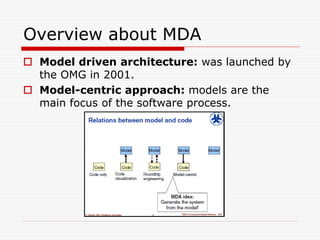
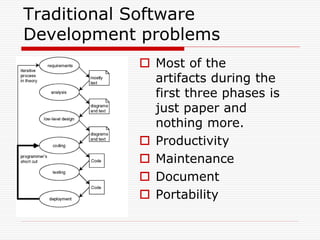
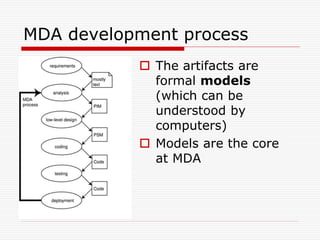
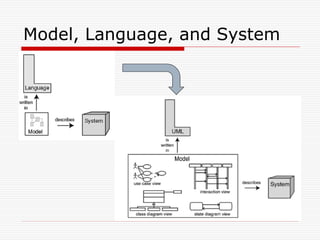
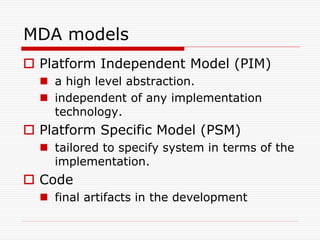
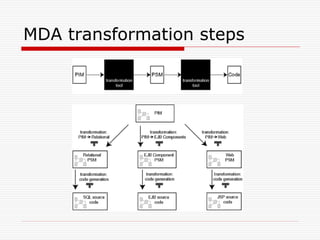
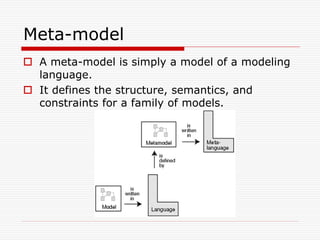
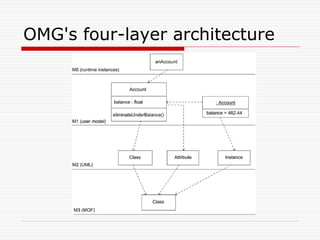
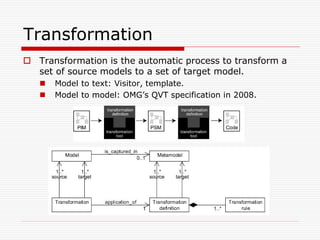
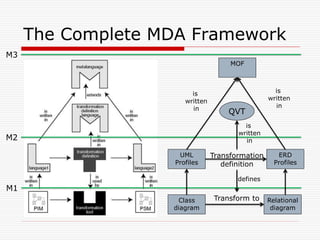
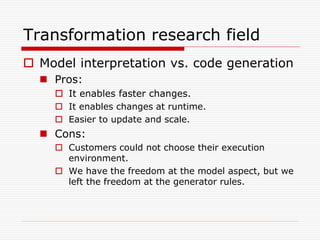
This document discusses Model Driven Architecture (MDA) and commonly researched problems related to MDA. It provides an introduction to MDA, outlining its model-centric approach and how it aims to address traditional software development problems. Commonly researched problems with MDA include how to evaluate UML for practical use, developing domain-specific modeling languages, model transformation, meta-model evolution, and applying MDA within agile practices. The document concludes that MDA provides benefits like increased productivity but also challenges like rigidity, and identifies areas for further MDA research.