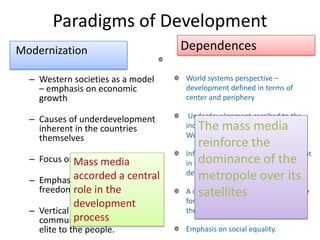
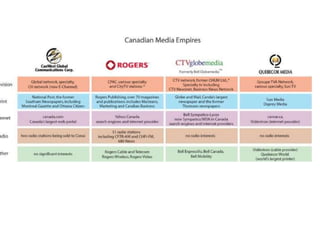
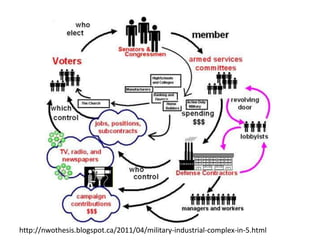
This document provides an overview of the concept of media imperialism and frameworks for understanding the relationship between media and development. It discusses the functions of media, links between media and development paradigms, and the emergence of the media imperialism thesis. Key assumptions and evidence for and against the media imperialism thesis are examined. Alternative perspectives such as reception theory, agency, and Everett Rogers' diffusion of innovations approach are also presented.