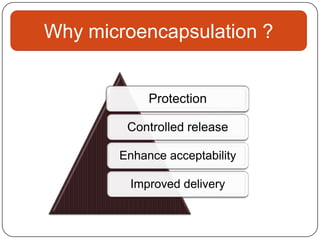
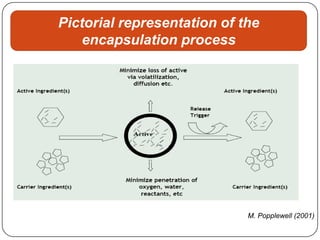
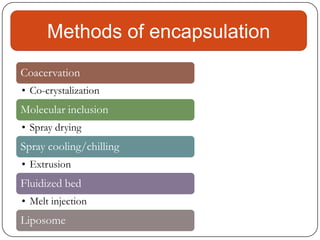
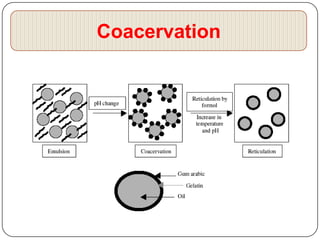
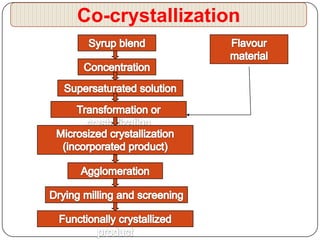
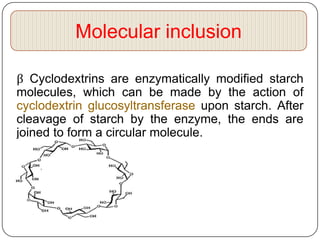
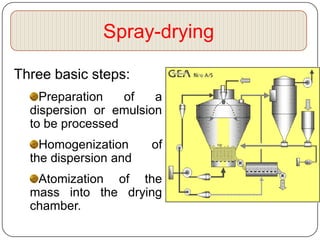
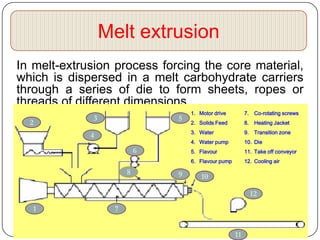
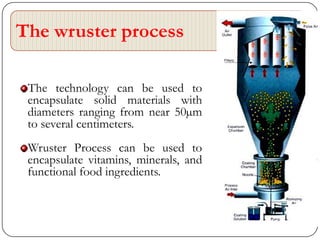
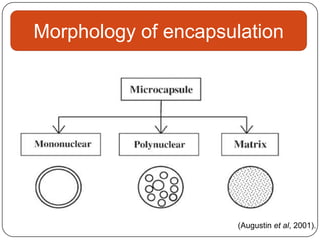
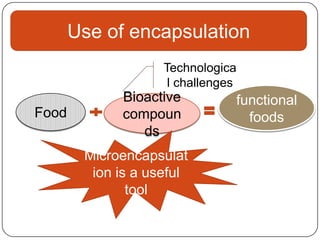
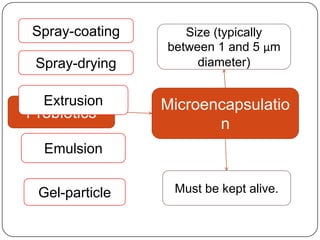
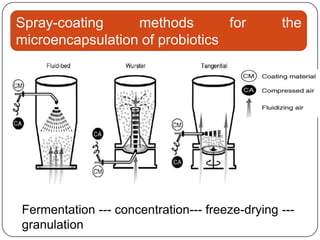
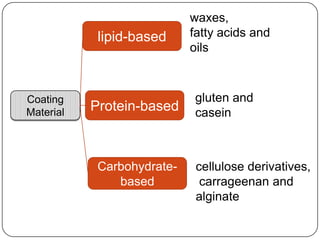
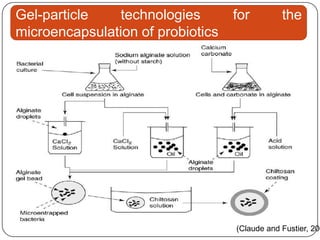
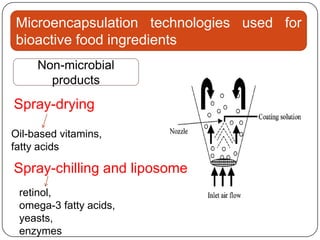
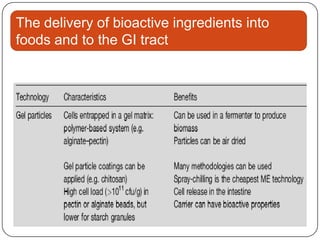
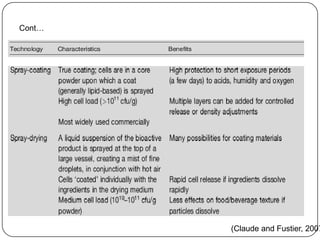
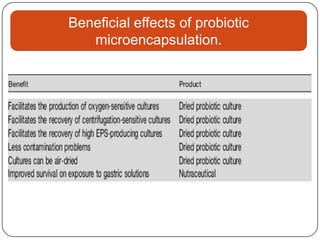
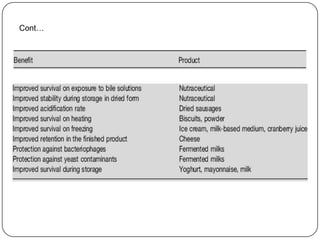
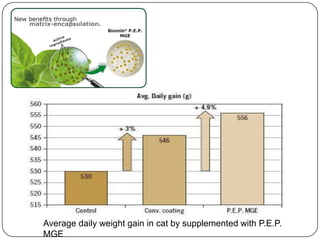
Microencapsulation is a technology that packages solids, liquids, or gases within miniature sealed capsules. It can protect ingredients, allow for controlled release, and improve delivery of bioactive compounds in foods. Common microencapsulation methods include coacervation, spray drying, extrusion, and fluidized bed coating. Microencapsulation promotes the stability, delivery, and health benefits of bioactive ingredients like probiotics, vitamins, minerals, and fish oils. It masks unpleasant flavors and protects ingredients from environmental factors. Studies show microencapsulation can increase probiotic survival in foods and the delivery of iron, calcium, and omega-3s to the gastrointestinal tract.