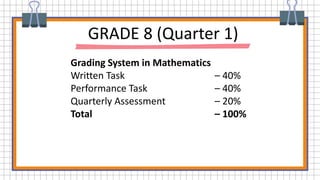
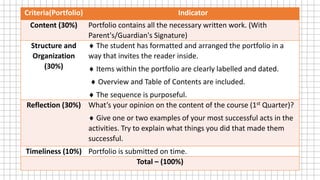
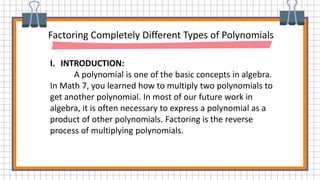
The document provides information about factoring polynomials with a common monomial factor. It defines key terms related to factoring such as binomial, trinomial, factor, and greatest common factor. It explains the steps to factor polynomials with a common monomial factor: 1) Find the greatest common factor of the numerical coefficients, 2) Find the common variable factor with the least exponent, 3) The product of the GCF and common variable is the greatest common monomial factor, 4) Divide the polynomial by the GCMF to obtain the other factor. Examples are provided to demonstrate the factoring process.