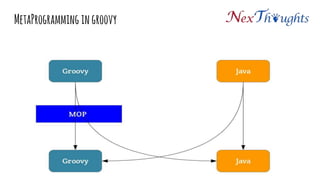
Groovy provides metaprogramming capabilities through its Meta-Object Protocol (MOP). The MOP allows dynamically injecting, synthesizing, and mixing methods at runtime. This is done by manipulating metaclasses, which contain metadata about classes and allow intercepting method calls. Demonstrations show adding methods to classes like Integer to check for evenness, intercepting method calls, and mixing methods from other types. Metaprogramming with Groovy's MOP provides flexibility to dynamically modify classes and their behavior.