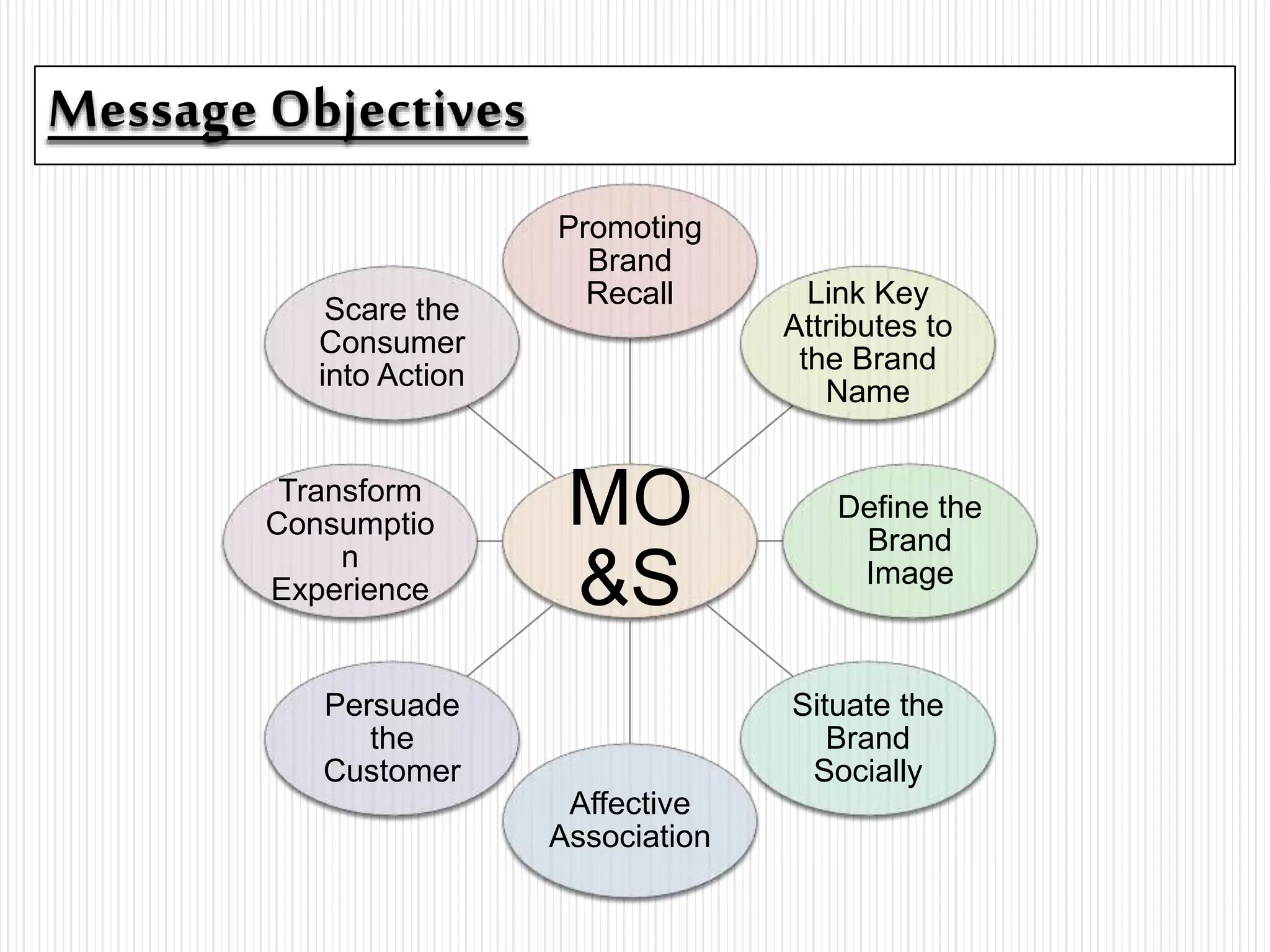
The document outlines the key elements of message strategy and design in advertising, emphasizing its components such as message execution, appeals, objectives, and target audience. It categorizes message strategies into cognitive, affective, and conative types, each serving different purposes, from impacting beliefs to eliciting emotional responses or prompting consumer actions. Additionally, it discusses the structure and importance of a message strategy brief in the advertising process.