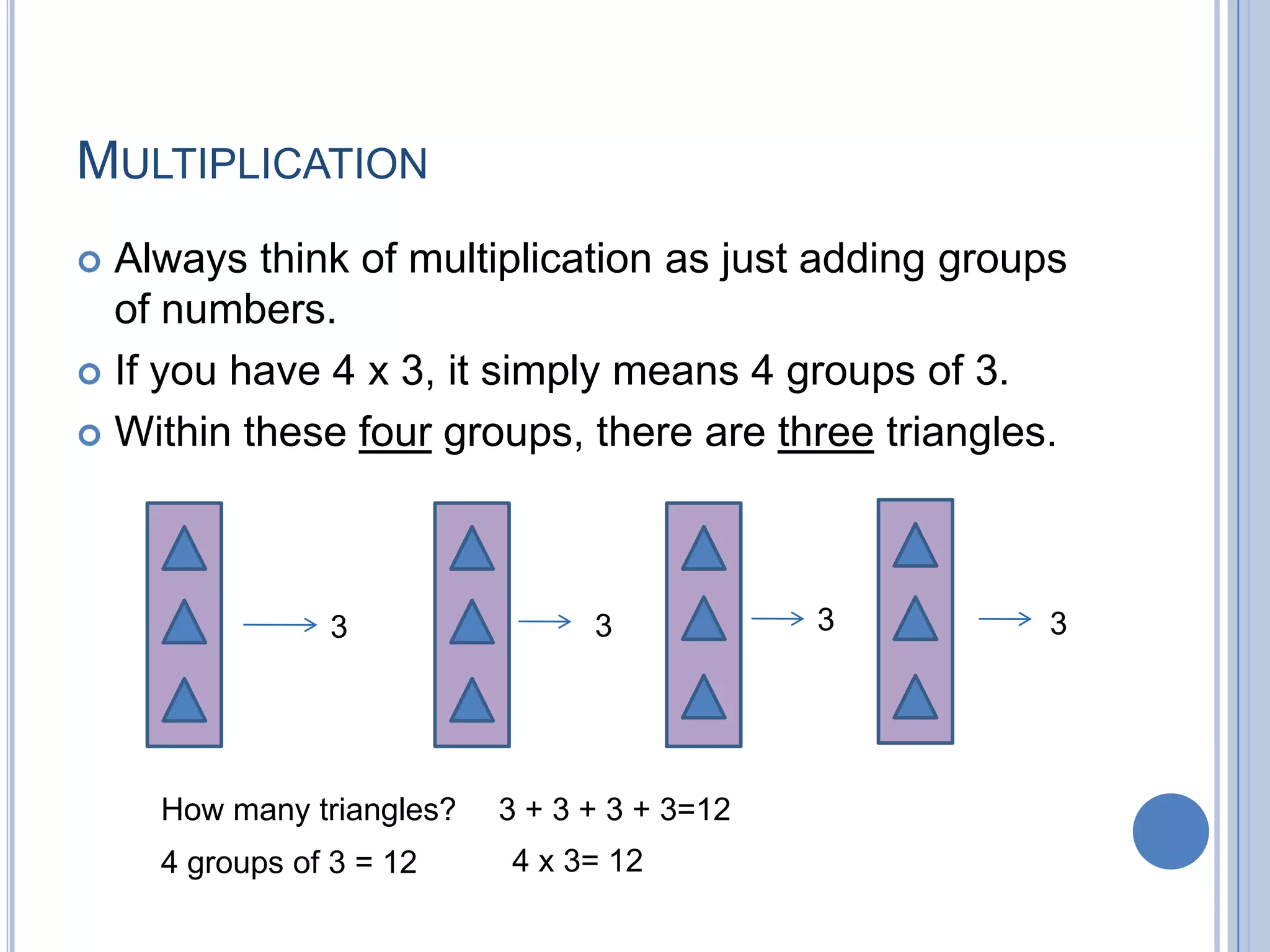
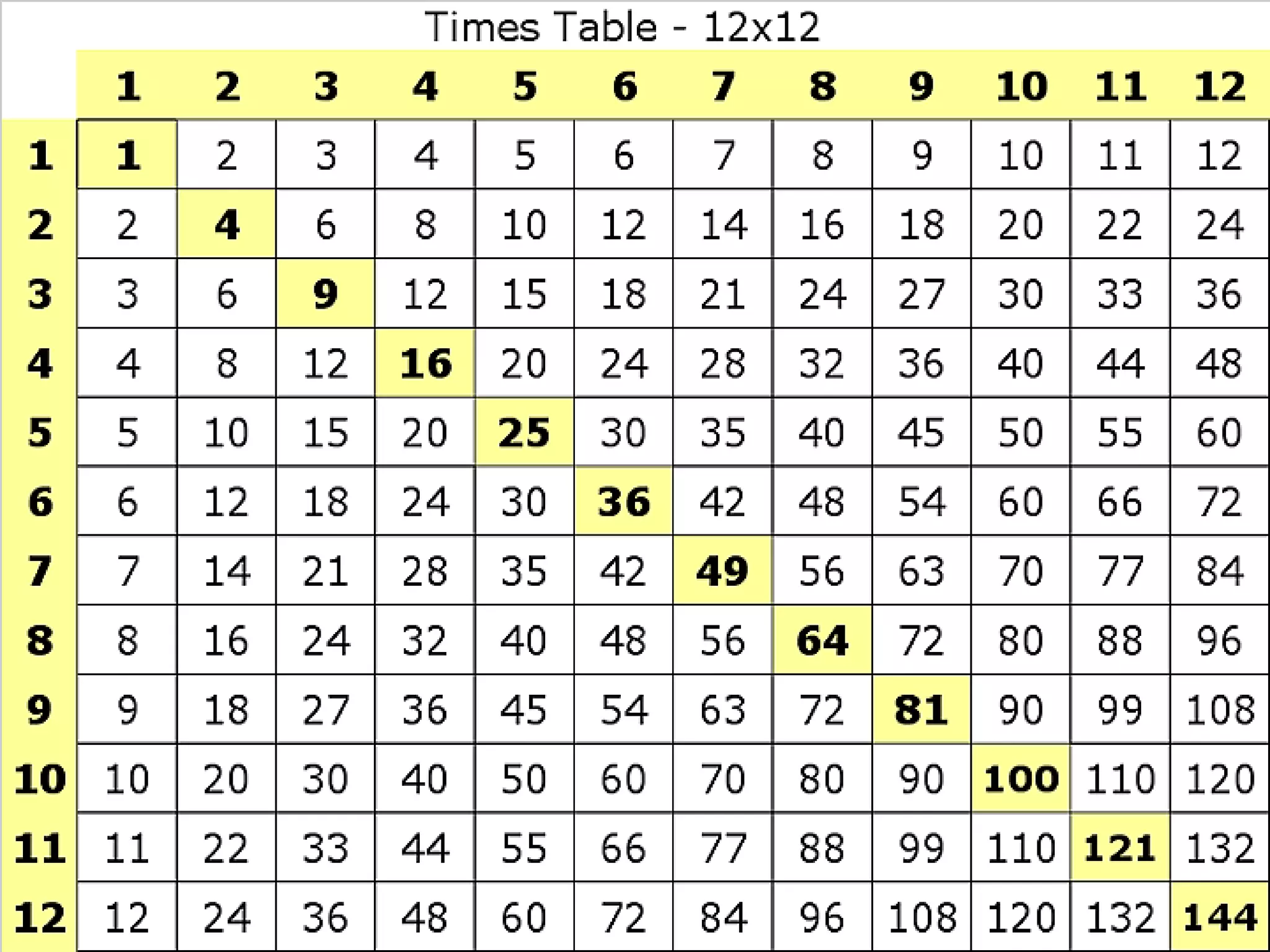
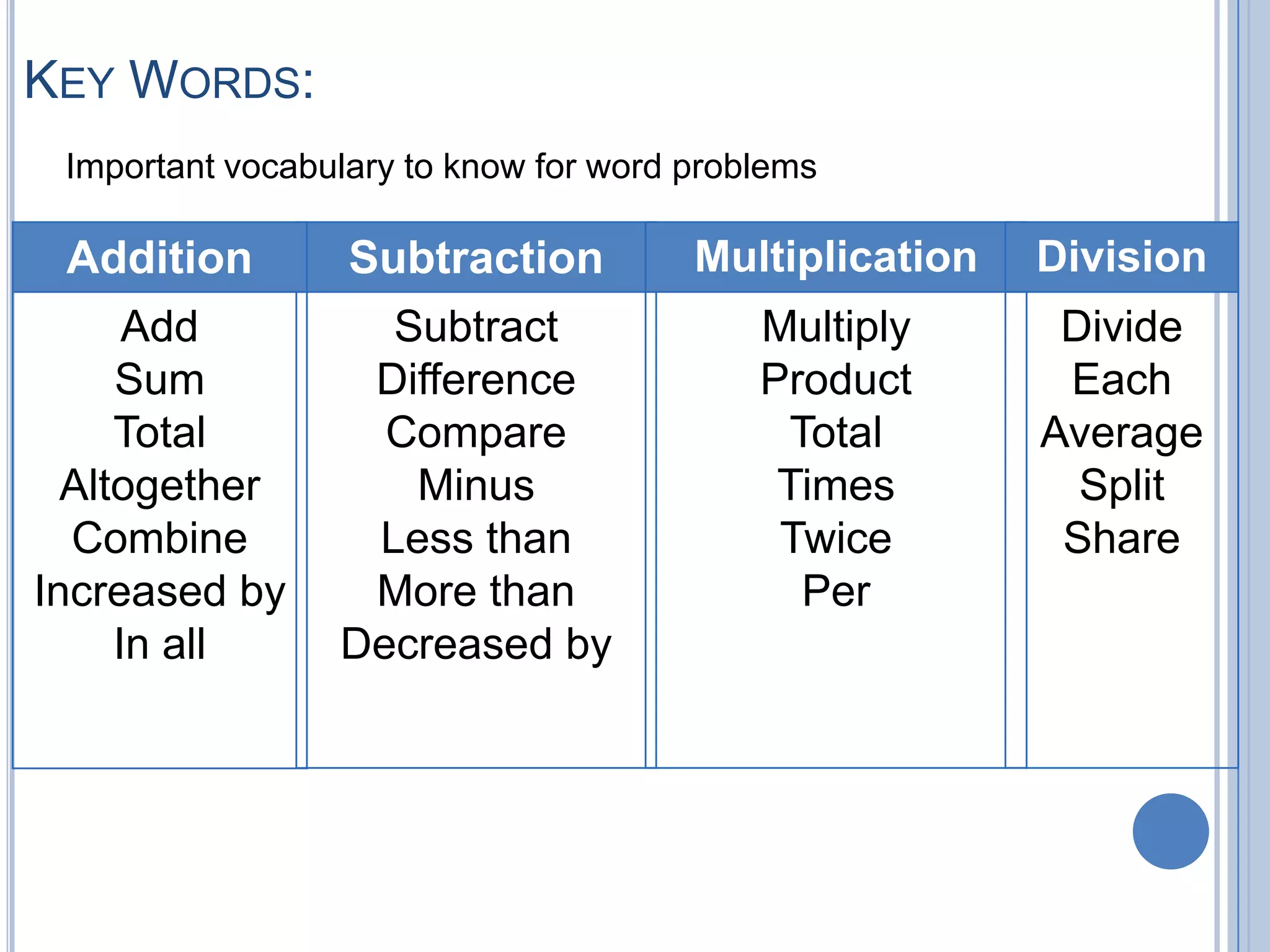
The document provides information for a math class including:
- Where to find attendance sheets and the class code.
- The teacher's background and why she loves teaching math.
- Expectations for success, materials needed, class structure, and guidelines.
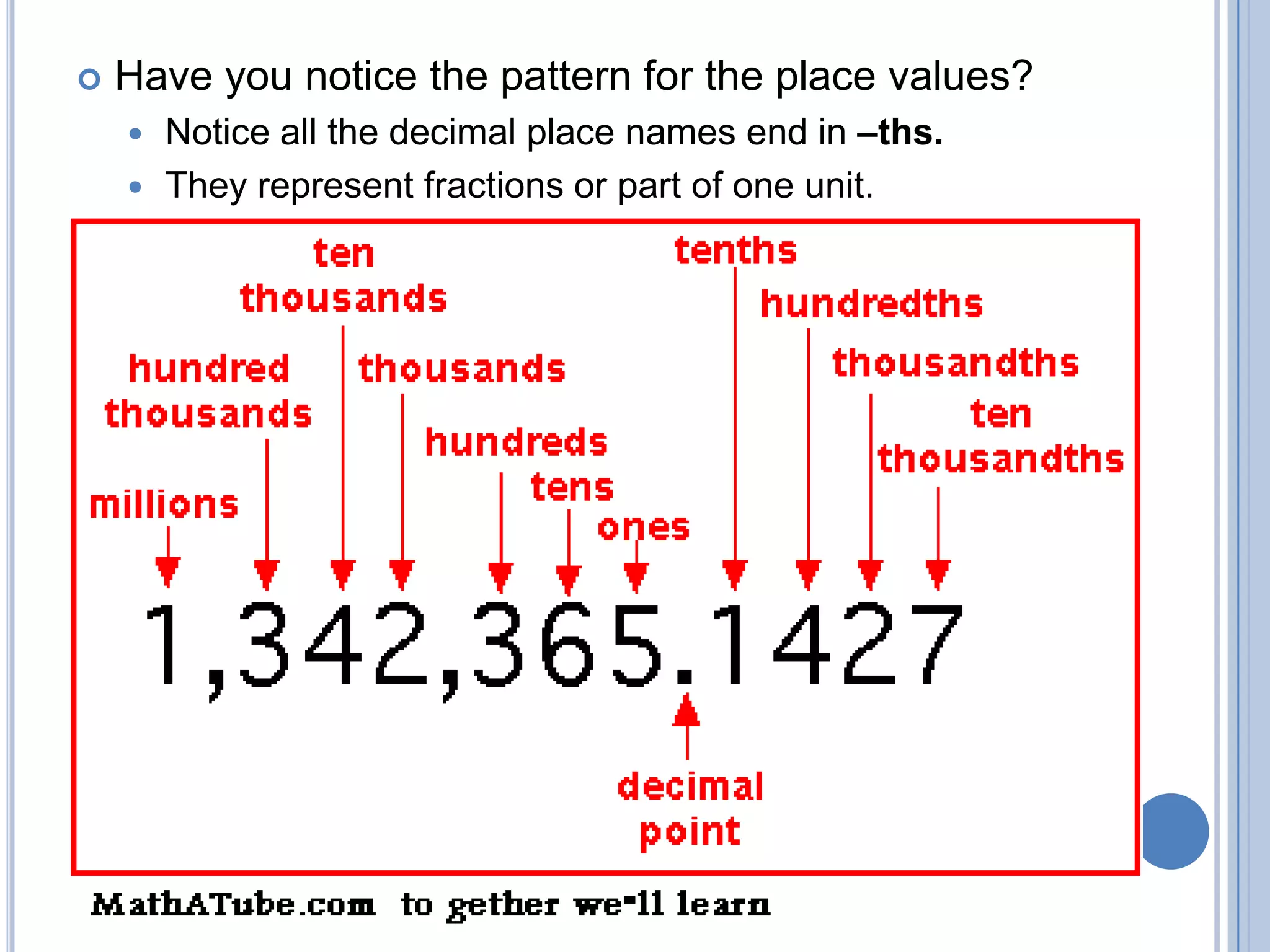
- An introduction to place value, operations, and solving word problems.