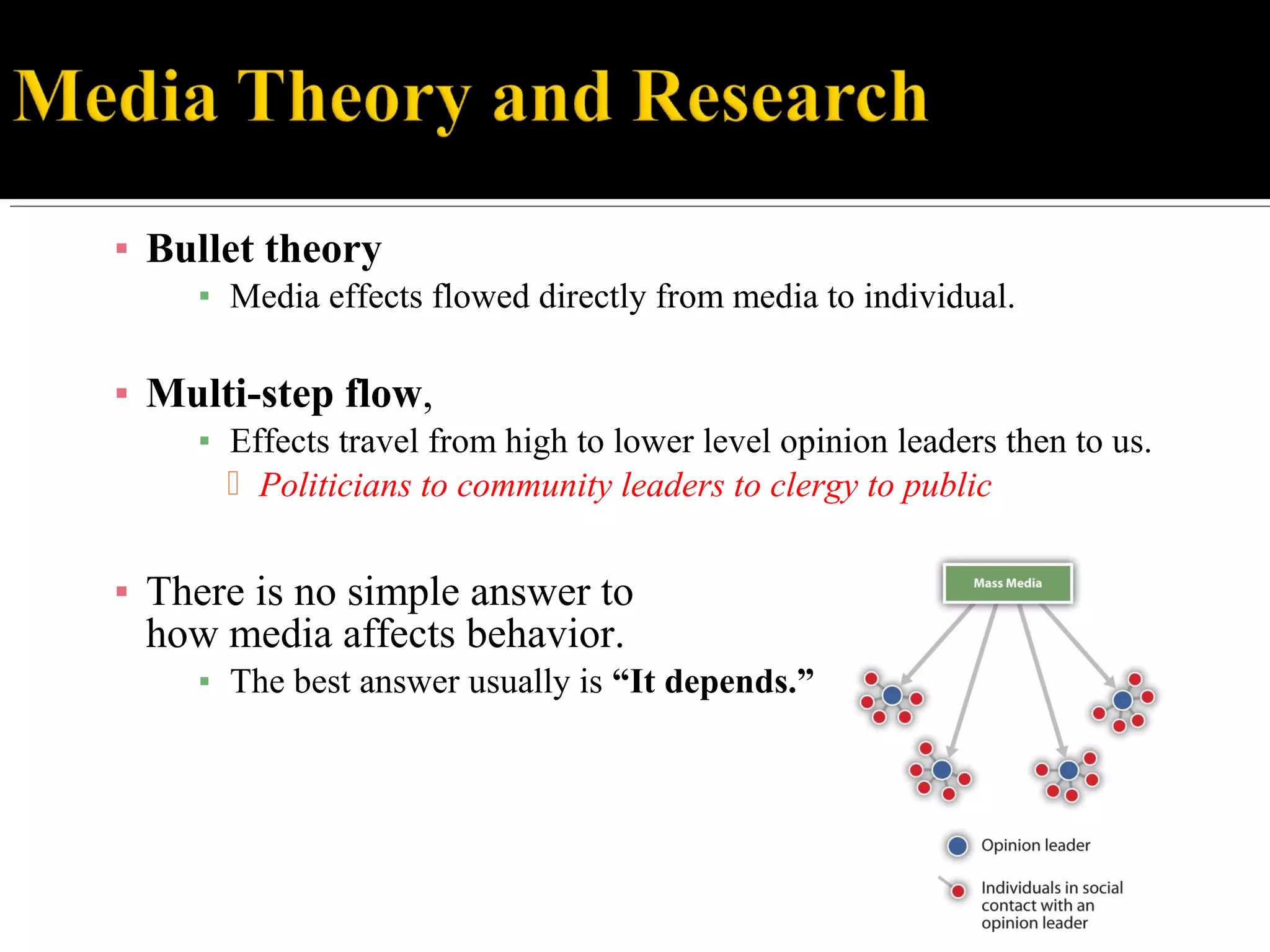
The document discusses the historical and theoretical frameworks surrounding media effects on society, highlighting early studies like the Payne Fund studies that explored the impact of movies and other media on youth behavior. It examines various models of media effects, including powerful, minimal, and mixed effects models, while also addressing social learning theory, diffusion of innovations, and agenda-setting in media. Overall, it suggests that the effects of media are complex and multifaceted, often depending on individual perceptions and social contexts.