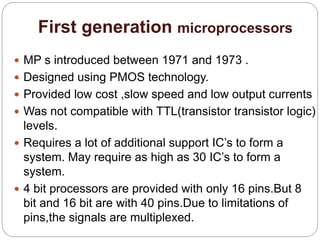
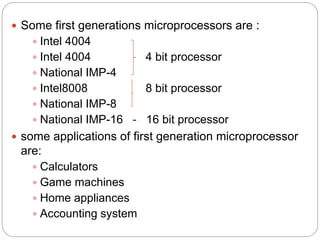
The document discusses the evolution of microprocessors over five generations from 1971 to present. The first generation used PMOS technology and included 4-bit and 8-bit processors like the Intel 4004. The second generation used NMOS technology and had 8-bit processors like the Intel 8080. The third generation used 16-bit processors made with HMOS technology like the Intel 8086. Fourth generation processors were 32-bit like the Intel 80486 and used HCMOS technology. The latest fifth generation includes advanced 32-bit processors like Intel Pentium that can execute multiple instructions per clock cycle and achieve processing speeds over 3GHz.