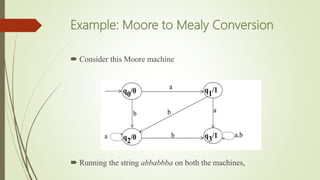
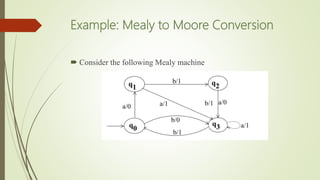
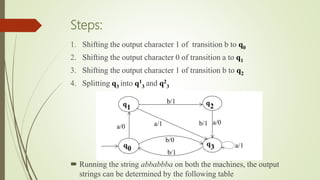
The document discusses mealy and moore machines, which are types of finite automatons that generate output strings corresponding to input strings. It explains the structure and characteristics of both machines, highlights their differences, and presents theorems about their equivalence. Additionally, it includes examples demonstrating how to convert between mealy and moore machines.