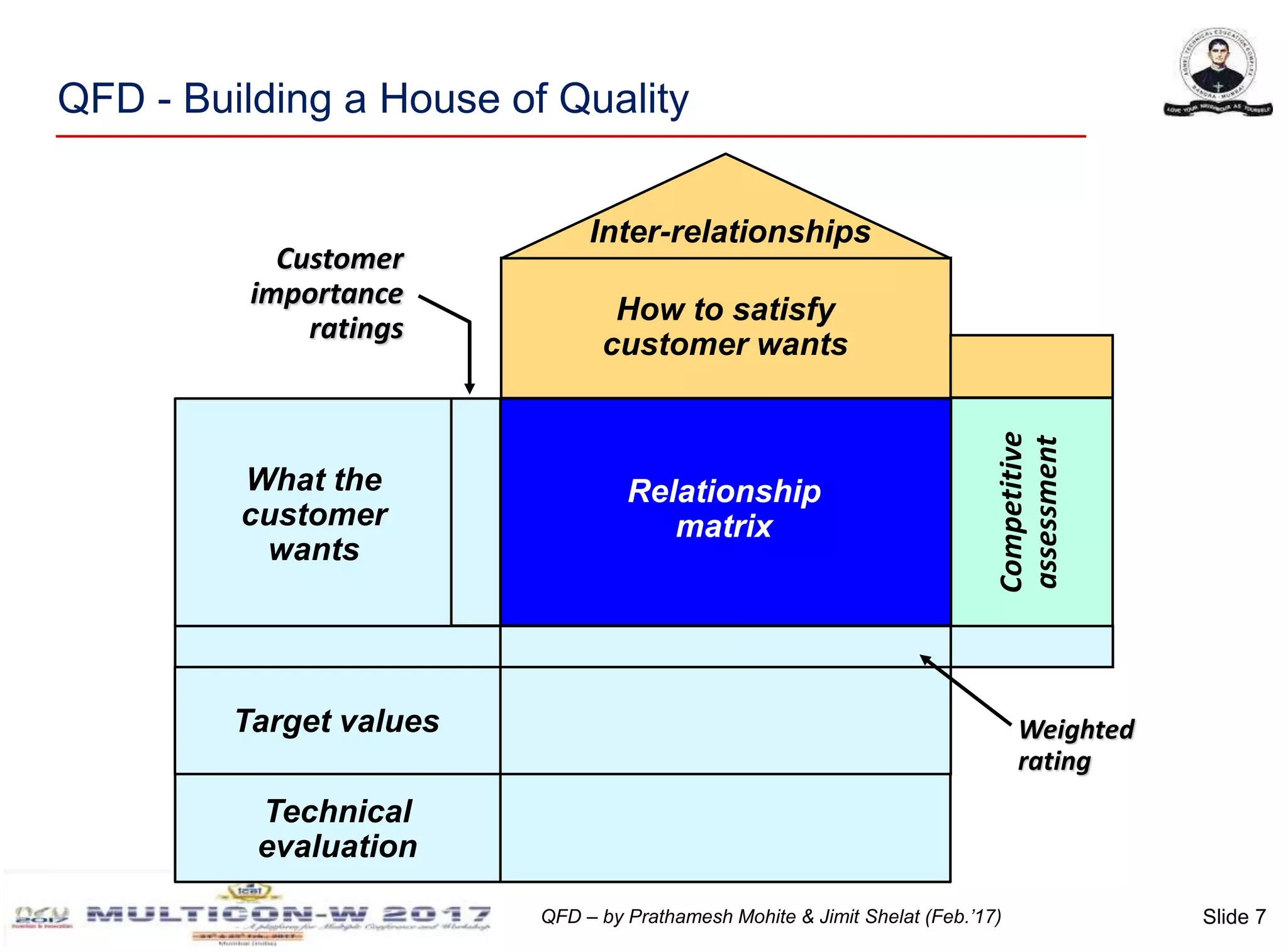
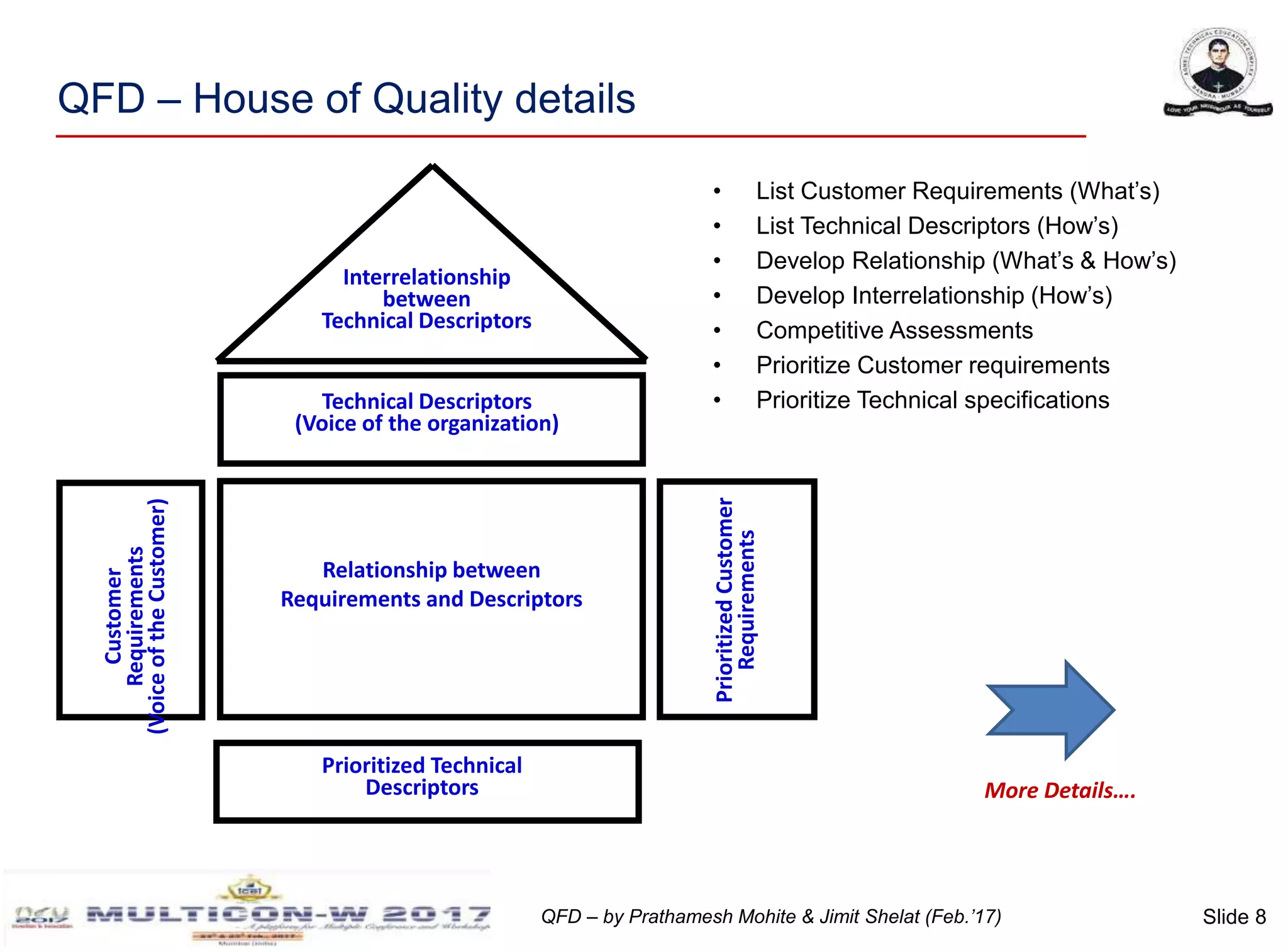
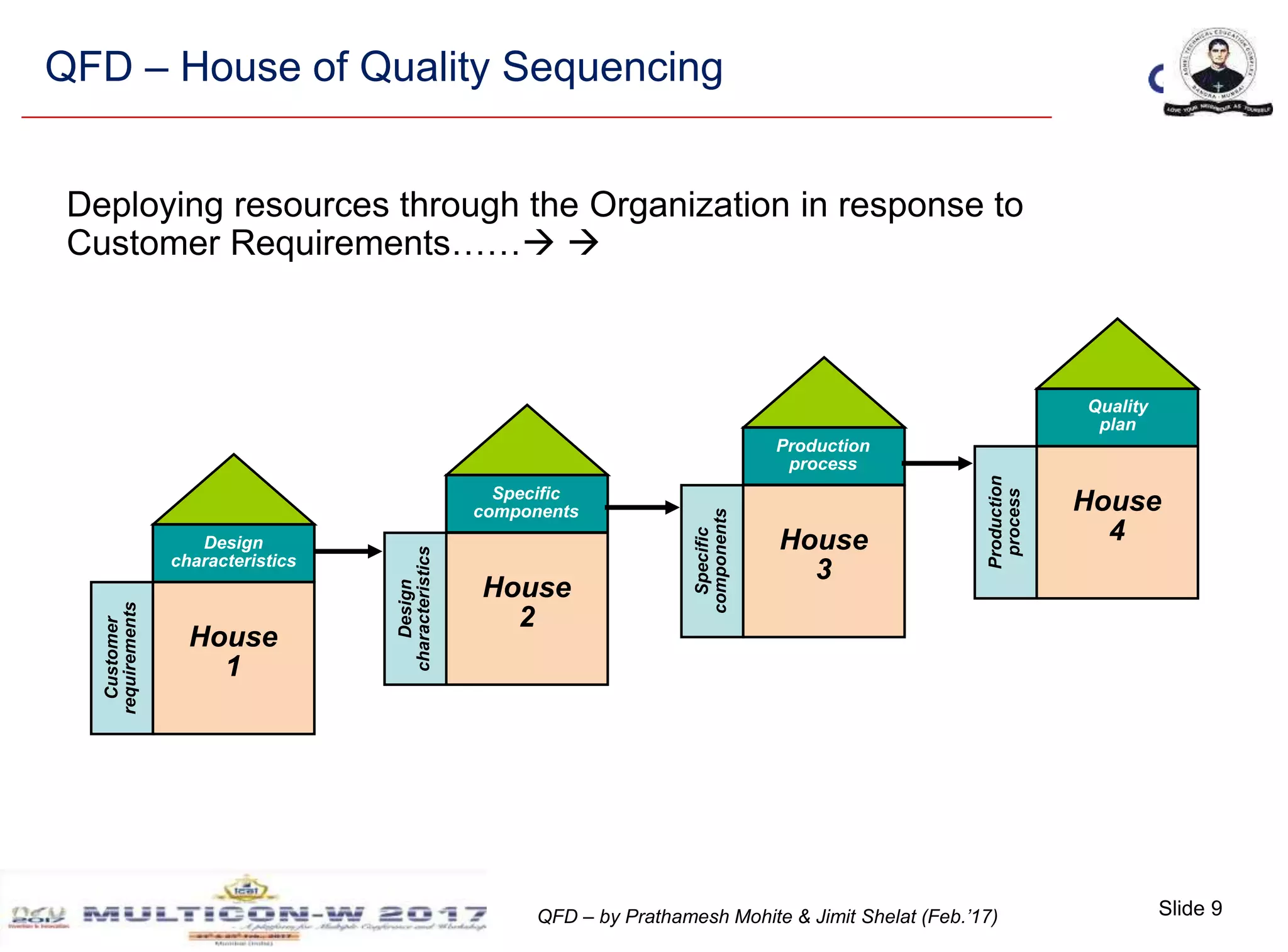
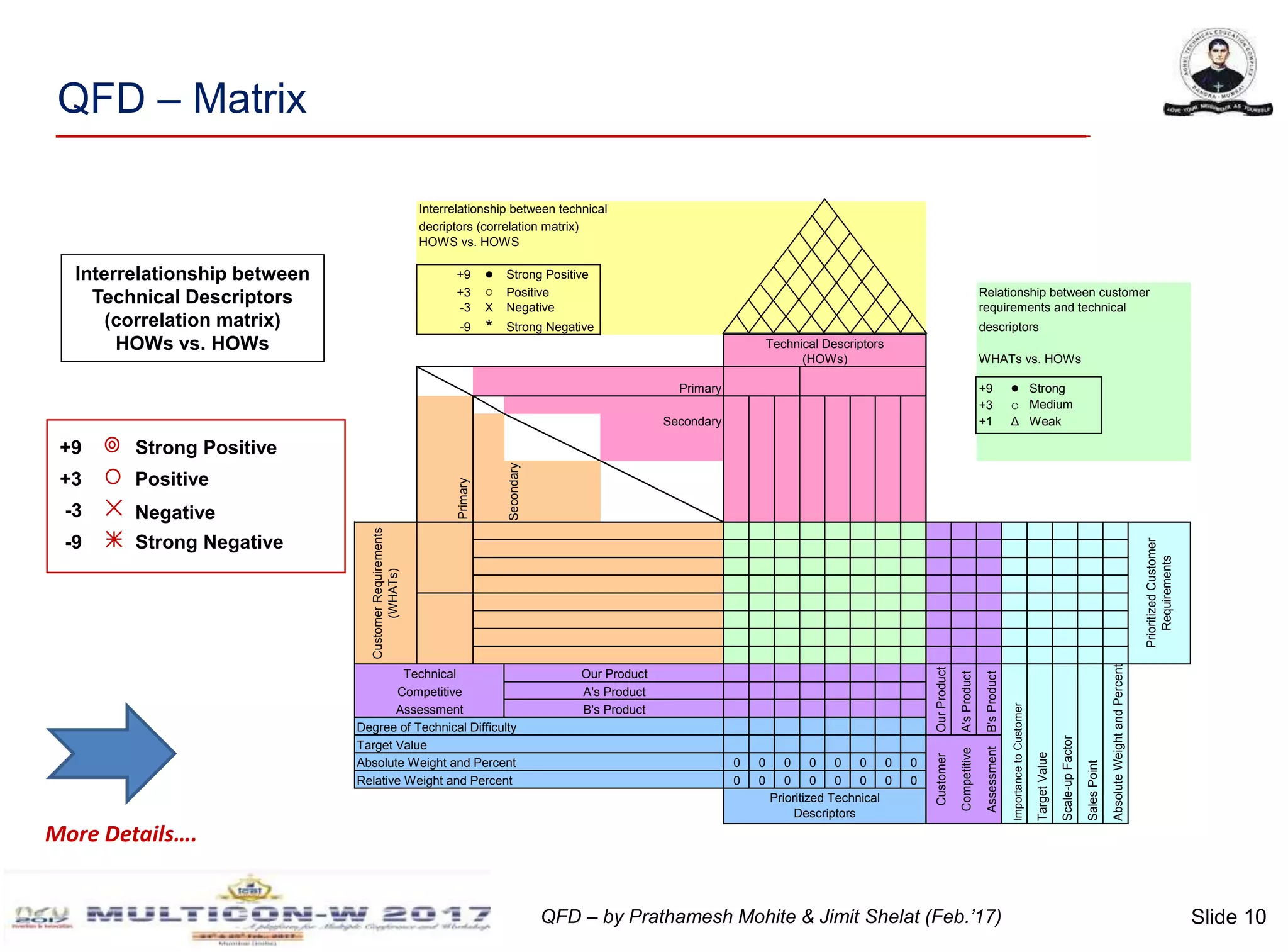
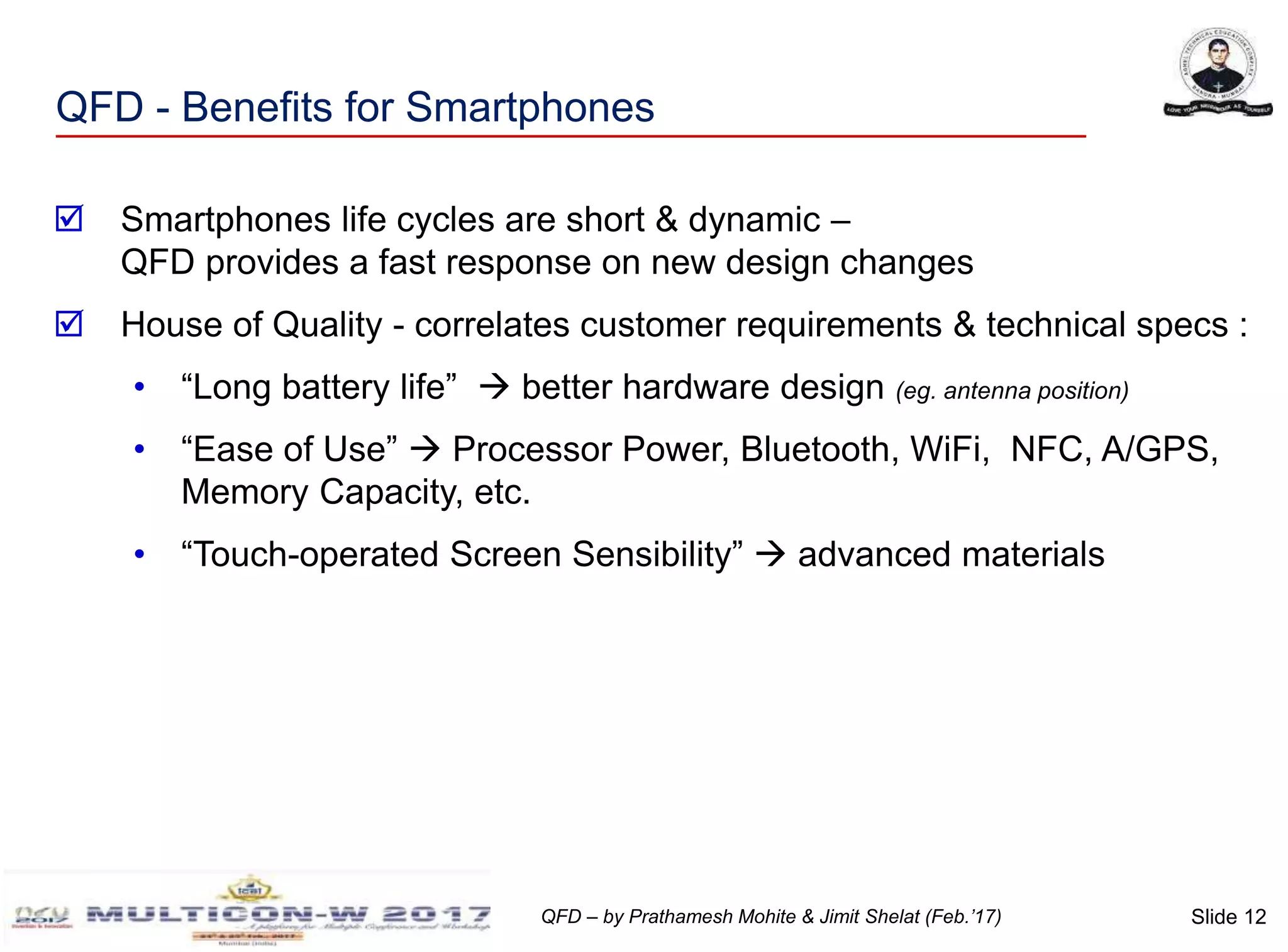
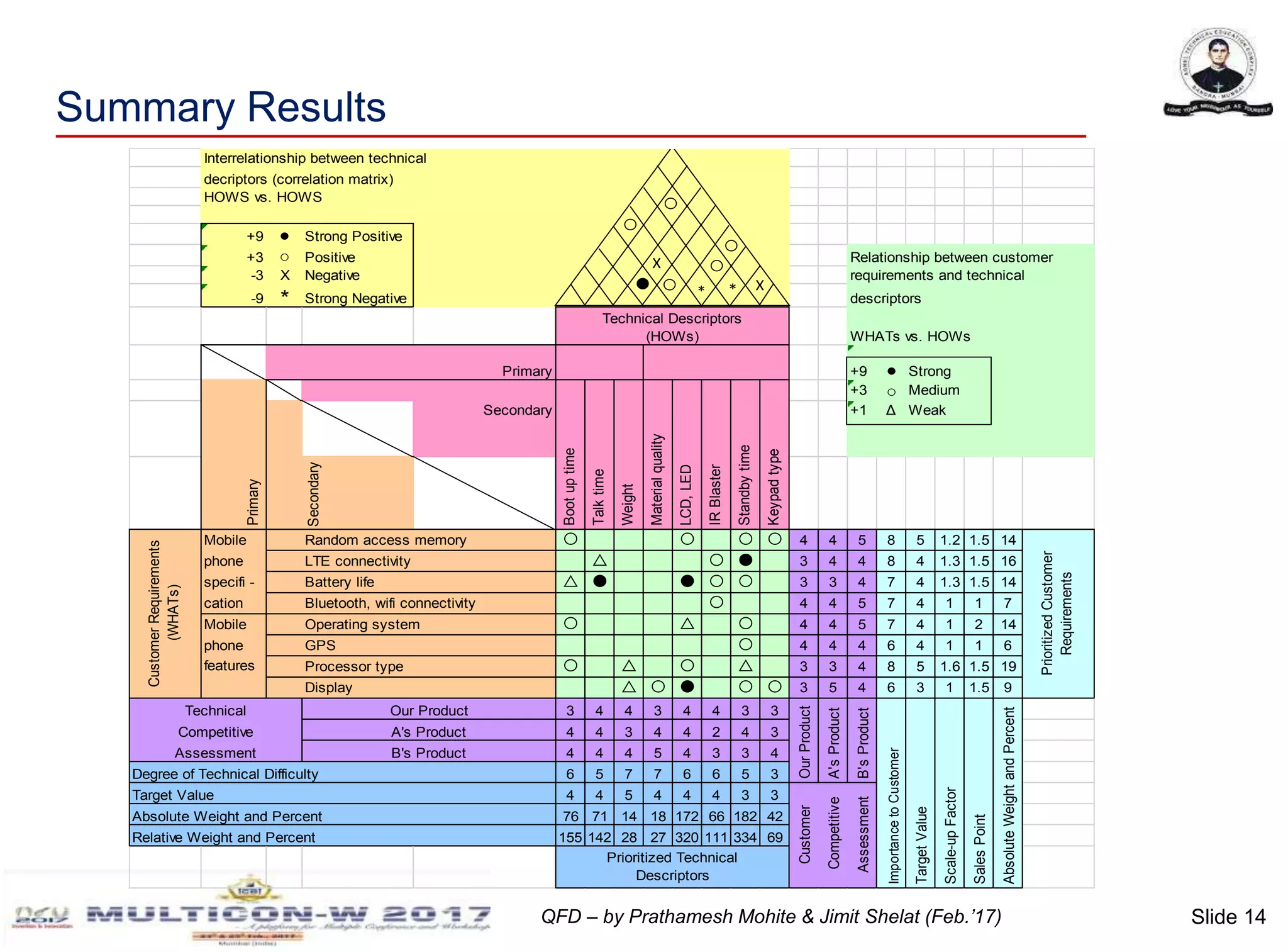
The document discusses the implementation of Quality Function Deployment (QFD) in smartphone design, emphasizing its role in translating customer needs into technical specifications to enhance customer satisfaction. It outlines the benefits of adopting QFD methodologies, including faster response to market changes and improved teamwork among engineers. Key areas of focus include optimizing product features such as battery life and user experience through systematic assessment of customer requirements and technical descriptors.