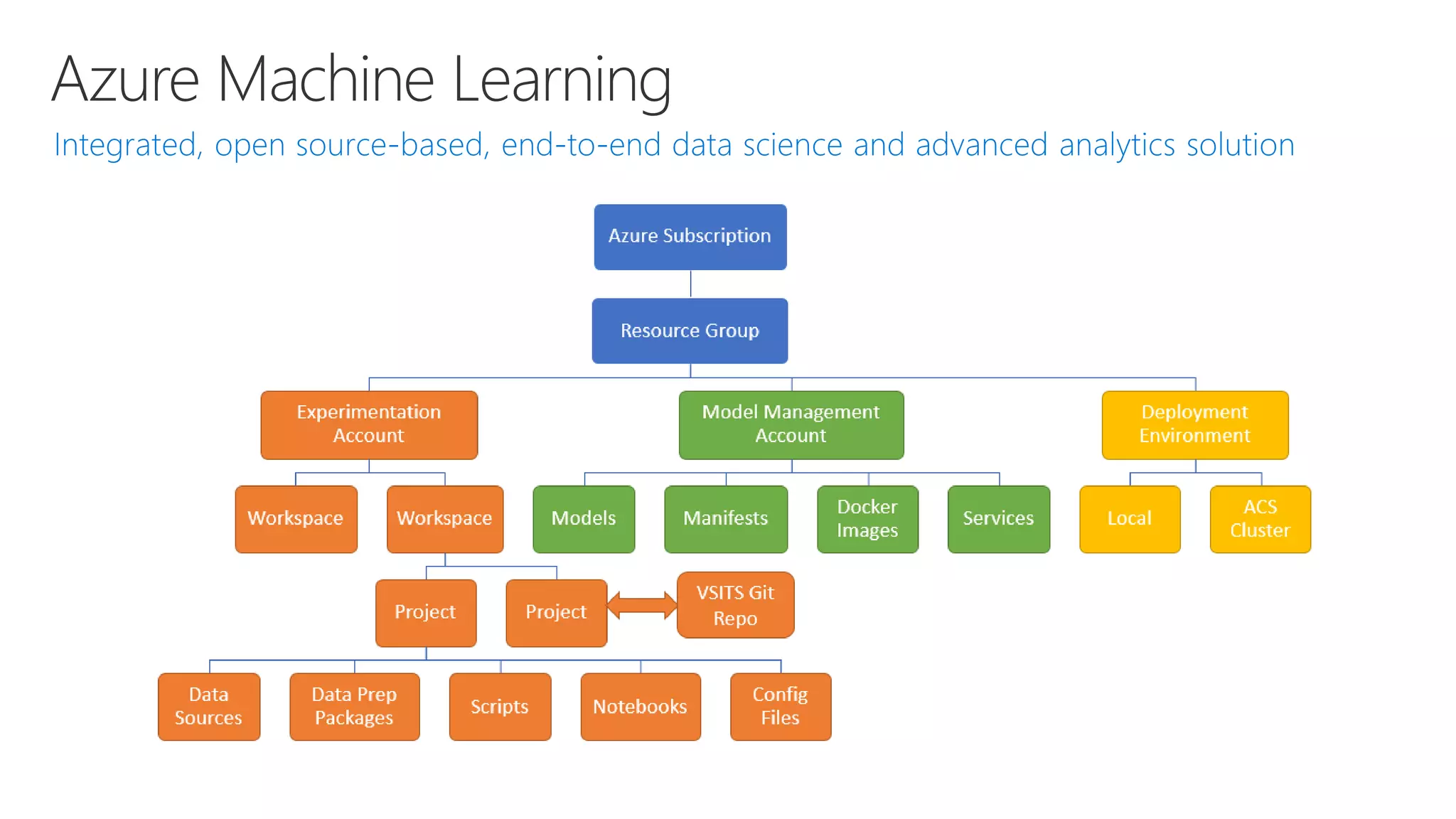
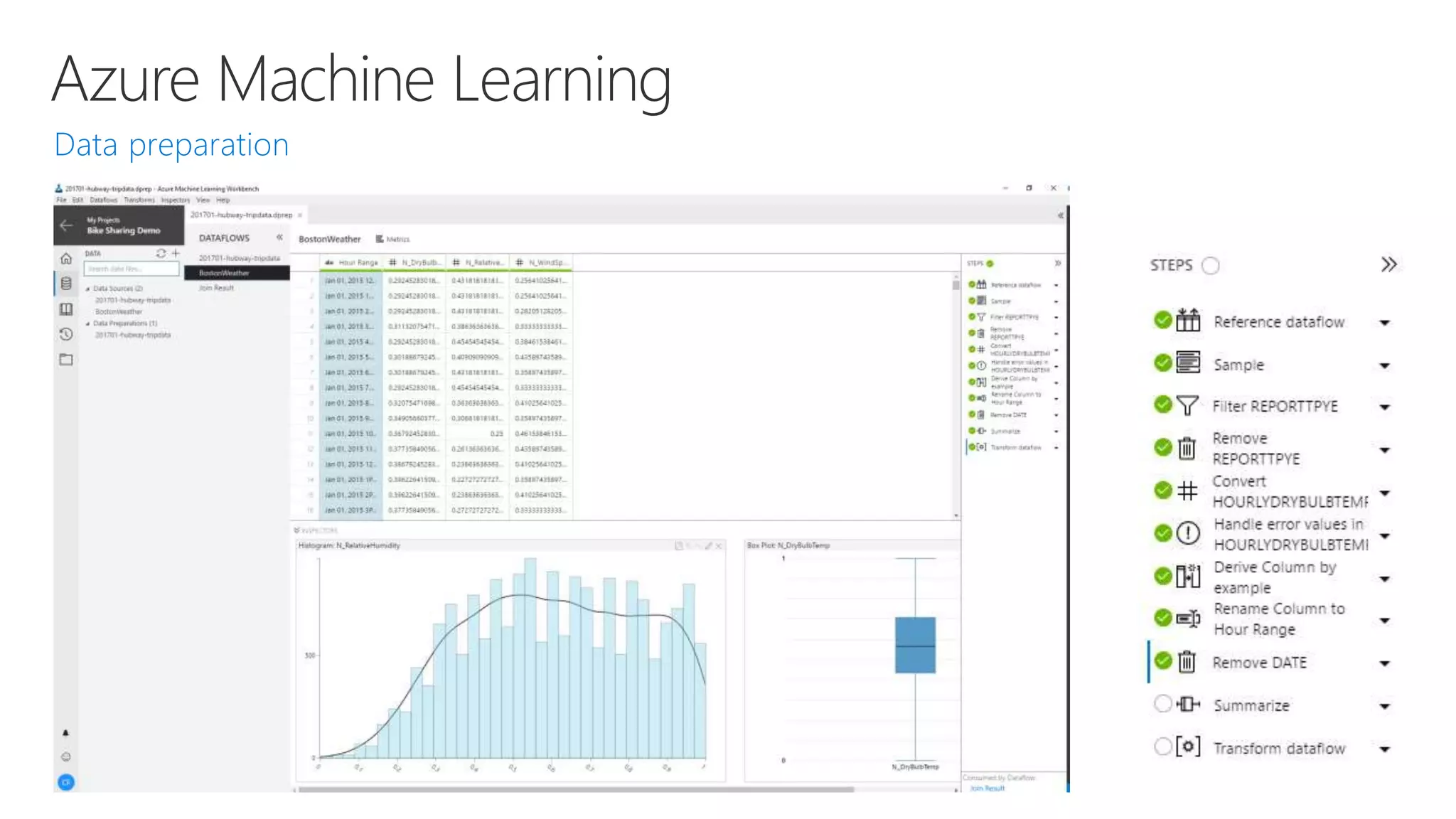
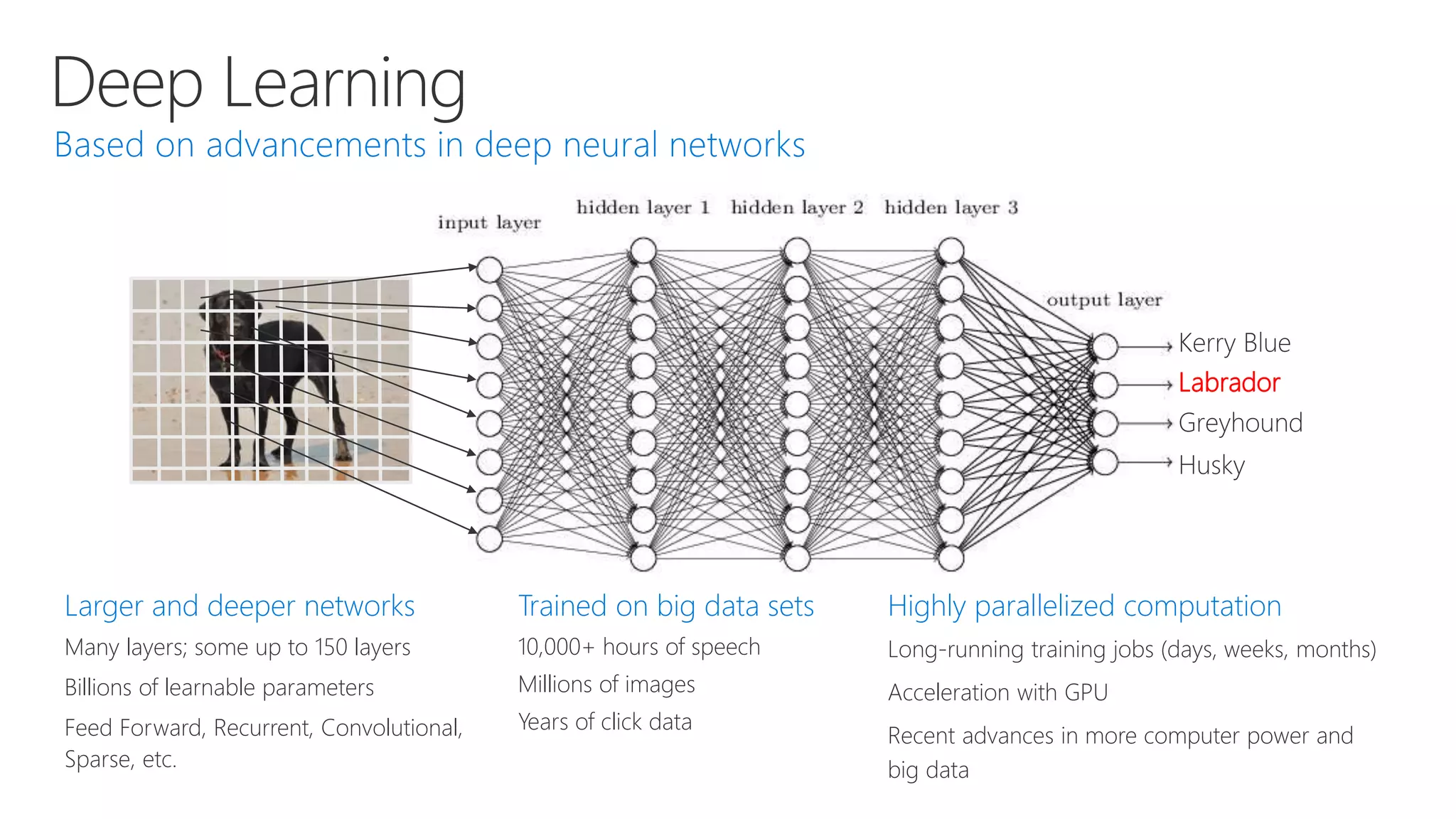
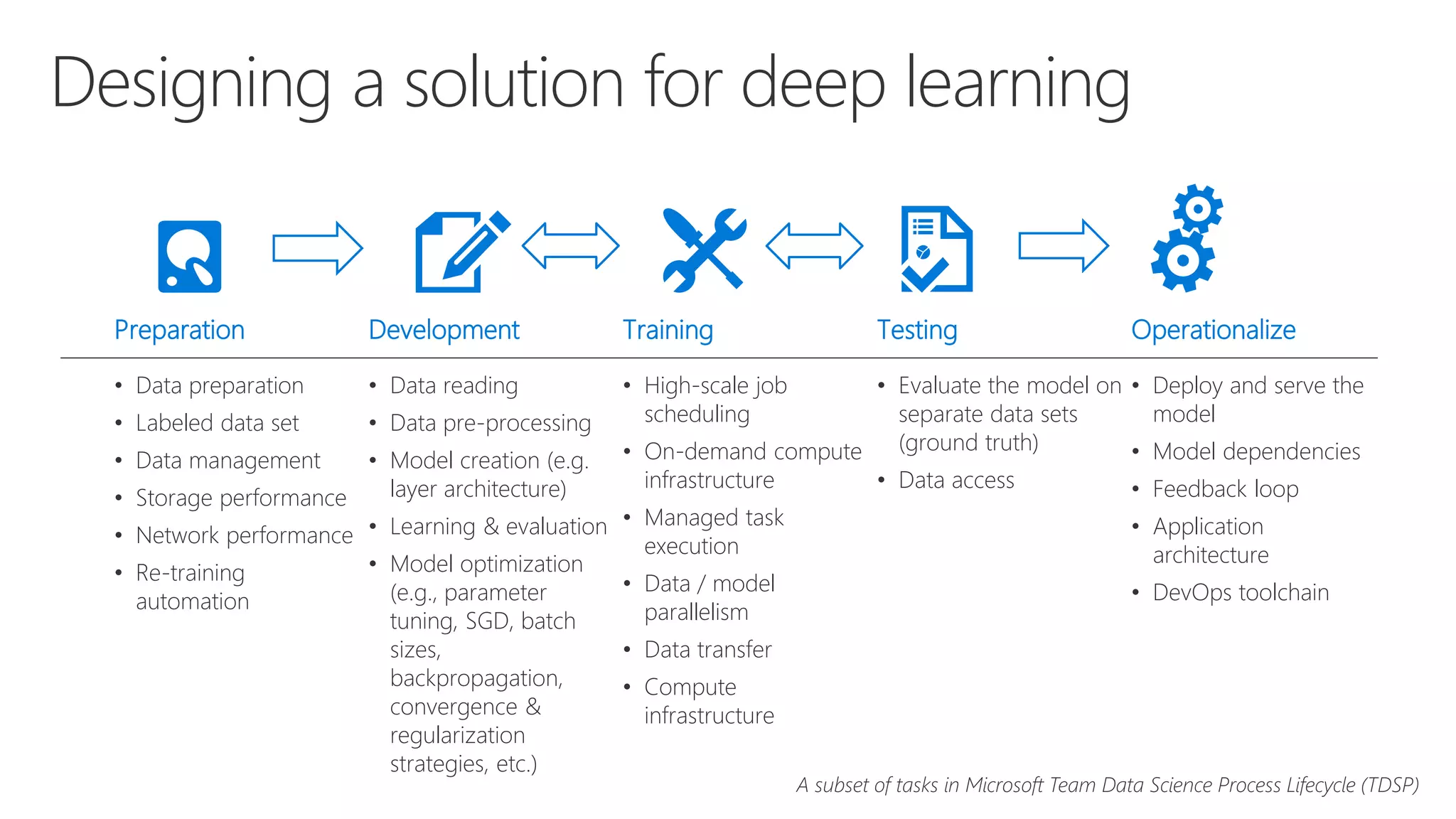
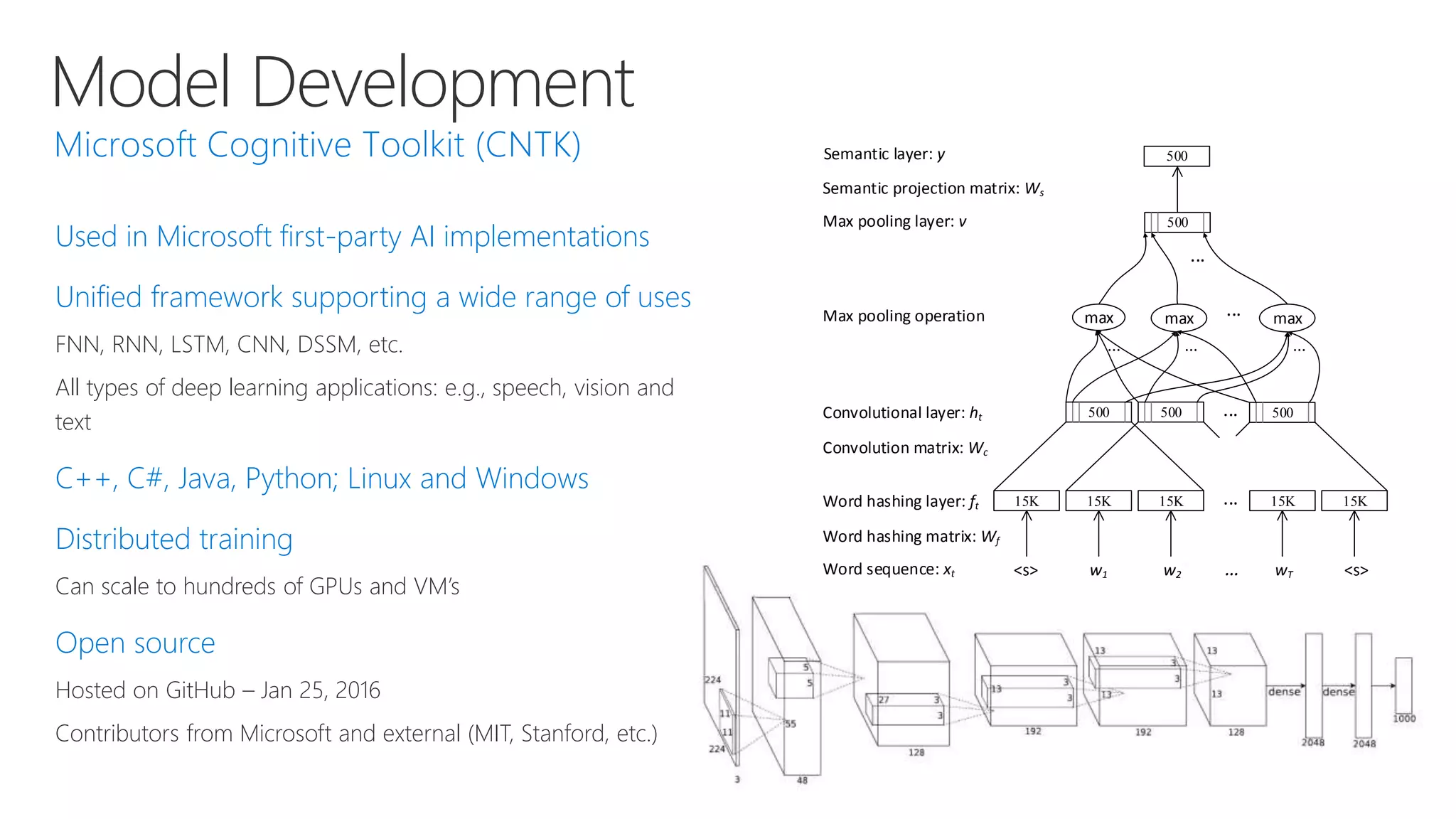
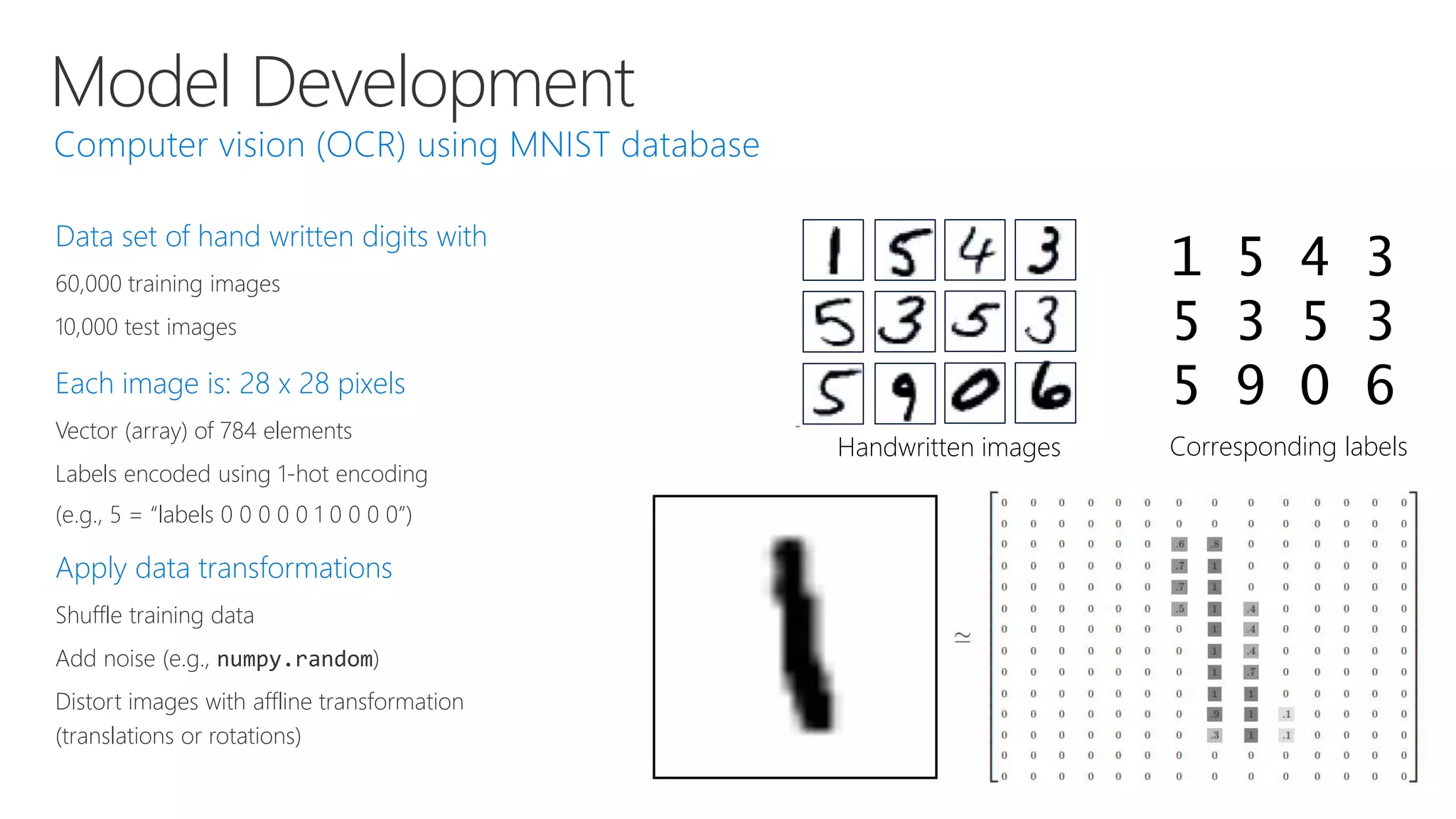
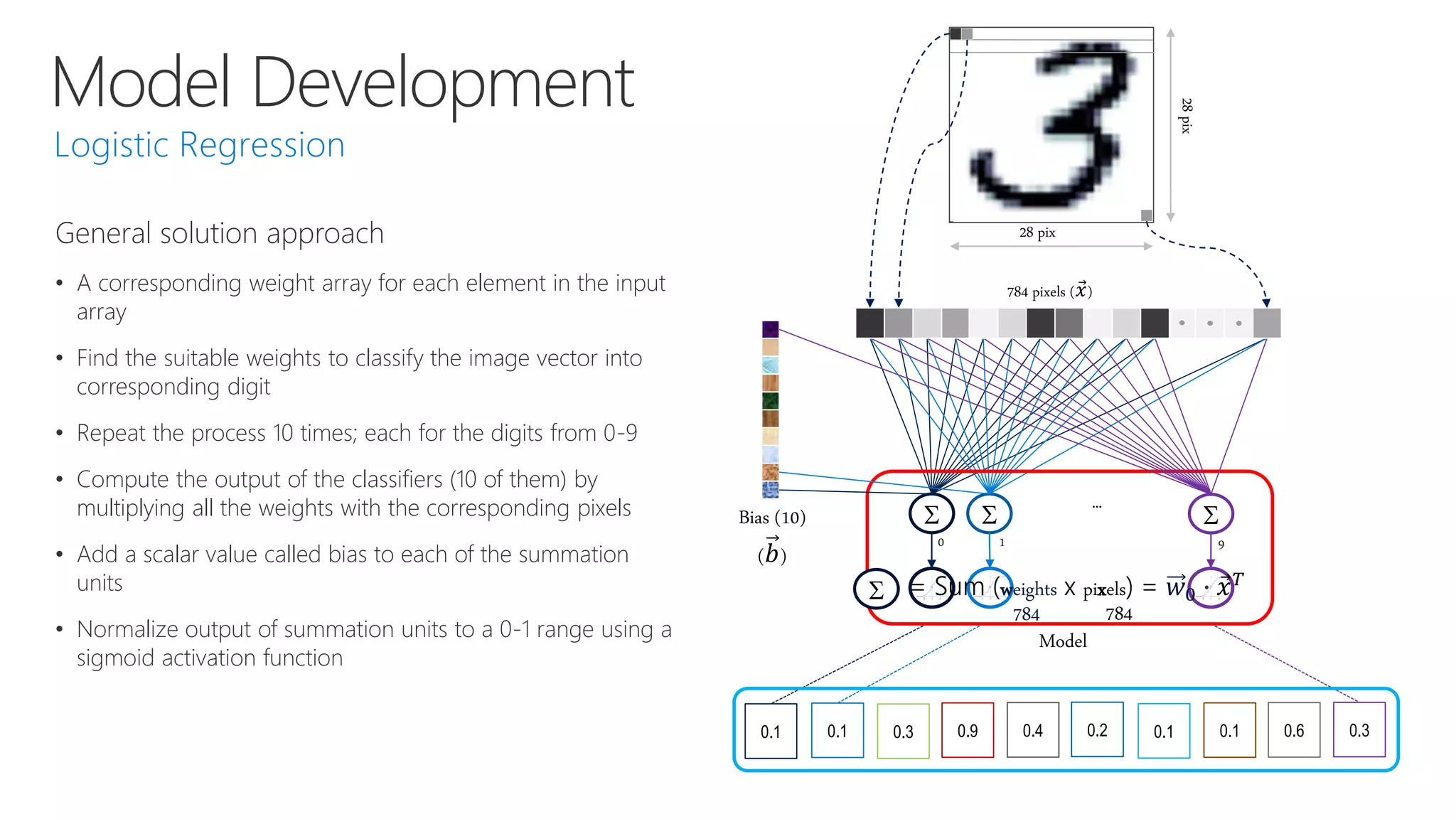
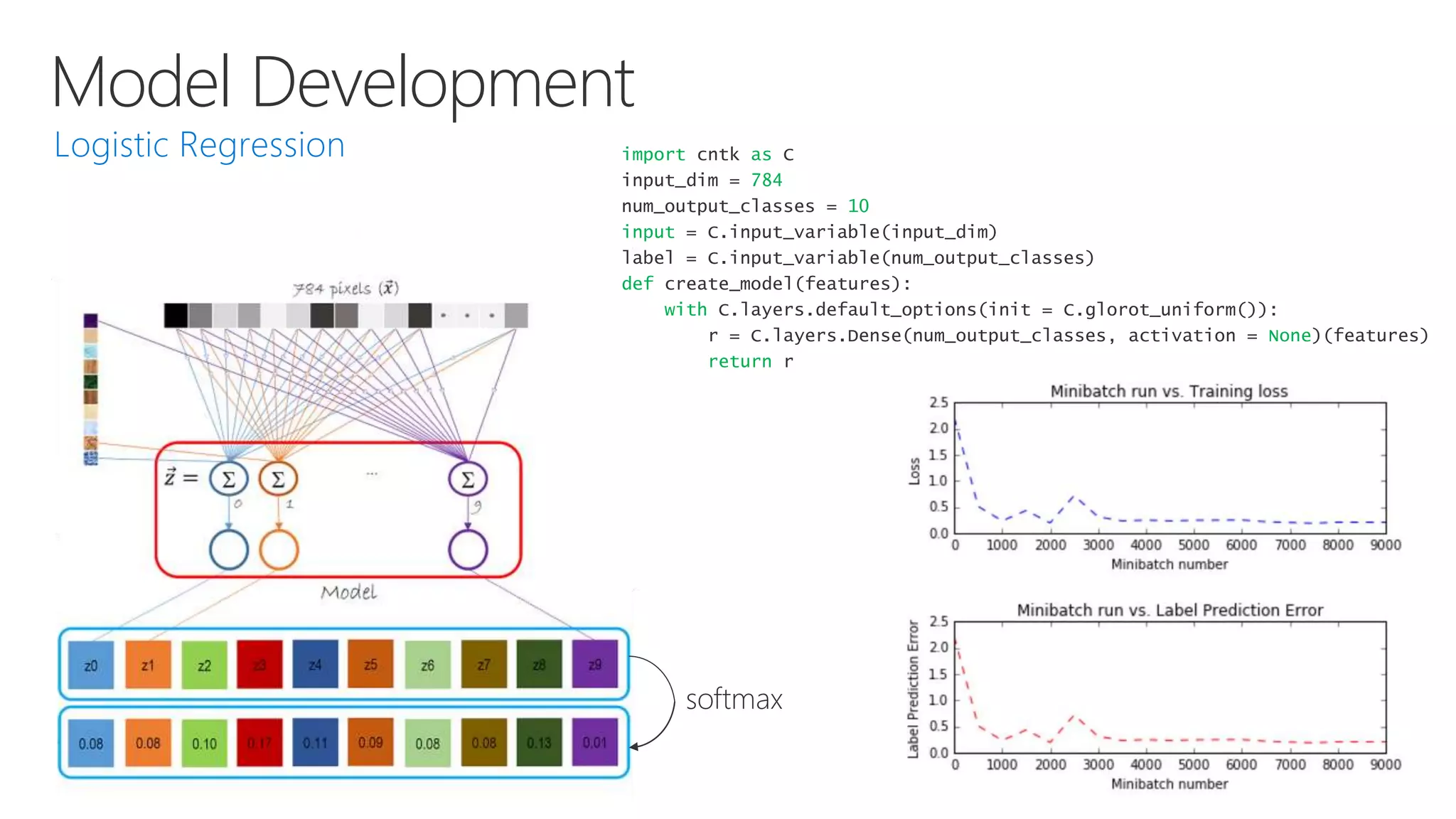
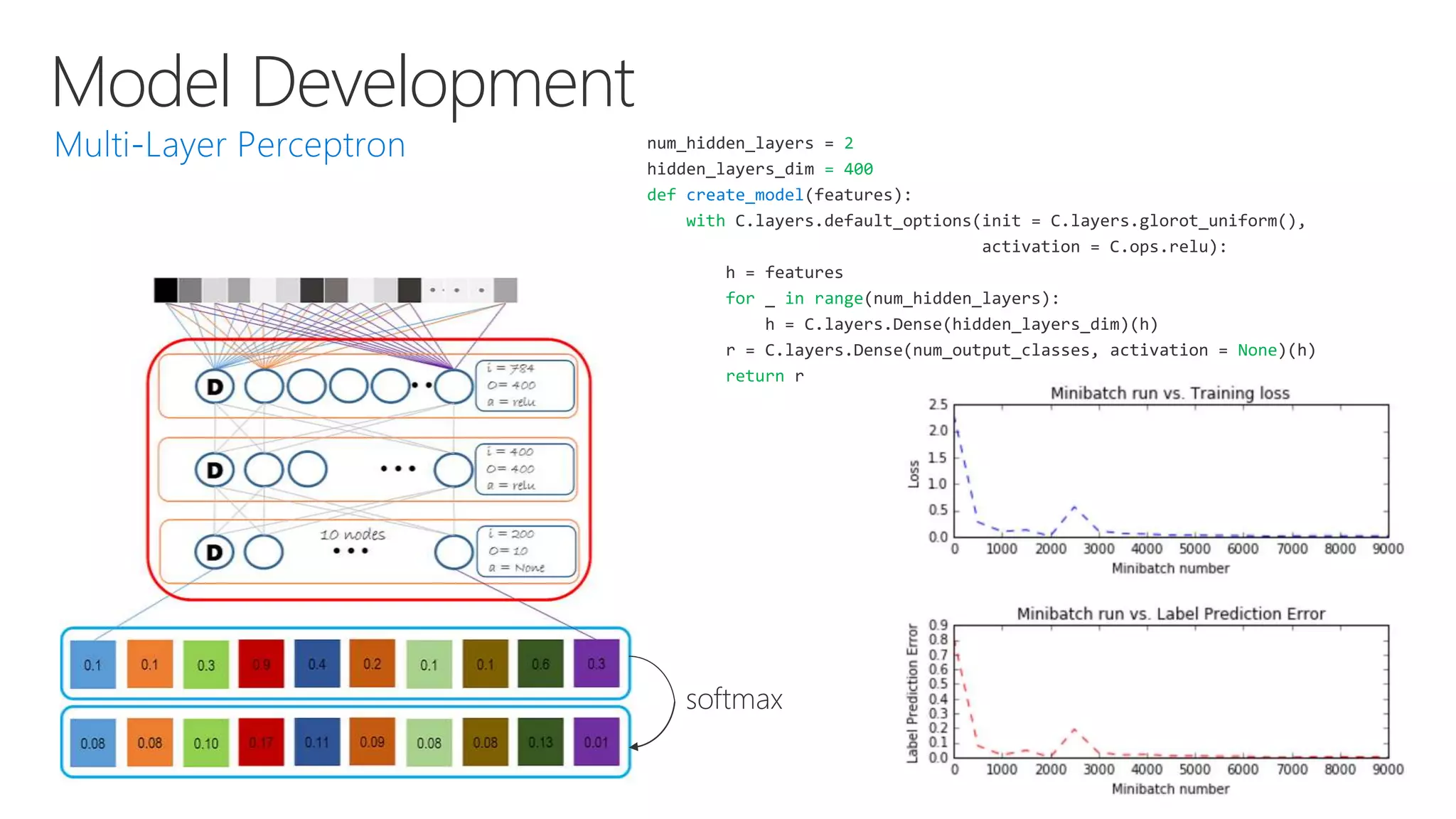
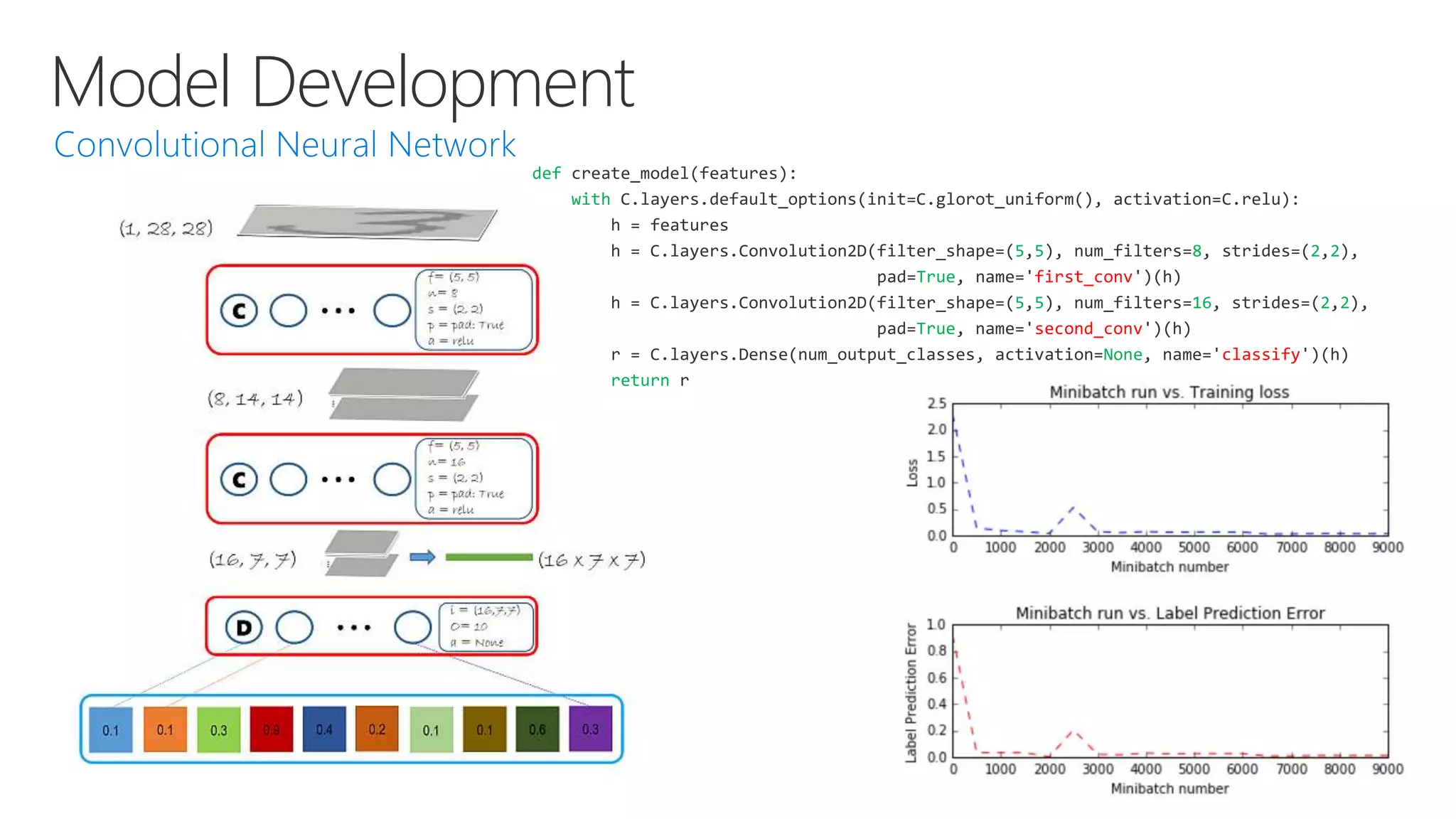
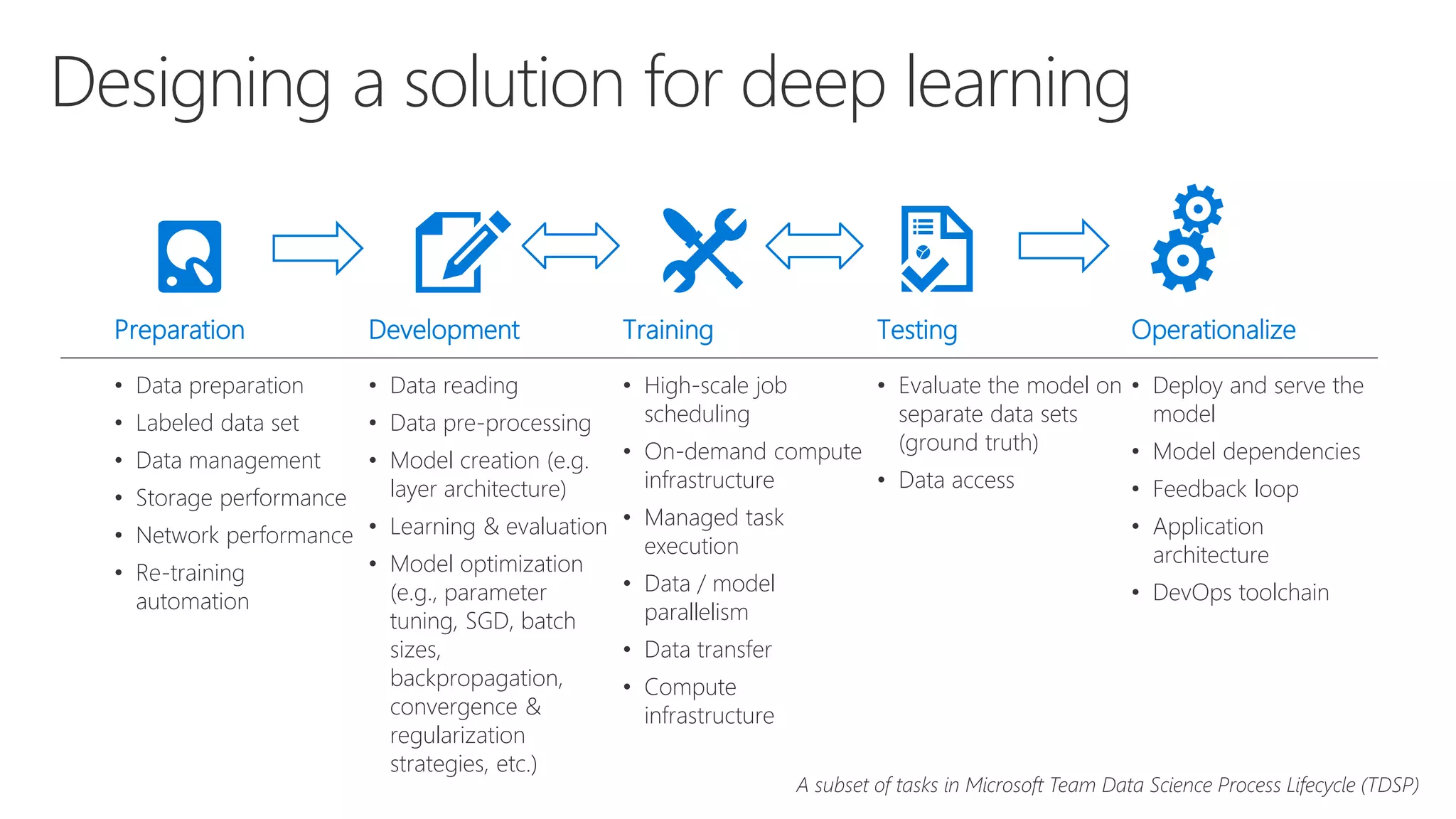
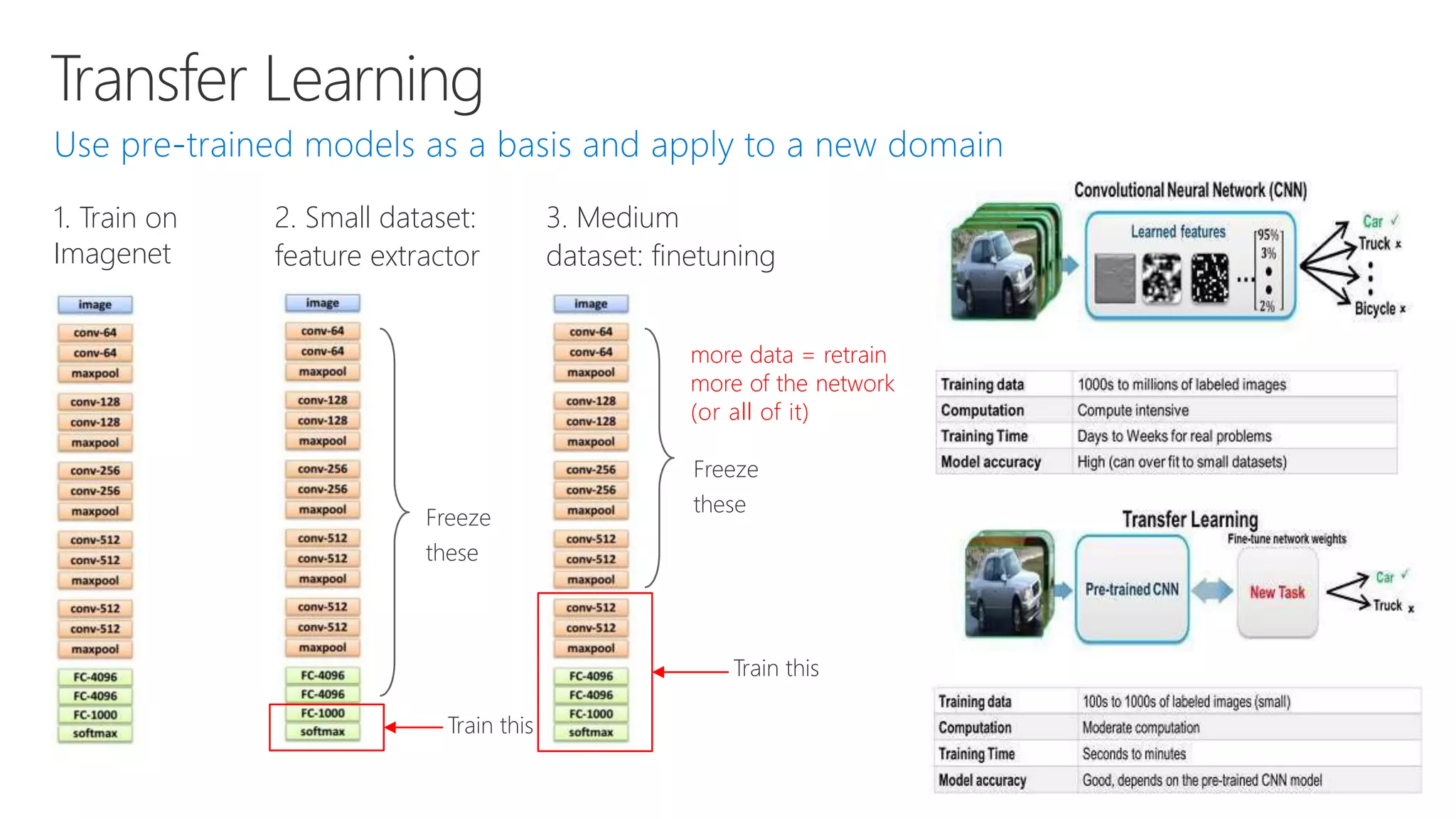
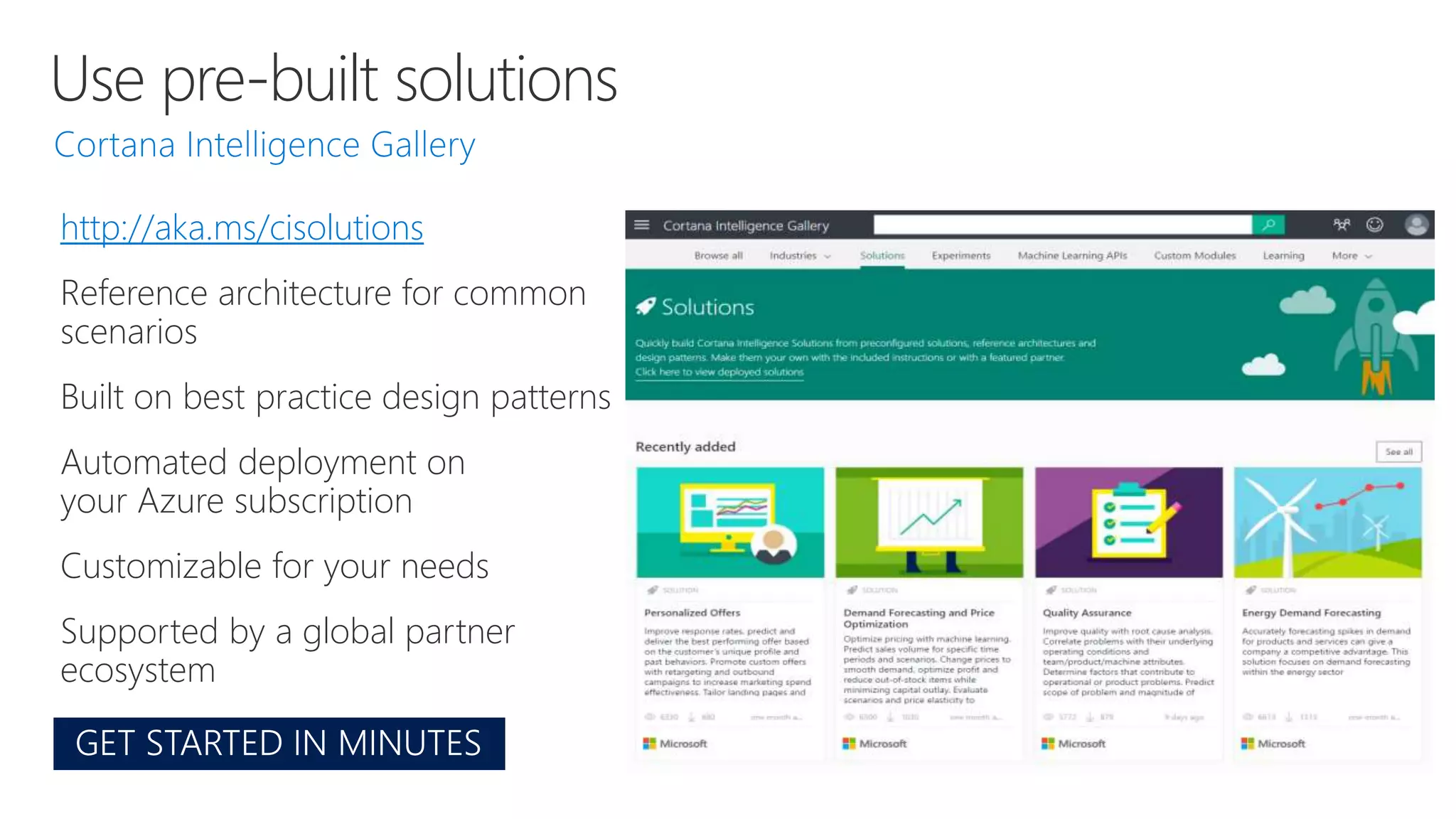
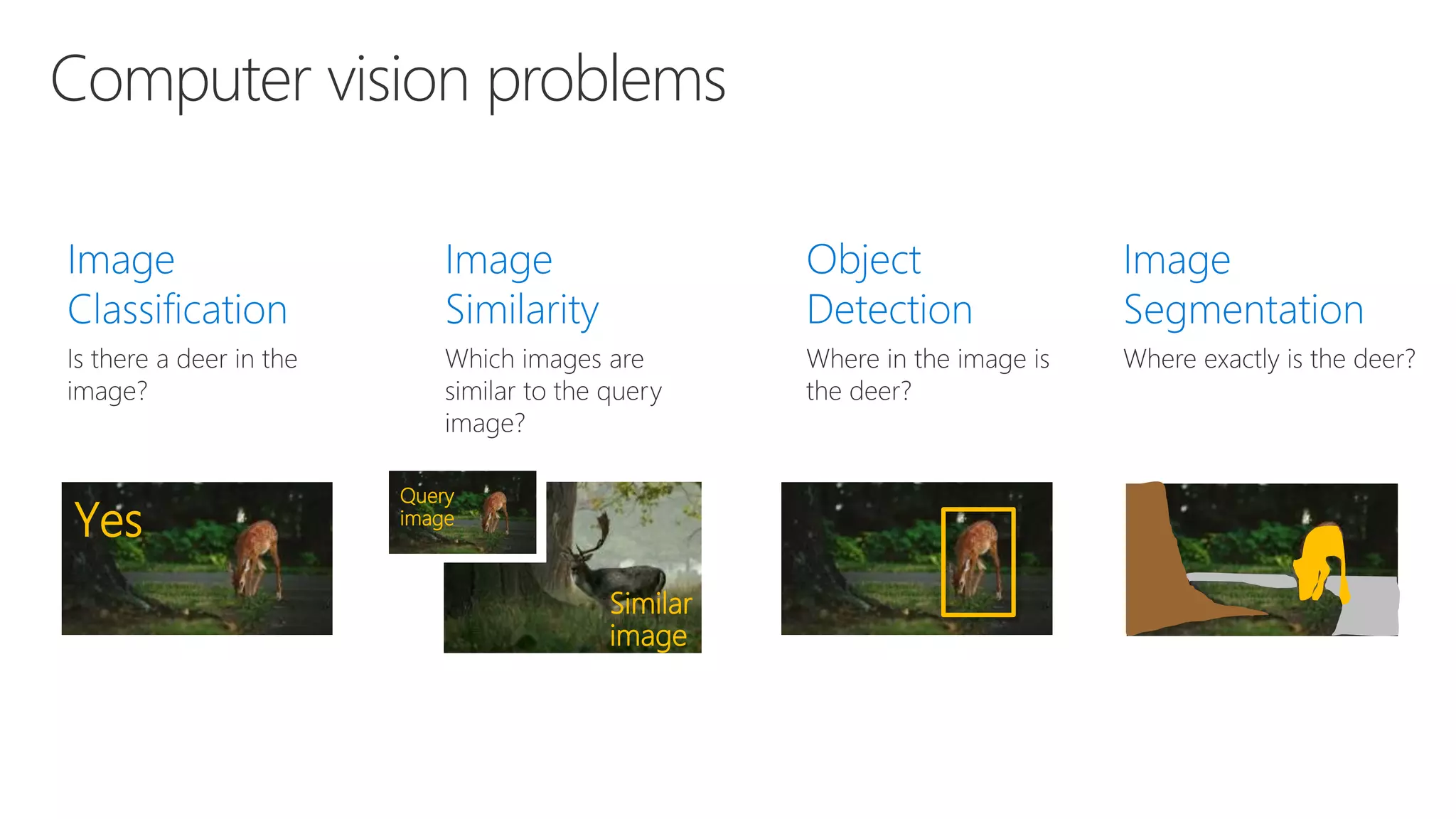
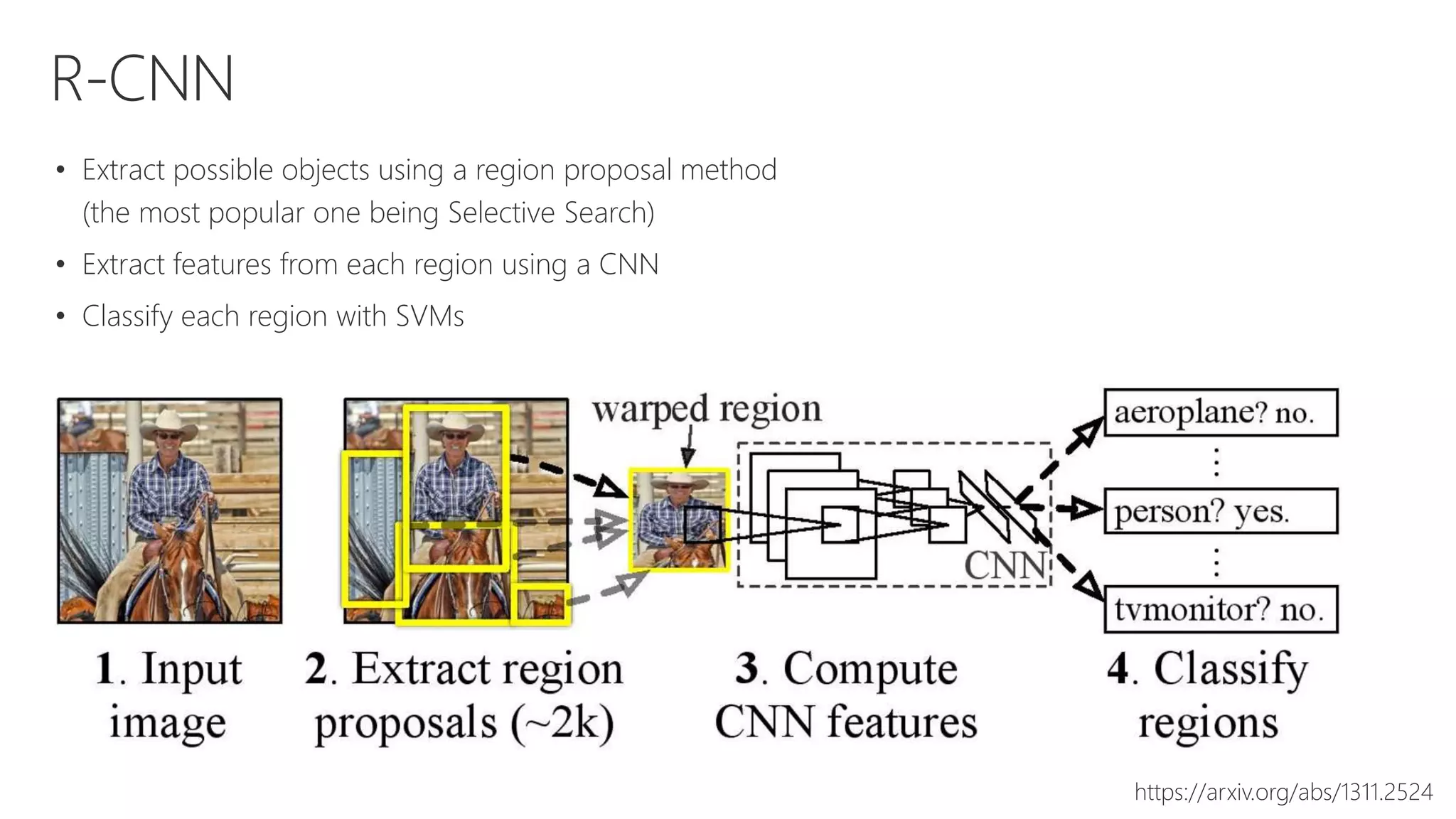
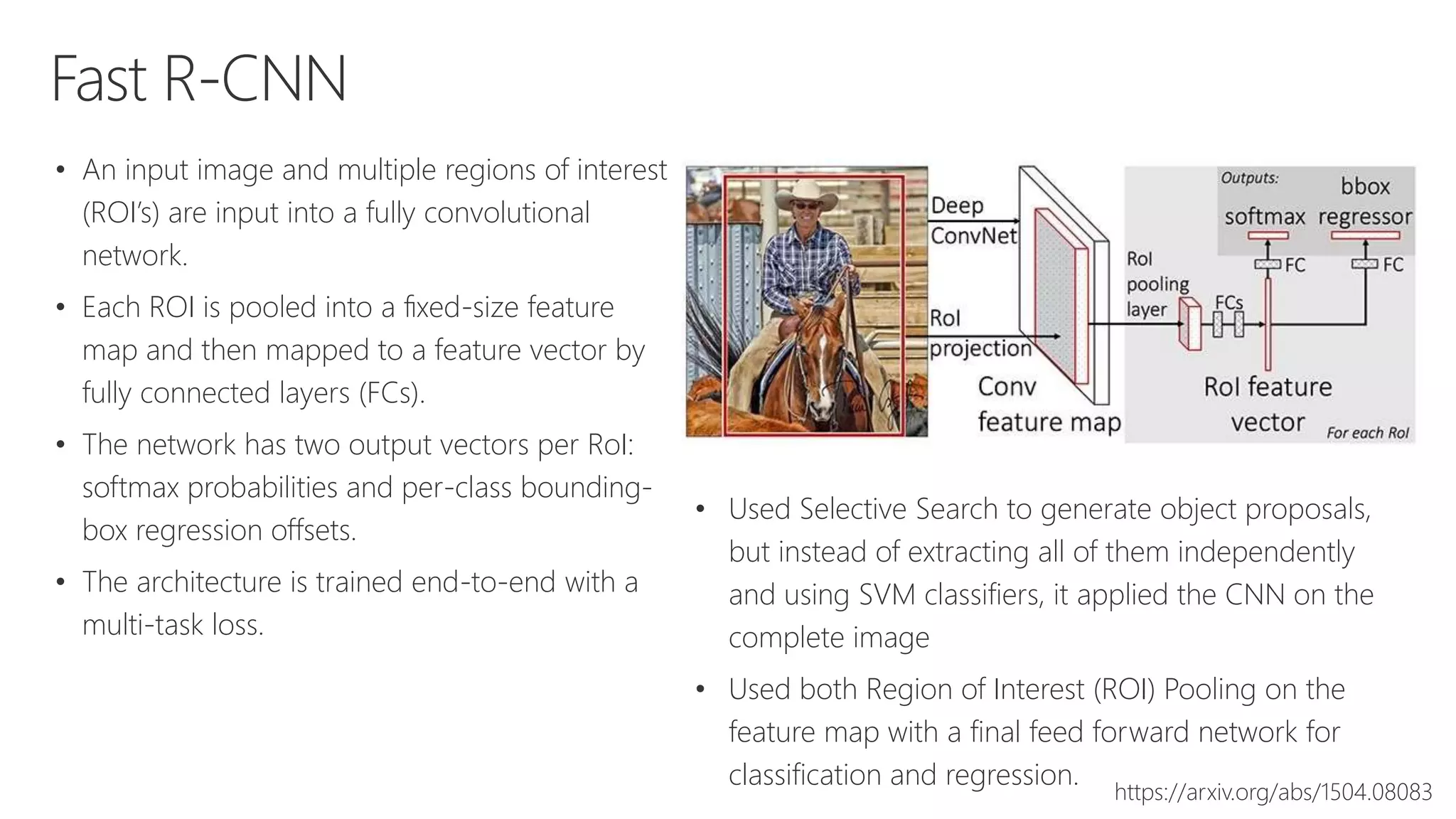
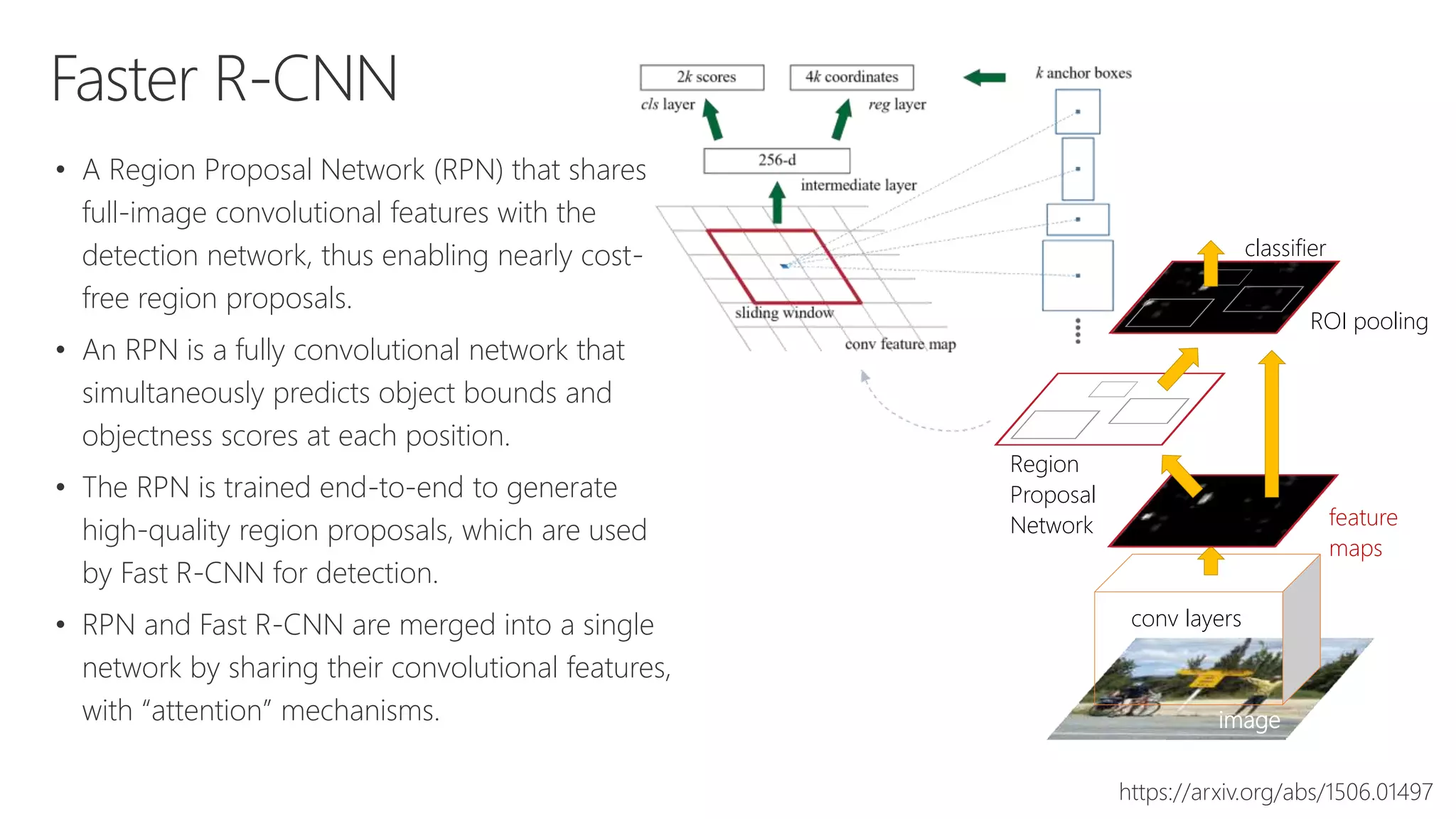
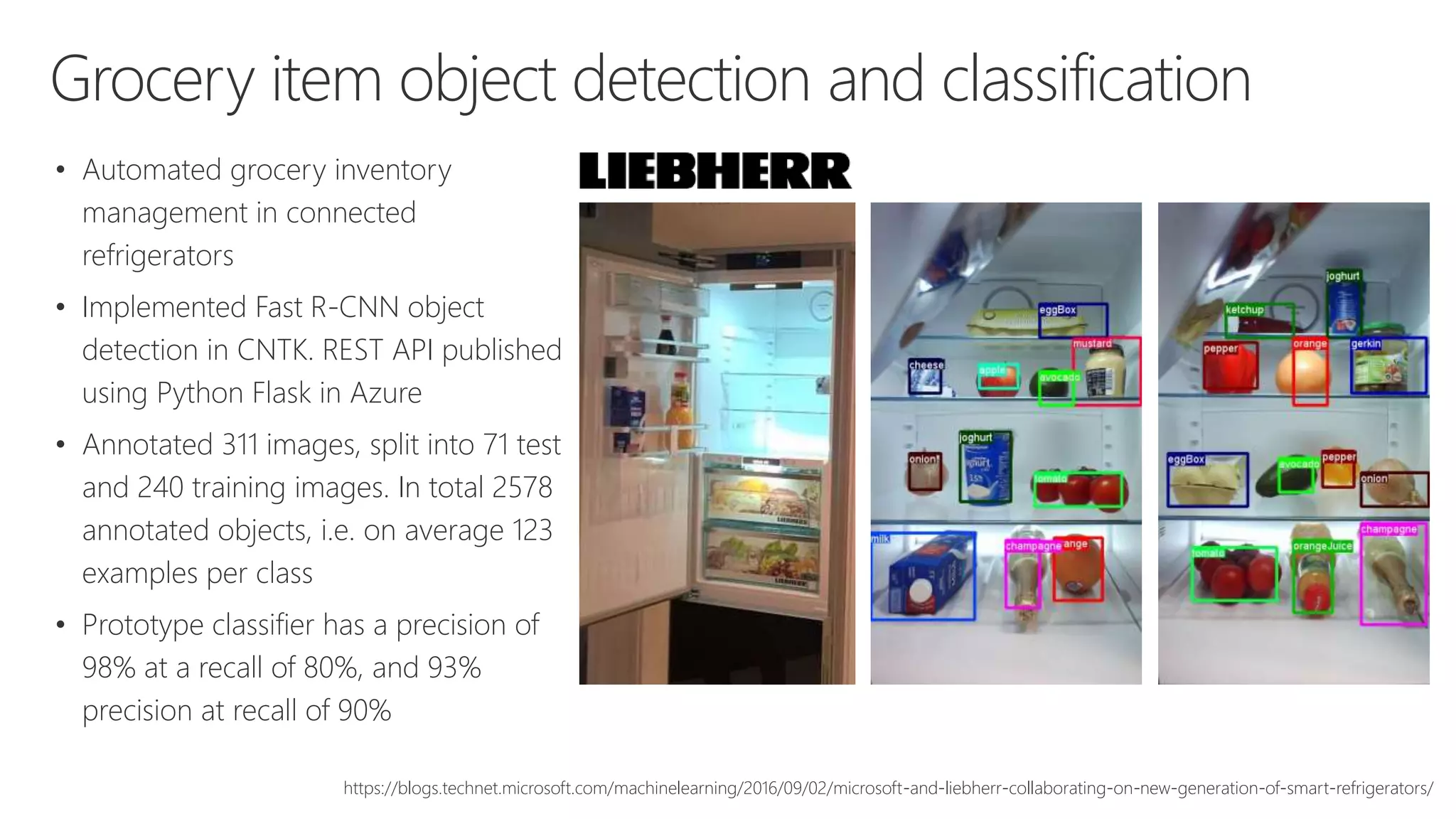
Microsoft provides an AI platform and tools for developers to build, train, and deploy intelligent applications and services. Key elements of Microsoft's AI offerings include:
- A unified AI platform spanning infrastructure, tools, and services to make AI accessible and useful for every developer.
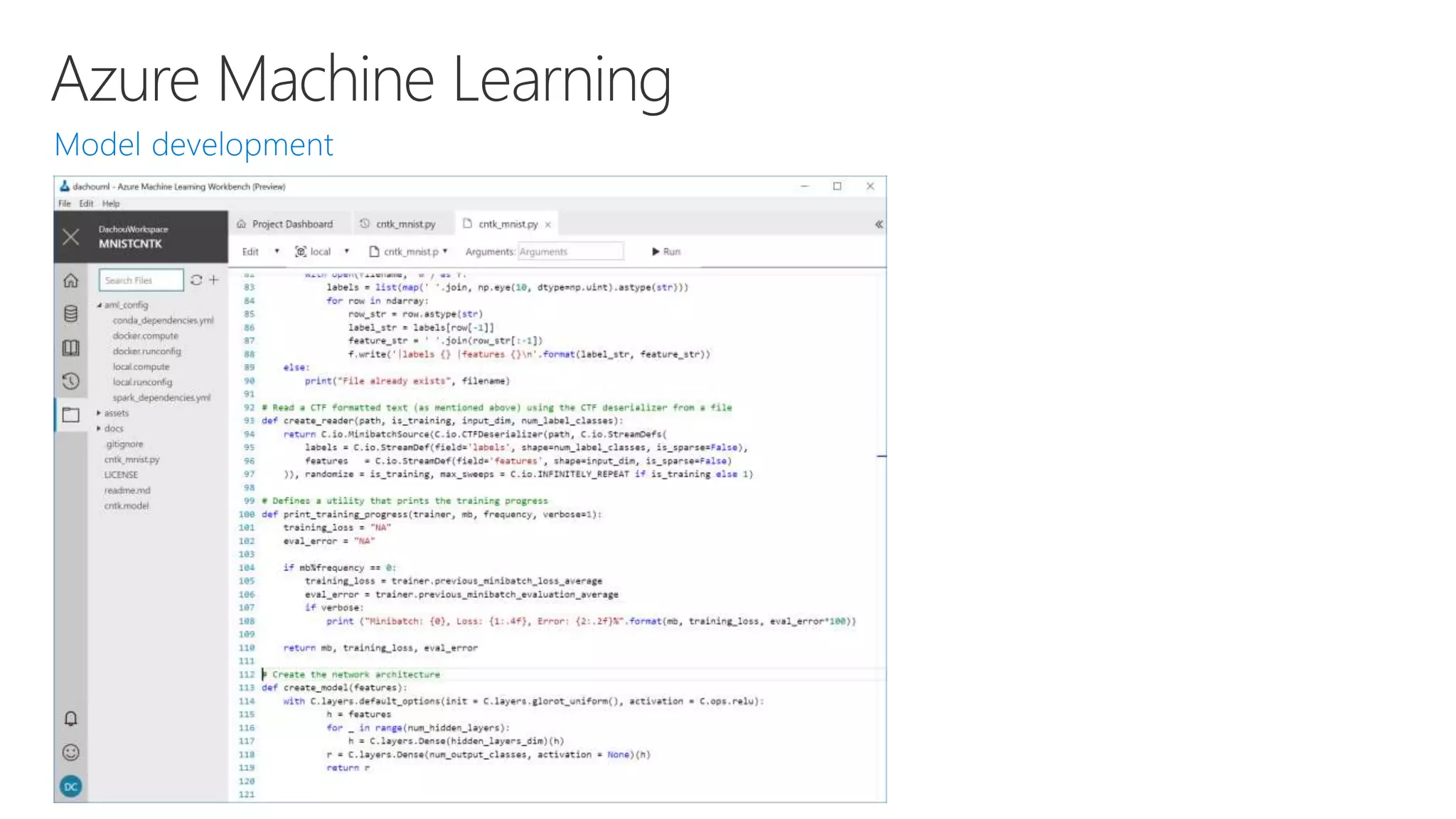
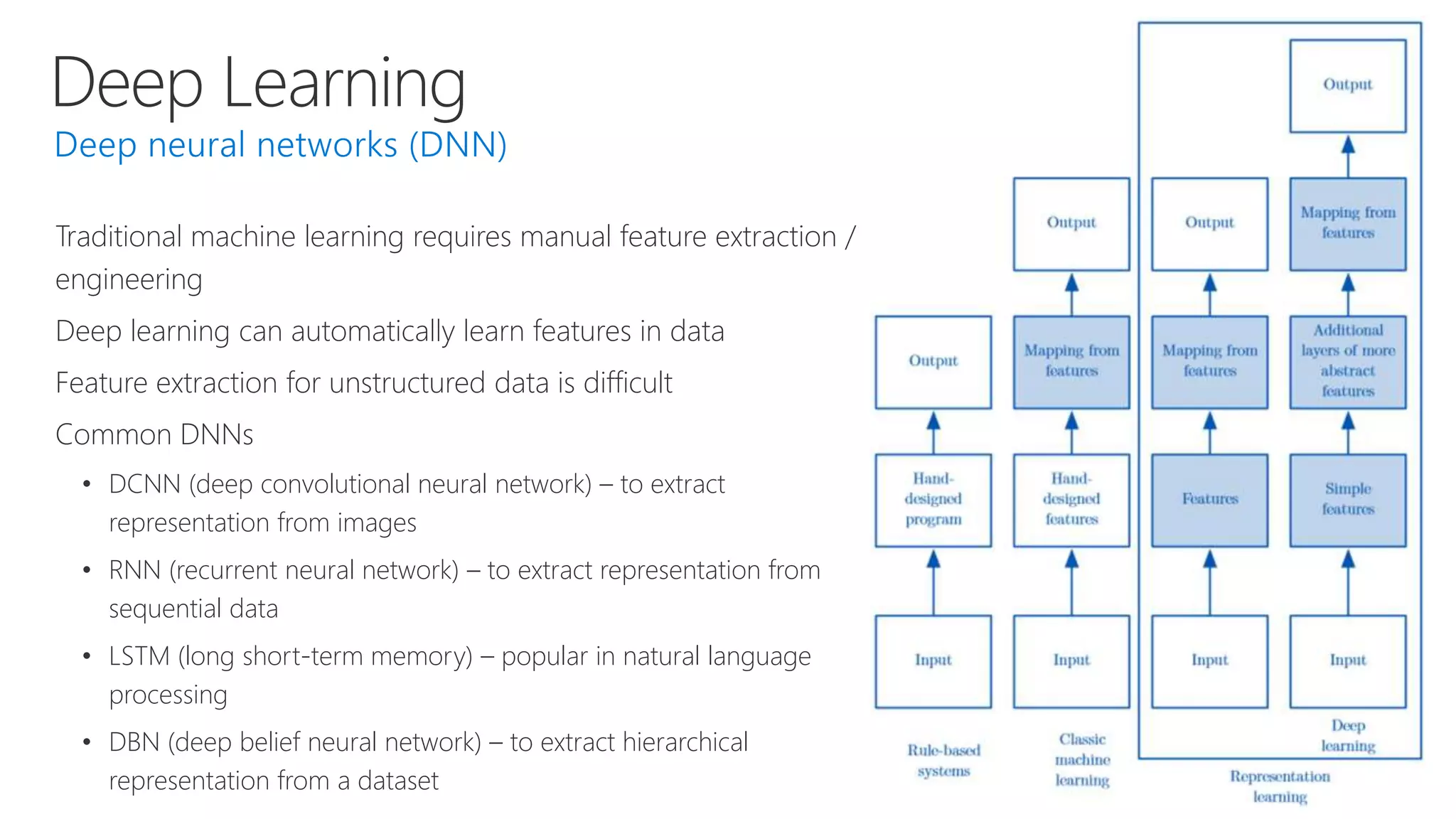
- Powerful tools for AI development including deep learning frameworks, coding and management tools, and AI services for tasks like computer vision, natural language processing, and more.
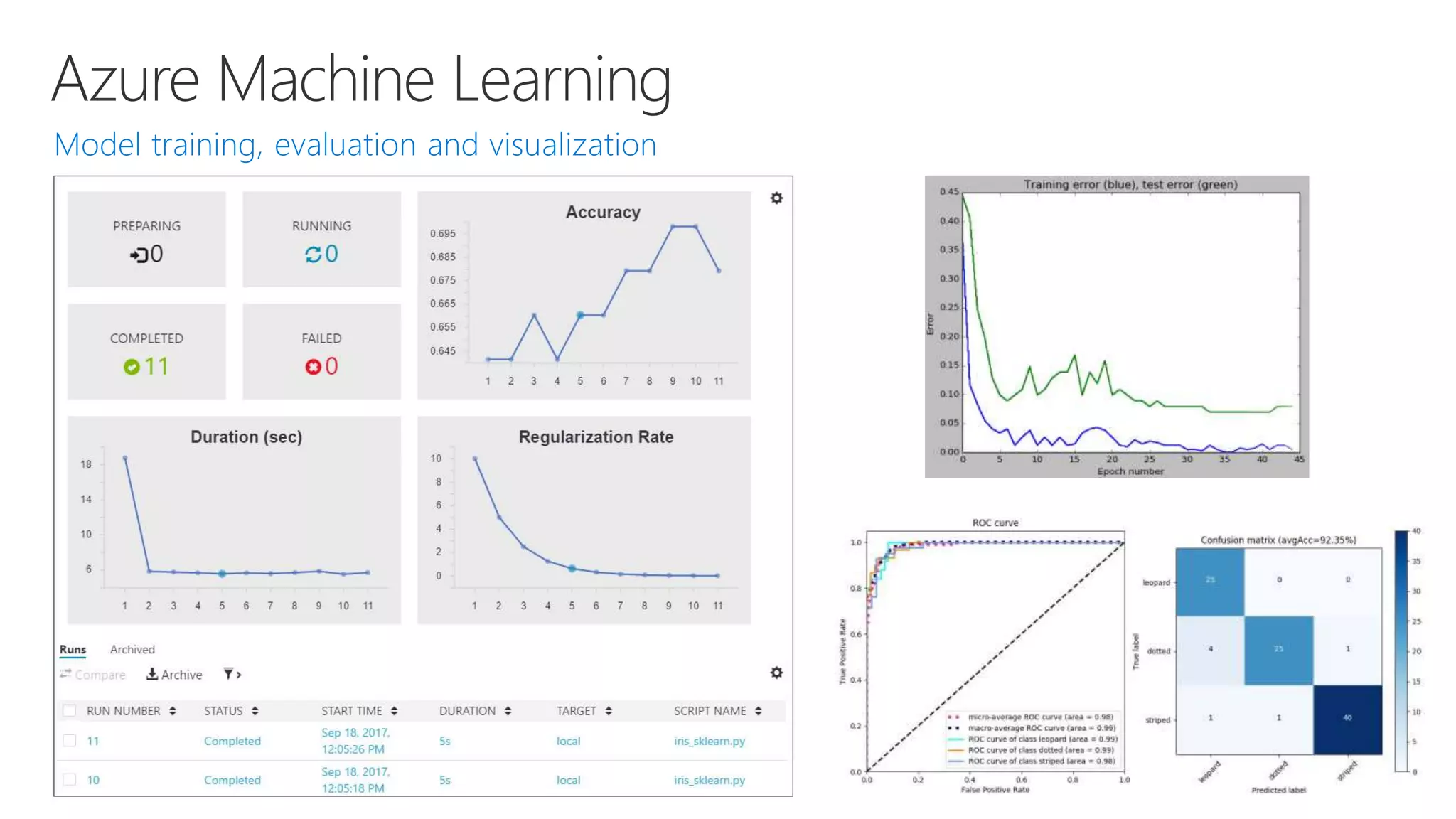
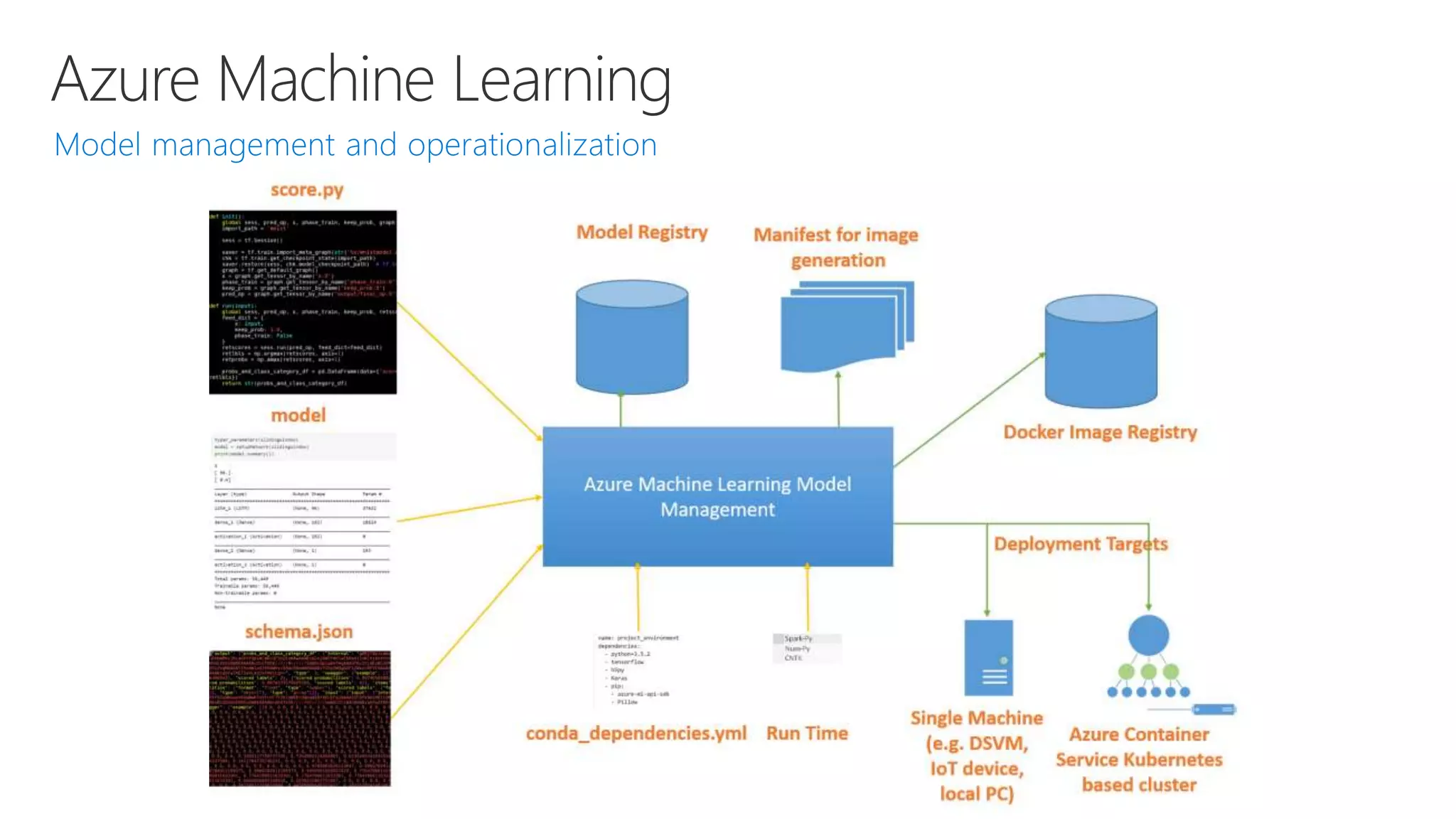
- Capabilities for training models at scale using GPU accelerated compute on Azure and deploying trained models as web APIs, mobile apps, or other applications.
- A focus on trusted, responsible, and inclusive AI that puts users in control and augments rather than replaces human