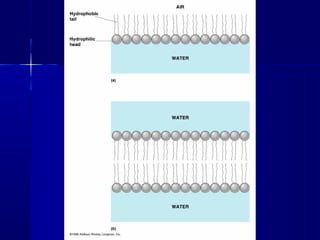
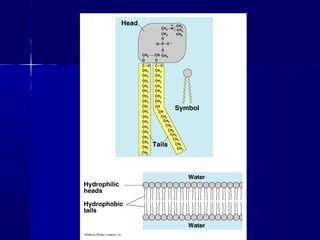
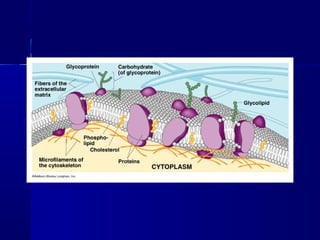
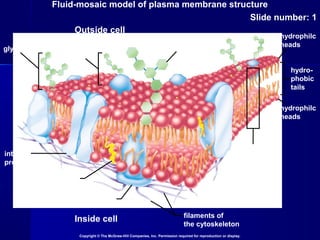
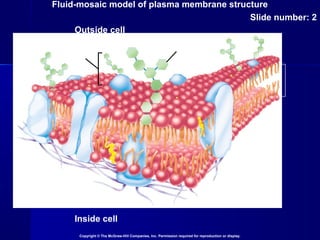
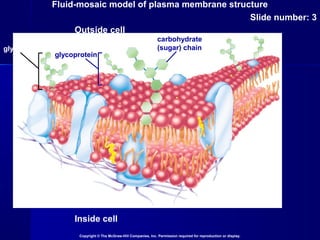
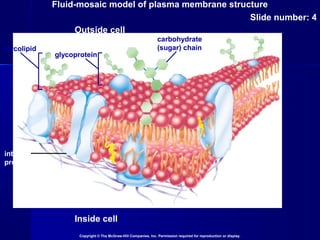
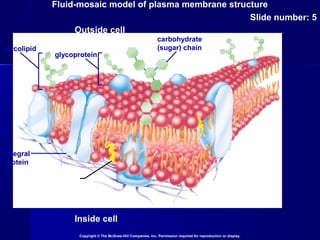
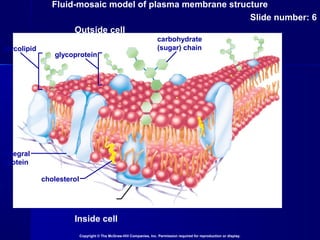
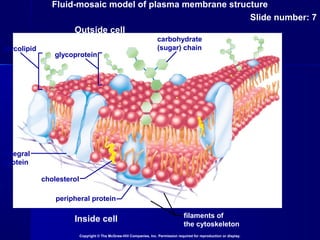
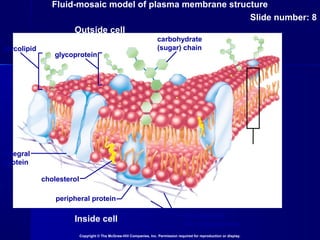
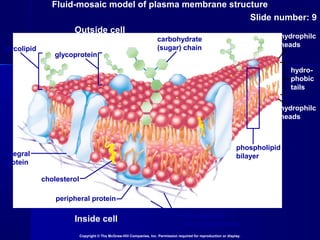
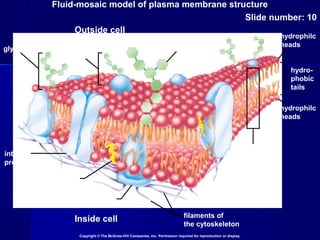
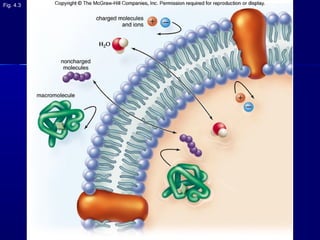
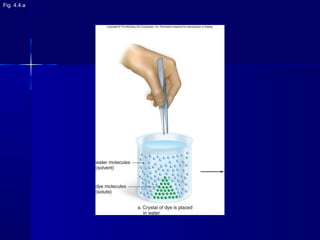
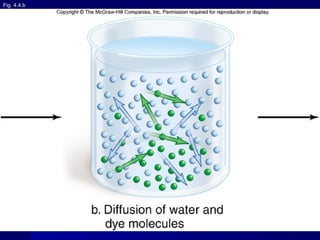
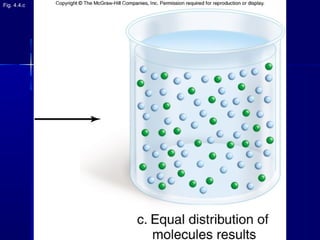
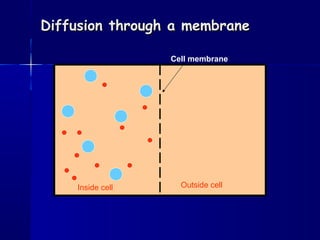
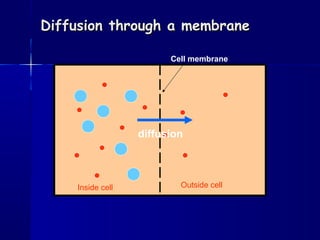
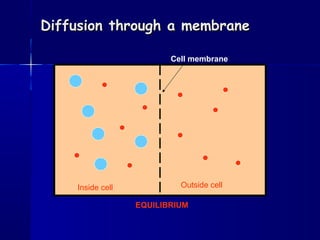
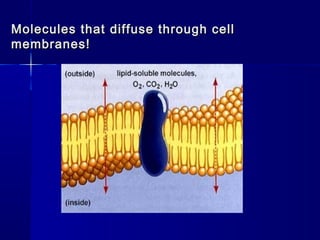
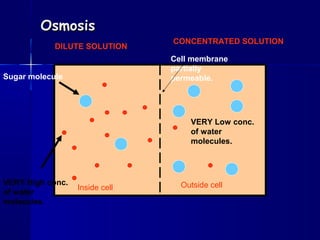
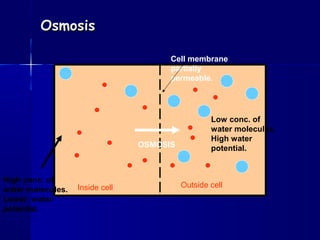
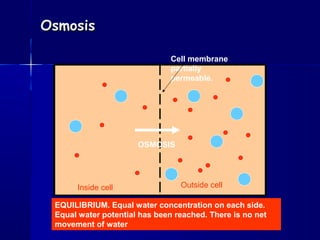
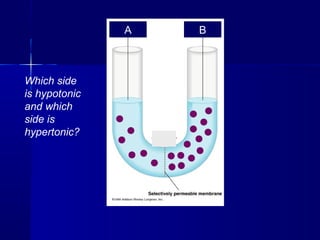
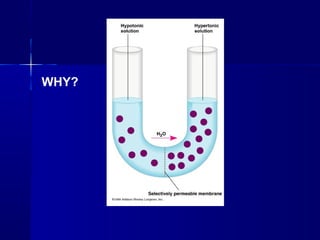
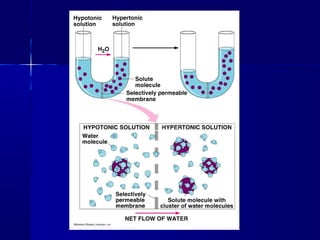
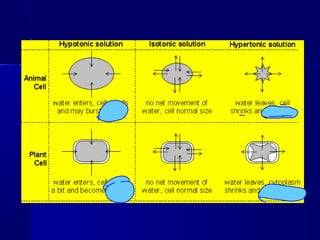
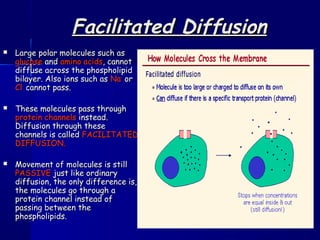
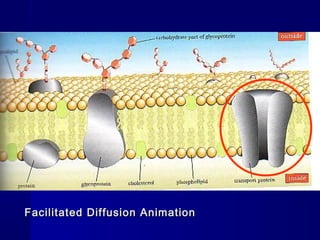
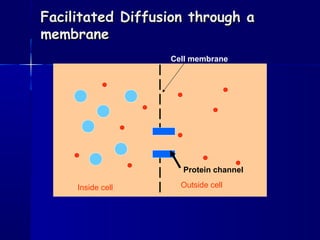
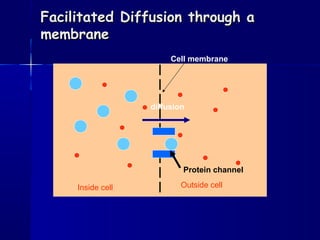
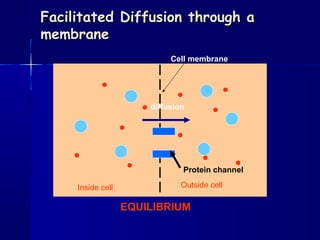
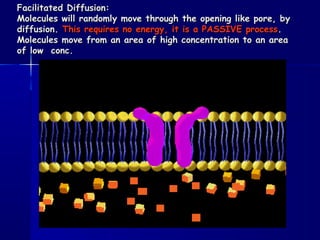
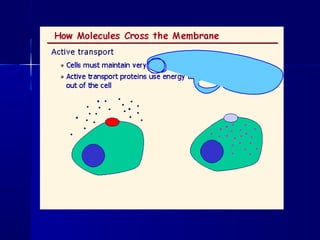
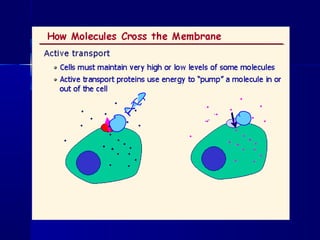
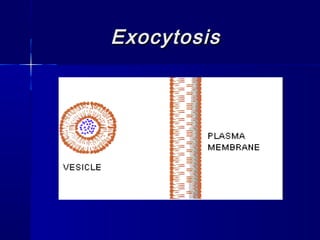
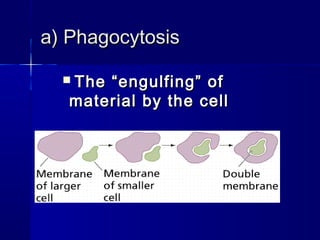
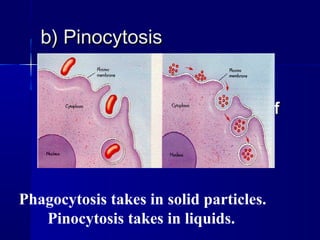
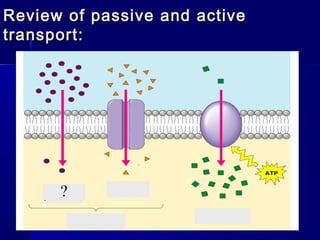
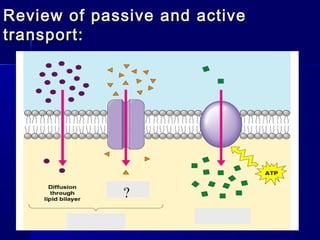
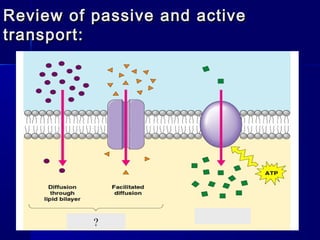
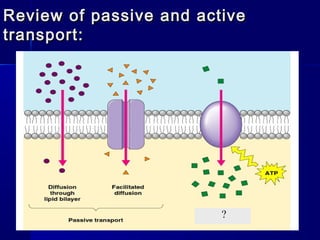
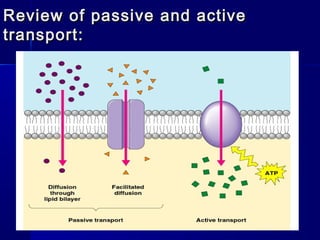
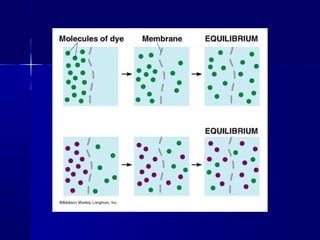
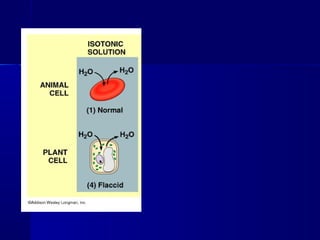
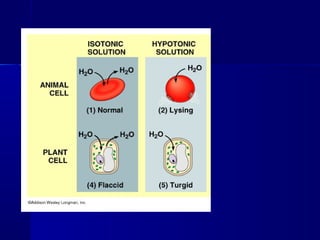
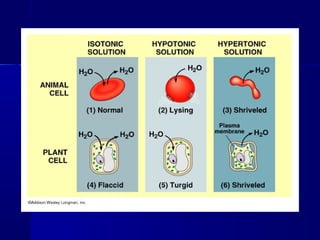
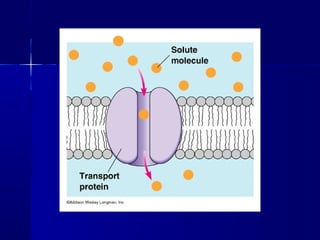
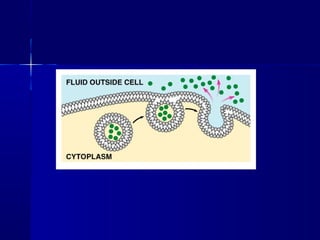
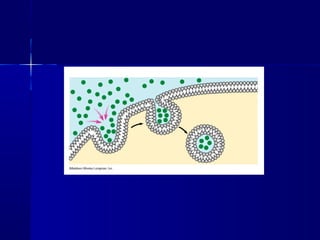
Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells by separating cells from their environments and controlling the passage of molecules. The cell membrane is a fluid mosaic of phospholipids and proteins that forms a selectively permeable bilayer. This structure allows materials to enter and exit cells through passive transport mechanisms like diffusion and osmosis, or active transport processes like endocytosis and exocytosis. Membrane proteins play important roles in these transport functions.